Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (2): 254-260.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0015
Previous Articles Next Articles
Combined use of adipose-derived stem cells and electrospun membrane for preparing sandwich-like cardiac cell sheets
- 1Shenzhen Key Laboratory for Anti-ageing and Regenerative Medicine, Health Science Center, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, Guangdong Province, China; 2Emergency Department, Xiaogan Maternity & Child Healthcare Hospital, Xiaogan 432100, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2017-08-22Online:2018-01-18Published:2018-01-18 -
Contact:Zhu Yan-xia, M.D., Associate professor, Shenzhen Key Laboratory for Anti-ageing and Regenerative Medicine, Health Science Center, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Wu Zhang-song, Shenzhen Key Laboratory for Anti-ageing and Regenerative Medicine, Health Science Center, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81301597; Special Funds for Shenzhen Emerging Strategic Industrial Development, No. JCYJ20150525092940984, JCYJ20160422090807181; Special Funds for the Cultivation of Guangdong College Students Scientific and Technological Innovation, No. pdjh2017b0442
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Zhang-song, Zhu Hong-xia, Luo Zhi-qiang, Pan Wan-chun, Yang Fang, Lin Xin-yan, Zhu Yan-xia.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
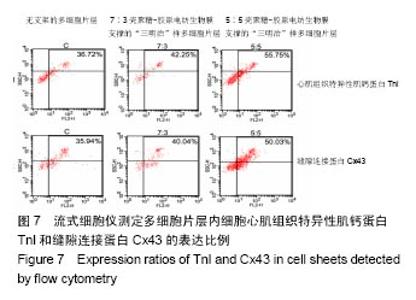
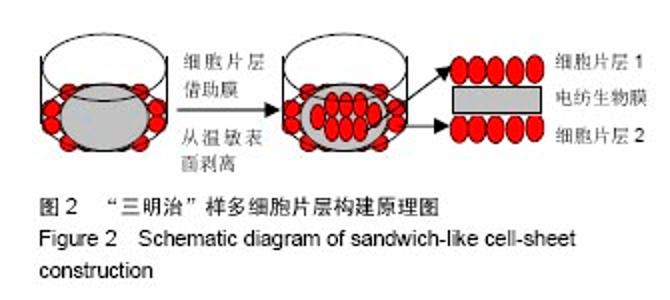
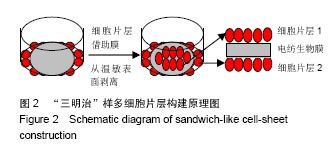
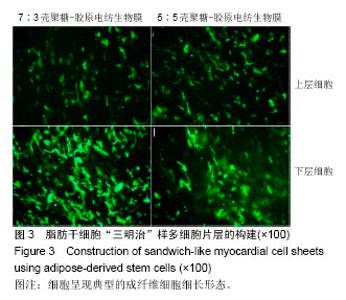
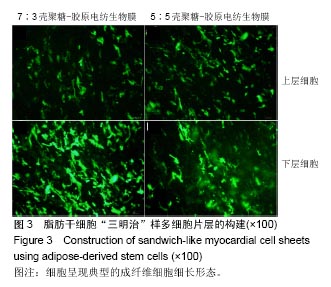
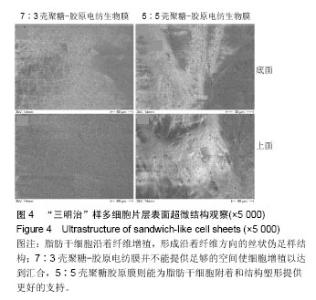
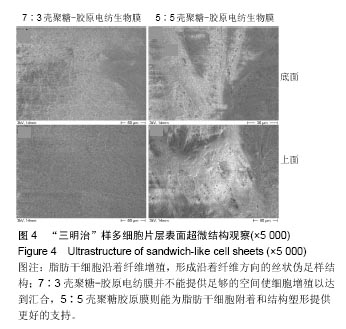
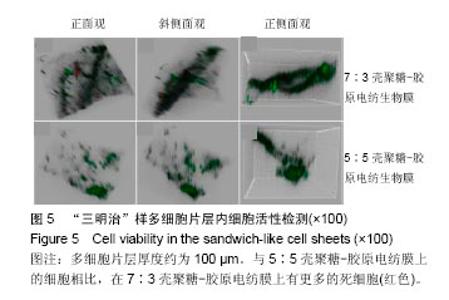
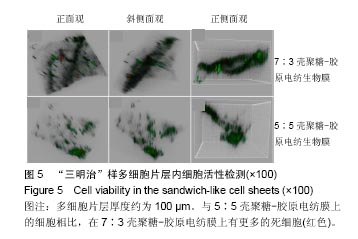
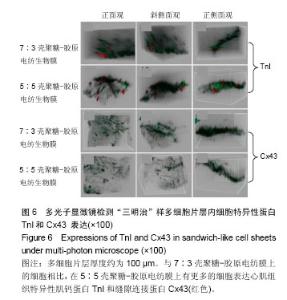
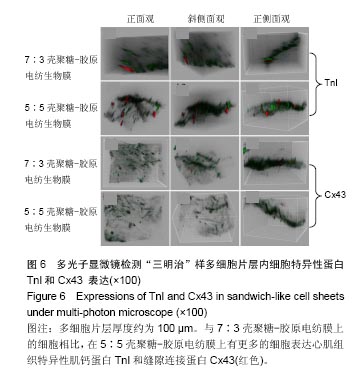
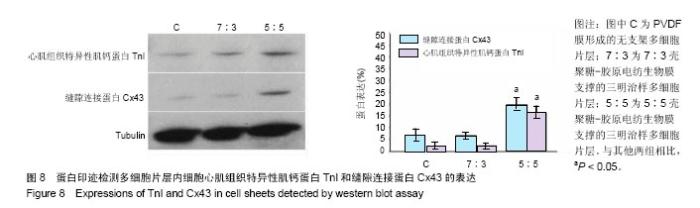
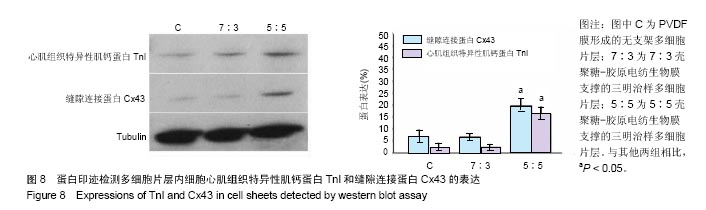
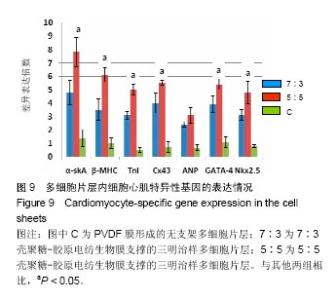
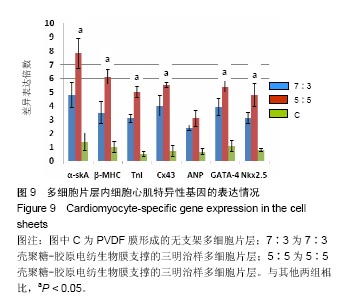
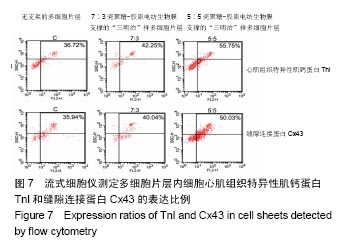
2.6 心肌特异性蛋白基因表达的定量分析 流式分析显示,脂肪干细胞在7∶3壳聚糖-胶原电纺膜上培养分化后,TnI和Cx43蛋白表达率分别为42.25%和40.04%(图7)。然而,在5∶5壳聚糖-胶原电纺膜上培养,TnI和Cx43蛋白表达率分别增加到55.75%和50.3%,这说明5∶5壳聚糖-胶原电纺膜更利于脂肪干细胞的分化。Western blot定量分析结果与流式分析结果一致(图8)。 实时定量PCR结果显示,在5∶5壳聚糖-胶原电纺膜上细胞内α-skA、β-MHC、TnI、Cx43、ANP、GATA-4和Nkx2.5 mRNA的表达均高于7∶3壳聚糖-胶原电纺膜上培养的细胞(图9)。"
| [1]Nunes SS,Song H,Chiang CK,et al.Stem Cell-Based Cardiac Tissue Engineering.J.of Cardiovasc.Trans Res. 2011;4: 592-602.[2]Bhaarathy V,Venugopal J,Gandhimathi C,et al.Biologically improved nanofibrous scaffolds for cardiac tissue engineering. Mater Biol Appl.2014;44:268-277.[3]Matsuura K,Haraguchi Y,Shimizu T,et al.Cell sheet transplantation for heart tissue repair. J Control Release. 2013;169:336-340.[4]Shimizu T,Sekine H,Yamato M,et al.Cell Sheet-Based Myocardial Tissue Engineering: New Hope for Damaged Heart Rescue.Curr Pharm Des.2009;15(24):2807-2814.[5]Miyagawa S,Sakaguchi T,Yoshikawa Y,et al.Impaired myocardium regeneration with skeletal cell sheets-a preclinical trial for tissue-engineered regeneration therapy. Transplantation.2010;90:364-372.[6]Miyahara Y,Nagaya N,Kataoka M,et al.Monolayered mesenchymal stem cells repair scarred myocardium after myocardial infarction.Nat Med.2006;12(368)459-465.[7]Heydarkhan-Hagvall S,Schenke-Layland K,Dhanasopon AP,et al.Three-dimensional electro -spun ECM-based hybrid scaffolds for cardiovascular tissue engineering.Biomaterials. 2008;29:2907-2914.[8]Tadakuma T,Tanaka N,Haraguchi Y,et al.Adevice for erapid transfer/transplantation of living cell sheets with the absence of cell damage.Biomaterials.2013;34:9018-9025.[9]Ji W,Yang F,Ma J,et al.Incorporation of stromal cell-derived factor-1 inPCL/gelatin electrospun membranes for guided bone regeneration.Biomaterials.2013;34:735-745.[10]Ye Y,Shi X,Chen X,et al.Chitosan-modified,collagen-based biomimetic nanofibrous membra -nes as selective cell adhering wound dressings in the treatment of chemically burned corneas.J Mater Chem B.2014;2:4226-4236.[11]Zhou T,Mo X,Sun J,et al.Development and Properties of Electrospun Collagen-chitosan Nanofibrous Membranes as Skin Wound Healing Materials.J Fiber Bioeng Informat.2014; 7:319-325.[12]Chihim JL,Joanne Y,Chunwah MY,et al.A comprehensive study on adsorption behaviour of direct, reactive and acid dyes on crosslinked and non-crosslinked chitosan beads.J Fiber Bioeng Informat.2014;7:35-52.[13]Cao Z,Dou C,Dong S,et al.Scaffolding Biomaterials for Cartilage Regeneration.J Nanomater.2014;2014:2526-2536.[14]Jayakumar R,Prabaharan M,Nair SV,et al.Novel chitin and chitosan nanofibers inbiomedical applications.Biotechnol Adv.2010;28:142-150.[15]Oyamada M,Kimura H,Yoamada Y,et al.The expression, phosphorylation and localization of connexin 43 and gap-junctional intercellular communication during the establishment of a synchronized contraction of cultured neonatal rat cardiac myocytes.Exp Cell Res. 1994;212: 351-358.[16]陈怡粤,王婷,吴张松等.利用电纺生物膜进行多细胞片层制备的方法研究[J].中华生物医学工程杂志, 2015,21(4):344-348.[17]Zhu Y,Liu T,Song K,et al.Adipose-derived stem cell: a better stem cell than BMSC.Cell Biochem Funct.2008;26:664-675.[18]Zhu Y,Liu T,Song K,et al.ADSCs differentiated into cardiomyocytes in cardiac microenv -ironment.Mol Cell Biochem.2009;324:117-129.[19]Kreutziger KL,Murry CE.Engineered human cardiac tissue. Pediatric Cardiol.2011;32:334-341.[20]Takamatsu H,Uchida S,Matsuda T,et al.In situ harvesting 409 of adhered target cells using thermoresponsive substrate under a microscope: Principle and instrumentation.J Biotechnol. 2008;134:297-304.[21]Fujita J,Itabashi Y,Tomohisa S,et al.Myocardial cell sheet therapy and cardiac function.Am J Physiol HeartCirc Physiol. 2012;303:1169-1182.[22]Alshammary S,Fukushima S,Miyagawa S,et al.Impact of cardiac stem cell sheet transplan -tation on myocardial infarction.Surg Today.2013;43(9):970-976. [23]Kelm JM,Fussenegger M.Scaffold-free cell delivery for use in regenerative medicine.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010;62(7-8): 753-764.[24]Shimizu T,Sekine H,Yang J,et al.Polysurgery of cell sheet grafts overcomes diffusion limits to produce thick, vascularized myocardial tissues.FASEB J. 2006;20(6): 708-710. [25]25 Hartman O,Zhang C,Elizabeth L,et al.Microfabricated electrospun collagen membranes for 3-D cancer models and drug screening applications.Biomacromolecules. 2009;10(8): 2019-2032.[26]Venugopal JR,Prabhakaran MP,Mukherjee S,et al.Biomaterial strategies for alleviation of myocardial infarction.J R Soc Interface. 2012;9(66):1-19. [27]Efimenko A,Starostina EE,Rubina KA,et al.Viability and angiogenic activity of mesench -ymal stromal cells from adipose tissue and bone marrow under hypoxia and inflammation in vitro.Tsitologiia. 2010;52(2):144-154.[28]Efimenko A,Starostina E,Kalinina N,et al.Angiogenic properties of aged adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells after hypoxic 431 conditioning.J Transl Med.2011;9(1):10-22.[29]Zhu Y,Liu T,Ye H,et al.Enhancement of adipose-derived stem cell differentiation in scaffolds with IGF-I gene impregnation under dynamic microenvironment.Stem Cells Dev. 2010; 19(10):1547-1556.[30]Bernke JP,Rodrigues ED,Wessling M,et al.Insights into the role of material surface topography and wettability on cell-material interactions.Soft Matter.2010;6(18):4377-4388.[31]Tanir TE,Hasirci V,Hasirci N,et al.Electrospinning of chitosan /poly (lactic acid-co-glycolic acid)/hydroxyapatite composite nanofibrous mats for tissue engineering applications.Polym Bull.2014;71(11):2999-3016. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [5] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [6] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [7] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [8] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [9] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [10] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [11] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [12] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [13] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [14] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [15] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||