Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (35): 5706-5714.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0316
Previous Articles Next Articles
Triaxial accelerometer applied in assessing physical activity: current status and prospects
Xie Haodong1, 2, Luo Jiong1, 2, Zhang Tingran1, 2
- 1College of Sports, Southwest University, State Key Laboratory of Physical Fitness Evaluation and Sports Function Monitoring, General Administration of Sport of China, Chongqing 400715, China; 2Institute for Sports Rehabilitation, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China
-
Contact:Luo Jiong, PhD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, College of Sports, Southwest University, State Key Laboratory of Physical Fitness Evaluation and Sports Function Monitoring, General Administration of Sport of China, Chongqing 400715, China; Institute for Sports Rehabilitation, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China -
About author:Xie Haodong, Master candidate, Research assistant, College of Sports, Southwest University, State Key Laboratory of Physical Fitness Evaluation and Sports Function Monitoring, General Administration of Sport of China, Chongqing 400715, China; Institute for Sports Rehabilitation, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China -
Supported by:the Basic Scientific Research Project of Central University of Southwest University, No. SWU1709433
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xie Haodong, Luo Jiong, Zhang Tingran. Triaxial accelerometer applied in assessing physical activity: current status and prospects[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(35): 5706-5714.
share this article
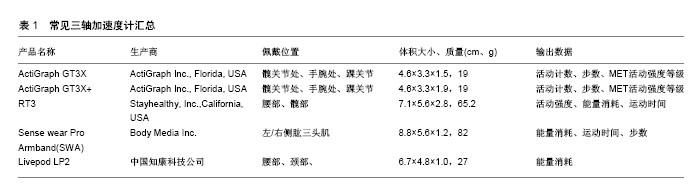
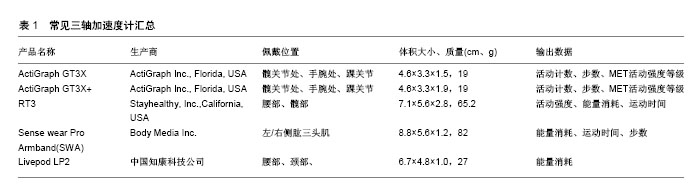
2.1 加速度计种类及工作原理 目前常见的加速度计多为压电感应,按照加速度计内部压电陶瓷的数量,可将加速度计分为单轴加速度计、三轴加速度计以及多轴加速度计。单轴加速度的代表计主要有ActiGraph 7164/71256、ActiGraph GT1M:两者的佩戴建议均为髋部、手腕部、踝部,相对于前者而言ActiGraph GT1M除具有记录能量消耗的功能外,还具有记录活动计数、步数、MET活动强度等级的功能;RT3/R3D(StayHealth公司生产),是国际上应用最广泛的三轴加速度计之一,值得一提的是RT3/R3D也是最早使用三轴技术的惯性感测器,RT3是在R3D的基础上生产的,可以说是R3D的加强版,相比之下,体积比R3D更小、携带更方便,具有记录活动强度、能量消耗、MET的功能。除此之外,ActiGraph系列三轴加速度计(GT3X、GT3X+等)也是目前广泛应用的加速度计,具有记录活动计数、步数、MET活动强度等级的功能,相对于RT3而言,ActiGraph系列三轴加速度计在国内的应用更为广泛(表1);IDEEA是典型的多轴加速度计,可以记录能量消耗、活动类型、步态类型的功能。并出现了复合传感器:将心电技术与加速度技术结合、将气压计与加速度计结合、将陀螺仪与加速度计结合等,复合型运动传感器的出现将为运动参与者提供更全面的运动信息,很大程度上也提高了对于能量消耗的预估精度。"
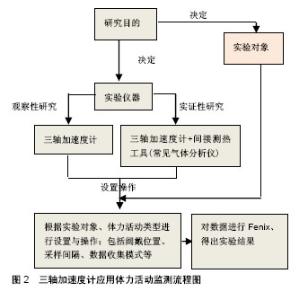
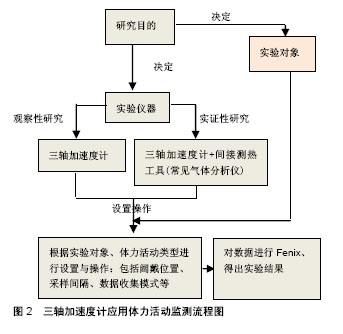
工作原理:物体在运动过程中会产生加速度,当加速度计感应到加速度时,压电模块产生形变,然后相关电路将这种介质的形变转换成电信号,电信号越强说明加速度值越大,反之则说明加速度值越小。加速度计的原理为结合牛顿的质量加速定律F=ma,和虎克的弹簧动作定律F=kDx,结合两个公式即为ma=kDx,F代表净外力,是物体所受力的向量和,m代表物体的重量,a代表物体的加速度,k代表弹簧系数,Dx为弹簧线性位移,所以利用净外力作用对于弹簧产生的线性位移推算出运动状态下加速度计三轴(X,Y,Z)空间下产生的重力加速度,然后通过不同的算法计算出能量消耗。 2.2 三轴加速度计用于身体活动的监测 三轴加速度计能够捕捉身体动作时产生的动作信号,如速度、加速度等运动学参数,还可以依据身体活动时产生的速度变化,准确地估算出身体活动量以及能量消耗程度等生理学参数,随着微机电技术的不断发展,以三轴加速度计为基础,并结合其他传感器的运动传感器越来越广泛地应用于体力活动监测中。 2.2.1 三轴加速度计在人体动作分析中的应用 在以往的研究中,经常使用三维动作捕捉系统来测量人体动作的时间空间参数(Temporal-spatial parameters)与人体运动学参数(Kinematics parameter),虽然三维动作捕捉系统可以准确地获得坐标系下的数据,但是由于三维动作捕捉系统价格昂贵、后期任务量繁重、需要依赖实验室环境,因此存在很大的局限性,随着微机电技术的发展,三轴加速度计结合陀螺仪制成的惯性测量装置,开始应用到人体动作分析中,惯性测量装置可以准确测量加速度和角速度,同时惯性测量装置体积小、质量轻、便于携带,因此不会影响到参与者的动作模式。 Mayaqoitia等[4]采用惯性测量装置(内含加速计与陀螺仪)和三维动作捕捉系统同时记录5种不同跑步机速度的下肢运动学参数,发现2种设备所测得的结果经多重相关系数检验r值在0.98-0.99之间。Henriksen等[5]在20名受试者的腰椎位置固定1个三轴加速计,分别测量不同日期但相同时间段下3种情境下的步态速度,研究发现从加速计的加速度曲线中看出单一步长度、步态周期长度与步态周期的组内相关系数介于0.77-0.96之间,因此认为,三轴加速度计在测量人体步态时,具有较高的重复性和微小误差值。Davey[6]将加速度计安置在游泳运动员的下背部,观察受试者蹬壁的加速度变化,结果发现,加速度计可以准确地测量高达95%以上的划手类型。黄贯伦等[7]将含有加速度计的六自由度惯性测量单元探讨不同钉鞋对于跳远运动的表现,研究发现:步频时间、支撑时间、摆动时间皆无相关分析部分(P > 0.05),而起跳时间与跳远成绩皆达显著差异(P < 0.05)。Shirota等[8]将含有三轴加速度固定于高尔夫运动员的腰部,来分析挥杆动作,发现各项数值与光学式动作分析所测得数值相关系数达0.9。Williamson等[9]认为加速度计配合陀螺仪所测得的关节角度会比单纯使用加速计、陀螺仪更加准确。黄钰萍等[10]指出加速度计评估坐到站的活动之参数值和光学式动作分析系统及测力台的数值有一致性,认为在进行坐到站实验中,将加速度计佩戴于靠近人体重心位置将更有利于提高测量的准确性。Favre等[11]在受试者的大腿与小腿上固定惯性测量装置,来获得步行时膝关节的坐标系数,结果显示:惯性测量装置测量关节坐标系数具有高重复性与高准确性。 综上,三轴加速度计在人体动作分析中与传统动作分析系统表现出高度一致性,因此三轴加速度计可用于人体动作分析中,可靠性很高。 2.2.2 三轴加速度计对人体活动中的能量消耗监测 人体运动时,体内的三大供能物质糖、脂肪、蛋白质与体内的O2发生反应,生成CO2和H2O,同时释放热量。耗氧量随运动量增加而增加,在特定范围内,运动者的耗氧量与单位时间内的肌肉做功成正比[12],加速度信号被转换成可量化的活动计数,然后可以通过方程或切点来解释[13]。三轴加速度计在人体活动活动中能量消耗监测主要分为:走跑类为代表的规律性运动、日常体力活动和闲暇活动等非规律性运动、特殊类运动(如蹬阶、爬山、游泳等),三轴加速度计的使用流程如图2所示。"

走、跑类活动是日常生活中最基本同时也是最规律的体力活动,因此,加速度计对此类活动的研究也是最多的。Vathsangam、Emken等[14-15]将三轴加速度计固定于髋关节处并以气体分析仪为校标,对不同速度跑步机上的行走活动能量消耗进行监测发现,发现三轴加速度计可以准确地预测能量消耗。Guinhouya等[16]研究指出三轴加速度计在测量快走、慢跑与快跑时所测得能量消耗数值与气体分析仪所测得值的相关系数维持在0.94-0.97之间,因此认为三轴加速度计在能量消耗预估中可靠性较高。然而也有学者得出了不同结论:RowIands等[17-18]研究发现,RT3、R3D与摄氧量的相关系数不存在显著差异,然而RT3的测量值比R3D略高;同一个试验中RT3的三轴Counts值,矢状轴和冠状轴的测试值与速度一直呈线性关系,而垂直轴在15 km/h以后出现平台。林玉琼等[19]以三轴加速度计为测量手段比较田径场与跑步机上不同步频跑走时能量消耗,并以气体分析仪为校标发现:当步频较低时,三轴加速度计会低估能量消耗,而当步频较高时又高估了能量消耗。Hussey等[20]对20名7-12岁的儿童为对象,运用三轴加速度传感器并以气体分析仪为校标,比较RT3的效度,在运动跑台上进行5种不同的坡度、速率跑,实验发现RT3预测儿童在3,6,9 km/h这3个速率时与气体分析仪所测得结果相关性很高。陆乐等[21]在20名大学生的髋部同一侧同时佩戴RT3三轴加速度计和ActiGraph单轴加速度计比较两者的有效性,并以气体分析仪为校标,测量5种不同速度步行或跑步时的能量消耗,发现无论何种速度下,RT3三轴加速度计测量能量消耗值均高于实测值,因此认为其比较适合于测量步行等中低速体力活动的能量消耗,而ActiGraph测量值均小于实际能耗,更适合跑步等快速体力活动。因此可以看出只有在中低活动强度下,表现出较高的精度。 然而相比于走跑类活动来说,日常体力活动高度不规律:形式更多、参与人群多样、参与环境更复杂等,这些都是三轴加速度计测量日常体力活动的难点。DeVoe等[22]研究指在跑步机上进行测试时,R3D所测的结果与最大耗氧量相关性达0.96,而测量日常体力活动时相关性为0.59。戴剑松等[23]将RT3携带于29名健康成年人左髋髂前上棘与腋前线交叉处,对他们的20种体力活动监测发现:将RT3佩戴于腰部时,能够较好地感测躯干不同类型的活动,RT3内建方程低估了几乎所有的活动能耗(下楼梯除外),且误差值相对较大,RT3内建模型低估步行的平均误差值达-1.82,低估幅度达到25%,低估日常生活活动的误差值为-2.23,低估幅度更达到26%;并根据三轴矢量和推导出自己的能耗回归公式与RT3自带模型相比较,发现所推导的回归公式测量身体活动的能耗值均小于RT3模型;指出如果仅采用线性回归模型,使用三轴加速度传感器未体现明显优于单轴加速度计。虽然在日常体力活动方面效度一般,但仍然是当下最有效的监测工具:朱琳等[24]应用ActiGraPh GT3X-Plus三轴加速度计对受试者进行为期7 d的日常体力活动监测,发现高中生有40%以上时间以静态活动状态为主,体力活动不足,工作日与非工作日对日常体力活动的影响显著;Peters等[25]通过对来自中国上海的城市男性和女性的身体活动进行客观测量的研究发现,老年人,肥胖者和目前的吸烟者体力活动水平显着低于年轻、瘦弱和不吸烟者同行,同时提出女性比男性花更多时间进行轻度身体活动。 除了走、跑类与日常体力活动外,还有一些特殊类的体力活动,例如:伴有坡度变化的运动、以上肢运动为主或者以下肢运动为主、骑行、水上运动等,针对这些特殊类运动,一些学者也进行了相关研究。DeVoe 等[22]指出加速度计在平地上所表现出的敏感性更高,但是对于坡度的变化不敏感。傅丽兰等[26]通过评估在3种不同坡度、速度的跑步机测试时由RT3三轴加速度计所测得的向量大小、估计的能量消耗和间接测热计所测得的耗氧量之间的相关性指出:三轴加速度计测量在跑步机上行走时的能量消耗,可以有效地感应速度变化,由RT3所测得的能量消耗值与气体分析仪所测得的能量消耗高度相关,但对坡度变化较不敏感,且易高估能量消耗的数值,同时指出,虽有应用上的限制,但是对于行走相关的能量消耗研究中仍是一种有效可靠的工具。Terrier等[27]以三轴加速度计为工具,研究上、下坡时能量消耗,结果发现相同坡度中,下坡时所消耗的能量均大于上坡,指出三轴加速度计无法准确测量上下坡时的能量消耗。郭珍汝等[28]在研究森林步道行走能量消耗研究中发现:能量消耗随坡度增加而增加,相同坡度时,下坡能量消耗大于上坡能量消耗;硬性地面的活动能量消耗高于软性地面。朱卫红等[29]通过研究发现:上肢活动能引起摄氧量的显著增加,手腕处佩戴加速度对活动频率感应更敏感。 综上所述,三轴加速度计在推算走跑类相关的体力活动消耗方面具有较好的效度,在具有坡度变化的体力活动中,对于坡度变化不敏感。由于日常体力活动的不规律性,在使用加速度计预估能量消耗时,要根据体力活动自身的特点,选择合适的佩戴位置与合适的加速度计。 2.3 影响三轴加速度预估能耗精度的因素 2.3.1 与仪器选择有关 目前三轴加速度计的种类繁多,然而主流的并得到广泛使用的三轴加速度计主要有Actigcaph系列三轴加速度计、RT3、 Livepod LP2以及新型三轴加速度计SWA等,同时一个系列加速度计可能含有好几个型号,例如Actigcaph系列三轴加速度计含有GT3X、GT3X+、GT3X-Plus等,然而究竟哪个系列三轴加速度计的精度更高,在实际操作中应如何选择仍然是一件困难的事情。因此有学者对不同三轴加速度计的精度进行对比,Kim等[30]研究表明SWA加速度计对于儿童活动强度的辨别度优于Actigcaph系列加速度计,然而Berntsen等[31]却指出SWA型加速度计会高估成年人静坐时的能量消耗,低估低强度体力活动,王军利 等[32]中国20名年轻成人为对象,在跑步机上分别进行4种不同速度的走跑运动各5 min,以间接测热法为校标,比较4种均采用三维运动传感技术的运动传感器的准确度:Actigcaph GT3X加速度计、LivePod iMate能耗仪、AM-120与HJ-302计步器,结果发现:在4种运动传感器中,GT3X三轴加速度计与间接测热法所测值的相关系数最高,不同运动速度时的相关系数R值介于0.70到0.90之间(P < 0.0 1),因此认为GT3X加速度计更适合中国成年人身体活动监测,而其他3种运动传感器误差相对较大。赵壮壮等[33]以26名大学生为对象,在实验室跑台条件下,通过走跑运动比较Actigraph GT3X,Livepod LP2(由北京知康国际开发),Armband 3种三轴加速度传感器测量人体走、跑运动能量消耗的信效度,结果发现:所有仪器在同一速度水平上,具有良好的一致性,在测量人体走跑运动能量消耗时,Livepod LP2具有最高的效度水平,而其他2种三轴加速度传感器均存在高估或者低估的现象。综上所述研究群体、体力活动类型都是仪器的选择时应考虑实际的因素,然而关于不同加速度计之间有效性比较的研究相对较少,因此在今后的研究中,不同加速度计之间效度比较仍然是一个重要的议题,而在实际情况的应用中,应根据研究对象、活动类型科学选择。 2.3.2 与佩戴位置有关 大多数研究中将加速度计佩戴于右侧髋部或腰后部,因为该位置更接近人体质心,研究表明两个位置所测得的能量能消耗数值差别并不大[34-35],孙泊等[36]通过跑台实验的研究,指出加速度计佩戴于腰部能较好地预估人体行走过程中的速度与能量消耗,然而 Howe等[37]认为由于多数研究中加速度计只是佩戴在腰背部,因此缺少对上肢活动能耗的监测,造成一定的误差,同时一些学者也认为长时间穿着腰部设备不舒适或不方便,儿童和青年研究中也发现类似的问题[38-39]。随着加速度技术的发展,一些学者开始将加速度计佩戴在其他部位来进行能量消耗监测。刘又慈 等[40]将RT3佩戴于髂前上棘、腓骨头近端、阿基利斯腱上15 cm处探讨原地蹬阶运动时RT3佩戴位置时之预测能量消耗能力,发现:不同蹬阶速度与阶高下的耗氧量与佩戴于膝关节之RT3向量(r=0.69,0.43)与能量消耗预估(r=0.37,0.75显著相关);原地蹬阶运动时,佩戴于膝关节能量预估数值较髋与踝处稳定且较接近于实测值。王佩凡等[41]将RT3佩戴于20名桌球(乒乓球)选手的不同位置(下背部、肩、肘和腕关节)同时佩戴RT3,以气体分析仪为效标,探讨不同佩戴位置时桌球运动的能量消耗,发现:在不同送球频率测试中,RT3与气体分析仪所测得的能量消耗及向量大小,会随着送球频率的增加而上升;RT3在相同送球频率测试中,4个位置所测得的数值依小到大顺序分别为下背部、肘关节、肩关节、腕关节;RT3应用在桌球正手击球测试中与气体分析仪有中至高度的县惯性,并可区辨不同送球频率的测试,因此建议佩戴于肘关节位置最佳。除上述佩戴位置外,也有学者将三轴加速度计佩戴于手腕处:Hesketh等[42]在女性腕部和髋关节处佩戴加速度计,对其孕期和产后的体力活动监测发现髋关节和手腕处加速度计数显示出中等程度至高度相关性,并指出对于孕期女性而言,手腕处佩戴加速度计优于髋关节处。Sirichana等[43]研究指出腕戴式三轴加速度计可靠地预测普通体力活动<6 METs时的能量消耗,佩戴在非主导手腕而非主导手腕上具有一致的相关性,廖立同等[44]在受试者手腕、躯干、脚踝3处同时携带RT3,研究身体不同部位加速度于心率的关系,发现:跑步时手部挥动产生的加速度与心跳显著相关,指出跑步时手臂前后摆动产生的加速度更适合代表身体活动量(r=0.817)。Scott等[45]以青少年为研究对象,通过 GENEActiv(腕式加速度计)和GT3X加速度对其日常体力活动进行监测,研究发现腕关节和髋关节加速计输出之间存在强烈的线性关系,与传统研究相比,在腕关节处佩戴加速度计在中高强度体力活动中表现出良好的平行效度。与此同时有研究在40名成年人3上同时佩戴3个加速度计(腰部、非主导手腕、主导手腕)对其体力活动进行监测发现:两个手腕的平均日加速度计输出数据与佩戴在腰部附近的ActiGraph的每分钟平均计数密切相关(r= 0.88,P < 0.001),并指出选择在非主导还是主导手腕上佩戴加速度计对结果没有影响[46]。然而也有学者得出了不同的结论:Kumahara等[47]发现如果将加速度计佩戴于手腕处监测日常体力活动,所测得结果与实测值相比,仅能解释总能耗的2%,并指出只有在上肢运动占日常体力活动能耗占比较高的情况下,应增加手腕处的加速度传器。Mannini等[46]认为由于手腕手势和运动的变化,手腕处加速度计数据处理仍然具有挑战性,比腰部数据还要复杂,近年来也有研究开始将三轴加速度计佩戴于胸部。Cleland等[48]表明放置在胸部的加速度计比使用放置在手腕上的加速度计使用各种机器学习算法更好地正确检测日常活动。Zhang等[49]研究发现使用通用的基于研究的加速度计,通过一个简单的颈部挂件,在胸部使用所记录的PA测量结果与传统的腰部位置记录的PA测量结果相比,与腕部位置相比更加接近。Plasqui等[50]指出不同的运动类型,身体各部位产生的加速度不同,在实际操作中要按照运动形态去决定加速度计的佩戴位置,因此身体活动类型是决定加速度计佩戴位置的重要因素,然而目前大多数研究将加速度计佩戴于腰部,而关于不同佩戴位置对于能量消耗影响的变异性研究较少,因此在今后的研究中应增加该方面的研究,以找出不同运动类型的最佳佩戴位置,以获得更准确的数据。 2.3.3 与采样间隔有关 不同的运动方式运动频率不同,Chen等[51]指出,人体进行走跑运动时,频率一般低于8 Hz,但是上肢运动频率却可以达到甚至超过 25 Hz。然而目前大多数加速度计运算时筛选的是0.25-7 Hz数据,这也是造成加速度计无法准确测量高频率运动能量消耗的原因。王超等[52]研究发现:与较短采样间隔相比,长的采样间隔会低估所有研究对象的体力活动,并指出对于儿童、青少年的体力活动监测宜采用较短采样间隔(如1 s),对于儿童青少年体力活动时间达到推荐量的情况可采用较长采样间隔(如60 s)。贺刚 等[53]指出:基于儿童的体力活动特点,宜采用较短的采样间隔。因此在实际操作中应根据不同活动类型的特点科学合理地设置采样间隔,如当测试慢频率运动时可以采用分钟为单位的采样间隔,而当测试频率较高的运动时(比如快速跑),可以采用以秒为单位的采样间隔,以此保证所采集数据的准确性,提高精度。 2.3.4 与身体活动类型有关 DeVoe等[22]在比较RT3和R3D测量活动能量消耗的研究中发现当运动强度发生微小变化时,传感器测量能耗值相应地发生变化。Bassett等[54]指出加速度计可以准确记录久坐行为和自由生活条件下较低强度范围内的体力活动,其他学者也得出了相同的结论:王欢等[55]以Cosmed K4b²气体分析仪为校标,比较3种常用加速度计(GT3、RT3、SWA)测量身体活动的有效性,发现低强度和高强度活动时加速度计与实测耗氧量(K4b2测量值)之间差异显著(P < 0.05),而在中低强度活动时的测量中误差较小。相对于单轴加速度而言,三轴加速度计能够更加全面的反映体力活动,这一点毋庸置疑,但是由于三轴加速度计的生产厂家不同、基于实验室所建立的内建方程不同以及后期人们使用三轴加速计时,设置、实验对象、实验环境等的不同,实验结果也不尽相同,因此不能找到一个完全适用的能耗预测模型,人们对于三轴加速度计的探索还在不断继续。Eston等[56]发现,在有身体移动的体力活动中垂直轴count值最大,而在没有移动的身体活动中冠状轴count值最大。 2.3.5 与推算方程和算法有关 Matthew等[57]表明表明加速度计垂直轴计数(accelerometry counts,AC)与体力活动能量消耗高度相关,因此传统的算法也是基于加速度计AC值所建立的能量消耗回归方程来推算能量消耗数值,虽然不同种类加速度计在测量能量消耗时所测得结果相似,但是值得注意的是不同种类加速度计内部的推算方程准确性并不相同,其推算方程是基于不同运动方式、不同对象所推算出来的,有的加速度计内部含有多种推算方程,至于哪种推算方程更加精确、适用范围更广仍然是个未知数。而且多数加速度计内置能量消耗推算公式都假设加速计所测得的counts值与实际身体活动量呈线性相关,即单位时间内产生计数越高的身体活动,代表其活动的激烈程度越高,但是不同研究所推导出推估公式,对于高强度或中强度所定义的切点不同,这也是影响加速度计推算能量消耗精度的重要因素。Leung等[58]指出只有对特定加速度的切点进行标准化才能获得更加准确地数据。Trost等[59]指出,ActiGraph加速度推算公式中,Freedon和Evenson在中高强度的分类正确性大于其他公式,但整体而言,Evenson在各种活动强度能耗预测中,效度最好,而国内学者王军利等[32]研究发现ActiGraph(GT3X)所自带的能耗算法中Frccdson VM3 Combination(2011)方程更适合中国年轻人群的运动能耗预测。戴剑松等[23]研究指出RT3自带模型不适合中国人群。 能量消耗预测方程类型也是影响其精度的重要因素。Crouter等[60]表明以走跑类运动形式为基础所建立的单一线性回归模型会在很大程度上低估上肢活动较多的日常体力活动。同时,汤强等[61]通过整理46篇关于加速度计在体力活动研究的文献指出:依据不同运动方式所建立的能量推算方程精度不一,每个方程均有其适合应用的范围,因此必须依对象、内容和环境等选择最合适的加速度计和方程,复杂的分段方程和非线性方程提高了推算精度,但其在研究中的应用效果还有待验证。王金昊等[62]在证明三轴加速度计可以预测运动员能量消耗的同时,并建立了分段加速度能耗预测方程,并指出其适用于相同方案的跑台运动测试。 无论哪种算法,归根到底都是对原始数据的处理,如何科学地实现对加速度计原始信号的处理是加速度计应用于体力活动监测的难题,如果这一问题得到解决,那么加速度计在体力活动监测方面将的精度将明显提升发挥更重要的作用,体力活动复杂多样,仅靠复杂的方程无法满足对于能量消耗的预测,只有实现体力活动的自动识别才能显著提高其预测的精度,而且活动类型识别这一技术已经广泛应用于机器人、医学以及土木工程领域,活动类型识别基本需要3个因素:资料接受、资料转换、运算软件[63-64],而在大数据分析背景下,数据挖掘和机器学习等新的数据分析方法得到迅速发展,目前神经网络分析方法已开始应用于身体活动类型识别和能量消耗推算,并取得了卓有成效的成果。Staudenmayer等[64]采用活动类型识别与神经网络分析方法,对4种不同类型体力活动(轻度体力活动、家务劳动、有规律重复性运动、多变化高强度运动)进行能量消耗预估发现:相比传统回归模式,神经网络分析模式对于体力活动能量消耗预测的误差最小,且在活动类型分类方面的准确性可达89%-97%。Trost等[65]指出神经网络分析方法在体力活动能量消耗预测方面,误差值显著低于传统回归模式。陈庆果等[66]研究发现:神经网络模型在体力活动预测方面整体上的准确性好于Heudlemau和Crouter模型,活动强度分类的准确性也更高。因此在未来体力活动监测中活动类型识别应该受到重视,以此提高对活动强度分类的准确性,与此同时加入数据挖掘和机器学习等新的数据分析方法和算法。 2.3.6 其他限制因素 ①三轴加速度计测量值会受到地心引力的影响,以及在使用过程中仪器松脱的都会造成三轴加速度计数与与耗氧量呈现出非线性关系;②三轴加速度计对于坡度变化不敏感,因此不适用于垂直运动做功较多的运动,如蹬阶、爬山等;③三轴加速度计对于活动频率范围在0-10 Hz的活动感测力敏感,因此对于静态、活动频率低的活动(如静坐),其预估能耗精度大打折扣。除此之外,测试对象的不同、性别、身高、体质量、参与者本身运动技术都会对三轴加速度计在能量消耗预测的精度造成一定的影响。同时也考虑测试环境的因素,DeVoe等[22]发现:无论哪一种加速度计,在户外所测得的能量消耗预值均大于跑步机上所测得测量值,林昱安等[67]研究指出:MOOV NOW(内置三轴加速度计、三轴陀螺仪)适合用来评估陆上运动时的身体活动量,而不适合观测水中运动状态,可见测试环境对于估测精度的影响也是值得考虑的因素。综上所述在使用三轴加速度计推算能量消耗时要根据实际情况,尽可能地考虑到更多的因素,仪器选择、佩戴位置、采样间隔等一定要与身体活动类型相结合,以此减少误差。同时三轴加速度计自身也存在缺陷,与其他传感器相结合以弥补三轴加速度计的缺点,同时更全面的记录运动参与者的信息,以达到更精确的结果,将会是三轴加速度计的发展趋势。"

| [1] Dyrstad SM,Hansen BH,Holme IM,et al.Comparison of self-reported versus accelerometer-measured physical activity. Med Sci Sports Exerc.2014;46(1):99-106.[2] Johnson M,Yun J,McCubbin JA.Validity evidence for self-report with assistance to measure physical activity behavior in adults with intellectual disabilities.Intellect Dev Disabil. 2014;52(4):273-281.[3] John D,Tyo B,Bassett DR. Comparison of four ActiGraph accelerometers during walking and running . Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010;42(2):368-374.[4] Mayagoitia RE,Nene AV,Veltink PH.Accelerometer and rate gyroscope measurement of kinematics an inexpensive alternative to optical motion analysis systems.J Biomech.2002;35(4):537-542.[5] Henriksen M,Lund H,Moe-Nilssen R,et al.Test–retest reliability of trunk accelerometric gait analysis.Gait Posture. 2004;19(3):288-297.[6] Davey NP.Acquisition and analysis of aquatic stroke data from an accelerometer based system. Masters of Philosophy Dissertation. Griffith University.Queensland. 2004:93-100.[7] 黄贯伦,林国全.以惯性测量装置应用于不同鞋子对跳远运动表现之比较[J].中原体育学报,2014,(4):140-146.[8] Shirota K,Watanabe K,Kurihara Y. Measurement and analysis of golf swing using 3-D acceleration and gyro sensor. IEEE.SICE Annual Conference.2012:356-360. [9] Williamson R,Andrews BJ. Detecting absolute human knee angle and angular velocity using acceleromaters and rate gyroscopes. Med Biol Eng Comput.2001;39(3):294-302.[10] 黄钰萍.三轴加速计应用于患者功能性活动坐到站评估之探究[J].医学与健康期刊,2015,4(1):6-10.[11] Favre J,Aissaoui R,Jolles BM,et al.Functional calibration procedure for 3D knee joint angle description using inertial sensors. J Biomech.2009; 42(14):2330-2335.[12] 焦纯,董秀珍,杨国胜.人体运动量及能耗的测量方法[J].国外医学:生物医学工程分册,2002,25(5):196-202.[13] Hinckson EA,Curtis A. Measuring physical activity in children and youth living with intellectual disabilities: A systematic review. Res Dev Disabil. 2013;34(1):72-86.[14] Vathsangam H,Emken B,Schroeder E,et al.Energy estimation of treadmill walking using on-body accelerometers and gyroscopes. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2010;2010:6497-6501. [15] Vathsangam H,Emken BA,Schroeder ET,et al. Hierarchical linear models for energy prediction using inertial sensors : a comparative study for treadmill walking. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput. 2013; 4(6):747-758.[16] Guinhouya CB,Huhert H,Dupont G,et al.Relationship between the MTI accelerometer (Actigraph) counts and running speed during continuous and intermittent exercise. J Sports Sci Med. 2005;4(4): 534-542.[17] Rowlands AV,Thomas PW,Eston RG,et al.Validation of the RT3 triaxial accelerometer for the assessment of physical activity.Med Sci Sport Exe.2004;36(3):518- 524.[18] Rowlands AV,Stone MR,Eston RG.Influence of speed and step frequency during walking and running on motion sensor output. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007;39(4):716-727.[19] 林玉琼,张予亲,余杰霖.三轴加速度计运动表的信效度研究[J].文化体育学刊,2014,17:55-58.[20] Hussey J,Bennett K,Dwyer JO,et al.Validation of the RT3 in the measurement of physical activity in children.J Sci Med Sport.2009; 12(1):130-133.[21] 陆乐,戴剑松,徐波. 加速度传感器测量不同速度运动时能量消耗的研究[J].西安体育学院学报,2013,30(1):104-107.[22] DeVoe D,Gotshall R,McArthur T.Comparison of the RT3 research tracker and TriTrac R3D acceleromerers.Percept Mot Skills.2003;97: 510-518.[23] 戴剑松,顾忠科,徐凯,等. RT3三轴加速度传感器测量多种类型身体活动效度研究[J].成都体育学院学报,2015,41(6):100-16,121.[24] 朱琳,陈佩杰.应用三轴加速度计(GT3X+)监测广州高中生日常体力活动的研究[J].广州体育学院学报,2013,33(1):85-88,96.[25] Peters TM,Moore SC,Xiang YB,et al.Accelerometer-measured physical activity in Chinese adults. Am J Prev Med. 2010 ;38(6): 583-591.[26] 傅丽兰,陈毓君.三度空间加速计于跑步机行走之向量大小及能量消耗与耗氧量相关性研究[J].物理治疗,2005,30(2):75-77.[27] Terrier P,Aminian K,Schutz Y.Can accelerometery accurately predict the energy cost of uphill/downhillwalking? Ergonomics.2001;44(1):48-62. [28] 郭珍汝.三轴加速规在森林步道行走能量消耗之研究[D].台湾大学,2008: 78-93.[29] 朱卫红.上肢活动加速度与能量消耗特征初探[J].苏州大学,2009.[30] Kim Y,Lee J,Bai Y,et al. Comparison between Sensewear Mini Armband and Actigraph accelerometers in classifying physical activity intensities in youth. Medicine &Science in Sports &Exercise.2012;44 (5):S478.[31] Berntsen S,Hageberg R,Aandstad A,et al. Objective assessment of sedentary behaviour and light physical activity in free living activities.Medicine&Science in Sports &Exercise.2012;44 (5):S490.[32] 王军利,张冰,贾丽雅,等.4种运动传感器测量身体活动能耗的有效性研究[J].天津体育学院学报,2012,27(5):427-431.[33] 赵壮壮,陈培友.不同加速度传感器测量人体走跑运动能量消耗对比研究[J].北京体育大学学报,2013,36(4):77-81.[34] McClain JJ,Craig CL,Sisson SB,et al.Comparison of Lifecorder EX and ActiGraph accelerometers under free-living conditions. Appl Physio Nutrit Metabol.2007;32(4):753-761. [35] Trost SG,McIver KL,Pate RR. Conducting accelerometet-based activity assessments in field-based research. Med Sci Sports Exe.2005;37(11): S531-S543.[36] 孙泊,刘宇,庄涛,等.基于腰部加速度计的行走能耗建模实验研究[J].体育科学,2013,33(4):36-40.[37] Howe CA,Staudenmayer JW,Freedson PS.Accelerometer prediction of energy expenditure: Vector magnitude versus vertical axis.Med Sci Sports Exe. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2009;41(12):2199-2206.[38] Audrey S,Bell S,Hughes R,et al.Adolescent perspectives on wearing accelerometers to measure physical activity in population-based trials. Eur J Public Health. 2013;23(3):475-480.[39] Robertson W,Stewart-Brown S,Wilcock E,et al. Utility of accelerometers to measure physical activity in children attending an obesity treatment intervention. J Obes.2011;2011. pii: 398918.[40] 刘又慈,傅丽兰,陈亮伃. 不同佩戴位置之三轴加速计于登阶运动时的能量消耗预估[J].体育学院论丛,2006,17(2):89-92.[41] 王佩凡,崔秀里. 不同配戴位置之三轴加速计于桌球正手运动时的能量消预估[J].交大体育学刊,2016,12(12).[42] Hesketh KR. Physical activity and sedentary behavior during pregnancy and postpartum,measured using hip and wrist-worn accelerometers. Preventive Medicine Reports.2017;10:337-345. [43] Sirichana W,Dolezal BA,Neufeld EV,et al.Wrist-worn triaxial accelerometry predicts the energy expenditure of non-vigorous daily physical activities. J Sci Med Sport. 2017; 20(8):761-765.[44] 廖立同,相子元.身体不同位置加速度分析跑步机跑步身体活动量之研究[J].华人运动生物力学期刊,2009,6(1)32-36.[45] Scott JJ,Rowlands AV,Cliff DP,et al.Comparability and feasibility of wrist- and hip-worn accelerometers in free-living adolescents. J Sci Med Sport. 2017;20(12):1101-1106. [46] Mannini A,Intille SS,Rosenberger M,et al. Activity recognition using a single accelerometer placed at the wrist or ankle. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2013,45 (11) :2193-2203.[47] Kumahara H,Tanaka H,Schutz Y. Daily physical activity assessment: what is the importance of upper limb movements vs whole body movements? Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004;28(9): 1107-1110.[48] Cleland I,Kikhia B,Nugent C,et al.Optimal placement of accelerometers for the detection of everyday activities. Sensors (Basel). 2013;13(7):9183-9200. [49] Zhang JH,Macfarlane DJ,Sobko T. Feasibility of a Chest-worn accelerometer for physical activity measurement. J Sci Med Sport. 2016;19(12):1015-1019.[50] Plasqui G,Westerterp KR.Physical activity assessment with accelerometers: An evaluation against doubly labeled water. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2007;15(10):2371-2389.[51] Chen KY,Bassett DR Jr. The technology of accelerometry-based activity monitors: current and future. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2005;37(11 Suppl):S490-500.[52] 王超,陈佩杰,庄洁,等. 加速度计以不同采样间隔测量儿童青少年日常体力活动时间的一致性研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2012,31(9):759-765, 771.[53] 贺刚,黄雅君,王香生.加速度计在儿童体力活动测量中的应用[J].体育科学,2011,31(8):72-76.[54] Bassett DR,Troiano RP,McClain JJ,et al. Wolff Accelerometer- based physical activity: total volume per day and standardized measures. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015;47(4):833-838.[55] 王欢,王馨塘,佟海青,等. 三种加速度计测量多种身体活动的效度比较[J].体育科学,2014,34(5):45-49.[56] Eston RG,Rowlands AV,Ngledew DK. Validity of heart rate,pedometry,and accelerometry for predicting the energy cost of children's activities. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1998;84(1):362-371.[57] Matthew CE. Calibration of accelerometer output for adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2005;37(11 Suppl):S512-5522.[58] Leung W,Siebert EA,Yun J. Measuring physical activity with accelerometers for individuals with intellectual disability: A systematic review. Res Dev Disabil. 2017;67:60-70.[59] Trost SG,Loprinzi PD,Moore R,et al.Comparison of aceelerometer cut points for predicting activity intensity in youth. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011;43(7):1360-1365.[60] Crouter SE,Churilla JR,Bassett DR Jr. Estimating energy expenditure using accelerometers. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2006;98(6):601-612. [61] 汤强,盛蕾,朱卫红. 体力活动研究中加速度计的应用[J].体育科学,2009, 29(1):79-81.[62] 王金昊,邱俊,李之俊. 跑台运动中运动员能量消耗的3种测试方法的比较研究[J]. 西安体育学院学报,2014,31(5): 582-588.[63] Mannini A,Sabatini AM. Machine learning methods for classifying human physical activity from on-body accelerometers. Sensors. Sensors (Basel). 2010;10(2):1154-1175.[64] Staudenmayer J,Pober D,Crouter S,et al. An artificial neural network to estimate physical activity energy expenditure and identify physical activity type from an accelerometer. J Appl Physiol.2009;107(4): 1300-1307.[65] Trost SG,Wong WK,Pfeiffer KA,et al. Aritificial neural networks to predict activity type and energy expenditure in youth. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2012;44(9):1801-1809. [66] 陈庆果,彭彪,杨世军,等.基于神经网络模型的加速度计活动强度算法研究[J].天津体育学院学报,2017,32(1): 45-50.[67] 林昱安.穿戴式装置于陆上与水中运动之信效度检验[J].运动表现期刊, 2017,4(1):63-65. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||