Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (9): 1357-1363.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0464
Previous Articles Next Articles
Vitreous cryopreservation and thawing of adipose-derived stem cells/demineralized bone matri
Liu Lei1, Yong Qi2, Li Na1, Yang Duo1, Zhang Guo-ying1, Cui Lei1
- 1Beijing Shijitan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100038, China; 2Department of Plastic Surgery, Third Affiliated Hospital of Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang 453000, Henan Province, China
-
Revised:2018-02-10Online:2018-03-28Published:2018-03-28 -
Contact:Cui Lei, M.D., Chief physician, Professor, Beijing Shijitan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100038, China -
About author:Liu Lei, Master candidate, Beijing Shijitan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100038, China -
Supported by:the Special Fund for the Clinical Medicine Development in Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals, No. XMLX2 01611
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Lei, Yong Qi, Li Na, Yang Duo, Zhang Guo-ying, Cui Lei. Vitreous cryopreservation and thawing of adipose-derived stem cells/demineralized bone matri[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(9): 1357-1363.
share this article
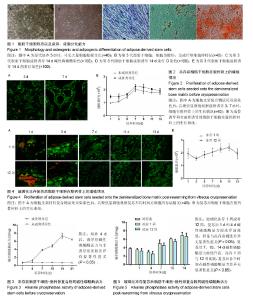
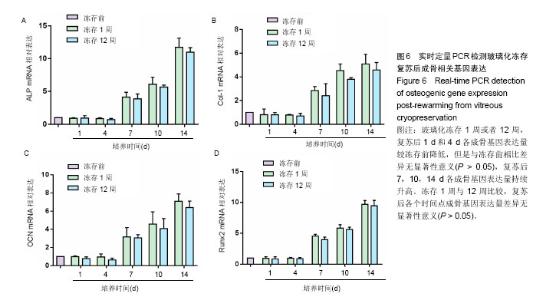
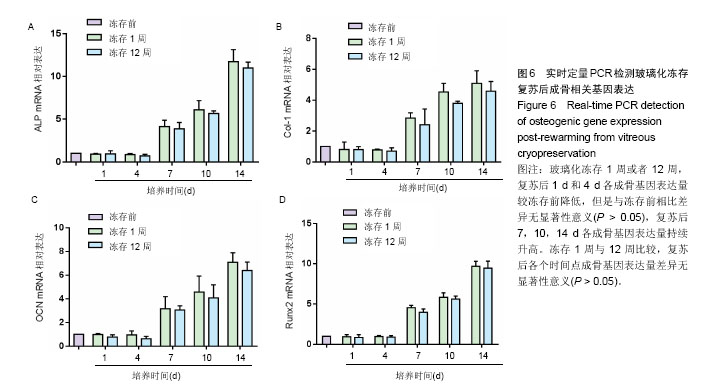
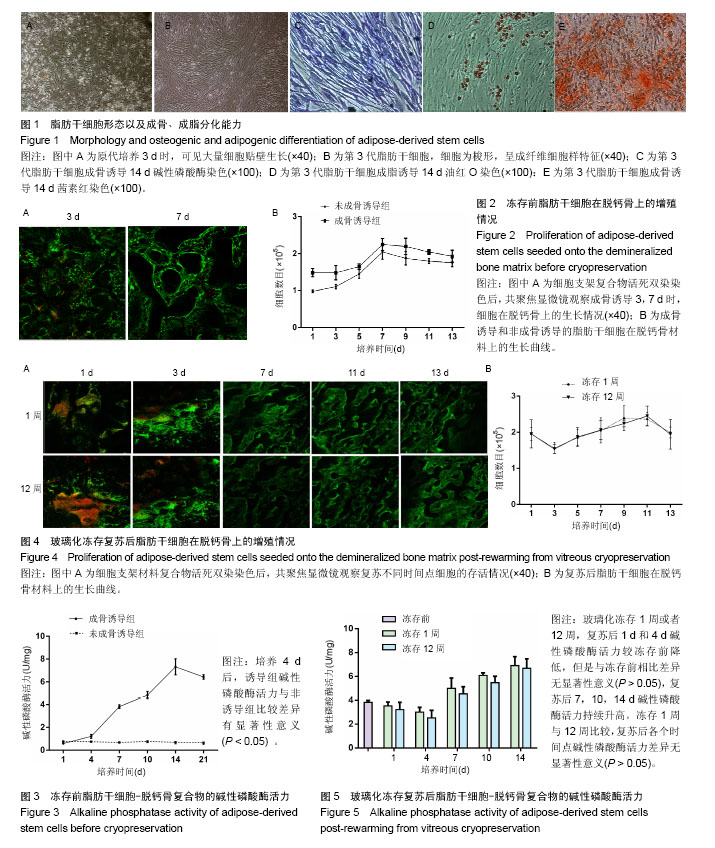
2.1 脂肪干细胞形态以及成骨、成脂分化能力 原代培养24 h后,少量细胞贴壁生长,可见较多红细胞悬浮,培养3 d半量换液,可见大量细胞贴壁生长(图1A)。传代培养第3代后,细胞仍呈梭形,放射状排列,呈成纤维细胞样特征,增殖能力旺盛(图1B)。第3代脂肪干细胞成骨诱导2周后行碱性磷酸酶染色和茜素红染色,诱导组细胞内可见蓝染的碱性磷酸酶颗粒(图1C),以及橘黄色的钙结节沉积(图1D);成脂诱导2周后行油红O染色,结果显示细胞内有红染的脂滴形成(图1E)。 2.2 玻璃化冻存前细胞在脱钙骨上的增殖情况 共聚焦显微镜观察,第3天时有大量的绿染活细胞黏附于支架材料上,第7天时细胞增殖明显,绿染的活细胞形态清晰可见,几乎无红染的死细胞。Hochest33258检测结果发现成骨诱导组和非成骨诱导组细胞数目均在第7天达到高峰随后进入平台期,诱导组和非诱导组保持相似的生长规律。结果证明脱钙骨有很好的组织相容性,可以保证细胞在支架材料上存活,由于第7天细胞数目达到高峰,选择诱导7 d后进行玻璃化冻存,见图2。 2.3 冻存前碱性磷酸酶活力 细胞支架材料复合物经成骨诱导后随着时间延长碱性磷酸酶表达逐渐升高,14 d达到高峰随后逐渐降低,而非诱导组碱性磷酸酶活力无明显变化,第4天以后诱导组碱性磷酸酶活力与非诱导组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图3。 2.4 复苏后细胞在支架材料的增殖情况 玻璃化冻存1周或者12周,共聚焦显微镜观察,复苏后第1天仍然可见较多绿染的活细胞,红染的死细胞数目较冻存前多,随着时间延长红染的死细胞逐渐减少,绿染的活细胞逐渐增多。Hochest33258细胞定量结果表明,与冻存前(成骨诱导1周)的细胞数相比,复苏后第1天细胞数目降低12.8%和13.3%,复苏后第3天细胞数目分别降低30.2%和31.2%,复苏3 d后细胞数目开始持续增加,第5天细胞数目到达冻存前的83.3%和82.2%,达到冻存前水平。玻璃化冻存1周与12周比较,复苏后在各个检测时间点的细胞数目无明显差异,见图4。 2.5 复苏后碱性磷酸酶活力 玻璃化冻存1周或者12周,复苏后1,4 d,碱性磷酸酶活力较冻存前降低,但是与冻存前差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),4 d后碱性磷酸酶活力持续升高。玻璃化冻存1周与12周比较,碱性磷酸酶活力差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图5。 2.6 复苏后成骨相关基因ALP、Runx-2、Col-1、OCN表达 玻璃化冻存1周或者12周,复苏后1 d和4 d各成骨基因表达量较冻存前降低,但是与冻存前相比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),4 d后各成骨基因表达量持续升高。冻存1周与12周比较,各个检测时间点成骨基因表达量差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图6。"
| [1] Sundararaj GD, Amritanand R, Venkatesh K, et al. The use of titanium mesh cages in the reconstruction of anterior column defects in active spinal infections: can we rest the crest. Asian Spine J. 2011;5(3): 155-161.[2] Sahoo NG, Pan YZ, Li L, et al. Nanocomposites for bone tissue regeneration. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2013;8(4):639-653.[3] Blokhuis TJ, Arts JJ. Bioactive and osteoinductive bone graft substitutes: definitions, facts and myths. Injury. 2011;42 Suppl 2:S26-29.[4] Zimmermann G, Moghaddam A. Allograft bone matrix versus synthetic bone graft substitutes. Injury. 2011;42 Suppl 2:S16-21.[5] Strioga M, Viswanathan S, Darinskas A, et al. Same or not the same? Comparison of adipose tissue-derived versus bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem and stromal cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(14): 2724-2752.[6] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, et al. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13(12):4279-4295.[7] Dimarino AM, Caplan AI, Bonfield TL. Mesenchymal stem cells in tissue repair. Front Immunol. 2013;4:201.[8] Obata A, Kasuga T. Stimulation of human mesenchymal stem cells and osteoblasts activities in vitro on silicon-releasable scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009;91(1):11-17.[9] Sheykhhasan M, Qomi RT, Ghiasi M. Fibrin Scaffolds Designing in order to Human Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Differentiation to Chondrocytes in the Presence of TGF-β3. Int J Stem Cells. 2015;8(2):219-227.[10] Sheykhhasan M, Qomi RT, Kalhor N, et al. Evaluation of the ability of natural and synthetic scaffolds in providing an appropriate environment for growth and chondrogenic differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Indian J Orthop. 2015;49(5):561-568.[11] Wu L, Cai X, Zhang S, et al. Regeneration of articular cartilage by adipose tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells: perspectives from stem cell biology and molecular medicine. J Cell Physiol. 2013;228(5):938-944.[12] Filardo G, Madry H, Jelic M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of cartilage lesions: from preclinical findings to clinical application in orthopaedics. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(8):1717-1729.[13] Holt DJ, Grainger DW. Demineralized bone matrix as a vehicle for delivering endogenous and exogenous therapeutics in bone repair. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64(12):1123-1128.[14] Pabaney AH, Reinard KA, Asmaro K, et al. Novel technique for cranial reconstruction following retrosigmoid craniectomy using demineralized bone matrix. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2015;136:66-70.[15] Schwartz Z, Hyzy SL, Moore MA, et al. Osteoinductivity of demineralized bone matrix is independent of donor bisphosphonate use. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(24):2278-2286.[16] Mandawala AA, Harvey SC, Roy TK, et al. Cryopreservation of animal oocytes and embryos: Current progress and future prospects. Theriogenology. 2016;86(7):1637-1644.[17] Yong KW, Wan Safwani WK, Xu F, et al. Cryopreservation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Clinical Applications: Current Methods and Challenges. Biopreserv Biobank. 2015;13(4):231-239.[18] Rall WF, Fahy GM. Ice-free cryopreservation of mouse embryos at -196 degrees C by vitrification. Nature. 1985;313(6003):573-575.[19] Slichter SJ, Jones M, Ransom J, et al. Review of in vivo studies of dimethyl sulfoxide cryopreserved platelets. Transfus Med Rev. 2014; 28(4):212-225. [20] Yong KW, Pingguan-Murphy B, Xu F, et al. Phenotypic and functional characterization of long-term cryopreserved human adipose-derived stem cells. Sci Rep. 2015;5:9596.[21] Miyagi-Shiohira C, Kurima K, Kobayashi N, et al. Cryopreservation of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell Med. 2015;8(1-2):3-7.[22] Schulz M, Risopatrón J, Matus G, et al. Trehalose sustains a higher post-thaw sperm motility than sucrose in vitrified human sperm. Andrologia. 2017;49(9). doi: 10.1111/and.12757. Epub 2017 May 25.[23] Zhang Z, Wang T, Hao Y, et al. Effects of trehalose vitrification and artificial oocyte activation on the development competence of human immature oocytes. Cryobiology. 2017;74:43-49.[24] 邢琼,王田娟,章志国,等.海藻糖应用于人类成熟卵母细胞玻璃化冷冻研究[J].安徽医药,2013,17(12):2134-2137.[25] Matsuo K, Takahashi T, Igarashi H, et al. Effects of different trehalose concentrations in a warming medium on embryo survival and clinical outcomes in vitrified human embryos. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2013; 76(4):214-220.[26] 符雪,王凌峰,陈吉,等. 海藻糖在低温保存组织中的应用研究现状[J].中国医疗前沿,2013,8(14):12-13.[27] Chen F, Zhang W, Wu W, et al. Cryopreservation of tissue-engineered epithelial sheets in trehalose. Biomaterials. 2011;32(33):8426-8435.[28] Yin H, Cui L, Liu G, et al. Vitreous cryopreservation of tissue engineered bone composed of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and partially demineralized bone matrix. Cryobiology. 2009;59(2):180-187.[29] 庸奇.脂肪干细胞-脱钙骨复合物玻璃化冻存的初步研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2014.[30] Drosse I, Volkmer E, Capanna R, et al. Tissue engineering for bone defect healing: an update on a multi-component approach. Injury. 2008;39 Suppl 2:S9-20.[31] Kofron MD, Opsitnick NC, Attawia MA, et al. Cryopreservation of tissue engineered constructs for bone. J Orthop Res. 2003;21(6):1005-1010.[32] Liu BL, McGrath JJ. Vitrification Solutions for the Cryopreservation of Tissue-Engineered Bone. Cell Preservation Technology. 2002; 2(2): 133-143.[33] Loutradi KE, Kolibianakis EM, Venetis CA, et al. Cryopreservation of human embryos by vitrification or slow freezing: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Fertil Steril. 2008;90(1):186-193.[34] James AW, Levi B, Nelson ER, et al. Deleterious effects of freezing on osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stromal cells in vitro and in vivo. Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(3):427-439.[35] Elder E, Chen Z, Ensley A, et al. Enhanced tissue strength in cryopreserved, collagen-based blood vessel constructs. Transplant Proc. 2005;37(10):4625-4629.[36] Song YC, Chen ZZ, Mukherjee N, et al. Vitrification of tissue engineered pancreatic substitute. Transplant Proc. 2005;37(1):253-255.[37] Song YC, An YH, Kang QK, et al. Vitreous preservation of articular cartilage grafts. J Invest Surg. 2004;17(2):65-70.[38] Kuleshova LL, Gouk SS, Hutmacher DW. Vitrification as a prospect for cryopreservation of tissue-engineered constructs. Biomaterials. 2007; 28(9):1585-1596. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [5] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [6] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [7] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [8] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [9] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [10] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [11] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [12] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [13] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [14] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [15] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||