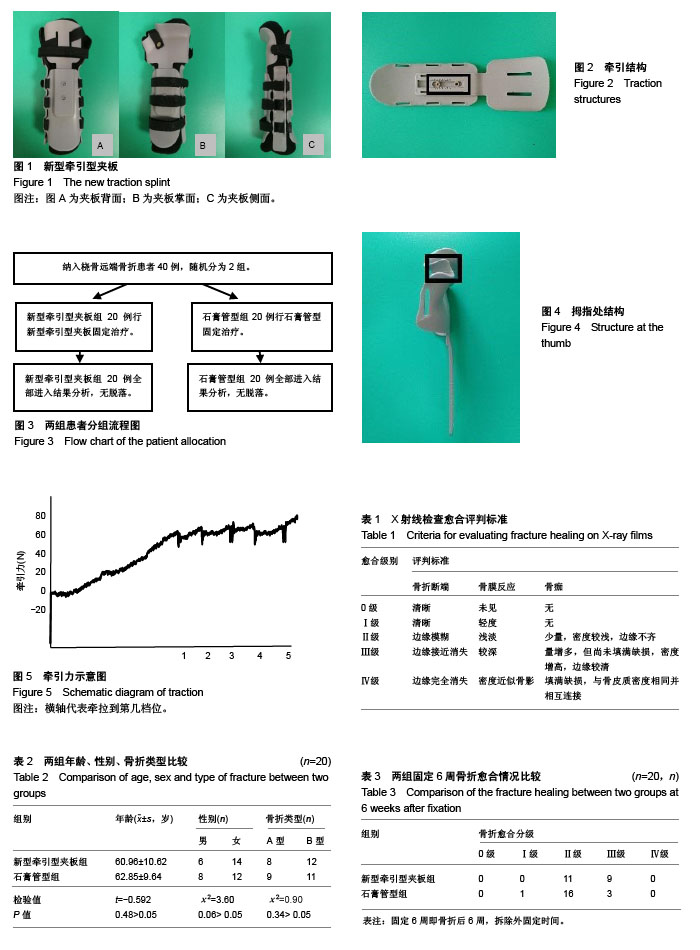
| [1] Hanel DP, Jones MD, Trumble TE, et al. Wrist fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 2002;33(1):35-57.[2] Koval K, Haidukewych GJ, Service B, et al. Controversies in the management of distal radius fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014;22(9):566-575.[3] Muller ME,Allgower M,Schneider R,et al. Manualofinternalfixation. Techniques recommend by the AO-ASIF group.3rd Edit.New York: Springer,1991.[4] Mulder MA, Walenkamp MM, Goslings JC, et al.Internal plate fixation versus plaster in displaced complete articular distal radius fractures, a randdomised controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17:68.[5] 赵继荣,李红专,慕向前.桡骨远端骨折的非手术治疗进展[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2015,23(12):77-80.[6] 周成洪,龙亨国,马一平.夹板固定与石膏固定治疗桡骨远端关节外骨折的疗效比较[J].中国骨伤,2007,20(7):474-475.[7] 王猛,何向阳,郭仪林,等.石膏托和夹板外固定治疗桡骨远端伸直型骨折的疗效比较[J].医学综述,2012,18(4):638-639.[8] 杜宁.骨折治疗的理想方法和原则[J].中国骨伤,2002,15(2):84-85.[9] 徐振东,刘曦明.微动促进骨折愈合的机制及临床应用研究现状[J].创伤外科杂志,2017,19(3):228-230+234.[10] 李颖,黎立,李俊玲,等.力学环境对骨折早期骨折端间充质干细胞募集的影响[J].国际骨科学杂志,2016,37(3):198-202.[11] 王亦璁.骨与关节损伤[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2001:659.[12] 王娟. 桡骨近端骨折、脱位的生物力学与临床研究[D].河北医科大学, 2013.[13] 江洁清,张继宗,刘旭丹.X线数字图像法推断前臂骨折形成时间[J].中国法医学杂志,2010,25(3):165-168.[14] 蒋协远,王大伟.骨科临床疗效评价标准[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2005: 37-48.[15] 周瑜,邹洪宇,陈波涛.功能锻炼及中药熏洗对桡骨远端骨折后关节僵凝的疗效观察[J].中国医药导刊,2013,15(2):207-208.[16] 薛彬,奚小冰,万世元,等.可塑性夹板中立位固定治疗伸直型桡骨远端骨折的临床研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2015,23(5):16-19.[17] 阳华. 不同方法治疗桡骨远端骨折的临床对比研究[D].中南大学,2013.[18] 谢健,袁惠霞.手法整复桡骨远端骨折[J].临床骨科杂志, 2018,21(2):254.[19] 徐善强,陈星,张兴平,等.功能锻炼对桡骨远端骨折拆除石膏外固定后腕关节康复的影响[J].中医正骨,2015,27(10):58-59+62.[20] 廖世亮,陈莉,杨熹.中药熏洗联合功能锻炼预防桡骨远端骨折后腕关节僵硬临床观察[J].实用中医药杂志, 2017,33(12):1369-1370.[21] 陈敏,白龙.高分子石膏夹板治疗桡骨远端Colles骨折[J].实用骨科杂志, 2012,18(8):734-736.[22] 刘李旭,戴鑫志,侯振宇,等.基于光栅投影法的3D扫描技术研究[J].电光与控制,2017,24(6):101-105.[23] 孟钊,王晨,郭旭朝,等.基于感压纸材料的小型猪上胸椎生物力学试验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2016,30(8):992-997.[24] 徐文鹏,王伟明,李航,等.面向3D打印体积极小的拓扑优化技术[J].计算机研究与发展,2015,52(1):38-44.[25] 杨新宇,詹成,李明,等.3D打印技术在医学中的应用进展[J].复旦学报(医学版),2016,43(4):490-494.[26] 耿长雨. 不同类型腕舟状骨骨折治疗方法的选择[D].河北医科大学,2017.[27] 丁锦希,谢睿,董锐,等.我国医用耗材分类采购制度初探[J].中国医疗器械杂志,2018,42(2):147-149.[28] 孔梅,李炜,李海丽,等.四种常用假肢材料与人体皮肤摩擦学特性的研究[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2008,5(5):1107-1111+1125.[29] 王燎,戴尅戎. 骨科个体化治疗与3D打印技术[J]. 医用生物力学,2014, 29(3):193-199.[30] 陶宝琛,姜昆,郑斌,等.智能气囊小夹板治疗桡骨远端伸直型关节内骨折的三维有限元分析研究[J].中华中医药杂志, 2017,32(4):1856-1859.[31] 吴雨芬,汪郁明,王一婷,等.生物医用纺织材料在康复医学中的应用[J].生物医学工程学进展,2017,38(4):208-214.[32] 何俊杰,周倬瑜,谭三元,等.计算机辅助3D打印在骨盆骨折个性化诊疗方案中的应用[J].现代诊断与治疗, 2015,26(12):2724-2725.[33] 刘李旭,戴鑫志,侯振宇,等.基于光栅投影法的3D扫描技术研究[J].电光与控制,2017,24(6):101-105. |