Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (6): 938-944.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0072
Previous Articles Next Articles
Synthesis and biological properties of strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite
- Changhai Hospital, Shanghai 200433, China
-
Received:2017-12-02Online:2018-02-28Published:2018-02-28 -
Contact:Wang Da-lin, M.D., Chief physician, Changhai Hospital, Shanghai 200433, China -
About author:Dai Zhao, Studying for master’s degree, Physician, Changhai Hospital, Shanghai 200433, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 51232007
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Dai Zhao, Wang Da-lin . Synthesis and biological properties of strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(6): 938-944.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
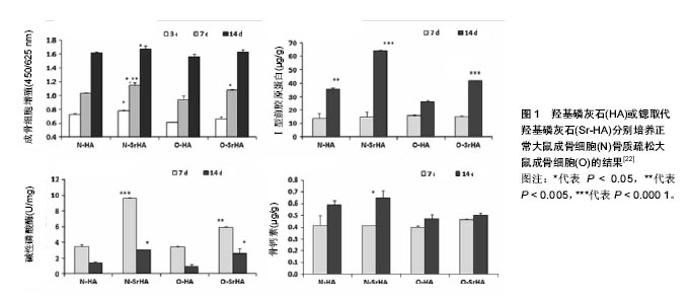
2.1 Sr-HA的制备方法 Sr-HA的制备方法可分为液相法和固相法,前者主要包括水热法、酸碱中和法、溶胶凝胶法,后者主要是指机械化学法。此外,本段还介绍两种一步制作Sr-HA涂层的方法。 2.1.1 液相法 水热法:水热法是指在高温、高压的密闭反应容器里,在水溶液中生长晶体,也称为水热合成法。Frasnelli等[24]配制了一系列Ca(NO3)2和Sr(NO3)2混合溶液,溶液中Sr/(Ca+Sr)摩尔比分别为0、5%、10%、25%、50%、75%和100%;然后根据(Ca+Sr)/P的摩尔比(1.67)准备(NH4)2HPO4溶液。在不断搅拌中将后者逐滴加入前者,反应全程控制在90 ℃、pH=10(用氨水调整pH)的氮气环境中。反应完毕后,固液混合物以10 000 r/min的转速离心3次,并用蒸馏水反复清洗后干燥得到Sr-HA粉体。透射电镜下,不同锶含量的Sr-HA晶体样本均呈棒状几何体,并聚集成团;随锶含量的增加,晶体尺寸沿长轴增加(45±14)nm至(124±42)nm。X射线衍射结果显示(Ca+Sr)/P比值在1.537-1.771之间,接近天然骨中的钙磷比;电感耦合等离子体光谱仪也证明了上述比值接近理论值1.67。红外光谱检测未发现其他杂质基团,说明该法合成的Sr-HA具有较高的的纯度。 水热法是合成Sr-HA使用最多的技术,这种技术生成晶体纯度高、杂质少,反应过程简单,适合量化生产,不过需要严格控制反应物比例和条件。反应过程基本上都处于pH=10的碱性环境中[25-28],但笔者在查阅文献时,发现Jiang等[29]在酸性条件下使用水热法成功合成了Sr-HA,姑且称之为“酸性水热法”。他们首先配置了两种混合液。溶液A:将2.1 mol Ca(NO3)2溶液、0.9 mol Sr(NO3)2溶液和0.29 g溴化三甲胺(作为表面活性剂)溶于40 mL蒸馏水,并用氨水和盐酸调节pH值至4.5,其中Sr/(Ca+Sr)摩尔比为0%、30%、50%和100%;溶液B:将2 mol(NH4)2HPO4和6 mol二水枸橼酸钠溶于20 mL蒸馏水。将溶液B加入溶液A,经剧烈搅拌后将混合溶液转移到100 mL特氟龙瓶,置于高压釜中并在180 ℃下保持1 d。待高压釜冷却至室温后,离心机分离出Sr-HA晶体后依次用去离子水和乙醇洗涤。生成的样品经过X射线衍射检测到Sr-HA特征峰,并随锶含量增加,峰值越高;红外光谱技术也检测到Sr-HA的特征性基团,不过杂质基团较多;透射电镜检测到晶体类似纳米棒状结构,高分辨率透射电镜清晰发现晶格纹理,其中30%Sr-HA的晶面间距(0.308 nm)与标准值(0.311 nm,JCPDS NO. 34-0842)非常接近。可见,“酸性水热法”虽然也能成功制备出Sr-HA晶体,但纯度不够。 酸碱中和法:是指酸性和碱性溶液在一定条件下混合后发生反应,生成沉淀的方法。酸碱中和法制备的晶体纯度不够,需要进一步烧结才能得到纯度较高的Sr-HA晶体。Capuccini等[30]将含有12 g Ca(OH)2的混悬液加入含有54.25 g Sr(NO3)2的去离子水溶液,随后分别在25,50, 80 ℃下,将含有8.8 g H3PO4的去离子水溶液以3.0- 4.0 mL/min的速度逐滴加入上述混合液,整个加液过程持续搅拌,加液完成后在室温下老化24 h。透射电镜观察到纳米棒状晶体,平均纳米粒子长度为(40±6) nm;ICP-OES检测获得的Sr-HA晶体中Sr/(Sr+Ca)比值约为10%,反应温度对该比值影响不大;样品烧结后经X射线衍射检测发现衍射图像中的杂质峰消失。 溶胶凝胶法:是指在液相下将含有高化学活性组分的化合物均匀混合形成稳定的溶胶体系,通过胶粒间缓慢聚合形成凝胶,再将凝胶干燥、烧结固化,获得产物的过程。Kaygili等[31]使用该法制备了Sr/(Sr+Ca)比分别为:0.45%、0.90%、1.35%、1.80%和2.25%的5种Sr-HA晶体。具体步骤为:按照上述比例配置合计摩尔量为 0.5 mol的Ca(NO3)2和Sr(NO3)2混合溶液和 0.3 mol(NH4)2HPO4溶液,将后者逐滴加入前者后,再加入0.5 mol柠檬酸溶液10 mL,并在90 ℃下剧烈搅拌6 h直到凝胶化。将凝胶在120 ℃下干燥15 h,再在750 ℃下煅烧 1.5 h即得晶体样品。X射线衍射检测所有样品纯度(目标化合物含量)超过95%,估算样品的平均微晶尺寸和结晶度分别是21-27 nm和66%-87%;但是,未发现各组参数与锶含量之间的相关关系。可见,该法获得的低锶含量Sr-HA纯度、结晶度都比较理想;而当锶取代比例在较低范围时,获得的晶体参数也相对稳定。 2.1.2 固相法 固相法主要包括机械化学法。机械化学法是指在高温条件下,反应物被置于研磨机中,通过机械和化学耦合机制发生反应,生成产物。 Vahabzadeh等[32]在800 ℃,将50 g羟基磷灰石与0.60 g SrO/75 mL无水乙醇混合物一起球磨6 h,制备出质量分数为1%的Sr-HA粉末。Fielding等[33]则在不改变上述反应介质的前提下,在反应体系中加入了100 g氧化锆作为研磨介质,充分混合后以70 r/min的转速研磨 6 h,然后烘干,再将烘干后的粉末在800 ℃下热处理 6 h得到Sr-HA粉末。机械化学法由于容易引入杂质,目前应用很少;在研磨过程中可以产生特定大小的粉体,故多数情况下是与等离子喷涂技术结合使用。 2.1.3 一步涂层制作法 制作Sr-HA涂层主要包括两种方法,即电化学沉积法和微弧氧化法。 电化学沉积法:该法实质上属于水热法的延伸,是将水热反应过程和电化学沉积过程置于同一反应体系内,一次性生成Sr-HA涂层。Yang等[34]使用该法制作了Sr-HA涂层。他们先制备了含有1.2×10-3 mol CaCl2、7.2× 10-4 mol (NH4)2HPO4、1.33×10-4 mol SrCl2、0.1mol NaCl的混合水溶液,然后把钛板浸入其中,在85 ℃、直流电压3 V下通电30 min,最后进行洗涤、干燥并用紫外线照射2 h。扫描电镜显示:钛表面形成薄层Sr-HA结晶,涂层厚度为6.0-7.0 μm,可见横截面直径为40-60 nm的短棒状结晶。相对于喷涂或者溅射等方法,电化学沉积法更加简便、高效、经济,而且便于控制涂层厚度。 微弧氧化法:是指通过电解液与相应电参数的组合,在铝、镁、钛等金属表面依靠弧光放电原位生长出陶瓷层的表面处理技术。Chung等[35]采用该法制作了Sr-HA涂层。他们首先制备了一组混合溶液,包括Na2HPO4、(CH3COO)2Sr和(CH3COO)2Ca,保持Na2HPO4摩尔量为0.12mol,通过改变(CH3COO)2Sr和(CH3COO)2Ca含量,使得Sr /(Sr + Ca)摩尔比为0%、3%、7%、15%、25%、50%、75%和100%。然后把钛板作为阳极置于上述混合液中,调整设备电压450 V、温度25 ℃下工作10 min制成涂层。X射线衍射证实了涂层中的Sr-HA,同时检测到少量CaTiO3和SrTiO3。扫描电镜显示涂层厚度为30-37 μm,呈均匀分布的多孔形态。函数分析显示涂层锶含量随着电解质锶含量增加而呈非线性增加,因此可以通过调节电解质的浓度可以产生所需Ca/Sr比的Sr-HA涂层。微弧氧化法制备的Sr-HA 涂层在纯度和结晶度上均可得到保证,不过由于生产成本高以及复杂的退火处理,商业化很难实现。 2.2 Sr-HA的物理特征 如前所述,由于Sr2+(0.113 nm)的离子半径大于Ca2+(0.099 nm),当锶占据羟基磷灰石晶格中钙的位点时,势必会引起晶体特征的变化,以及以此为基础的各种物理特征改变。 晶体尺寸的变化:前文提到,Frasnelli等[24]通过水热法制备梯度锶含量的Sr-HA粉体,其晶体尺寸随锶含量的增加而增加。Krishnan等[26]也观察到相似的结果,他们分别制备了HA和Sr/Ca+Sr摩尔比为50%的Sr-HA粉体样品,经透射电镜测量,两者晶体尺寸分别约为70,180 nm;而经X射线衍射的检测数据进行估算,两者晶体尺寸约为25.73,33.62 nm;两种方法证明了同样的变化趋势。 结晶度和溶解度的变化:Ni等[27]制备的Sr-HA样品中,锶的摩尔比别为1%、5%和10%。从X射线衍射图像中的主峰宽度逐渐增宽判断,Sr-HA结晶度随锶含量的增加而逐渐减小。他们还通过固体滴定法检测了粉体的溶解度,并制作了对数溶解度曲线。通过测定,他们发现随锶含量的增加,样品溶解度逐渐增加;根据曲线外推3种样品在pH=7.4的对数溶解度分别为1× 10-7 mol/L、8×10-7 mol/L和2×10-6 mol/L;而且从溶液测得释放出钙和锶的量也成逐渐增大的趋势,进一步佐证了溶解度的变化趋势。溶解度的增加有利于锶元素在局部释放、发挥特定的生物学性能。 机械性能的变化:Fielding等[33]测试了Sr-HA涂层与羟基磷灰石涂层机械性能的区别,他们通过等离子喷涂法分别制作了这两种涂层,经过检测两种涂层的黏合强度分别为(18.21±4.8),(17.4±2.9)MPa,差异无统计学意义。由于该研究中Sr-HA粉体的锶含量较低,无法判断其实际的粘合强度,不过由于锶对钙的取代,羟基磷灰石晶体结构及稳定性发生改变,机械性能会变差。Sariibrahimoglu等[36]则测量了Sr/Ca+Sr为25%和50%的Sr-HA掺入聚氨酯支架后的断裂伸长率和拉伸强度变化,结果比纯聚氨酯支架的指标显著降低。由此可见,锶掺入羟基磷灰石后,会引起机械性能的降低,不过目前的研究缺乏系统性,确定结论为时尚早。 2.3 Sr-HA的体外生物学性能 2.3.1 生物相容性 研究证明,锶取代羟基磷灰石的生物相容性良好,不仅不会抑制细胞增殖,一定比例的Sr-HA甚至会促进细胞增殖。 Frasnelli等[24]制备了含有不同锶含量的Sr-HA粉体悬浮液,并用上述悬浮液组对人骨肉瘤细胞株Saos-2进行培养。扫描电镜未发现处理组(即不同锶含量的Sr-HA)和对照组(羟基磷灰石)存在细胞形态上的区别;用MTT法测试培养1周后细胞,发现处理组的细胞存活率比对照组增加了25%-37%,且具有统计学意义;通过荧光染色分析细胞凋亡情况,发现所有处理组的荧光分析都是阴性的,表明所有处理组都未引起细胞凋亡。Fielding等[33]则通过MTT法测定了人胚胎成骨细胞系hFOB 1.19在Sr-HA涂层上的增殖情况,发现Sr-HA组比羟基磷灰石组增殖效果更好,扫描电镜也显示细胞呈现健康生长的形态特征。 2.3.2 促进成骨作用 Sr-HA对成骨分化的促进作用似乎已得到证明,不过之前的研究较少涉及分子和基因表达层面,近年来,有研究人员进行深层次的探究。Zhou等[37]检测了在Sr-HA涂层上生长的成骨细胞的蛋白及相应mRNA合成情况。他们在钛基体上制备了两种不同表面形貌(纳米颗粒状和纳米短棒状)的Sr-HA涂层样品,并在样品上培养人类胚胎成骨细胞。结果发现,实验组的成骨相关蛋白——碱性磷酸酶、骨桥蛋白、骨钙蛋白和Ⅰ型胶原,以及Runt相关转录因子2、成骨相关转录因子抗体、骨桥蛋白和Ⅰ型胶原的mRNA合成均随培养时间的延长呈增加趋势,而且表面结构为纳米棒状涂层比纳米颗粒涂层的增加更为明显;而Sr-HA纳米棒间距不同,结果也存在明显差异:间距为(67.3±3.8)nm和(95.7±4.2)nm增加趋势更明显。同期进行的细胞外基质矿化实验,与上述结果相对应。该研究表明,Sr-HA涂层不仅增强了成骨相关基因表达和蛋白合成,而且使更多的基质蛋白分泌到细胞外基质中加速矿化,不过促进成骨分化效能与涂层表面形貌有一定关系。 Yang等[38]检测了Sr-HA对间充质干细胞的促成骨分化作用。他们除了观察碱性磷酸酶、Ⅰ型胶原、骨桥蛋白及矿化结节等常规指标之外,还检测了Wnt/β-catenin信号通路中的一些指标,而该通路在骨骼发育及骨稳态中发挥核心作用。与空白对照和阳性对照相比,常规指标均体现出显著增加的趋势:碱性磷酸酶表达为例,成骨分化2周后,Sr-HA组和阳性对照(成骨细胞培养基)中碱性磷酸酶标准化表达分别为(716.9±19.1)%和(416.5±55.8)%,差别具有统计学意义。而Wnt/β-catenin信号通路中关键分子:β-连环蛋白、卷曲8在Sr-HA组的标准化表达分别为(469.9±48.4)%和(1435±198)%,明显高于阳性对照组[(234.4±28.5)%和(285.4±57.6%)];另外一种关键分子蛋白磷酸酶2A作为Wnt信号传导抑制剂,在Sr-HA组的表达水平明显低于阳性对照组。这些数据从分子层面和信号转到的角度证明了Sr-HA对于促进成骨分化的积极作用。 2.3.3 抑制破骨作用 作为抗骨质疏松药雷奈酸锶的主要成分,锶元素被证明有抑制破骨细胞活性,而针对Sr-HA对破骨细胞的作用研究较少。 Chung等[35]用电化学沉积法在钛片上制备了不同锶含量的Sr-HA涂层,并将RAW264.7破骨细胞置于涂层环境培养,以评价Sr-HA对破骨细胞的作用。结果发现,当涂层中的Sr/(Ca+Sr)比例超过38.9%时,Sr-HA涂层开始出现对破骨细胞的有效抑制,这与Fonseca等[39]的研究的作用并减少处于分化状态的破骨细胞数量。也就是说,引入羟基磷灰石的锶元素,不仅具备了促成骨作用,还对一致,他们证明Sr能够抑制核因子κB受体活化因子配体破骨细胞有抑制作用,这与引言中提到的锶元素“双重调节作用”相契合,说明锶元素的引入使这种新型材料的生物学性能得到了提升。 值得一提的是,Boanini等[22]比较了Sr-HA对正常成骨细胞和骨质疏松大鼠成骨细胞的影响,实验选择了白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α作为检测指标,二者在骨质疏松症中影响成骨细胞和破骨细胞活性。结果表明,在细胞培养第7天,正常成骨细胞-Sr-HA和骨质疏松大鼠成骨细胞-Sr-HA组的白细胞介素6显著降低,肿瘤坏死因子α在正常成骨细胞-Sr-HA组中亦显示出较低的值;而且,骨质疏松大鼠成骨细胞在Sr-HA组比羟基磷灰石组有更高的增殖度(图1),这表明锶对骨质疏松大鼠成骨细胞的白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α产生了早期下调效应,并抵消了在骨质疏松大鼠成骨细胞中观察到白细胞介素6的增加,而白细胞介素6据报道与骨吸收的RANK/RANKL/OPG机制相关[40]。这表明Sr-HA不仅对正常或异常成骨细胞系具有促进增殖分化作用,还能抑制病理条件下(如骨质疏松症)的骨吸收,有一定的临床指导意义。 "
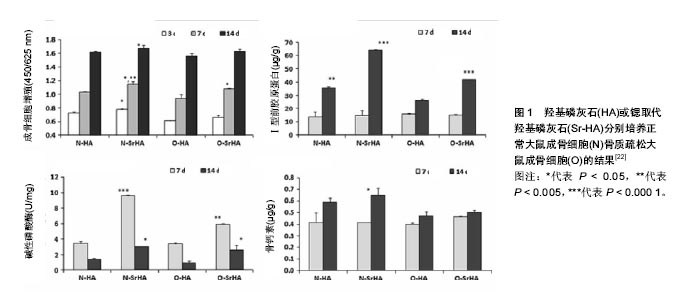
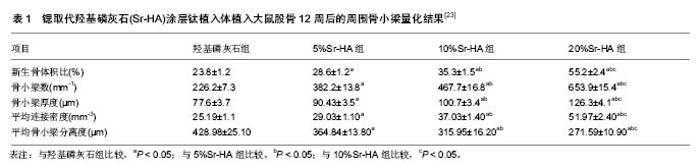
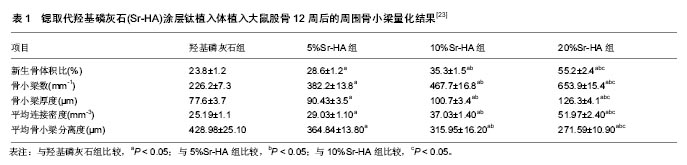
2.4 Sr-HA的体内生物学性能 2.4.1 Sr-HA粉体促进骨修复 Kaygili等[31]通过溶胶凝胶法合成了羟基磷灰石和5种不同锶含量的Sr-HA粉体,然后将他们分别填充进新西兰兔胫骨的孔洞内,饲养12 d后进行组织学观察。结果发现,对照组(羟基磷灰石组)在缺损部位出现包含成纤维细胞和早期骨小梁的弥漫纤维组织,而实验组的缺损部位则由不同数量的板层骨和纤维组织填充,其中,Sr/Sr+Ca摩尔比为0.45%的Sr-HA具有最佳愈合反应,即完整骨小梁形成。这一系列实验验证了低水平锶对骨修复中的积极作用。 2.4.2 Sr-HA涂层促进骨整合 Tao等[23]用电化学沉积法制备了4组不同锶含量(Sr/Sr+Ca=0、5%、10%、20%)的Sr-HA涂层钛植入体,并将植入体植入大鼠股骨,饲养12周后进行评估(表1)。三维显微CT图像发现,锶的掺杂改善了植入体周围骨整合,其中20%Sr-HA涂层的效果最佳;以植入体周围骨小梁数为例,4组数值依次分别为226.2±7.3、382.2±13.8、467.7±16.8、653.9± 15.4,且每两组之间均具有统计学差异;其他指标如平均骨小梁厚度和间距等也有相同变化趋势。生物力学测试结果表明,5%、10%和20%Sr-HA组的最大拔出力分别是HA组的1.34、1.51和2.25倍,且20%Sr-HA组的最大拔出力显著高于低锶含量组,说明植入物骨整合效果的增强与锶含量呈正相关。 2.4.3 Sr-HA支架促进骨修复 Yang等[38]将胶原- Sr-HA(100%锶取代)、胶原-羟基磷灰石和胶原3种材料制备的支架植入大鼠颅骨缺损部位,并对实验动物进行CT扫描和组织切片观察。植入1个月后,CT图像显示Sr-HA组缺损区域减小,而且缺损区域的CT密度值大于羟基磷灰石组和空白对照组;3组定量结果依次分别为(219.4±37.1),(121±14.2),(15.7±3.3)HU,前者对比后两者差异显著。组织学切片及染色检查发现,Sr-HA组新生骨组织的成熟度高于羟基磷灰石组和空白对照组,而且Sr-HA组骨缺损区域中形成丰富的骨样细胞外基质和成熟的新生骨结构。由此可见,对比纯羟基磷灰石支架,引入锶的胶原支架在大鼠体内促进骨修复作用非常明显。"
| [1]Vestermark MT.Strontium in the bone-implant interface.Dan Med Bull.2011;58(5):B4286.[2]McElderry JD,Zhu P, Mroue KH,et al.Crystallinity and compositional changes in carbonated apatites: Evidence from 31P solid-state NMR, Raman, and AFM analysis.J Solid State Chem.2013;206(1):192-198.[3]Heslop DD,Bi Y,Baig AA,et al.A comparative study of the metastable equilibrium solubility behavior of high-crystallinity and low-crystallinity carbonated apatites using pH and solution strontium as independent variables.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2005;289(1):14-25.[4]Laurencin D,Almora-Barrios N,de Leeuw NH,et al.Magnesium incorporation into hydroxyapatite. Biomaterials. 2011;32(7): 1826-1837.[5]Xu L,Jiang L,Xiong C,et al.Effect of different synthesis conditions on the microstructure, crystallinity and solubility of Mg-substituted hydroxyapatite nanopowder.Adv Powder Technol. 2014;25(3): 1142-1146.[6]Cox SC,Jamshidi P,Grover LM,et al.Preparation and characterisation of nanophase Sr, Mg, and Zn substituted hydroxyapatite by aqueous precipitation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;35(35):106-114.[7]Abert J,Bergmann C,Fischer H.Wet chemical synthesis of strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite and its influence on the mechanical and biological properties.Ceram Int. 2014;40(7): 9195-9203.[8]Fu DL,Jiang QH,He FM,et al.Fluorescence microscopic analysis of bone osseointegration of strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite implants.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B.2012;13(5):364-371.[9]Pors Nielsen S.The biological role of strontium.Bone 2004;35(3): 583-588.[10]Boivin G,Deloffre P,Perrat B,et al.Strontium distribution and interactions with bone mineral in monkey iliac bone after strontium salt (S 12911) administration.J Bone Miner Res.1996;11(9): 1302-1311.[11]Brennan TC,Rybchyn MS,Green W,et al.Osteoblasts play key roles in the mechanisms of action of strontium ranelate.Br J Pharmacol.2009;157(7):1291-1300.[12]Fromigué O,Haÿ E,Barbara A,et al.Calcium sensing receptor-dependent and receptor-independent activation of osteoblast replication and survival by strontium ranelate.J Cell Mol Med.2009;13(8b):2189-2199.[13]Caverzasio J.Strontium ranelate promotes osteoblastic cell replication through at least two different mechanisms. Bone. 2008;42(6):1131-1136.[14]Atkins GJ,Welldon KJ,Halbout P,et al.Strontium ranelate treatment of human primary osteoblasts promotes an osteocyte-like phenotype while eliciting an osteoprotegerin response.Osteoporos Int. 2009;20(4):653-664.[15]Yamaguchi T.The calcium-sensing receptor in bone.J Bone Miner Metab.2008;26(4):301-311.[16]Teitelbaum SL.Bone Resorption by Osteoclasts. Science. 2000; 289(5484):1504-1508.[17]Bonnelye E,Chabadel A,Saltel F,et al.Dual effect of strontium ranelate: stimulation of osteoblast differentiation and inhibition of osteoclast formation and resorption in vitro.Bone. 2008;42(1): 129-138.[18]Buehler J,Chappuis P,Saffar JL,et al.Strontium ranelate inhibits bone resorption while maintaining bone formation in alveolar bone in monkeys (Macaca fascicularis).Bone.2001;29(2):176-179.[19]Canalis E,Hott M,Deloffre P,et al.The divalent strontium salt S12911 enhances bone cell replication and bone formation in vitro.Bone.1996;18(6):517-523.[20]Takahashi N,Sasaki T,Tsouderos Y,et al.S 12911-2 inhibits osteoclastic bone resorption in vitro. J Bone Miner Res. 2003; 18(6):1082-1087.[21]Li ZY,Lam WM,Yang C,et al.Chemical composition, crystal size and lattice structural changes after incorporation of strontium into biomimetic apatite.Biomaterials.2007;28(7):1452-1460.[22]Boanini E,Torricelli P,Fini M,et al.Osteopenic bone cell response to strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2011;22(9):2079-2088.[23]Tao ZS,Bai BL,He XW,et al.A comparative study of strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite coating on implant's osseointegration for osteopenic rats.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2016;54(12):1959-1968.[24]Frasnelli M,Cristofaro F,Sglavo VM,et al.Synthesis and characterization of strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2017;71:653-662.[25]Khajuria DK,Vasireddi R,Trebbin M,et al.Novel therapeutic intervention for osteoporosis prepared with strontium hydroxyapatite and zoledronic acid: In vitro and pharmacodynamic evaluation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2017;71:698-708.[26]Krishnan V,Bhatia A,Varma H.Development, characterization and comparison of two strontium doped nano hydroxyapatite molecules for enamel repair/regeneration.Dent Mater. 2016;32(5): 646-659.[27]Ni GX,Shu B,Huang G,et al.The effect of strontium incorporation into hydroxyapatites on their physical and biological properties.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2012;100(2):562-568.[28]Zhang W,Shen Y,Pan H,et al.Effects of strontium in modified biomaterials.Acta Biomaterialia. 2011;7(2):800-808.[29]Jiang F,Wang DP,Ye S,et al.Strontium-substituted, luminescent and mesoporous hydroxyapatite microspheres for sustained drug release.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2014;25(2):391-400.[30]Capuccini C,Torricelli P,Boanini E,et al.Interaction of Sr-doped hydroxyapatite nanocrystals with osteoclast and osteoblast-like cells.J Biomed Mater Res A.2009;89(3):594-600.[31]Kaygili O,Keser S,Kom M,et al.Strontium substituted hydroxyapatites: Synthesis and determination of their structural properties, in vitro and in vivo performance.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;55:538-546.[32]Vahabzadeh S,Roy M,Bandyopadhyay A,et al.Phase stability and biological property evaluation of plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings for orthopedic and dental applications.Acta Biomaterialia. 2015;17:47-55.[33]Fielding GA,Roy M,Bandyopadhyay A,et al. Antibacterial and biological characteristics of silver containing and strontium doped plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings.Acta Biomaterialia. 2012;8(8):3144-52.[34]Yang H,Lin M,Xu Y,et al.Osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on strontium-substituted nano-hydroxyapatite coated roughened titanium surfaces.Int J Clin Exp Med.2015;8(1):257-264.[35]Chung CJ,Long HY.Systematic strontium substitution in hydroxyapatite coatings on titanium via micro-arc treatment and their osteoblast/osteoclast responses.Acta biomaterialia. 2011; 7(11):4081-4087.[36]Sariibrahimoglu K,Yang W,Leeuwenburgh SC,et al.Development of porous polyurethane/strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite composites for bone regeneration.J Biomed Mater Res A.2015; 103(6):1930-1939.[37]Zhou J,Li B,Lu S,et al.Regulation of osteoblast proliferation and differentiation by interrod spacing of Sr-HA nanorods on microporous titania coatings. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013; 5(11):5358-5365.[38]Yang F,Yang D,Tu J,et al.Strontium enhances osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and in vivo bone formation by activating Wnt/catenin signaling.Stem Cells. 2011; 29(6):981-991.[39]Fonseca JE.Rebalancing bone turnover in favour of formation with strontium ranelate: implications for bone strength. Rheumatology. 2008;47(Suppl 4):iv17-19.[40]Steeve KT,Marc P,Sandrine T,et al.IL-6, RANKL, TNF-alpha/IL-1: interrelations in bone resorption pathophysiology.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.2004;15(1):49-60.[41]Garbani M,Xia W,Rhyner C,et al. Allergen-loaded strontium-doped hydroxyapatite spheres improve allergen-specific immunotherapy in mice.Allergy. 2017;72(4): 570-578.[42]Li H,Jiang F,Ye S,et al.Bioactive apatite incorporated alginate microspheres with sustained drug-delivery for bone regeneration application.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2016;62:779-786. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||