Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (1): 70-76.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0413
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells versus bone marrow mononuclear cells for treating cerebral palsy
Dai Guang-hui, Liu Xue-bin, Zhang Zan, Cheng Hong-bin, Wang Xiao-dong, An Yi-hua
- Department of Neurosurgery, General Hospital of Chinese People’s Armed Police Force, Beijing 100039, China
-
Revised:2017-08-19Online:2018-01-08Published:2018-01-08 -
About author:Dai Guang-hui, M.D., Attending physician, Department of Neurosurgery, General Hospital of Chinese People’s Armed Police Force, Beijing 100039, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Dai Guang-hui, Liu Xue-bin, Zhang Zan, Cheng Hong-bin, Wang Xiao-dong, An Yi-hua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells versus bone marrow mononuclear cells for treating cerebral palsy[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(1): 70-76.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
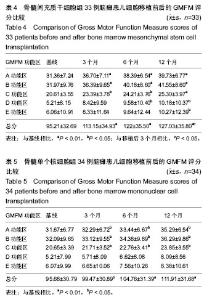
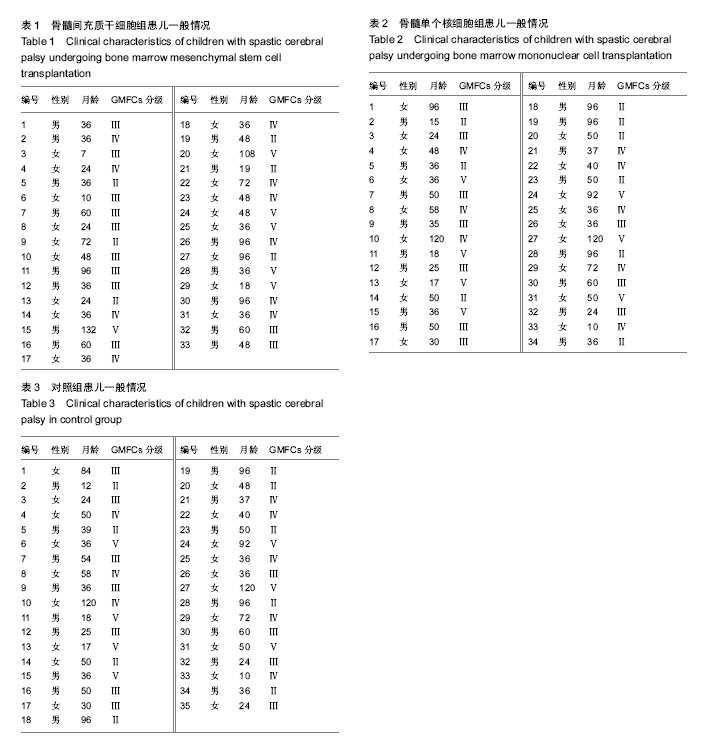
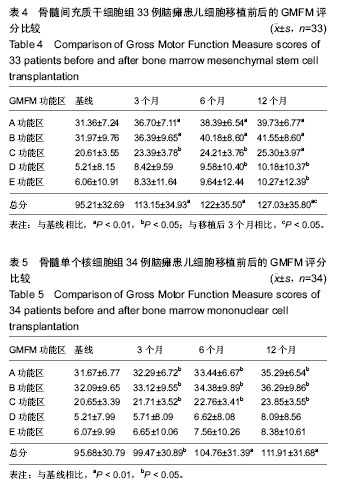
2.4 BMMSC组脑瘫患儿细胞移植治疗前后粗大运动功能的变化 见表4。治疗后3个月GMFM评分与移植前相比,A、B、C功能区得分均有显著改善(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);GMFM总分也有明显提高(P < 0.01);D、E功能区评分较移植前有所提高,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。治疗后6个月GMFM评分与移植前相比,A、B、C、D功能区得分有显著改善(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);GMFM总分也显著提高(P < 0.05);E区评分与移植前比较无显著变化(P > 0.05)。治疗后12个月GMFM评分与移植前相比,A、B、C、D、E功能区得分有显著改善(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);GMFM总分也显著提高(P < 0.01)。 2.5 BMMNC组脑瘫患儿细胞移植治疗后粗大运动功能的变化 见表5。治疗后3个月GMFM评分与移植前相比,A、B、C功能区得分有显著改善(P < 0.05);GMFM总分也有明显提高(P < 0.01);D、E功能区评分较移植前有所提高,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。治疗后6个月GMFM评分与移植前相比,A、B、C功能区得分有显著改善(P < 0.05);GMFM总分也显著提高(P < 0.05);D、E功能区评分与移植前比较无显著变化(P > 0.05)。治疗后12个月GMFM评分与移植前相比,A、B、C功能区得分有显著改善(P < 0.05);GMFM总分也显著提高(P < 0.01)。"
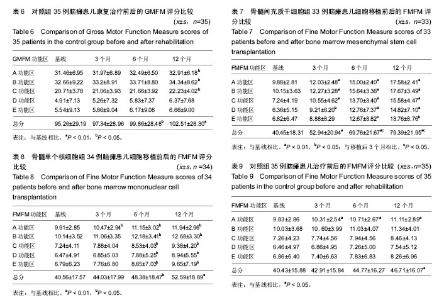
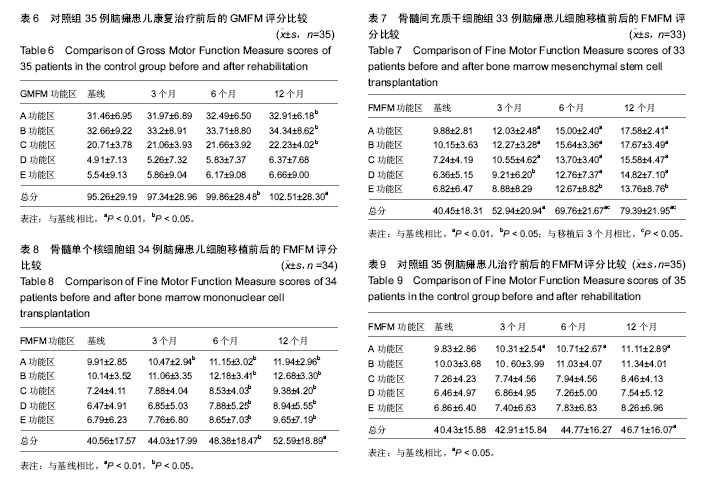
对照组脑瘫患儿治疗后粗大运动功能的变化 见表6。治疗后3个月GMFM评分与治疗前相比,A、B、C、D、E功能区得分、GMFM总分较康复治疗前有所提高,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。治疗后6个月GMFM评分与康复治疗前相比,A、B、C、D、E功能区得分、GMFM总分较康复治疗前有所提高,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。治疗后12个月GMFM评分与康复治疗前相比,A、B、C功能区得分有显著改善(P < 0.05);GMFM总分也显著提高(P < 0.01)。D、E功能区得分提高差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 2.7 各组、各时间段GMFM评分对比 各组治疗后3个月,BMMSC组A功能区得分他两组比较差异有显著性意义 (P < 0.05),BMMNC组和对照组之间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);C功能区得分MSC组和BMMNC组、BMMNC组和对照组之间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),BMMSC组和对照组之间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);B、D、E功能区得分及GMFM总分各组之间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 各组治疗后6个月,BMMSC组A、B功能区得分MFM总分和其他两组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),BMMNC组和对照组之间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);C功能区得分BMMSC组和BMMNC组、BMMNC组和对照组之间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),BMMSC组和对照组之间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);D、E功能区得分各组之间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 各组治疗后12个月,BMMSC组A、B、C功能区得分及GMFM总分和其他两组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),BMMNC组和对照组之间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);D、E功能区得分各组之间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 2.8 BMMSC组脑瘫患儿细胞移植治疗前后的精细运动功能的变化 见表7。细胞移植治疗后3个月FMFM评分与移植前相比,A、B、C、D功能区得分有显著改善(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);FMFM总分也有显著改善(P < 0.01);E功能区评分较移植前有所提高,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。治疗后6个月FMFM评分与移植前相比,A、B、C、D、E功能区得分有显著改善(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);GMFM总分也显著提高(P < 0.01);治疗后12个月FMFM评分与移植前相比,A、B、C、D、E功能区得分有显著改善(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);FMFM总分也显著提高(P < 0.01)。 2.9 BMMNC组脑瘫患儿细胞移植治疗前后的精细运动功能的变化 见表8。细胞移植治疗后3个月FMFM评分与移植前相比,A功能区得分有显著改善(P < 0.05);B、C、D、E功能区得分,FMFM总分较移植前有所提高,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。治疗后6个月FMFM评分与移植前相比,A、B、C、D、E功能区得分有显著改善(P < 0.05);FMFM总分也显著提高(P < 0.05);治疗后12个月FMFM评分与移植前相比,A、B、C、D、E功能区得分有显著改善(P < 0.05);FMFM总分也显著提高(P < 0.01)。 2.10 对照组脑瘫患儿治疗前后的精细运动功能的变化 见表9。治疗后3个月FMFM评分与治疗前相比,A功能区得分有显著改善(P < 0.05);B、C、D、E功能区得分,FMFM总分较治疗前有所提高,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。治疗后6个月FMFM评分与治疗前相比,A功能区得分有显著改善(P < 0.05);B、C、D、E功能区得分,FMFM总分较治疗前有所提高,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);治疗后12个月FMFM评分与治疗前相比,A功能区得分、FMFM总分有显著改善(P < 0.05)。 2.11 各组、各时间段FMFM评分对比 各组治疗后3个月,BMMSC组A、C功能区得分和其他两组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),BMMNC组和对照组之间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);B、D、E功能区得分及GMFM总分各组之间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 各组治疗后6个月,BMMSC组A、B、C、D、E功能区得分及GMFM总分和其他两组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),BMMNC组和对照组之间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 各组治疗后12个月,BMMSC组A、B、C、D、E功能区得分及GMFM总分和其他两组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),BMMNC组和对照组之间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 2.12 不良反应 ①头晕头痛:BMMNC组有6例(6/33)患儿、BMMSC组中有6例(6/34)患儿术后48 h内出现低颅压反应,表现为轻度头晕头痛,偶伴恶心、呕吐,呕吐呈非喷射性。上述症状下床活动后加重,平卧时症状缓解或消失。嘱这些患者采取去枕平卧位、静脉点滴生理盐水后症状缓解和消失;②发热:BMMNC组有6例(6/33)患儿、BMMSC组中有6例(6/34)患儿在术后出现了发热,均在38.5 ℃以下,无需处理,均在数小时内下降至正常。"
| [1] Shevell MI, Majnemer A, Morin I. Etiologic yield of cerebral palsy: a contemporary case series. Pediatr Neurol. 2003;28(5):352-359.[2] Paneth N, Hong T, Korzeniewski S. The descriptive epidemiology of cerebral palsy. Clin Perinatol. 2006;33(2):251-267.[3] Holt RL, Mikati MA. Care for child development: basic science rationale and effects of interventions. Pediatr Neurol. 2011;44(4):239-253.[4] Sharma A, Sane H, Gokulchandran N, et al. A clinical study of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells for cerebral palsy patients: a new frontier. Stem Cells Int. 2015;2015:905874.[5] Feng M, Lu A, Gao H, et al. Safety of Allogeneic Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells Therapy in Patients with Severe Cerebral Palsy: A Retrospective Study. Stem Cells Int. 2015;2015:325652.[6] Shroff G, Gupta A, Barthakur JK. Therapeutic potential of human embryonic stem cell transplantation in patients with cerebral palsy. J Transl Med. 2014;12:318.[7] Tan H, Kang X, Lu S, et al. The therapeutic effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells after optic nerve damage in the adult rat. Clin Interv Aging. 2015;10:487-490.[8] Wang X, Cheng H, Hua R, et al. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells on gross motor function measure scores of children with cerebral palsy: a preliminary clinical study. Cytotherapy. 2013;15(12):1549-1562.[9] Li M, Yu A, Zhang F, et al. Treatment of one case of cerebral palsy combined with posterior visual pathway injury using autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Transl Med. 2012;10:100.[10] Wang X, Hu H, Hua R, et al. Effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells on motor functions of identical twins with cerebral palsy: pilot study on the correlation of efficacy and hereditary factors. Cytotherapy. 2015;17(2):224-231.[11] Wang S, Cheng H, Dai G, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation significantly improves neurological function in patients with sequelae of traumatic brain injury. Brain Res. 2013;1532:76-84. [12] Knox V, Evans AL. Evaluation of the functional effects of a course of Bobath therapy in children with cerebral palsy: a preliminary study. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2002;44(7):447-460.[13] Fan HC, Ho LI, Chi CS, et al. Current proceedings of cerebral palsy. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(3):471-485.[14] Zhu J, Xiao Y, Li Z, et al. Efficacy of Surgery Combined with Autologous Bone Marrow Stromal Cell Transplantation for Treatment of Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stem Cells Int. 2015;2015:318269.[15] Taguchi A, Sakai C, Soma T, et al. Intravenous Autologous Bone Marrow Mononuclear Cell Transplantation for Stroke: Phase1/2a Clinical Trial in a Homogeneous Group of Stroke Patients. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(19):2207-2218.[16] Cheng H, Liu X, Hua R, et al. Clinical observation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in treatment for sequelae of thoracolumbar spinal cord injury. J Transl Med. 2014;12:253.[17] Nakamura K, Mieda T, Suto N, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells as a potential therapeutic tool for spinocerebellar ataxia. Cerebellum. 2015;14(2):165-170.[18] Ren C, Geng RL, Ge W, et al. An observational study of autologous bone marrow-derived stem cells transplantation in seven patients with nervous system diseases: a 2-year follow-up. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014;69(1):179-187.[19] Mundkur N. Neuroplasticity in children. Indian J Pediatr. 2005;72(10): 855-857.[20] Wang L, Ji H, Zhou J, et al. Therapeutic potential of umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells transplantation for cerebral palsy: a case report. Case Rep Transplant. 2013;2013:146347.[21] Chen G, Wang Y, Xu Z, et al. Neural stem cell-like cells derived from autologous bone mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of patients with cerebral palsy. J Transl Med. 2013;11:21.[22] Bae KS, Park JB, Kim HS, et al. Neuron-like differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Yonsei Med J. 2011;52(3): 401-412.[23] Chen A, Siow B, Blamire AM, et al. Transplantation of magnetically labeled mesenchymal stem cells in a model of perinatal brain injury. Stem Cell Res. 2010;5(3):255-266.[24] Alvarez P, Carrillo E, Vélez C, et al. Regulatory systems in bone marrow for hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells mobilization and homing. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:312656.[25] Zhang MJ, Sun JJ, Qian L, et al. Human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells enhance the expression of neurotrophic factors and protect ataxic mice. Brain Res. 2011;1402:122-131.[26] Liu R, Zhang Z, Lu Z, et al. Human umbilical cord stem cells ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by regulating immunoinflammation and remyelination. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(7): 1053-1062.[27] Lee RH, Pulin AA, Seo MJ, et al. Intravenous hMSCs improve myocardial infarction in mice because cells embolized in lung are activated to secrete the anti-inflammatory protein TSG-6. Cell Stem Cell. 2009;5(1):54-63.[28] Sun L, Wang D, Liang J, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in severe and refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(8):2467-2475.[29] Li XY, Zheng ZH, Li XY, et al. Treatment of foot disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus using human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells: response and correction of immunological anomalies. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(27):4893-4899.[30] Sharma A, Gokulchandran N, Sane H, et al. Autologous bone marrow mononuclear cell therapy for autism: an open label proof of concept study. Stem Cells Int. 2013;2013:623875.[31] Liu SY, He YB, Deng SY, et al. Exercise affects biological characteristics of mesenchymal stromal cells derived from bone marrow and adipose tissue. Int Orthop. 2017;41(6):1199-1209.[32] Dharmasaroja P. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of ischemic stroke. J Clin Neurosci. 2009;16(1):12-20. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [14] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [15] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||