Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (15): 2446-2452.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0155
Previous Articles Next Articles
A meta-analysis of pneumatic tourniquet used in total knee arthroplasty
Gu Pei-lun, Dong Jin-bo, Wang Wei-shan, Chen Lei, Yu Hong-tao, Li Yue-jun, Gao Peng, Wang Kai
- Orthopedics Center, First Affiliated Hospital, Medical School of Shihezi University, Shihezi 832000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2018-05-28Published:2018-05-28 -
Contact:Dong Jin-bo, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Associate professor, Orthopedics Center, First Affiliated Hospital, Medical School of Shihezi University, Shihezi 832000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Gu Pei-lun, Master candidate, Physician, Orthopedics Center, First Affiliated Hospital, Medical School of Shihezi University, Shihezi 832000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81160225
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gu Pei-lun, Dong Jin-bo, Wang Wei-shan, Chen Lei, Yu Hong-tao, Li Yue-jun, Gao Peng, Wang Kai . A meta-analysis of pneumatic tourniquet used in total knee arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(15): 2446-2452.
share this article
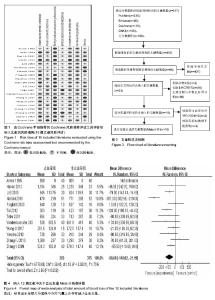
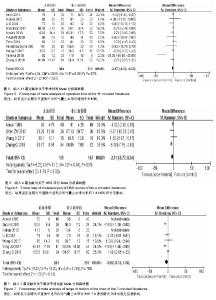
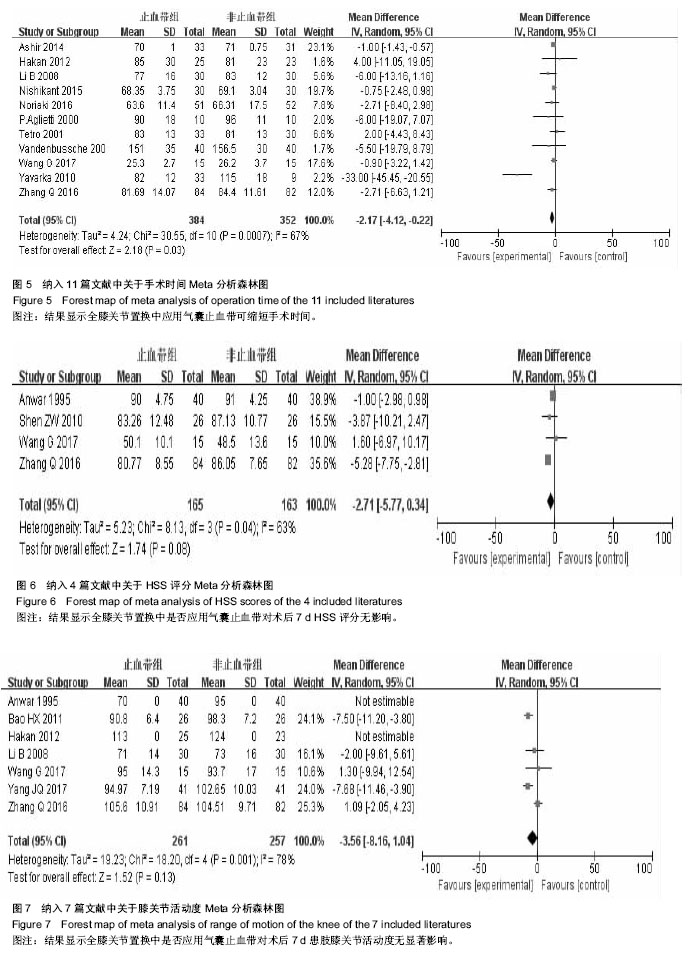
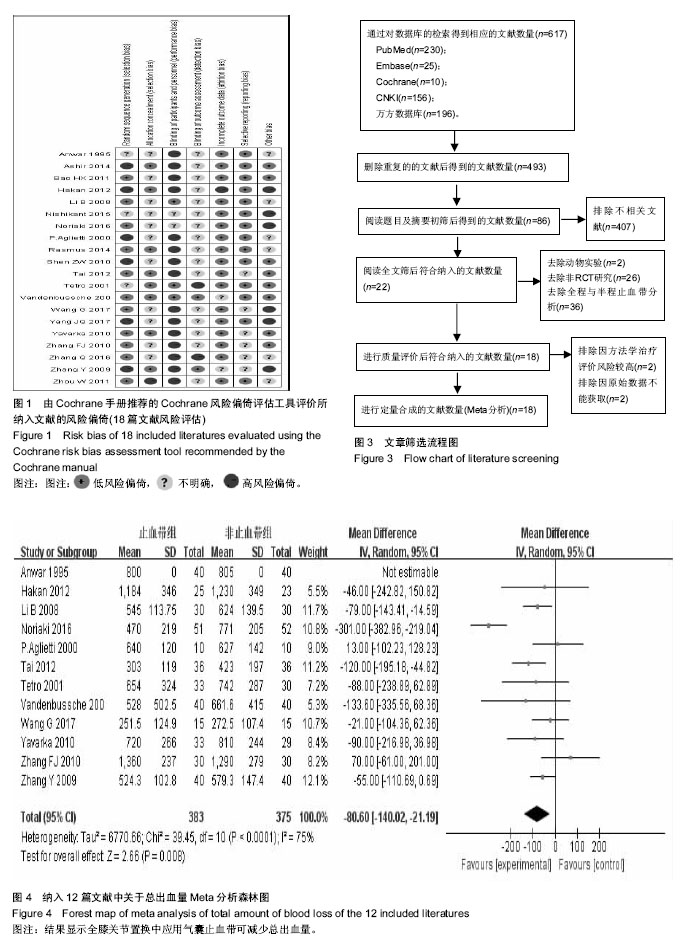
2.1 文献检索结果 初步检索共获得617篇文献,去除重复文献124篇,将剩余的493篇文献阅读题目及摘要,去除不相关文献,初筛出86篇随机对照试验,通过阅读全文,共22篇文献被纳入,其中2篇文献由于质量评价高偏倚风险被排除,2篇文献因无法获得原始数据被排除,最终纳入文献18篇[1-18],共1 234例患者,其中止血带组为623例,非止血带组为611例(图3)。所有文献均有纳入及排出标准,所有纳入文献均可查及人口学特征。9篇研究报道了随机分组具体情况[3,5,7,13-14,16-18],7篇文献报道了分配隐藏情况[2,4,9,11-13,16],3篇文献具体说明盲法实施情况[5,12-13]。 2.2 纳入文献人口学特征 共有18篇文献被纳入[1-18],共有1 234例患者被纳入分析,止血带组为623例,非止血带组为611例,每篇文献的患者例数从10例到84例不等。所有研究地点均有描述,9项研究地点在中国(大陆8项及台湾1 项)[3,5,9-10,13-14,16-18],2项研究在英国[1,6],其他研究各所在地为:伊朗、丹麦、法国、瑞典、日本及意大利[2,4,7-8,11-12,15]。有16项研究报道了止血带压力[1-13,16-18],为240-300 mm Hg (1 mm Hg=0.133 kPa)。所有研究均报道了麻醉方式,3项研究为全身麻醉[9,13-14],其他均为脊髓麻醉及神经阻滞麻醉。10项研究报道了引流管使用情况,其中8项常规放置引流20-48 h,2项研究未放置引流装置[6,18]。1项研究为双膝关节置换,为自身对照,仅仅纳入观察指标为:手术时间,膝关节活动度及HSS评分,失血量及目测类比评分不被纳入分析。 2.3 Meta分析结果 2.3.1 总出血量 总出血量为术中及术后出血量之和。共有12项研究报道了总出血量的均值和标准差[1-12]。12项研究中存在异质性(P < 0.000 1,I²=75%),故分析采用随机效应模型,使用WMD值进行效应量合并分析,得出结果表明失血量差异有显著性意义(WMD=-80.60,95%CI:-140.02至-21.19) (图4)。 2.3.2 手术时间 共有11篇研究[2-7,10-11,13-15],736例病例被纳入分析,均报道了手术时间均值及标准差。各项研究结果存在异质性(P=0.000 7,I²=67%),采用随机效应模型分析,应用WMD值进行效应量合并分析,结果表明:两组病例中结果差异存在显著性意义(WMD=-2.17,95%CI:-4.12-0.22)(图5)。 2.3.3 HSS评分 膝关节HSS评分为:美国特种外科医院对膝关节评分系统,有4项研究报道术后7 d患肢膝关节HSS评 分[1,11,13,16],各项研究结果存在异质性(P=0.04,I²=63%),采用随机效应模型分析,应用WMD值进行效应量合并分析,结果表明两组患者膝关节HSS评分差异无显著性意义(WMD=-2.71,95%CI:-5.77-0.34)(图6)。 2.3.4 膝关节活动度 膝关节活动度正常范围为-5°-135°。有7项研究阐述了术后7 d膝关节活动范围[1,5,10,11,13,17,18],各项研究结果存在异质性(P=0.001,I²=78%),采用随机效应模型分析,应用WMD值进行效应量合并分析,结果表明两组患者中术后7 d患肢膝关节活动度无显著性意义(WMD=-3.56,95%CI:-8.16-1.04)(图7)。 "
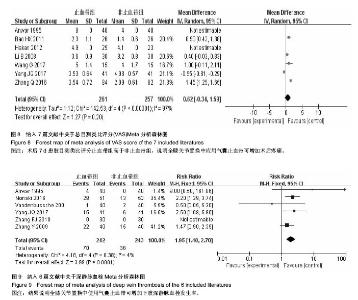
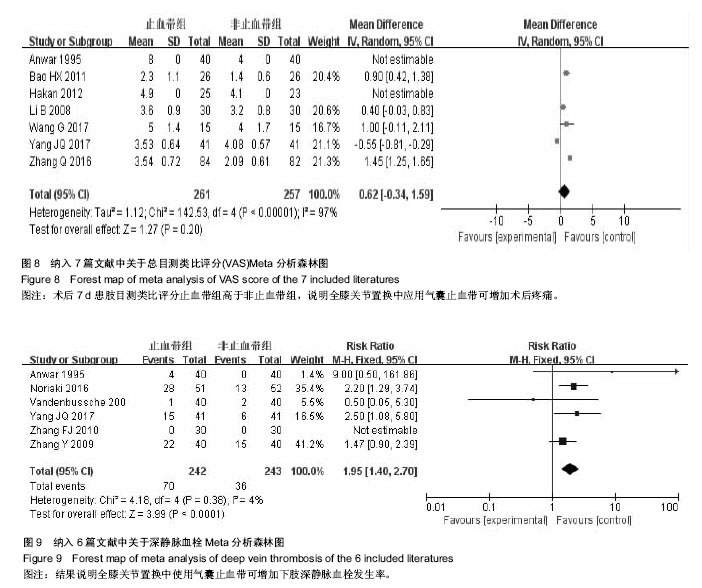
2.3.5 疼痛情况 采用目测类比评分法(Visual Analogue Scale/Score,VAS)评估疼痛情况,共有7项研究报道了平均VAS值及标准差[1,5,10-11,13,17-18]。各项研究结果存在高度异质性(P < 0.000 01,I²=97%),考虑异质性原因可能为个体差异,感觉及痛觉耐受能力不一,先试采用敏感性分析减少异质性,随机去除两组研究结果,行统计学分析,得出结论与原结论一致,说明分析结果具有可靠性,采用随机效应模型分析,应用WMD值进行效应量合并分析,结果表明术后7 d患肢目测类比评分差异有显著性意义(WMD=0.62,95%CI:-0.34-1.59)(图8)。 2.3.6 不良反应 共有6项研究报道了平均深静脉血栓发生率[1,4,6,9,12,18]。各项研究中无异质性(P=0.38,I²=4%),使用固定效应模型进行分析,应用RR值进行效应量合并分析,下肢深静脉血栓发生率差异有显著性意义(RR=1.95,95%CI:1.40-2.70)(图9)。 2.4 发表偏倚分析 以总失血量为例,进行Egger直线回归检验,提示纳入研究发表偏倚无显著性意义(P=0.59)。"
| [1] Abdel-Salam A, Eyres KS. Effects of tourniquet during total knee arthroplasty. A prospective randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995;77(2):250-253.[2] Yavarikia A, Amjad GG, Davoudpour K. The influence of tourniquet use and timing of its release on blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Pak J Biol Sci. 2010;13(5):249-252.[3] Tetro AM, Rudan JF. The effects of a pneumatic tourniquet on blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Can J Surg. 2001;44(1):33.[4] Vandenbussche E, Duranthon LD, Couturier M, et al. The effect of tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2002;26(5):306-309 .[5] Håkan L, Per A, Lars G. Tourniquet use in total knee replacement does not improve fixation, but appears to reduce final range of motion. Acta Orthop. 2012;83(5):499.[6] Mori N, Kimura S, Onodera T, et al. Use of a pneumatic tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty increases the risk of distal deep vein thrombosis: a prospective, randomized study. Knee. 2016;23(5):887.[7] Aglietti P, Baldini A, Vena LM, et al. Effect of tourniquet use on activation of coagulation in total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;(371): 169.[8] Tai TW, Chang CW, Lai KA, et al. Effects of tourniquet use on blood loss and soft-tissue damage in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(24):2209-2215.[9] Zhang FJ, Xiao Y, Liu YB, et al. Clinical effects of applying a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty on blood loss. Chin Med J (Engl). 2010;123(21): 3030-3033.[10] Li B, Wen Y, Wu H, et al. The effect of tourniquet use on hidden blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2009;33(5):1263-1268.[11] 王刚,曹晓瑞,陈晓勇,等.膝关节置换中止血带的使用对术后加速康复的影响[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2017,10(1):27-32.[12] 张阳,钱齐荣,吴海山,等.止血带对全膝关节置换术后深静脉血栓形成的影响[J].中华骨科杂志,2009,29(10):910-914.[13] Zhang Q, Dong J, Gong K, et al. Effects of tourniquet use on perioperative outcome in total knee arthroplasty. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016;30(4):421.[14] Kumar N, Yadav C, Singh S, et al. Evaluation of pain in bilateral total knee replacement with and without tourniquet: a prospective randomized control trial. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2015;6(2):85.[15] Ejaz A, Laursen AC, Kappel A, et al. Faster recovery without the use of a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2014;85(4):422-426 .[16] 沈忠伟,童培建,邵营钢,等.止血带对全膝关节置换术后肿胀及功能影响的临床研究[J].浙江临床医学,2010,12(3):261-262.[17] 鲍航行,王金法,蔡运火,等.全膝关节置换术后止血带性缺血再灌注损伤的临床研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2011,13(3):242-246 .[18] 杨健齐,魏鲁青,张健平,等.全膝关节置换中止血带应用对假体骨水泥厚度影响的对照研究[J].重庆医学,2017,46(6):782-785 .[19] 潘凡武,毕树雄.气压止血带在四肢骨科手术中应用研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2011,32(1):33-36 .[20] Huda R, Solanki D R, Mathru M. Inflammatory and redox responses to ischaemia/reperfusion in human skeletal muscle. Clin Sci. 2004;107(5): 497-503.[21] Smith TO, Hing CB. Is a tourniquet beneficial in total knee replacement surgery? A meta-analysis and systematic review. Knee. 2009;17(2): 141-147. [22] Thorey F, Stukenborgcolsman C, Windhagen H, et al. The effect of tourniquet release timing on perioperative blood loss in simultaneous bilateral TKA. 2010.[23] Sehat KR, Evans R, Newman JH. How much blood is really lost in total knee arthroplasty?Correct blood loss management should take hidden loss into account. Knee.2005;7(3):151-155.[24] Chen S, Li J P, Peng H, et al. The influence of a half-course tourniquet strategy on peri-operative blood loss and early functional recovery in primary total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2014;38(2):355-359 .[25] Johnson DP. Infection after knee arthroplasty. Clinical studies of skin hypoxia and wound healing. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 2009;252(1):1-48 .[26] 周媛.人工全膝关节置换术后感染相关危险因素分析[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2014.[27] Shimizu M, Kubota R, Nasu M, et al. The influence of tourniquet during total knee arthroplasty on perioperative blood loss and postoperative complications. Masui. 2016;65(2):131-135 .[28] Katsumata S, Nagashima M, Kato K, et al. Changes in coagulation-fibrinolysis marker and neutrophil elastase following the use of tourniquet during total knee arthroplasty and the influence of neutrophil elastase on thromboembolism. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2005;49(4): 510-516.[29] Kato N, Nakanishi K, Yoshino S, et al. Abnormal echogenic findings detected by transesophageal echocardiography and cardiorespiratory impairment during total knee arthroplasty with tourniquet. Anesthesiology. 2002;97(97):1123-1128. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [4] | Zhong Hehe, Sun Pengpeng, Sang Peng, Wu Shuhong, Liu Yi. Evaluation of knee stability after simulated reconstruction of the core ligament of the posterolateral complex [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 821-825. |
| [5] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Influence of anterior cruciate ligament defect on the mid-term outcome of fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 860-865. |
| [6] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [7] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [8] | Liu Xin, Yan Feihua, Hong Kunhao. Delaying cartilage degeneration by regulating the expression of aquaporins in rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 668-673. |
| [9] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [10] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [11] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [12] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [13] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [14] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [15] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||