Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 2413-2421.doi: 10.12307/2026.615
Gut microbiota tryptophan metabolite indole-3-propionic acid alleviates inflammatory bowel disease-related osteoporosis in a mouse model
Qiu Xueli1, Cui Hao1, 2, Wu Chenyang1, Tao Lide1, Yao Yuqian1, Tian Bo1, Bai Jinyu1, Zhang Yingzi1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215004, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Suzhou Medical College of Soochow University, Suzhou 215004, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2025-02-20Accepted:2025-06-11Online:2026-04-08Published:2025-08-27 -
Contact:Zhang Yingzi, Associate chief physician, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215004, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Qiu Xueli, MS candidate, Department of Orthopedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215004, Jiangsu Province, China Cui Hao, Department of Orthopedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215004, Jiangsu Province, China; Suzhou Medical College of Soochow University, Suzhou 215004, Jiangsu Province, China Qiu Xueli and Cui Hao contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:Gusu Health Talent Program of Suzhou, No. (2022)161 (to ZYZ); Gusu Scientific Research Fund of Suzhou, No. GSWS2022041 (to ZYZ); "Nuclear Medicine Innovation" Project of China National Nuclear Corporation, No. ZHYLYB2021005 (to ZYZ); Research Project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission, No. H2023139 (to ZYZ); Youth Talent Elite Program of China National Nuclear Corporation (to ZYZ); Zhongying Young Scholar Program of Soochow University (to ZYZ); Jiangsu Graduate Research and Practice Innovation Program, No. KYCX24_3344 (to QXL [project investigator] and ZYZ [supervisor])
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Qiu Xueli, Cui Hao, Wu Chenyang, Tao Lide, Yao Yuqian, Tian Bo, Bai Jinyu, Zhang Yingzi. Gut microbiota tryptophan metabolite indole-3-propionic acid alleviates inflammatory bowel disease-related osteoporosis in a mouse model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2413-2421.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
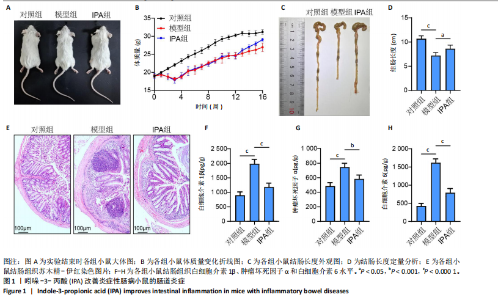
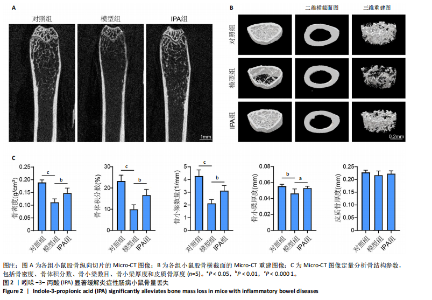
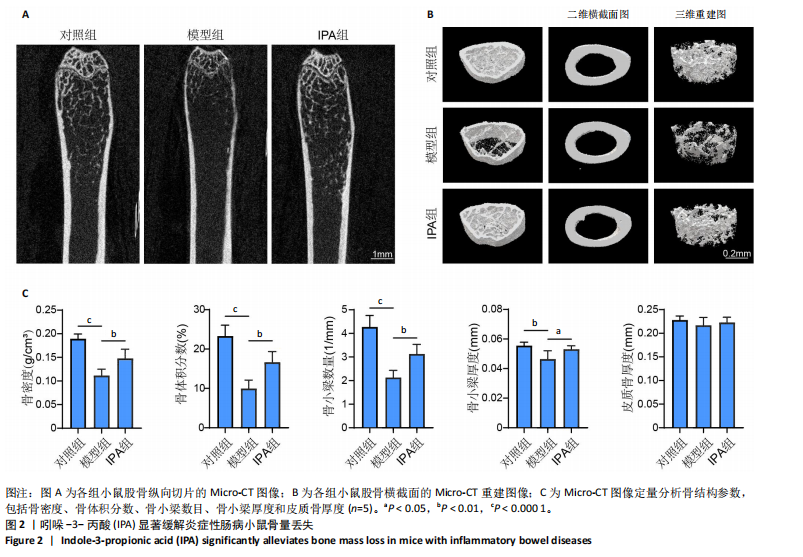
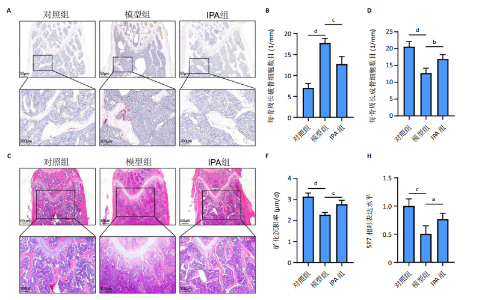
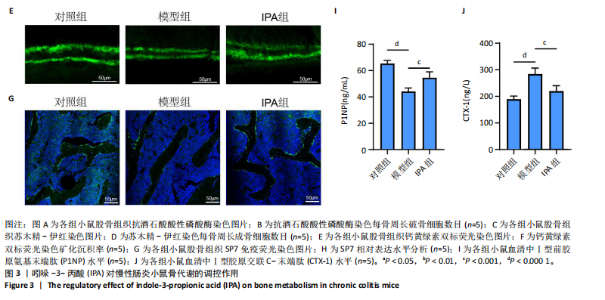
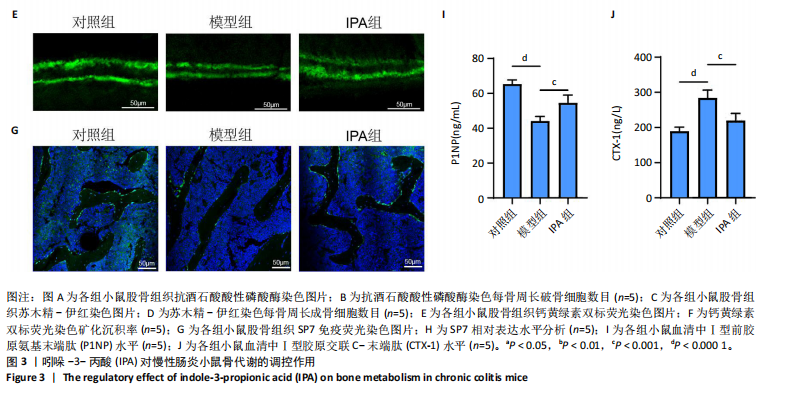
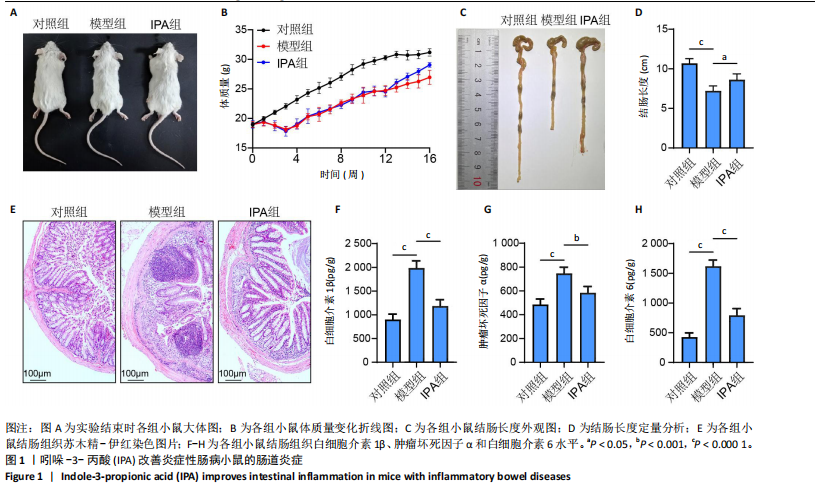
2.1 实验动物数量分析 15只Balb/c小鼠全部纳入结果分析。 2.2 IPA缓解炎症性肠病小鼠的肠道炎症 大体观察显示,与对照组相比,模型组小鼠体型明显减小,而IPA组小鼠体型接近对照组小鼠(图1A)。实验过程中严密观察各组小鼠的体质量变化,结果显示:在前12周,模型组及IPA组小鼠体质量增长明显慢于对照组小鼠,而在IPA干预后小鼠体质量增长显著快于模型组小鼠(图1B)。 解剖小鼠取结肠进行长度测量,结果显示:与对照组相比,模型组小鼠结肠显著缩短,而IPA组小鼠结肠长度部分恢复(图1C,D)。各组小鼠结肠行苏木精-伊红染色,结果显示:对照组小鼠结肠组织结构完整,隐窝排列紧密、腺体结构清晰,未见炎症细胞浸润,表明肠道健康无损伤;模型组小鼠结肠组织表现出隐窝结构紊乱、腺体萎缩且伴有大量炎症细胞浸润等显著的炎症特征;与模型组相比,IPA组小鼠结肠组织结构部分恢复,隐窝结构较为清晰,炎症细胞浸润显著减少(图1E)。 ELISA检测各组小鼠结肠组织炎症因子水平,结果显示:与对照组相比,模型组白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平显著上升(P < 0.000 1),提示炎症性肠病伴随着显著的促炎因子升高。与模型组相比,IPA组白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平明显降低(白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6:P < 0.000 1,肿瘤坏死因子α:P < 0.001),表明IPA能够有效减轻炎症性肠病诱导的肠道炎症因子表达,发挥抗炎保护作用(图1F-H)。 2.3 IPA对炎症性肠病小鼠骨结构的保护作用 取各组小鼠股骨进行Micro-CT扫描并通过软件三维重建以分析骨微结构(骨小梁及皮质骨)。图2A为各组小鼠股骨纵向切片的Micro-CT图像。对照组小鼠股骨表现出完整的骨小梁结构和正常的骨量;模型组小鼠股骨骨量显著下降,骨小梁结构严重破坏,表现出典型的骨质疏松特征;IPA组小鼠股骨骨量部分恢复,骨小梁结构较模型组更为完整。图2B为各组小鼠股骨横截面Micro-CT重建图像,包含二维横截面图和三维重建图。二维横截面图显示各组小鼠皮质骨厚度几乎不变;而在三维重建图像中,模型组小鼠骨小梁密度与对照组相比显著稀疏,结构显著破坏,整体骨量下降;而IPA组三维图像显示骨小梁密度恢复,结构改善,接近对照组水平。图2C为Micro-CT图像定量分析骨结构参数,结果显示:与模型组相比,IPA组骨矿物质密度、骨体积分数、骨小梁数目和骨小梁厚度显著增加;3组之间皮质骨厚度没有显著差异。 2.4 IPA调控骨代谢缓解炎症性肠病介导的骨量下降 小鼠股骨远端抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶染色分析显示,对照组破骨细胞数量较少,骨吸收活性正常;模型组破骨细胞数量显著增加(P < 0.000 1),提示骨吸收活性增强;IPA组破骨细胞数量显著减少(P < 0.001),提示IPA可通过下调破骨功能缓解骨吸收异常(图3A,B)。苏木精-伊红染色结果显示:对照组骨小梁结构完整且骨质致密;模型组小鼠的骨小梁数量显著减少(P < 0.000 1),结构严重破坏,表现出典型的骨质疏松特征;而IPA组骨小梁数目与结构部分恢复(P < 0.01)(图3C,D)。钙黄绿素双标荧光染色结果显示,与对照组相比,模型组矿化沉积率显著下降,提示骨形成能力受损(P < 0.000 1);IPA组较模型组明显改善(P < 0.001),提示IPA能够通过调控骨形成部分恢复骨代谢平衡(图3E,F)。免疫荧光染色结果显示,对照组SP7表达较高,反映出活跃的成骨细胞功能;而模型组SP7表达显著降低(P < 0.001),成骨细胞活性受损;IPA组SP7表达有所恢复(P < 0.05),提示IPA在促进成骨细胞功能方面具有积极作用(图3G,H)。血清学分析进一步支持了上述组织学发现,模型组小鼠P1NP水平显著降低而CTX-1水平显著升高,表明模型组小鼠骨形成能力降低而骨吸收能力增加;与模型组相比,IPA组小鼠P1NP水平增加而CTX-1水平降低,提示IPA调控骨代谢的双重功能从而缓解炎症性肠病小鼠骨量丢失(图3I,J)。"
| [1] MOLODECKY NA, SOON IS, RABI DM, et al. Increasing incidence and prevalence of the inflammatory bowel diseases with time, based on systematic review. Gastroenterology. 2012;142(1):46-54.e42. [2] NG SC, SHI HY, HAMIDI N, et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet. 2017;390(10114):2769-2778. [3] AGRAWAL M, CHRISTENSEN HS, BØGSTED M, et al. The Rising Burden of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Denmark Over Two Decades: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Gastroenterology. 2022;163(6):1547-1554.e5. [4] GILLILAND A, CHAN JJ, DE WOLFE TJ, et al. Pathobionts in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Origins, Underlying Mechanisms, and Implications for Clinical Care. Gastroenterology. 2024;166(1):44-58. [5] SINGH N, BERNSTEIN CN. Environmental risk factors for inflammatory bowel disease. United European Gastroenterol J. 2022;10(10):1047-1053. [6] CABALLERO-FLORES G, PICKARD JM, NÚÑEZ G. Microbiota-mediated colonization resistance: mechanisms and regulation. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2023;21(6):347-360. [7] MIRSEPASI-LAURIDSEN HC, VALLANCE BA, KROGFELT KA, et al. Escherichia coli Pathobionts Associated with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2019;32(2):e00060-18. [8] TIE Y, HUANG Y, CHEN R, et al. Current insights on the roles of gut microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease-associated extra-intestinal manifestations: pathophysiology and therapeutic targets. Gut Microbes. 2023;15(2):2265028. [9] KNIGHTS D, LASSEN KG, XAVIER RJ. Advances in inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis: linking host genetics and the microbiome. Gut. 2013;62(10):1505-1510. [10] BECKER C, NEURATH MF, WIRTZ S. The Intestinal Microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. ILAR J. 2015;56(2):192-204. [11] KOSTIC AD, XAVIER RJ, GEVERS D. The microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease: current status and the future ahead. Gastroenterology. 2014;146(6):1489-1499. [12] 严冰,孙菁.炎症性肠病与代谢综合征关系的研究进展[J].中华炎性肠病杂志,2022,6(1):70-73. [13] FRIEDRICH M, POHIN M, POWRIE F. Cytokine Networks in the Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Immunity. 2019; 50(4):992-1006. [14] WANG L, YU W, YIN X, et al. Prevalence of Osteoporosis and Fracture in China: The China Osteoporosis Prevalence Study. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(8):e2121106. [15] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2022,15(6):573-611. [16] ABEGUNDE AT, MUHAMMAD BH, ALI T. Preventive health measures in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22(34): 7625-7644. [17] CLYNES MA, HARVEY NC, CURTIS EM, et al. The epidemiology of osteoporosis. Br Med Bull. 2020;133(1):105-117. [18] LI JY, CHASSAING B, TYAGI AM, et al. Sex steroid deficiency-associated bone loss is microbiota dependent and prevented by probiotics. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(6):2049-2063. [19] YU M, PAL S, PATERSON CW, et al. Ovariectomy induces bone loss via microbial-dependent trafficking of intestinal TNF+ T cells and Th17 cells. J Clin Invest. 2021;131(4):e143137. [20] GUO M, LIU H, YU Y, et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG ameliorates osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats by regulating the Th17/Treg balance and gut microbiota structure. Gut Microbes. 2023;15(1):2190304. [21] GUAN Z, XUANQI Z, ZHU J, et al. Estrogen deficiency induces bone loss through the gut microbiota. Pharmacol Res. 2023;196:106930. [22] LIN X, XIAO HM, LIU HM, et al. Gut microbiota impacts bone via Bacteroides vulgatus-valeric acid-related pathways. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):6853. [23] NI J, WU GD, ALBENBERG L, et al. Gut microbiota and IBD: causation or correlation? Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;14(10):573-584. [24] SANTANA PT, ROSAS SLB, RIBEIRO BE, et al. Dysbiosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Pathogenic Role and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(7):3464. [25] ROGLER G. Resolution of inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;2(7):521-530. [26] MIGLIORINI F, COLAROSSI G, ESCHWEILER J, et al. Antiresorptive treatments for corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis: a Bayesian network meta-analysis. Br Med Bull. 2022;143(1):46-56. [27] MORGAN S, HOOPER KM, MILNE EM, et al. Azathioprine Has a Deleterious Effect on the Bone Health of Mice with DSS-Induced Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(23):6085. [28] CHOTIYARNWONG P, MCCLOSKEY EV. Pathogenesis of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis and options for treatment. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020;16(8):437-447. [29] JIA X, YANG R, LI J, et al. Gut-Bone Axis: A Non-Negligible Contributor to Periodontitis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021;11:752708. [30] ZHANG YW, SONG PR, WANG SC, et al. Diets intervene osteoporosis via gut-bone axis. Gut Microbes. 2024;16(1):2295432. [31] ZHANG YW, CAO MM, LI YJ, et al. The regulative effect and repercussion of probiotics and prebiotics on osteoporosis: involvement of brain-gut-bone axis. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(25):7510-7528. [32] ZHANG YW, WU Y, LIU XF, et al. Targeting the gut microbiota-related metabolites for osteoporosis: The inextricable connection of gut-bone axis. Ageing Res Rev. 2024;94:102196. [33] LU Y, YANG W, QI Z, et al. Gut microbe-derived metabolite indole-3-carboxaldehyde alleviates atherosclerosis. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):378. [34] ZHAO ZH, XIN FZ, XUE Y, et al. Indole-3-propionic acid inhibits gut dysbiosis and endotoxin leakage to attenuate steatohepatitis in rats. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51(9):1-14. [35] ZHUANG H, REN X, JIANG F, et al. Indole-3-propionic acid alleviates chondrocytes inflammation and osteoarthritis via the AhR/NF-κB axis. Mol Med. 2023;29(1):17. [36] YIN Y, LU X, LI Z, et al. Risk Factors for Worsening of Bone Loss in Patients Newly Diagnosed with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2022;2022:1498293. |
| [1] | Chen Huiting, Zeng Weiquan, Zhou Jianhong, Wang Jie, Zhuang Congying, Chen Peiyou, Liang Zeqian, Deng Weiming. Tail anchoring technique of vertebroplasty in treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with intravertebral cleft: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2145-2152. |
| [2] | Zeng Xuan, Weng Rui, Ye Shicheng, Tang Jiadong, Mo Ling, Li Wenchao. Two lumbar rotary manipulation techniques in treating lumbar disc herniation: a finite element analysis of biomechanical differences [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2153-2161. |
| [3] | Cheng Qisheng, Julaiti·Maitirouzi, Xiao Yang, Zhang Chenwei, Paerhati·Rexiti. Finite element analysis of novel variable-diameter screws in modified cortical bone trajectory of lumbar vertebrae [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2162-2171. |
| [4] | Hu Xiongke, Liu Shaohua, Tan Qian, Liu Kun, Zhu Guanghui. Shikonin intervention with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves microstructure of femur in aged mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1609-1615. |
| [5] | Wen Guangwei, Zhen Yinghao, Zheng Taikeng, Zhou Shuyi, Mo Guoye, Zhou Tengpeng, Li Haishan, Lai Yiyi. Effects and mechanisms of isoginkgetin on osteoclastogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1348-1358. |
| [6] | Huang Jie, Zeng Hao, Wang Wenchi, Lyu Zhucheng, Cui Wei. Visualization analysis of literature on the effect of lipid metabolism on osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1558-1568. |
| [7] | Wu Zhilin, , He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Shi Xian, Yuan Song, Zhang Jun, Wang Hao . DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [8] | Zhang Haiwen, Zhang Xian, Xu Taichuan, Li Chao. Bibliometric and visual analysis of the research status and trends of senescence in osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1580-1591. |
| [9] | Yang Zhijie, Zhao Rui, Yang Haolin, Li Xiaoyun, Li Yangbo, Huang Jiachun, Lin Yanping, Wan Lei, HuangHongxing. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: predictive values of muscle mass, grip strength, and appendicular skeletal muscle index [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1073-1080. |
| [10] | Zhou Jian, Zhang Tao, Zhou Weili, Zhao Xingcheng, Wang Jun, Shen Jie, Qian Li, Lu Ming. Effects of resistance training on quadriceps mass and knee joint function in patients with osteoporosis and sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1081-1088. |
| [11] | Cao Wenqi, Feng Xiuzhi, Zhao Yi, Wang Zhimin, Chen Yiran, Yang Xiao, Ren Yanling. Effect of macrophage polarization on osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 917-925. |
| [12] | Zeng Hao, Sun Pengcheng, Chai Yuan, Huang Yourong, Zhang Chi, Zhang Xiaoyun. Association between thyroid function and osteoporosis: genome-wide data analysis of European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1019-1027. |
| [13] | Wang Meng, Lu Tan, Li Minjie, Liu Zhicheng, Guo Xiaoyong. Finite element analysis of stress distribution of anchors at different implantation depths under different bone density conditions in rotator cuff tears [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 561-569. |
| [14] | Xu Jiamu, Yang Cheng, Li Weimin, Wang Chunqing. Role and pathogenesis of pyroptosis and inflammatory factors in osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 691-700. |
| [15] | Yang Fengli, Zhou Chao, Xiong Wei, Zhou Yuxiang, Li Dengshun, Wang Xin, Li Zhanzhen. 3D printed poly-L-lactic acid bone scaffolds in repair of bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 507-515. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||