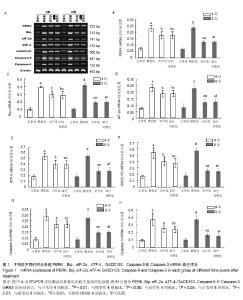
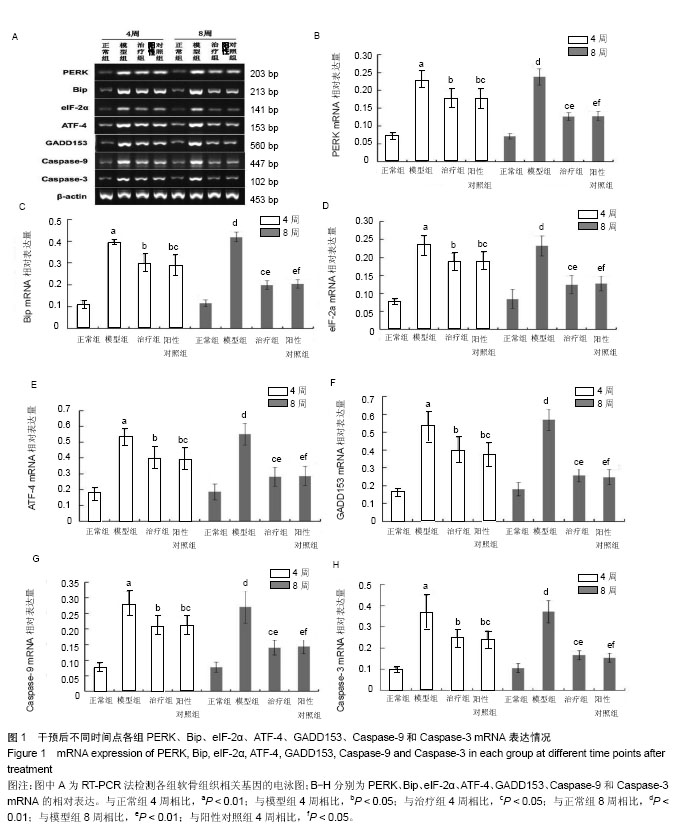
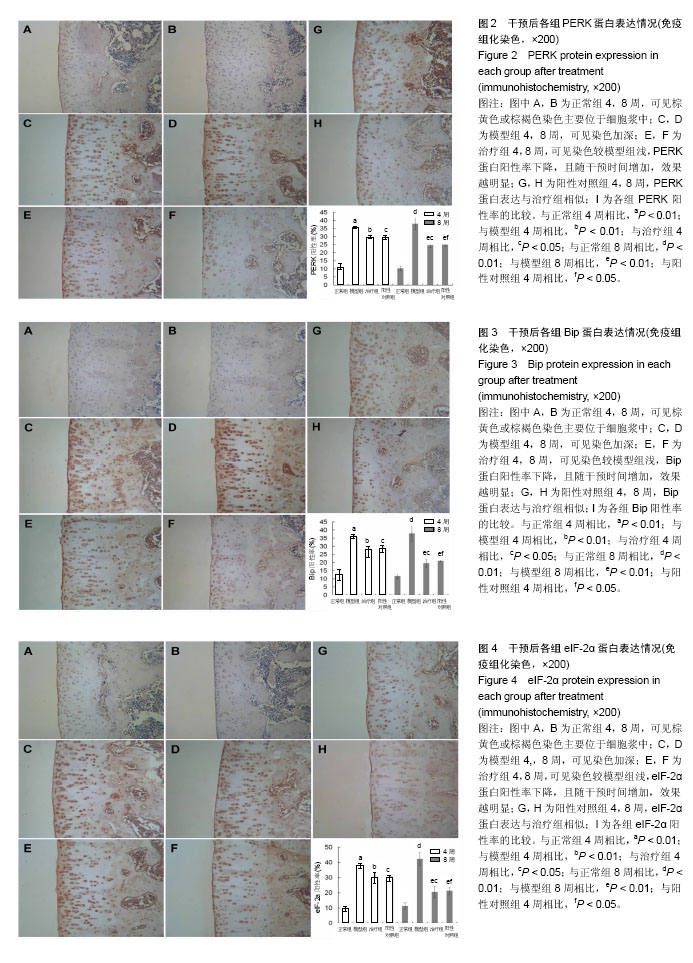
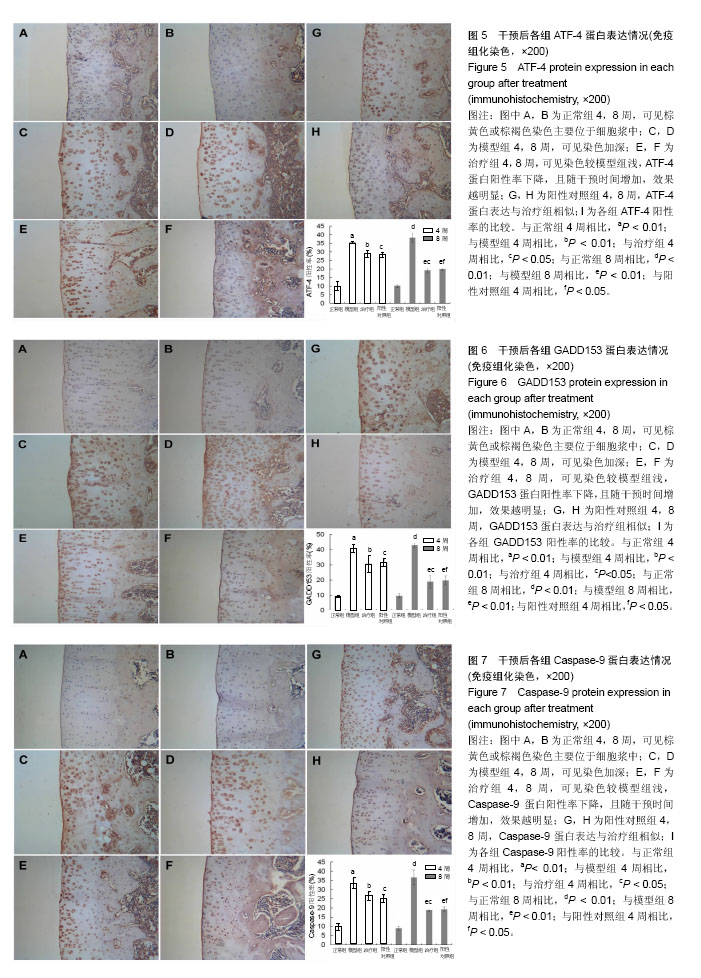
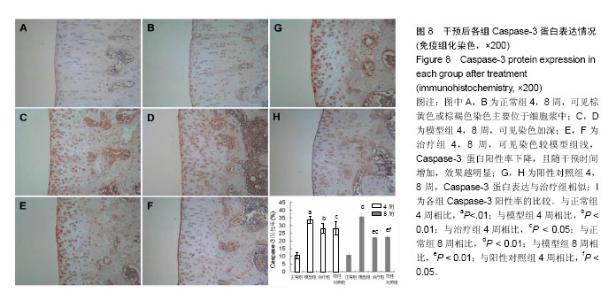
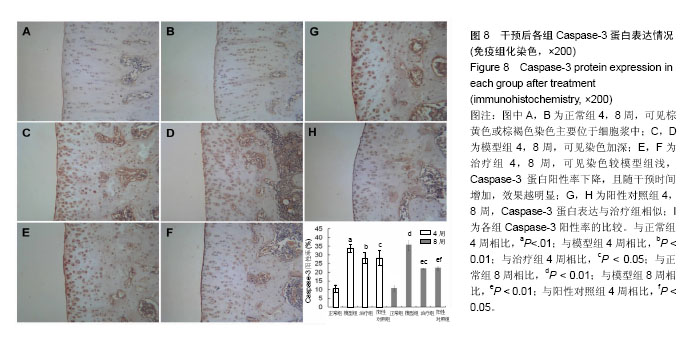
| [1] Dahm DL, Al-Rayashi W, Dajani K, et al. Patellofemoral arthroplasty versus total knee arthroplasty in patients with isolated patellofemoral osteoarthritis. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2010; 39(10):487-491.[2] Vuolteenaho K, Moilanen T, Knowles RG, et al. The role of nitric oxide in osteoarthritis. Scand J Rheumatol.2007;36(4): 247-258.[3] Shakoor MA, Rahman MS, Azad AK, et al. Effects of isometric quadriceps muscle strengthening exercise on chronic osteoarthritis of the knee. Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull.2010; 36(1): 20-22.[4] 李宁华,薛庆云,张毅,等.中国六城市中老年人群X线膝骨关节炎流行病学分析[J].实用医学杂志,2008,24(16):2887-2888.[5] Meng Z, Huang R. Topical Treatment of Degenerative Knee Osteoarthritis. Am J Med S. 2018;355(1):6-12.[6] Proffen B, Vavken P, Dorotka R. Surgical management of osteoarthritis. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2013;163(9-10):243-250.[7] 刘献祥. 中医药治疗膝骨性关节炎的研究现状[J].中医正骨, 2012,24(1): 5-9.[8] Roush JK, Cross AR, Renberg WC, et al. Evaluation of the effects of dietary supplementation with fish oil omega-3 fatty acids on weight bearing in dogs with osteoarthritis. J Am Vet Med Assoc.2010;236(1): 67-73.[9] 李西海,梁文娜.软骨下骨骨重塑与骨关节炎的关系[J].国际骨科学杂志. 2007,28(1):35-37.[10] Sandell LJ, Aigner T. Articular cartilage and changes in arthritis. An introduction: Cell biology of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res.2001;3(2):107-113.[11] Malemud CJ. Protein kinases in chondrocyte signaling and osteoarthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(427 Supp l): 145-151. [12] Mistry D, Oue Y, Chambers MG, et al. Chondrocyte death during murine osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2004;12(2):131-141.[13] Zhang P, McGrath B, Li S, et al. The PERK eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha kinase is required for the development of the skeletal system, postnatal growth, and the function and viability of the pancreas. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22(11): 3864-3874.[14] Wang FM, Galson DL, Roodman GD, et al. Resveratrol triggers the pro-apoptotic endoplasmic reticulum stress response and represses pro-survival XBP1 signaling in human multiple myeloma cells. Exp Hematol.2011;39(10): 999-1006.[15] 吴广文,褚剑锋,许惠凤,等.独活寄生汤的药理作用及其在治疗骨性关节炎中的应用[J].中医正骨,2012,24(1):37-39.[16] 王武炼,叶锦霞,刘献祥,等.独活寄生汤加减内服外洗治疗膝骨性关节炎66例临床观察[J].福建中医药大学学报,2011,21(2):44-45.[17] 周腊梅,王亚克.独活寄生汤治疗膝骨关节炎的临床疗效观察[J].成都中医药大学学报,2014,37(3):46-48,78.[18] 邝高艳,严可,柴爽,等.独活寄生汤加减治疗膝骨关节炎疗效及安全性的Meta分析[J].中医药导报,2016,22(17):59-62.[19] 万美珍,邓紫玉,代龙金.独活寄生汤治疗肝肾不足型膝骨关节炎的临床疗效观察[J].中国社区医师,2017,33(14):92-93.[20] 刘云,张敏.独活寄生汤联合运动疗法治疗膝骨关节炎临床观察[J].风湿病与关节炎,2017,6(2):29-32.[21] 吴广文,王武炼,潘彩彬,等.独活寄生汤含药血清对大鼠退变软骨细胞线粒体凋亡通路的影响[J].风湿病与关节炎, 2014,3(10):5-9.[22] 李西海,梁文娜,党传鹏,等.补肾壮筋汤抑制炎性细胞因子表达延缓骨关节炎软骨退变的研究[J].风湿病与关节炎, 2014,3(5):20-25.[23] 黄继汗,黄晓晖,陈志扬,等.药理试验中动物间和动物与人体间的等效剂量换算[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学. 2004,9(9):1069-1072.[24] Soslow RA, Dannenberg AJ, Rush D, et al. Cox-2 is expressed in human pulmonary, colonic, and mammary tumors. Cancer.2000;89(12): 2637-2645.[25] 许守明,陈双喜,何艳霞.细胞凋亡与细胞色素C[J].安徽农学通报.2009, 15(15):38-39. [26] Grishko V, Xu M, Wilson G, et al. Apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction in human chondrocytes following exposure to lidocaine, bupivacaine, and ropivacaine. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2010;92(3): 609-618.[27] Rösler S, Haase T, Claassen H, et al. Trefoil factor 3 is induced during degenerative and inflammatory joint disease, activates matrix metalloproteinases,and enhances apoptosis of articular cartilage chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum.2010;62(3):815-825.[28] Yu SM, Kim SJ. Endoplasmic reticulum stress (ER-stress) by 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2DG) reduces cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression and N-glycosylation and induces a loss of COX-2 activity via a Src kinase-dependent pathway in rabbit articular chondrocytes. Exp Mol Med.2010; 42(11): 777-786.[29] Oliver BL, Cronin CG, Zhang-Benoit Y, et al. Divergent stress responses to IL-1beta, nitric oxide, and tunicamycin by chondrocytes. J Cell Physiol.2005; 204(1): 45-50.[30] Hamamura K, Yokota H. Stress to endoplasmic reticulum of mouse osteoblasts induces apoptosis and transcriptional activation for bone remodeling. FEBS Lett.2007; 581(9):1769-1774.[31] Jager R, Bertrand MJ, Gorman AM, et al. The unfolded protein response at the crossroads of cellular life and death during endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biol Cell.2012;104(5): 259-270.[32] Rodriguez D, Rojas-Rivera D, Hetz C. Integrating stress signals at the endoplasmic reticulum: The BCL-2 protein family rheostat. Biochim Biophys Acta.2011;1813(4): 564-574.[33] Rasheva VI, Domingos PM. Cellular responses to endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis. Apoptosis.2009;14(8): 996-1007.[34] Grishko V, Xu M, Wilson G, et al. Apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction in human chondrocytes following exposure to lidocaine, bupivacaine, and ropivacaine. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2010;92(3): 609-618.[35] Seol JW, Lee HB, Lee YJ, et al. Hypoxic resistance to articular chondrocyte apoptosis—a possible mechanism of maintaining homeostasis of normal articular cartilage. FEBS J.2009;276(24): 7375-7385.[36] 王海泉.盐酸氨基葡萄糖胶囊治疗膝骨性关节炎的疗效观察[J].中国医院用药评价与分析,2016,16(5):603-605. |