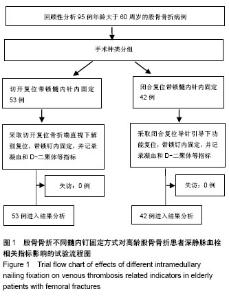
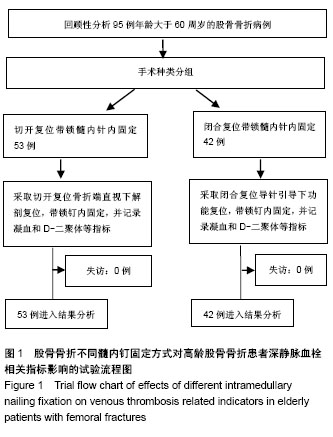
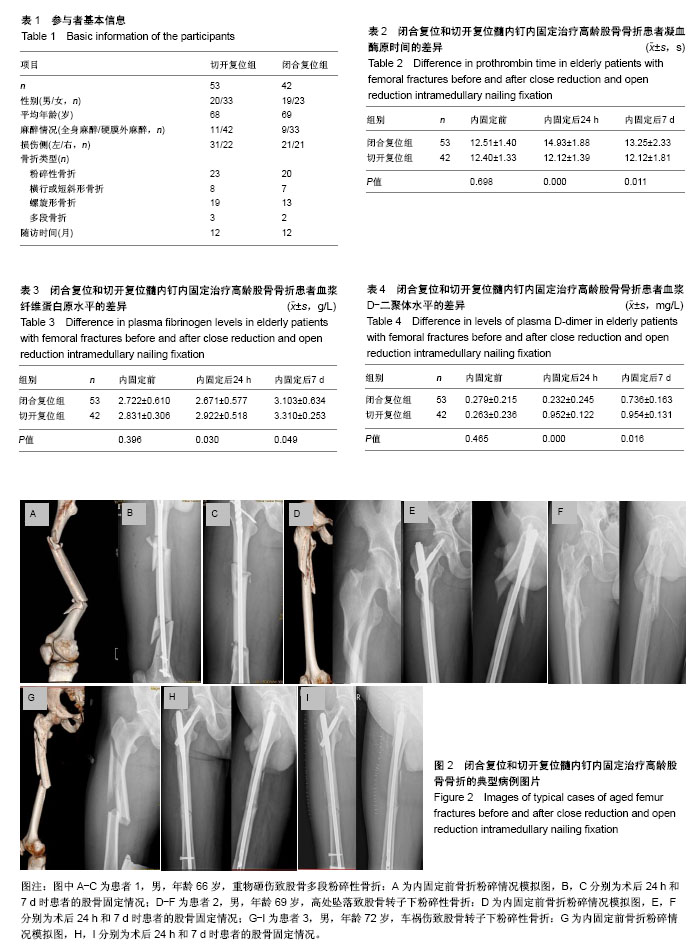
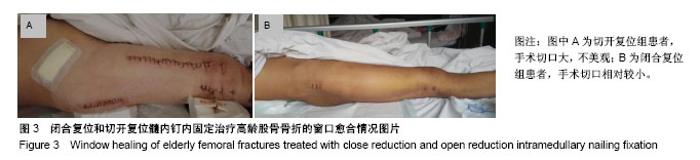
| [1] 区锦燕,刘晓捷,吴征杰,等.创伤骨折患者术前行血管超声检查及测定D-二聚体的意义[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2010,8(26):706-708.[2] Byrne JP, Nathens AB, Gomez D, et al. Timing of femoral shaft fracture fixation following major trauma: A retrospective cohort study of United States trauma centers. PLoS Med. 2017;14(7):e1002336. [3] Kohan L, Field CJ, Kerr DR. Early complications of hip resurfacing. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(6):997-1002. [4] 朱增强.高龄人股骨骨折术前应用低分子肝素预防静脉血栓的临床意义[J].中国保健营养,2015(12):168-169.[5] Li J, Wu G, Ji WF, et al. Case-control study on ultra-early application with intermittent pneumatic compression to prevent postoperative deep venous thrombosis of intertrochanteric femoral fracture in elderly patients. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2012;25(1):32-34.[6] 区锦燕,廖荣宗,周曙,等.股骨多段闭合骨折病人术前凝血功能的变化[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2004,24(7):555-556.[7] 王乐民,魏林.肺栓塞与深静脉血栓形成[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2001.[8] Ji HM, Lee YK, Ha YC, et al. Little impact of antiplatelet agents on venous thromboembolism after hip fracture surgery. J Korean Med Sci. 2011;26(12):1625-1629. [9] Willard RN, Muñiz AE, Chuidian F. Delayed subdural hematoma after receiving enoxaparin for prevention of thromboembolic events from high-risk surgery. Am J Emerg Med. 2012;30(6):1017.e5-8.[10] 贾伟,刘建龙,刘亚波.急性股骨干骨折患者深静脉血栓的诊断及治疗[J].山东医药,2009,49(24):10-12.[11] McGurk KJ, Collier BR, Bradburn EH, et al. Association between blood transfusion, transfusion setting, and the risk of venous thromboembolism in patients with isolated orthopedic trauma. Am Surg. 2016;82(9):247-248.[12] Aliakbar A, Witwit I, Al-Algawy AAH. Closed external fixation for failing or failed femoral shaft plating in a developing country. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11(8):RC04-RC06.[13] 林焱斌,李仁斌,张怡元,等.交锁髓内钉小切口感触辅助复位结合自体髓内取骨植骨治疗股骨干骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2012, 14(3):262-264.[14] Li N, Liu H, Gong X, et al. Diagnosis and management of atypical femoral fractures: clinical efficacy in 11 cases. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016;96(17):1349-1353. [15] 魏俊强,刘利蕊,潘进社,等.仰卧位与侧卧位闭合复位髓内钉内固定治疗股骨干骨折的疗效比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2013, 15(8):660-665.[16] Rether JR, Muñoz Vives JM, Bail HJ, et al. Experiences with a helical femoral nail (LFN®). A multicenter study. Unfallchirurg. 2013;116(7):582-588.[17] Vichard P, Gagneux E, Garbuio P, et al. Ascending intramedullary nailing of the femur. Technique. Initial results. Indications. Chirurgie. 1996;121(2):137-143.[18] Post GR, Guillory E, Wade CL, et al. Effect of serum immunoglobulins on routine coagulation tests:a comparison of coagulation analyzers using mechanical and optical clot detection. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2017;47(6):744-746.[19] Amiral J, Vissac AM, Seghatchian J. Laboratory assessment of Activated Protein C Resistance/Factor V-Leiden and performance characteristics of a new quantitative assay. Transfus Apher Sci. 2017;56(6):906-913.[20] 邱贵兴,戴尅戎,杨庆铭,等.预防骨科大手术后深静脉血栓形成的专家建议[J].中国临床医生,2006,34(1):27-28.[21] Weitz JI, Fredenburgh JC, Eikelboom JW. A test in context: D-dimer. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70(19):2411-2420.[22] Rafee A, Herlikar D, Gilbert R, et al. D-dimer in the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis following total hip and knee replacement: a prospective study. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2008; 90(2):123-126.[23] 白雪,杨军,王毅,等.P-选择素,D-二聚体对关节置换术后深静脉血栓早期诊断的价值[J].上海医学,2007,30(2):140-141.[24] Zia A, Russell J, Sarode R, et al. Markers of coagulation activation, inflammation and fibrinolysis as predictors of poor outcomes after pediatric venous thromboembolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Thromb Res. 2017;160:1-8.[25] Schoot RA1, Kremer LC, van de Wetering MD, et al. Systemic treatments for the prevention of venous thrombo-embolic events in paediatric cancer patients with tunnelled central venous catheters. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;(9): CD009160. [26] Rabinovich A, Cohen JM, Kahn SR. Predictive value of markers of inflammation in the postthrombotic syndrome: a systematic review: inflammatory biomarkers and PTS. Thromb Res. 2015;136(2):289-297. [27] Rabinovich A, Cohen JM, Kahn SR. The predictive value of markers of fibrinolysis and endothelial dysfunction in the post thrombotic syndrome. A systematic review. Thromb Haemost. 2014;111(6):1031-1040. [28] Douketis J, Tosetto A, Marcucci M, et al. Patient-level meta-analysis: effect of measurement timing, threshold, and patient age on ability of D-dimer testing to assess recurrence risk after unprovoked venous thromboembolism. Ann Intern Med. 2010;153(8):523-531.[29] Marik PE, Cavallazzi R. Extended anticoagulant and aspirin treatment for the secondary prevention of thromboembolic disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2015;10(11):e0143252.[30] Goldenberg NA. Thrombophilia states and markers of coagulation activation in the prediction of pediatric venous thromboembolic outcomes: a comparative analysis with respect to adult evidence. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2008:236-244. |