Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (2): 323-328.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0025
Properties of gelatin methacryloyl and its application in the skin tissue engineering
- 1Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010110, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Burn and Plastic Surgery, the 253rd Hospital of PLA, Hohhot 010010, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2017-09-28Online:2018-01-18Published:2018-01-18 -
Contact:Chen Xiang-jun, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Burn and Plastic Surgery, the 253rd Hospital of PLA, Hohhot 010010, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wu Xing, Studying for master’s degree, Physician, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010110, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Xing, Liu Zhao-xing, Lin Huan-huan, Liu Sha, Sun Wei-jing, Chen Xiang-jun.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
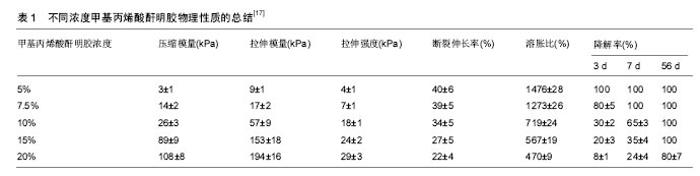
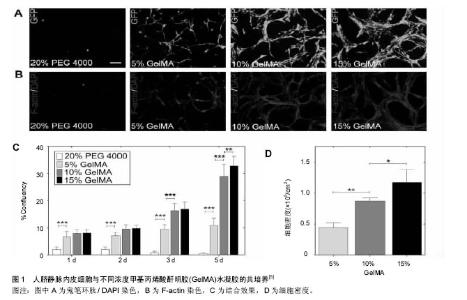
2.1 GelMA的材料学特性 2.1.1 GelMA的组成 GelMA的主要成分是明胶,可衍生自多种来源,明胶是通过胶原蛋白部分不可逆水解产生的多分散肽混合物,该过程改变了胶原蛋白的三级结构,降低了因不同原料来源所导致的变异性。当温度低于30 ℃,胶原三重螺旋溶液冷却,可部分重新形成网眼尺寸为数十纳米内的凝胶[1]。明胶缺乏热稳定性,需要通过物理或化学方式将明胶转化成稳定材料。基于明胶的性能可与他材料设计组合形成一个通用平台[2]。明胶具有可交联性,可应用于多项生物医学领域,例如再生医学、药物递送和组织黏合剂[3]。在明胶中引入甲基丙烯酰胺基团使其具有光敏性[4],可通过甲基丙烯酰胺基团和明胶的光化学反应,将待固化的液体材料永久性转化成固体[5]。 2.1.2 GelMA的光交联性 GelMA水凝胶可通过光交联技术来设计,即GelMA前体溶液在光引发剂和特定波长紫外光的协同下,结合不同的生物制造方法,包括微模制、光掩模、生物打印、自组装和微流体等技术,构建出各种形状的凝胶微控制结构。大量研究已探索通过设计光掩模图案来间接控制水凝胶微图案,但该技术无法设计出复杂的3D微凝胶图案。为此研究者开发了微镜器件投影印刷系统,通过逐层光聚合方法设计3D微结构的水凝胶。Gauvin等[6]就报道了应用投影立体光刻系统设计可控微结构的GelMA水凝胶,成功地获得了具有可调机械性能(范围从1-800 kPa)的GelMA支架。 2.1.3 GelMA的生物活性 GelMA主要成分是廉价的变性胶原,拥有精氨酸-甘氨酸-天门冬氨酸基序(RGD)细胞结合基序和基质金属蛋白酶反应肽基序[7-9]。由于RGD和基质金属蛋白酶反应肽基序的存在,GelMA支架可维持细胞生长增殖活力,调节细胞行为。GelMA可用于细胞的2D和3D培养,具有良好的细胞黏附性,能促进细胞的增殖[10]、迁移和分化[11],可用来研究细胞外基质和细胞之间的相互作用。GelMA良好的生物学特性已被广泛应用于各种组织工程中,如骨、软骨、心脏和血管组织工程等[12]。Annabi等[13]仿生心脏组织结构设计出高度弹性GelMA底物,该弹性机械支架模拟心肌细胞动态力学性质,促进心肌细胞的附着、对准、扩散、细胞间通讯。GelMA除了用于弹性软组织工程[14],还用于细胞信号传导、生物传感、药物和基因传递的研究。 2.2 GelMA的组织工程学特性 2.2.1 GelMA的细胞支架作用 光交联后GelMA形成微观3D空间网络结构,控制种子细胞行为,可用于研究细胞与生物材料的相互作用[7]。GelMA可被特征性设计成用于细胞生长和组织形成的天然细胞外基质类似物支架[15]。Aubin等[8]在GelMA微图案化上分别培养出多种细胞,以形成不同组织:用于血管形成的人脐静脉内皮细胞、用于骨骼肌的啮齿动物成肌细胞C2C12、心肌组织的心脏侧群细胞和作为一般模型的成纤维细胞NIH 3T3。表明细胞可遵循GelMA微图案增殖、调整和延长,该结果对皮肤的组织工程研究有着深远影响。Nichol 等[5]展示了NIH 3T3成纤维细胞和人脐静脉内皮细胞与GelMA 2D和3D形式的结合,创建可灌注的工程化组织,功能细胞被包封在含有内皮细胞的GelMA微通道中,以产生微血管化仿生组织(图1)。所以GelMA适合在微尺度上形成可控的工程血管化组织。Zamanianet等[16]模仿人肝细胞结构设计完整的功能组织,通过几何形状控制自组装结构,制造负载细胞的微凝胶[16],将HepG2细胞与NIH3T3成纤维细胞共培养在GelMA微凝胶内,能够实现细胞在微凝胶边界处的相互作用。有报道表明,基于GelMA的细胞应答性质允许细胞伸长和迁移,人脐静脉内皮细胞可黏附和增殖在GelMA互连孔结构中,并在1周内达到汇合[15]。通过GelMA微图案化方式,不仅可增强明胶凝胶黏弹性、抑制降解,还可通过控制取代度、聚合物浓度[5]、引发剂浓度和交联时间来调节凝胶性能,来研究负载细胞的活性。 2.2.2 GelMA可负载多种组织来源的皮肤组织工程种子细胞 GelMA水凝胶在皮肤组织工程研究中取得了不凡的突破。Zhao等[17]的研究表明,GelMA支架机械性质是调节角质形成细胞行为的关键因素,可支持角质形成细胞黏附、增殖和分化,通过调节GelMA性能可形成多层表皮样组织(表1)。皮肤组织工程的种子细胞来源广泛,间充质干细胞能作为有效果的种子细胞来源用于再生骨和软骨[18]、血管、皮肤和心血管系统等[19]。人体内的脂肪组织分布广泛,取材方便,脂肪组织内含有大量脂肪干细胞。Eke等[20]设计含有脂肪干细胞的真皮替代品,可快速刺激新生血管形成,改善伤口表皮再生。凝胶的透明度允许伤口部位完整暴露在视野中,便于观察创面。水凝胶为脂肪干细胞增殖提供了合适的微环境,体内研究表明,负载干细胞的水凝胶是空白对照组血管形成速度的3倍。总之,装载有脂肪干细胞的GelMA 水凝胶显示出促进伤口愈合、加快新生血管生成的特性。GelMA水凝胶可同时负载多种细胞,实现细胞共培养,研究细胞间的协同促进作用。Zhang等[21]在GelMA水凝胶内构建3D共培养系统,培养不同细胞比例的人脐带间充质干细胞和人脐静脉内皮细胞,结果表明GelMA水凝胶对两种细胞有较小的细胞毒性,当人脐带间充质干细胞与人脐静脉内皮细胞比例为50∶50时,表现出最效率的细胞增殖和血管生成。与单一培养相比,共培养系统中GelMA水凝胶上的中角质形成细胞保持良好的分化状态,与细胞增殖相关的基因表达显著增加。通过以上手段调节GelMA水凝胶性能、控制微观结构、负载多种类细胞,将为GelMA水凝胶在临床创面的应用提供理论基础。"
2.3 GelMA水凝胶在皮肤组织工程中的应用 2.3.1 GelMA水凝胶科促进损伤修复加速创面愈合 在GeLMA中加入物理材料可改变相关的生物学活性。Zhao等[22]制备GelMA电纺丝支架,使用基于光可交联的GelMA水凝胶构建完全3D细胞化的细胞外基质支架。并展示了一种简单有效的技术来构建用于加速伤口愈合的GelMA电纺丝3D纤维支架。静电纺丝纳米纤维支架包括可裁剪的机械性能和降解性,可在2周内实现皮肤组织损伤的快速修复和再生。基于GelMA可光致交联性优点,可通过改变曝光时间来调节复合水凝胶物理性能,如保水性、刚度、强度、弹性、降解性。柔软的水凝胶纤维支架可以支持细胞黏附、增殖和迁移,在2周内促进皮肤组织的形成和再生。纤维状GelMA 凝胶支架的可调节性和稳定性,可与戊二醛交联的明胶或聚乳酸共乙醇酸等其他候选底物相区分,被广泛应用于重建组织缺损。GelMA纤维支架完全细胞化的能力可在体外构建皮肤模型,作为皮肤替代品或伤口敷料用于创面治疗。局部随机皮瓣,也称为皮下神经皮瓣,用于缺损组织修复和重建[23],但皮瓣的长与宽比及其他慢性基础性疾病都影响着皮瓣的远端血运状态,皮瓣的远端坏死始终是导致手术失败的主要问题,主要由于缺血再灌注损伤,供血不足和血流动力学损伤等造成的[24]。坏死将导致伤口延期愈合,增加二次手术的风险,限制了临床上局部随机皮瓣的应用[25]。因此,增加血管密度和血流量将有助于随机皮瓣存活,3D功能血管网络的发展对于局部随机皮瓣的存活是有好处的。基于GelMA电纺纤维膜柔软的机械性能和可控的降解性能,Sun等[26]使用GelMA静电纺丝材料证明了3D纤维支架技术加速血管形成的有效性。此外,还观察到水凝胶可支持内皮细胞和真皮成纤维细胞在支架中黏附、增殖和迁移,这些都有利于新生血管的形成。在大鼠模型中,将GelMA纤维支架植入皮瓣后,发现皮瓣存活率高于对照组,可刺激大量微血管形成,这对丰富皮瓣血运是可观的。可见GelMA水凝胶可用于形成生物医学微血管网络,开发复杂的工程组织敷料。 2.3.2 GelMA皮肤组织工程水凝胶的广泛应用前景 聚合物水凝胶是有广泛前景的敷料,可用于治疗非愈合创口[27-28]。水凝胶是天然或人工合成的3D网络,可调节模拟人体组织的物理化学性质。衍生于细胞外基质蛋白(如胶原蛋白或弹性蛋白)的天然聚合物组织敷料有利于创面愈合,因为它们在体外和体内均具有一定的生物相容性和生物降解性[29]。GelMA水凝胶中RGD和基质金属蛋白酶反应肽基序的存在,可加速创伤愈合过程,减轻因创面延迟愈合带来的一系列并发症。如有感染倾向的大面积创面,若不及时处理将加深创面并发脓毒症、内脏器官并发症、多器官功能衰竭而危机患者生命。当创面经常规清创后应用GelMA水凝胶,其空间3D微结构将促进创面血管化,使相应症状将得道缓解。大量新生血管将为创面床提供富氧血液、免疫球蛋白和白细胞来抵御创面感染,促进创面新生毛细血管和肉芽组织的形成,是加速创面愈合的重要因素。 GelMA水凝胶主要的成分为明胶。与胶原相比,明胶具有更高的溶解性和更低的抗原性[30],可提高创面内胶原含量刺激胶原沉积。胶原是细胞外基质的主要成分,应用于创面的GelMA水凝胶内胶原含量极为丰富,有利于创面愈合。GelMA良好的组织相容性可直接覆盖创面,为创面提供大量营养物质。皮肤创面愈合包括表皮再生和结缔组织修复。再上皮化先于真皮修复,加速创面愈合[31],再上皮化被认为是皮肤伤口愈合的主要步骤[32]。基于其强大的机械性、降解性和生物学特性,GelMA水凝胶能重建功能表皮,补充胶原诱导角质形成细胞,支持人类表皮组织分化为多层再生角质细胞,而且GelMA水凝胶可替代缺损皮肤提供早期的障碍功能,这对保持创面湿润,防止创面感染具有至关重要的作用[33]。 聚合物支架可递送生物大分子、生长因子和其他小分子试剂来促进伤口愈合和预防感染[27-28]。GelMA水凝胶是亲水性聚合物交联网络,具有一定的溶胀性,可在水中溶胀,以扩增为其原始质量的许多倍。所以GelMA水凝胶可吸收伤口渗出液,保持创面湿润,避免神经末梢直接暴露在空气中,减轻疼痛。湿润环境避免了创面形成干痂,创面渗出液里含有多种生长因子如血小板源生长因子、转化生长因子β等也将吸附于GelMA水凝胶上,这又会促进成纤维细胞增殖、角化细胞迁移和伤口的最终再上皮化[34],这些生长因子对创面愈合过程起着重要调节作用。例如转化生长因子β影响细胞生长和细胞发育的许多方面,以及在伤口愈合和瘢痕形成过程中发挥重要作用[35],刺激血管生成、成纤维细胞增殖、肌成纤维细胞分化、胶原合成、肉芽组织形成和再上皮化等方面,这些都是创伤愈合所必需的。 水凝胶的物理和生物化学性质主要取决于其自身的组成,决定于其聚合方法和交联密度。可调节的GelMA浓度和物理、生物学特性可满足皮肤代用品在不同类伤口的要求[36]。GelMA是可光聚合的,在组织工程中可控制曝光时长和光掩模形状,合成随意形敷料[5],贴合创面边缘,适应不规则的创面治疗。GelMA可注射形式可填充任意形状的伤口床,Lin等[37]将混有人内皮细胞集落形成细胞和间充质干细胞的GelMA水凝胶以液体形式注射到免疫缺陷小鼠皮下,经透皮紫外光交联可见,生物工程化血管网络与宿主脉管系统形成功能吻合,并且均匀分布在整个构建体中。所以GelMA水凝胶可作为填料对局部凹陷部位进行透皮交联填充。GelMA的光聚合性、最佳机械性能、生物降解性和生物相容性的独特组合[5],使其成为了具有广泛应用前景的皮肤组织工程材料。GelMA重建表皮的特征也与其他报道的底物区别开来,包括聚碳酸酯膜或脱细胞猪肠[38-39],它们均不能根据患者自身的随意性伤口量身定制,并且物理和化学性质不易于修饰。 "

| [1]Van Vlierberghe S,Dubruel P,Schacht E.Effect of Cryogenic Treatment on the Rheological Properties of Gelatin Hydrogels.J Bioact Compat Polym.2010;25:498-512.[2]Annabi N,Tamayol A,Uquillas JA,et al.25th anniversary article: Rational design and applications of hydrogels in regenerative medicine.Adv Mater.2014;26(1):85-124.[3]Thiele J,Ma Y,Bruekers S,et al.25th Anniversary article: designer hydrogels for cell cultures: a materials selection guide.Adv Mater.2014;26(1):125-148.[4]Fu Y,Xu K,Zheng X,et al.3D cell entrapment in crosslinked thiolated gelatin-poly (ethylene glycol) diacrylate hydrogels. Biomaterials.2012;33(1):48-58.[5]Nichol JW,Koshy ST,Bae H,et al.Cell-laden microengineered gelatin methacrylate hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2010;31(21): 5536-5544.[6]Gauvin R,Chen YC,Lee JW.Microfabrication of complex porous tissue engineering scaffolds using 3D projection stereolithography.Biomaterials.2012;33(15):3824-3834.[7]Xing Y,Shepherd N,Lan J,et al.MMPs/TIMPs imbalances in the peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid are associated with the pathogenesis of HIV-1-associated neurocognitive disorders.Brain Behav Immun. 2017;65:161-172.[8]Aubin H,Nichol JW,Hutson CB,et al.Directed 3D cell alignment and elongation in microengineered hydrogels. Biomaterials.2010;31(27):6941-6951.[9]Vandooren J,Swinnen W,Ugarte-Berzal E,et al.Endotoxemia shifts neutrophils with TIMP-free gelatinase B/MMP-9 from bone marrow to periphery and induces systematic upregulation of TIMP-1. Haematologica. 2017;102(10):1671-1682. [10]Mosiewicz KA,Kolb L,Van Der Vlies AJ,et al.In situ cell manipulation through enzymatic hydrogel photopatterning.Nat Mater.2013;12(11):1072.[11]West JL.Protein-patterned hydrogels: Customized cell microenvironments.Nat Mater.2011;10(10):727-729.[12]Yue K,Trujillo-de Santiago G,Alvarez MM,et al.Synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl(GelMA)hydrogels.Biomaterials.2015;73: 254-271.[13]Annabi N,Tsang K,Mithieux SM,et al.Highly elastic micropatterned hydrogel for engineering functional cardiac tissue.Adv Funct Mater.2013;23(39):4950-4959.[14]Annabi N,Mithieux SM,Zorlutuna P,et al.Engineered cell-laden human protein-based elastomer. Biomaterials. 2013;34(22): 5496-5505.[15]Alge DL,Anseth KS.Bioactive hydrogels: Lighting the way.Nat Mater.2013;12(11):950.[16]Zamanian B,Masaeli M,Nichol JW,et al.Interface‐directed self‐assembly of cell-laden microgels.Small. 2010;6(8): 937-944.[17]Zhao X,Lang Q,Yildirimer L,et al.Photocrosslinkable gelatin hydrogel for epidermal tissue engineering.Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(1):108-118.[18]Pittenger MF.Characterization of MSCs: From Early Studies to the Present[M]//Mesenchymal Stromal Cells.Springer New York,2013:59-77.[19]Caplan AI.Adult mesenchymal stem cells for tissue engineering versus regenerative medicine. J Cell Physiol. 2007;213(2):341-347.[20]Eke G,Mangir N,Hasirci N,et al.Development of a UV crosslinked biodegradable hydrogel containing adipose derived stem cells to promote vascularization for skin wounds and tissue engineering.. Biomaterials.2017;129:188-198.[21]Zhang X,Li J,Ye P,et al.Coculture of mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial cells enhances host tissue integration and epidermis maturation through AKT activation in gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel-based skin model.Acta Biomater.2017; 59:317-326. [22]Zhao X,Sun X,Yildirimer L,et al.Cell infiltrative hydrogel fibrous scaffolds for accelerated wound healing.Acta Biomaterialia.2017;49:66-77.[23]Estevão LRM,Medeiros JP,Baratella-Evêncio L,et al.Effects of the topical administration of copaiba oil ointment (Copaifera langsdorffii) in skin flaps viability of rats.Acta Cirurgica Brasileira. 2013;28(12):863-869.[24]Yang M,Sheng L,Li H,et al.Improvement of the skin flap survival with the bone marrow‐derived mononuclear cells transplantation in a rat model.Microsurgery. 2010;30(4): 275-281.[25]Ozturk A,F?rat C,Parlakp?nar H,et al.Beneficial effects of aminoguanidine on skin flap survival in diabetic rats.Exp Diabetes Res.2012;2012:721256. [26]Sun X,Lang Q,Zhang H,et al.Electrospun photocrosslinkable hydrogel fibrous scaffolds for rapid in vivo vascularized skin flap regeneration.Adv Funct Mater. 2017;27(2). DOI:10.1002/adfm.201770008[27]Ng VW,Chan JM,Sardon H,et al.Antimicrobial hydrogels: a new weapon in the arsenal against multidrug-resistant infections.Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2014;78:46-62.[28]Salomé Veiga A,Schneider JP.Antimicrobial hydrogels for the treatment of infection.Pept Sci. 2013;100(6):637-644.[29]Zhao L,Li X,Zhao J,et al.A novel smart injectable hydrogel prepared by microbial transglutaminase and human-like collagen: Its characterization and biocompatibility.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2016;68:317-326.[30]Gorgieva S,Kokol V.Collagen-vs. gelatine-based biomaterials and their biocompatibility: review and perspectives2,Croatia: INTECH open access publisher,2011:17-53.[31]Braiman-Wiksman L,Solomonik I,Spira R,et al.Novel insights into wound healing sequence of events.Toxicol Pathol.2007;35(6):767-779.[32]Winter GD.Oxygen and epidermal wound healing[M]//Oxygen Transport to Tissue—III.Springer US, 1978:673-678.[33]Wagner JK,Parra EJ,Norton HL,et.al.Skin responses to ultraviolet radiation: effects of constitutive pigmentation, sex, and ancestry.Pigment Cell Res.2002;15(5):385-390.[34]Xiao Y,Reis LA,Feric N,et al.Diabetic wound regeneration using peptide-modified hydrogels to target re-epithelialization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(40):E5792-E5801.[35]Penn JW,Grobbelaar AO,Rolfe KJ.The role of the TGF-β family in wound healing, burns and scarring: a review.Int J Burns Trauma.2012;2(1):18-28. [36]Hutson CB,Nichol JW,Aubin H,et al.Synthesis and characterization of tunable poly (ethylene glycol): gelatin methacrylate composite hydrogels.Tissue Eng Part A. 2011; 17(13-14):1713-1723.[37]Lin RZ,Chen YC,Moreno-Luna Ret al.Transdermal regulation of vascular network bioengineering using a photopolymerizable methacrylated gelatin hydrogel. Biomaterials.2013;34(28):6785-6796. [38]Poumay Y,Dupont F,Marcoux S,et al.A simple reconstructed human epidermis: preparation of the culture model and utilization in in vitro studies.Arch Dermatol Res. 2004;296(5): 203-211.[39]Jannasch M,Groeber F,Brattig NW,et al.Development and application of three-dimensional skin equivalents for the investigation of percutaneous worm invasion.Exp Parasitol. 2015;150:22-30.[40]Annabi N,Yue K,Tamayol A,et al.Elastic sealants for surgical applications.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015;95(Pt A):27-39. [41]Mehdizadeh M,Yang J.Design strategies and applications of tissue bioadhesives.Macromol Biosci.2013;13(3):271-288. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Li Jing, Xie Jianshan, Cui Huilin, Cao Ximei, Yang Yanping, Li Hairong. Expression and localization of diacylglycerol kinase zeta and protein kinase C beta II in mouse back skin with different coat colors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1196-1200. |
| [3] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [4] | Ma Binxiang, He Wanqing, Zhou Guangchao, Guan Yonglin. Triptolide improves motor dysfunction in rats following spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 701-706. |
| [5] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [6] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [7] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [8] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [9] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [10] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [11] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [12] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [13] | Xu Xiaoming, Chen Yan, Song Qian, Yuan Lu, Gu Jiaming, Zhang Lijuan, Geng Jie, Dong Jian. Human placenta derived mesenchymal stem cell gel promotes the healing of radiation skin damage in SD rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3976-3980. |
| [14] | Zhang Degang, Liu Dong, Li Peng, Wang Zhaolin, Zhang Kai, Zhang Xinjun. Short-term follow-up of elastic intramedullary nail and plate in the treatment of displaced middle clavicle type B fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3860-3864. |
| [15] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||