Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (23): 6051-6061.doi: 10.12307/2026.370
Previous Articles Next Articles
Molecular mechanism and natural drug screening for ferroptosis-targeted therapy in rheumatoid arthritis
Zhou Wen, Yang Hongwei
- Department of Laboratory, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300211, China
-
Received:2025-05-24Accepted:2025-09-17Online:2026-08-18Published:2026-01-04 -
Contact:Yang Hongwei, MS, Chief technician, Department of Laboratory, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300211, China -
About author:Zhou Wen, MS, Technician in charge, Department of Laboratory, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300211, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Wen, Yang Hongwei. Molecular mechanism and natural drug screening for ferroptosis-targeted therapy in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6051-6061.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
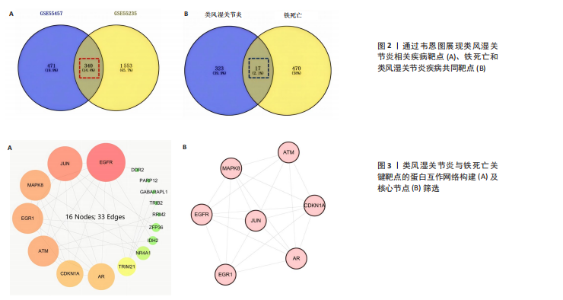
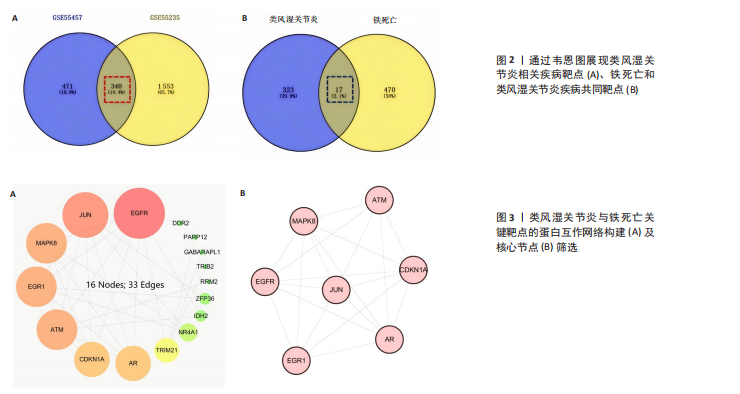
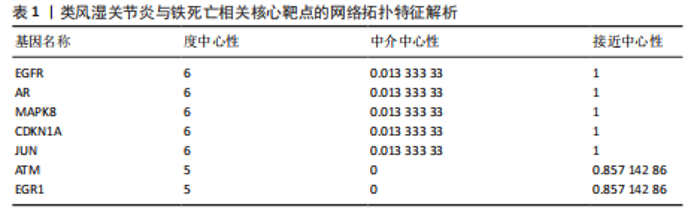
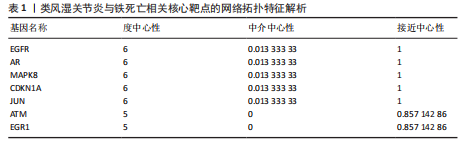
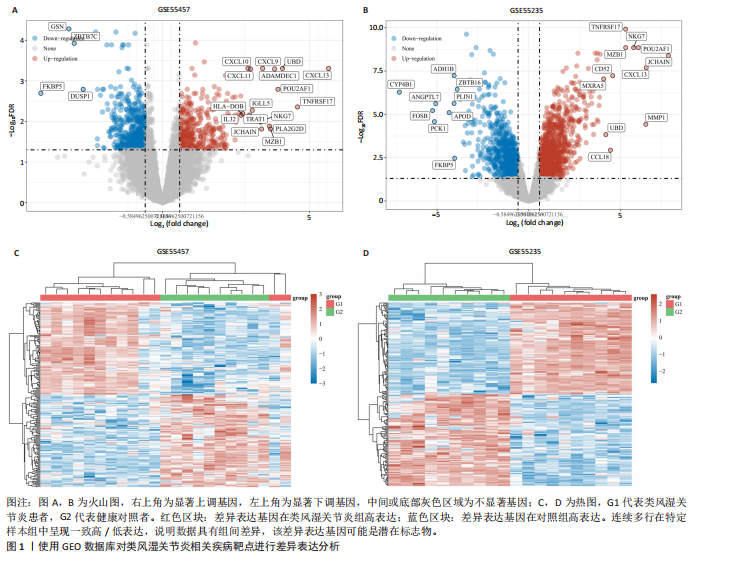
2.1 类风湿关节炎相关疾病靶点与铁死亡相关靶点的筛选 从GEO数据库中筛选出与类风湿关节炎相关的2个基因表达数据集GSE55457和GSE55235)。对这2个数据集进行limma差异表达分析(图1A-D)后,分别鉴定出811个(GSE55457)和1 893个(GSE55235)差异表达基因,其交集共包含340个共同差异表达靶点(图2A);进一步结合FerrDb数据库中的487个铁死亡相关基因,筛选获得17个与类风湿关节炎和铁死亡均相关的关键靶点(图2B),提示这些靶点可能在类风湿关节炎病理过程中发挥重要作用,并可能与铁死亡调控机制存在潜在关联。 2.2 铁死亡与类风湿关节炎共同靶点的蛋白互作网络体系构建及拓扑学深度分析 将筛选获得的17个关键靶点导入STRING 11.5数据库构建蛋白质相互作用网络,并将生成的CSV格式文件导入Cytoscape软件进行可视化分析。结果显示,铁死亡与类风湿关节炎相关的差异表达靶点蛋白质相互作用网络包含16个节点和33条相互作用边(图3A)。通过Cytoscape中的NetworkAnalyzer插件进行网络拓扑学分析,获得各节点的拓扑参数(表1)。其中,EGFR、AR、MAPK8、CDKN1A、JUN、ATM和EGR1等靶点在网络中占据重要地位(图3B)。在拓扑学分析中,采用3个关键指标评估节点重要性:接近中心性反映节点到网络其他节点的平均最短路径长度;节点度表示直接相连的相邻节点数量;中介中心性则通过计算经过该节点的最短路径数量来表征其在网络信息传递中的枢纽作用。 2.3 类风湿关节炎与铁死亡关键靶点的GO基因功能注释及KEGG通路富集分析 为系统探究铁死亡相关靶点在类风湿关节炎中的潜在作用机制,对筛选获得的17个关键靶点进行了GO基因功能注释和KEGG通路富集"
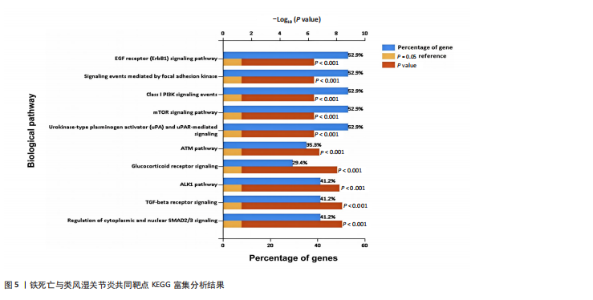
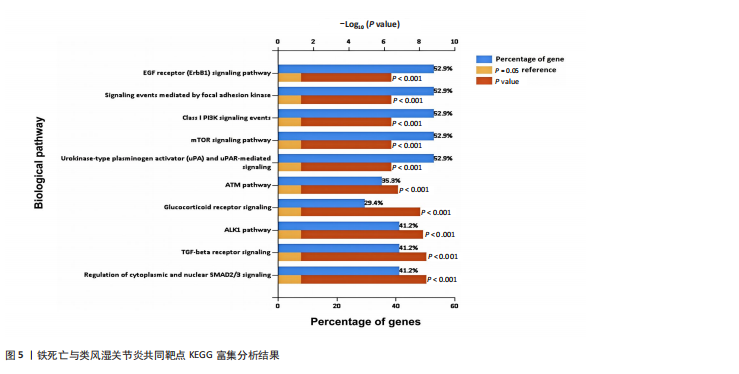
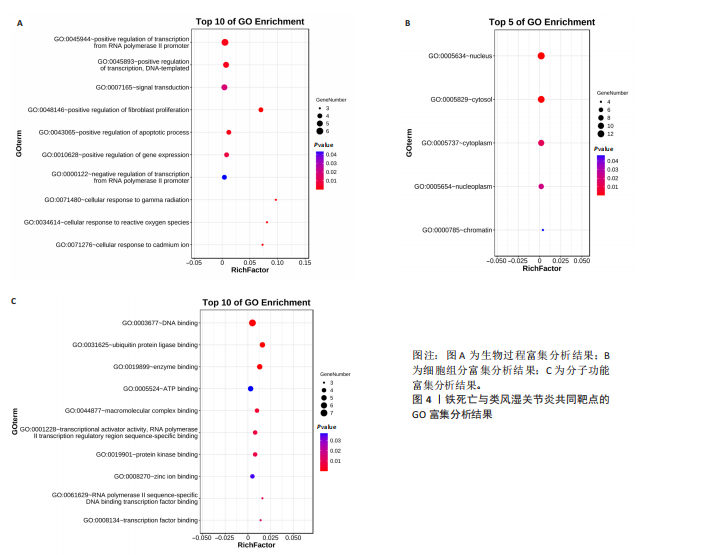
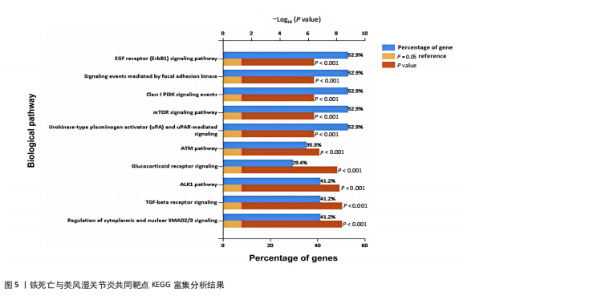
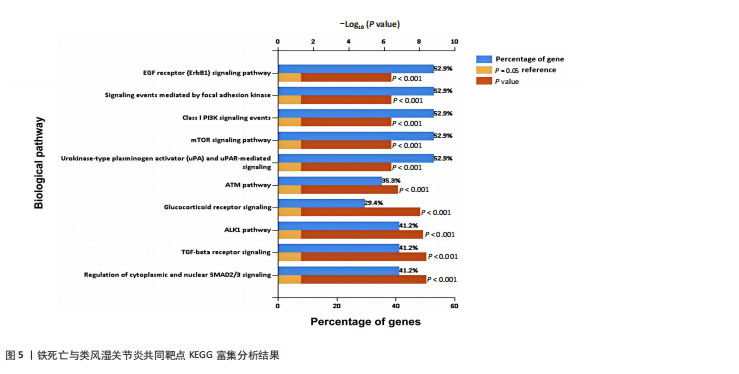
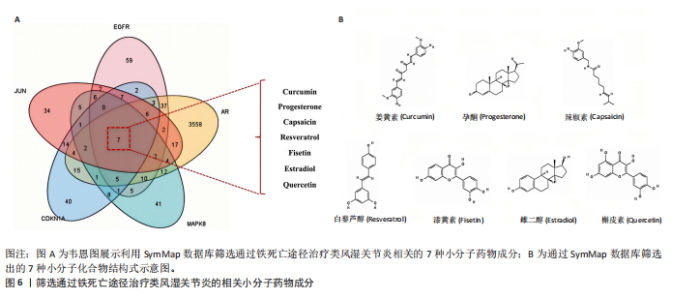
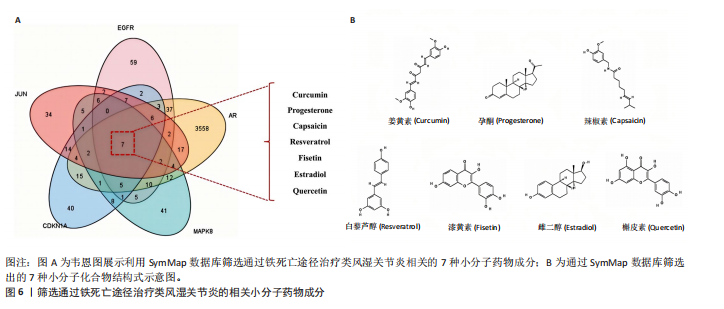
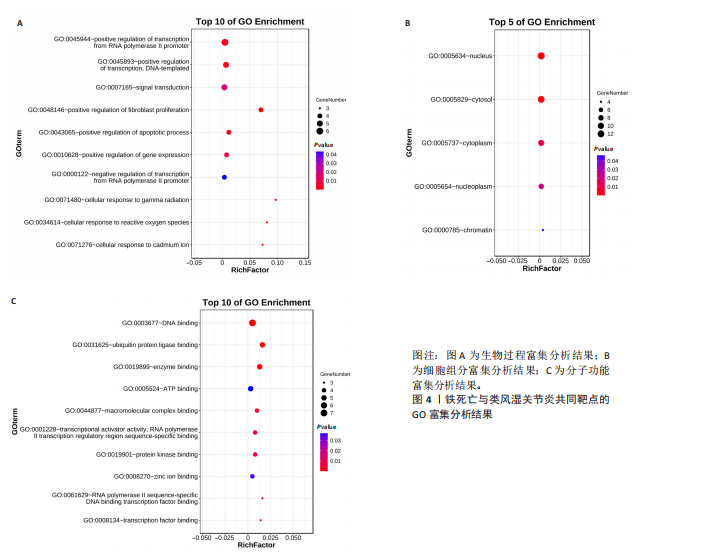
分析。通过生物信息学方法,从分子功能、生物过程和信号通路等多个层面,全面解析这些靶点在类风湿关节炎治疗中的生物学意义及其可能的作用机制。 富集分析结果按显著性水平排序如下:生物过程分析显示铁死亡相关靶点主要参与转录调控、信号转导、细胞凋亡过程以及对活性氧和离子的应激反应等生物学过程,这些功能可能与类风湿关节炎的治疗机制密切相关,如图4A所示。 细胞组分分析显示,铁死亡相关靶点主要定位于细胞核、细胞质及核质等细胞结构区域,提示这些亚细胞定位特征可能在类风湿关节炎治疗过程中发挥重要作用,如图4B所示。 分子功能分析显示,铁死亡相关靶点主要通过DNA结合、泛素蛋白连接酶结合、酶结合以及ATP结合等方式发挥其生物学功能,这些分子相互作用模式可能在类风湿关节炎治疗中具有重要调控作用,如图4C所示。 KEGG信号通路富集结果提示:铁死亡途径参与类风湿关节炎治疗的分子机制可能与多个关键信号网络存在交互作用。具体而言,SMAD2/3依赖的胞内信号转导系统、转化生子因子β介导的信号级联、ALK1相关信号转导机制以及糖皮质激素受体调控网络等生物学过程均显示出潜在的功能联系。上述信号通路间的相互作用模式及其与铁死亡的调控关系如图5所示。 2.4 利用SymMap数据库筛选靶向铁死亡治疗类风湿关节炎的相关小分子药物成分 通过上述分析,筛选出5个与铁死亡及类风湿关节炎疾病相关的核心共同作用靶点,即EGFR、AR、MAPK8、CDKN1A与JUN,导入SymMap数据库平台,筛选出各自相"
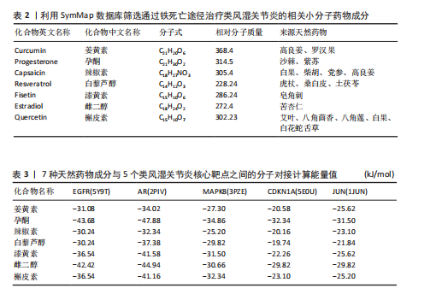
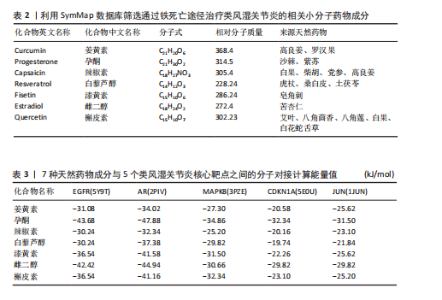
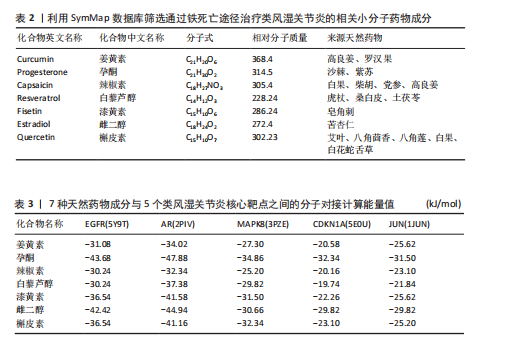
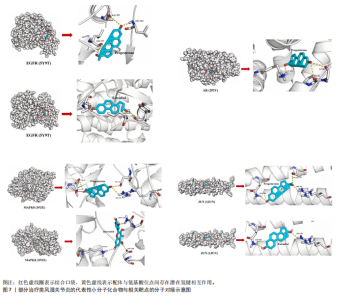
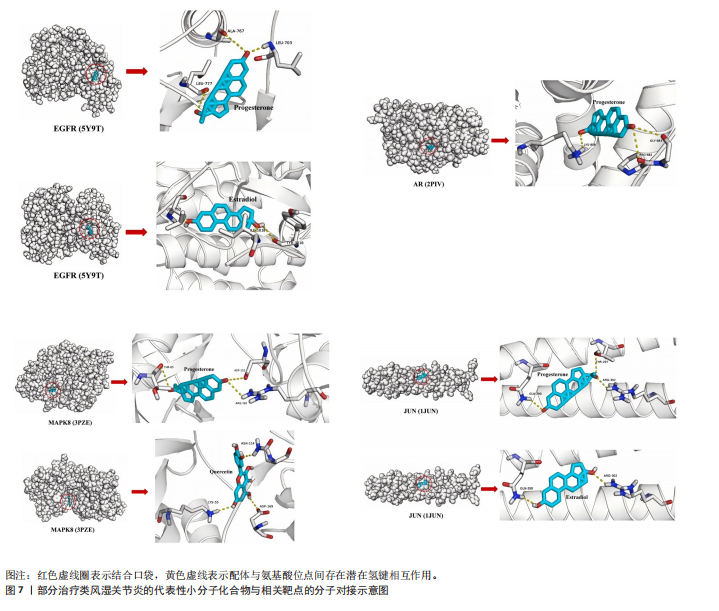
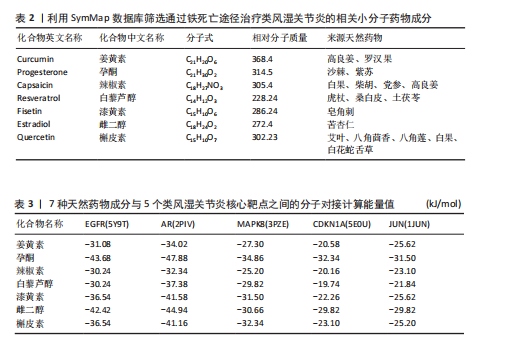
关的小分子化合物药物,再取交集处理后,共得到7个小分子化合物,这7个小分子可被认为对上述5个蛋白靶点均有潜在治疗作用(图6A);进一步通过TCMSP(https://old.tcmsp-e.com/tcmsp.php)数据库及相关部分文献检索,研究发现姜黄素主要来源于高良姜、罗汉果,孕酮主要来源于沙棘、紫苏,辣椒素主要来源于白果、柴胡、党参等,白藜芦醇主要来源于虎杖、桑白皮等,漆黄素主要来源于皂角刺,雌二醇主要来源于苦杏仁,槲皮素主要来源于艾叶、八角茴香等(表2及图6B)。 2.5 7种小分子化合物药物与对应靶点的计算生物学分析 分子对接结果表明,筛选出的小分子药物成分与其对应靶点的结合能均为负值(小于0 kJ/mol),这表明这些小分子与靶点能够自发结合。通常情况下,结合能越低,说明配体与受体结合的构象越稳定,相互作用的可能性也越大。经过分析,孕酮、雌二醇和槲皮素对上述5个潜在类风湿关节炎核心靶点的结合能力普遍优于其他小分子成分,从而提示这3种化合物有望通过铁死亡途径治疗类风湿关节炎相关疾病,见表3与图7。"
| [1] 冷冬月,李旭峰,方兴刚.吴茱萸碱抑制HMGB1/TLR-4/NF-κB信号通路对类风湿关节炎大鼠的改善作用[J].河北医药, 2023,45(18):2760-2764. [2] WEYAND CM, GORONZY JJ. The immunology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Immunol. 2021; 22(1):10-18. [3] ALIVERNINI S, FIRESTEIN GS, MCINNES IB. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunity. 2022;55(12):2255-2270. [4] YANG M, SU Y, XU K, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis increases the risk of malignant neoplasm of bone and articular cartilage: a two-sample bidirectional mendelian randomization study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023;25(1):219. [5] 李杰,邓泽辉,王英,等.托珠单抗联合泼尼松和甲氨蝶呤治疗难治性中重度类风湿关节炎临床评价[J].中国药业,2024, 33(4):97-100. [6] 彭延刚.艾拉莫德联合布洛芬治疗类风湿关节炎的临床效果[J].临床合理用药, 2023,16(7):27-29+33. [7] BERGSTRA SA, SEPRIANO A, KERSCHBAUMER A, et al. Efficacy, duration of use and safety of glucocorticoids: a systematic literature review informing the 2022 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023;82(1):81-94. [8] PIRMARDVAND CHEGINI S, VARSHOSAZ J, TAYMOURI S. Recent approaches for targeted drug delivery in rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis and treatment. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup2):502-514. [9] STOCKWELL BR, JIANG X, GU W. Emerging Mechanisms and Disease Relevance of Ferroptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 2020;30(6):478-490. [10] 郑恩会,钟晓琳,蒋宗哲,等.中药及其天然产物通过靶向铁死亡治疗肝癌研究进展[J.天然产物研究与开发,2025,37(8): 1578-1584+1534. [11] 刘微微,王国辉.关于铁死亡在缺血性脑卒中中的研究进展[J].微量元素与健康研究,2025,42(2):71-74. [12] 余伟杰,刘爱峰,陈继鑫,等.基于生物信息学及机器学习分析椎间盘退变伴铁死亡的关键基因及潜在中药预测[J].中国中药杂志,2025,50(19):5482-5497. [13] LUO H, ZHANG R. Icariin enhances cell survival in lipopolysaccharide-induced synoviocytes by suppressing ferroptosis via the Xc-/GPX4 axis. Exp Ther Med. 2021; 21(1):72. [14] SHA N, VANNUCCI M, BROWN PJ, et al. Gene selection in arthritis classification with large-scale microarray expression profiles. Comp Funct Genomics. 2003;4(2):171-181. [15] 李楠,杨海芯,曾珊,等.桂枝芍药知母汤对类风湿关节炎Th17/Treg细胞失衡及JAK2/STAT3信号通路的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2023,38(6):2567-2571. [16] DI MATTEO A, BATHON JM, EMERY P. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2023;402(10416):2019-2033. [17] ZHANG Y, GAO Z, CHAO S, et al. Transdermal delivery of inflammatory factors regulated drugs for rheumatoid arthritis. Drug Deliv. 2022;29(1):1934-1950. [18] HU H, LUAN L, YANG K, et al. Psychometric validation of Chinese Health Assessment Questionnaire for use in rheumatoid arthritis patients in China. Int J Rheum Dis. 2017;20(12):1987-1992. [19] MIGUEL-LAVARIEGA D, ELIZARARRÁS-RIVAS J, VILLARREAL-RÍOS E, et al. Perfil epidemiológico de la artritis reumatoide [Epidemiological profile of rheumatoid arthritis]. Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc. 2023;61(5):574-582. [20] ALPIZAR-RODRIGUEZ D, FINCKH A. Is the prevention of rheumatoid arthritis possible. Clin Rheumatol. 2020;39(5):1383-1389. [21] WANG X, KONG Y, LI Z. Advantages of Chinese herbal medicine in treating rheumatoid arthritis: a focus on its anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024;11:1371461. [22] 阚玉娜,谢佳明,马立威,等.中药活性成分改善类风湿性关节炎作用机制研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2021, 23(10):139-145. [23] AKAGI R, AKATSU Y, FISCH KM, et al. Dysregulated circadian rhythm pathway in human osteoarthritis: NR1D1 and BMAL1 suppression alters TGF-β signaling in chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(6):943-951. [24] VAN DER KRAAN PM. The changing role of TGFβ in healthy, ageing and osteoarthritic joints. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;13(3): 155-163. [25] YING J, WANG P, ZHANG S, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta1 promotes articular cartilage repair through canonical Smad and Hippo pathways in bone mesenchymal stem cells. Life Sci. 2018;192:84-90. [26] WANG Q, TAN QY, XU W, et al. Cartilage-specific deletion of Alk5 gene results in a progressive osteoarthritis-like phenotype in mice. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017; 25(11):1868-1879. [27] NERVIANI A, BOUTET MA, GHIRARDI GM, et al. Axl and MerTK regulate synovial inflammation and are modulated by IL-6 inhibition in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):2398. [28] ZHAO L, LIU M, ZHENG K, et al. Fufang Duzheng tablet attenuates adjuvant rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting arthritis inflammation and gut microbiota disturbance in rats. Heliyon. 2024;10(12):e32705. [29] WEI Y, LUO L, GUI T, et al. Targeting cartilage EGFR pathway for osteoarthritis treatment. Sci Transl Med. 2021;13(576):eabb3946. [30] 涂华微.类风湿关节炎患者血清腺苷脱氨酶水平及外周血单个核细胞腺苷受体基因表达的研究[D].南充:川北医学院,2024. [31] JIANG Y, QIAO Y, HE D, et al. Adaptor protein HIP-55-mediated signalosome protects against ferroptosis in myocardial infarction. Cell Death Differ. 2023;30(3):825-838. [32] 李玉杰,吴巧萍,李情操,等.铁死亡相关基因在类风湿性关节炎中的作用机制[J].浙江医学,2024,46(24):2619-2625+2692. [33] ZHAO C, SUN G, LI Y, et al. Forkhead box O3 attenuates osteoarthritis by suppressing ferroptosis through inactivation of NF-κB/MAPK signaling. J Orthop Translat. 2023;39:147-162. [34] LIU Y, GU W. p53 in ferroptosis regulation: the new weapon for the old guardian. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29(5):895-910. [35] 范丹丹.miR-126-3p与自噬相关基因对类风湿关节炎发病机制影响的研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2022. [36] 秦齐刚.基于虚拟筛选从中药中发现抗RA药效物质基础及作用机制研究[D].重庆:重庆科技学院,2022. [37] 伍甜,张杰.姜黄素对类风湿关节炎免疫细胞群调节机制研究进展[J].中医临床研究,2025,17(18):65-74. [38] WANG H, ZHANG M, HU Y, et al. Deciphering the role of ferroptosis in rheumatoid arthritis: Synovial transcriptome analysis and immune infiltration correlation. Heliyon. 2024;10(13):e33648. [39] 李维彤,谢亚,吕中阳,等.辣椒素在骨关节炎中的作用研究进展[J].实用老年医学,2024,38(2):198-202. [40] 郑云松,皮浩吕,何子晗,等.基于AKT-HK2-NF-κB信号通路的辣椒素对CIA大鼠的作用机制[J].贵州医科大学学报,2024, 49(11):1615-1621. [41] 李雨,王杰,陈铭勰,等.辣椒素对CIA大鼠关节滑膜组织抗炎作用及机制[J].贵州医科大学学报,2023,48(5):508-514. [42] LIU X, WANG Z, QIAN H, et al. Natural medicines of targeted rheumatoid arthritis and its action mechanism. Front Immunol. 2022;13:945129. [43] 陈倩雯,何奕坤,沈佳莹,等.白藜芦醇治疗类风湿关节炎研究进展[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2022,42(10):1266-1272. [44] NANDAVE M, ACHARJEE R, BHADURI K, et al. A pharmacological review on SIRT 1 and SIRT 2 proteins, activators, and inhibitors: Call for further research. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;242(Pt 1):124581. [45] FERNÁNDEZ-RODRÍGUEZ JA, ALMONTE-BECERRIL M, RAMIL-GÓMEZ O, et al. Autophagy Activation by Resveratrol Reduces Severity of Experimental Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2021;65(2):e2000377. [46] 龙晨,杨硕,潘彬,等.基于网络药理学和实验验证白藜芦醇治疗类风湿性关节炎的作用机制[J].现代药物与临床, 2024,39(6):1425-1435. [47] 李浩,姚血明,姚晓玲,等.漆黄素调控焦亡相关蛋白对人类风湿关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞增殖、迁移及周期阻滞影响[J].中国药理学通报,2024,40(10):1937-1944. [48] 杭小雨.雌二醇对类风湿性关节炎中ASIC1a介导的关节软骨损伤的作用及其机制研究[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2021. [49] 蒋海旭,许杰,陆清怡.槲皮素治疗类风湿关节炎的研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(5):243-250. [50] 魏欣,王士民,孙成,等.基于网络药理学研究白仙风汤剂治疗类风湿性关节炎的药理机制[J].药物评价研究,2019, 42(5):858-868. [51] 许义方,许文昌.基于网络药理学和分子对接技术探讨阳和汤治疗类风湿性关节炎的作用机制[J].中医临床研究, 2025,17(4):95-104. [52] 张鸽,黄炜.尼尔雌醇联合醋酸甲羟孕酮治疗围绝经期妇女类风湿性关节炎的临床观察[J].中国药房,2014,25(24): 2275-2277. [53] ISHIZUKA M, HATORI M, SUZUKI T, et al. Sex steroid receptors in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Sci (Lond). 2004;106(3):293-300. [54] 李霞,张丹,赵彩虹,等.性激素、催乳素与类风湿关节炎[J].大连大学学报, 2002,23(4):102-105. [55] CUI J, SHEN Y, LI R. Estrogen synthesis and signaling pathways during aging: from periphery to brain. Trends Mol Med. 2013;19(3):197-209. [56] KHOSLA S, MELTON LJ 3RD, RIGGS BL. The unitary model for estrogen deficiency and the pathogenesis of osteoporosis: is a revision needed?. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(3):441-451. [57] BASU A, SCHELL J, SCOFIELD RH. Dietary fruits and arthritis. Food Funct. 2018; 9(1):70-77. [58] JI JJ, LIN Y, HUANG SS, et al. Quercetin: a potential natural drug for adjuvant treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2013;10(3): 418-421. [59] 吴志鹏,张迪,高乐,等.从铁死亡探讨中药抑制类风湿关节炎的研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2025,27(9):94-100. [60] 王丽娟,孟美辰,王志远,等.铁死亡在关节疾病中的作用及研究进展[J].山东第一医科大学(山东省医学科学院)学报,2024,45(10):628-631. [61] 梁霄,李娅兰,张筠昊,等.基于TLR2/p38 MAPK/NF-κB信号通路探讨独活寄生汤对类风湿性关节炎大鼠的抗炎作用及机制[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2023,29(11):43-52. |
| [1] | Lyu Guoqing, Aizimaitijiang·Rouzi, Xiong Daohai. Irisin inhibits ferroptosis in human articular chondrocytes: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1359-1367. |
| [2] | Guo Ying, Tian Feng, Wang Chunfang. Potential drug targets for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: large sample analysis from European databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1549-1557. |
| [3] | Wu Zhilin, , He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Shi Xian, Yuan Song, Zhang Jun, Wang Hao . DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [4] | Zheng Yin, Wu Zhenhua, Zhang Cheng, Ruan Kexin, Gang Xiaolin, Ji Hong. Safety and efficacy of immunoadsorption therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: a network meta-analysis and systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1260-1268. |
| [5] | Liu Fengzhi, Dong Yuna, Tian Wenyi, Wang Chunlei, Liang Xiaodong, Bao Lin. Gene-predicted associations between 731 immune cell phenotypes and rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1311-1319. |
| [6] | Bao Zhuoma, Hou Ziming, Jiang Lu, Li Weiyi, Zhang Zongxing, Liu Daozhong, Yuan Lin. Effect and mechanism by which Pterocarya hupehensis skan total flavonoids regulates the proliferation, migration and apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 816-823. |
| [7] | Zou Rongji, Yu Fangfang, Wang Maolin, Jia Zhuopeng. Triptolide inhibits ferroptosis and improves cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat model of cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 873-881. |
| [8] | Yang Xiao, Bai Yuehui, Zhao Tiantian, Wang Donghao, Zhao Chen, Yuan Shuo. Cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: mechanisms and regenerative challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 926-935. |
| [9] | Zheng Peng, Jia Xiaoning, Tao Jingwei, Fan Xiao. Tetramethylpyrazine improves iron metabolism disorders in a rat model of spinal cord injury via the Keap-1/Nrf2 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6134-6141. |
| [10] | Huang Yushan, Wang Rongrong, Li Xiangmiao, Bai Jinzhu. Prostaglandin E1 pretreatment inhibits ferroptosis in endothelial cells in a rat model of spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(22): 5716-5727. |
| [11] | Tao Xiangyu, Wang Shuang, Li Yuhan, Cao Jimin, Sun Teng. Effects of piRNA CFAPIR in doxorubicin-induced ferroptosis models of rat and human cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(22): 5756-5769. |
| [12] | Xie Peisen, Guan Zhenpeng, Wei Xianjie, Zhang Keshi, Kang Qingyuan, Xiao Wentao, Guo Xiaoshuai. Cerium dioxide nanoparticles regulate expression of inflammatory factors in M1 macrophages and affect fibroblast co-culture system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 375-383. |
| [13] | Liao Xingzhuan, Li Guangdi, Wu Yabin, Liu Xingyu, Wan Jiajia. Molecular mechanisms underlying non-coding RNA regulation of ferroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(18): 4713-4725. |
| [14] | Han Jie, Yao Guojun, Huang Yebao, Xu Zhiwei, Shao Weigang, Shang Kebin, Wu Yachao, Liao Zhen. Genetic structure of co-morbidity between frailty and rheumatoid arthritis: a genome-wide association analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4548-4556. |
| [15] | Yu Le, Nan Songhua, Shi Zijian, He Qiqi, Li Zhenjia, Cui Yinglin. Mechanisms underlying mitophagy, ferroptosis, cuproptosis, and disulfidptosis in Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4446-4456. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||