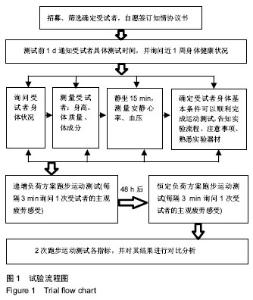
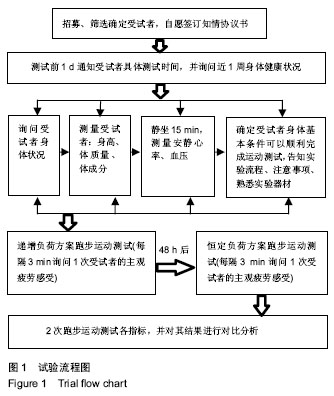
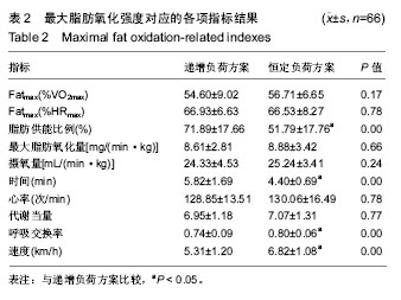
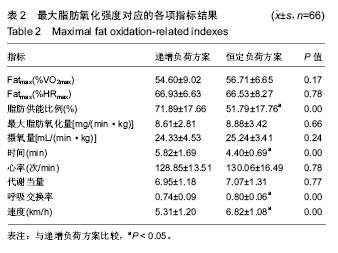
| [1] 2010年国民体质监测公报[EB].www.sport.gov.cn/.2011-09-02.[2] 2014年国民体质监测公报[OL].www.gov.cn/.2016-05-13.[3] 谭思洁,郭振等,王建雄.最大脂肪氧化强度运动干预肥胖症理论与应用研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2013,28(10):975-977.[4] 谭思洁,郭振.9-10岁肥胖男童最大脂肪氧化强度运动减重处方的研究[J].体育科学,2016,36(9):36-39.[5] 赵建宇.40-60岁不同体脂百分比人群最大脂代谢强度及影响因素的研究[D].北京:北京体育大学,2015.[6] 刘琴芳.运动减肥的机制及运动处方[J].中国体育科技,2002,38(11):66.[7] Amati F, Dube JJ, Alvarez-Carnero E, et al. Skeletal muscle triglyycerides, diacylglycerols, and ceramides in insulin resistance: another paradox in endurance-trained athletes. Diabetes. 2011; 60(10):2588-2597.[8] Tan S, Yang C, Wang J. Physical training of 9-10-year-old children with obesity to lactate threshold intensity. Pediatr Exerc Sci. 2010;22(3): 477-485..[9] Bircher MS, Knechtle B, Muller G, et al. Is the highest Fat Oxidation Rate Coincident with the Anaerobic Threshold in Obese Women and Men. Eur J Sport Sci. 2005;5(2):79-87.[10] Dumortier M, Brandou F, Perez-Martin A, et al. Low intensity endurance exercise targeted for lipid oxidation improves body composition and insulin sensitivity in patients with the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Metab. 2003;29(5):509-518.[11] Brandou F, Dumortier M, Garandeau P, et al. Effects of a two-month rehabilitation program on substrate utilization during exercise in obese adolescents. Diabetes Metab. 2003;29(1):20-27.[12] 李奕,郭路.最大脂肪代谢强度在大学生耐力运动处方中的应用[J].长江大学学报(自然版),2015,12(28):67-70.[13] 高峰,崔文丽.代谢综合征运动处方制定的新模式-最大脂代谢强度运动处方[J].中国运动医学杂志,2012,31(9):835-838.[14] 张勇,李之俊.训练者和无训练者脂肪氧化动力学与最大脂肪氧化强度研究[J].体育科学,2013,33(2):61-67.[15] Crisp NA, Fournier PA, Licari MK, et al. Adding sprints to continuous exercise at the intensity that maximizes fat oxidation:implication for acute energy balance and enjoyment. Metabolism. 2012,62(9): 1280-1288.[16] Cheneviere X, Borrani F, Sangsue D, et al. Gender differences in whole-body fat oxidation kinetics during exercise. Apply Physiol Nutr Metab. 2011;36(1):88-95.[17] 张勇,李之俊.无训练年轻女性骑车与跑步的脂肪动力学及最大脂肪氧化研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2013,32(5):408-412.[18] Haufe S, Engeli S, Budziarek P, et al. Determinants of exercise-induced fat oxidation in obese women and men. Horm Metab Res. 2010;42(3):215-221.[19] Crisp NA, Guelfi KJ, Licari MK, et al. Does exercise duration affect Fatmax in overweight boys? Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012;112(7):2557-2564.[20] Moro C, Polak J, Hejnova J, et al. Atrial natriuretic peptide stimulates lipid mobilization during repeated bouts of endurance exercise. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Matab. 2006;290(5):E864-E869.[21] 宋伟,胡柏平.最大脂肪代谢强度与有氧耐力及RPE关系的试验研究[J].陕西师范大学学报(自然科学版),2013,11(1):104-108.[22] Ahemd K, Tunaru S, Tang C, et al. An autocrine lactate loop medicates insulin-dependent inhibition of lipolysis through GRR81. Cell Metab. 2010;11(4):311-319.[23] 张勇.运动与脂肪氧化动力学及最大脂肪氧化研究[D].上海:上海体育学院,2013.[24] Scharhag-Rosenberger F, Meyer T, Walitzek S, et al. Effects of one year aerobic endurance training on resting metabolic rate and exercise fat oxidation in previously untrained men and women. Metabolic endurance training adaptations. Int J Sports Med. 2010;31(7):498-504.[25] Van Loon LJC, Greenhaff PL, Constantin-Teodosiu D, et al. The effect of increasing exercise intensity on muscle fuel utilization in human. J Physiol. 2001;536(1):295-304.[26] Cheneviere X, Malatesta D, Peters EM, et al. A mathematical model to describe fat oxidation kinetics during graded exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2009;41(8):1615-1625.[27] Bernard T, Vercruyssen F, Mazure C, et al. Constant versus variable-intensity during cycling effect on subsequent running performance. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2007;99(2):103-111.[28] Kang J, Mangine GT, Ratamess NA, et al. Influence of intensity fluctuation on exercise metabolism. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2007;100(3): 253-260.[29] 彭慧玲.基于脂肪最大氧化的运动强度研究[D].杭州:浙江师范大学,2012.[30] Bergman BC, Butterfiele GE, Wolfel E, et al. Evaluation of exercise and training on muscle lipid metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1999;276: 106-117.[31] Nordby P, Saltin B, Helge JW. Whole-body fat oxidation determined by grader exercise and indirect calorimetey: a role for muscle oxidation capacity? Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2006;16:209-214.[32] Achten J, Jeukendrup AE. Maximal fat oxidation during exercise in training men. Int J Sports Med. 2003;24:603-698.[33] 邓树勋,王建,乔德才.运动生理学[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2009.[34] Astorino TA. Is the ventilator threshold coincident with maximal fat oxidation during submaximal exercise in women? Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2000;40(3):209-216.[35] Stisen AB, Stougaard O, Langfort J, et al. Maximal fat oxidation rates in endurance trained and untrained women. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2006; 98(5):497-506. |