Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (18): 4713-4725.doi: 10.12307/2026.767
Molecular mechanisms underlying non-coding RNA regulation of ferroptosis in osteoarthritis
Liao Xingzhuan1, Li Guangdi1, 2, Wu Yabin1, Liu Xingyu3, Wan Jiajia1
- 1Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 3Shanghai Children’s Medical Center, Guizhou Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2025-09-03Accepted:2025-10-18Online:2026-06-28Published:2025-12-08 -
Contact:Li Guangdi, MD, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Liao Xingzhuan, MS candidate, Physician, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Regional Science Fund of National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82160432 (to LGD); Basic Research Project of Guizhou Provincial Department of Science and Technology, No. Qiankeheji ZK[2022]-General 427 (to LGD); National Natural Science Foundation of Guizhou Medical University, No. 20NSP045 (to LGD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liao Xingzhuan, Li Guangdi, Wu Yabin, Liu Xingyu, Wan Jiajia. Molecular mechanisms underlying non-coding RNA regulation of ferroptosis in osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(18): 4713-4725.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
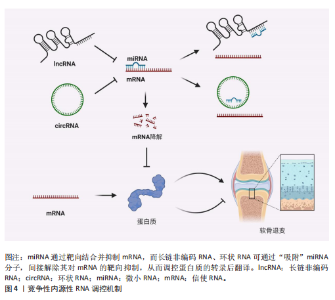
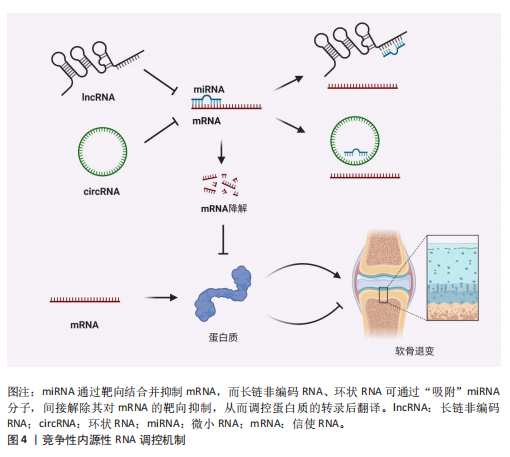
2.1 非编码RNA概述及在骨关节炎中的作用 非编码RNA是指由基因组转录而来的不编码蛋白质的RNA分子,根据其长度和形状,非编码RNA分为多种类型,包括微小RNA、长链非编码RNA、环状RNA等[18,22],由于不具备编码蛋白质的功能,在过去很长一段时间内,被普遍视作“无用之物”。但是随着广泛深入的研究,许多研究者发现非编码RNA参与多种生物学过程,它们可调节生理和发育过程甚至疾病的发生发展,并且有可能成为疾病治疗的靶点[23]。 竞争性内源性RNA是一类能够通过共享的微小RNA反应元件竞争性结合相同微小RNA的RNA分子,从而调控彼此表达水平[24]。这类RNA包括蛋白编码mRNA、假基因转录物、长链非编码 RNA、环状 RNA等,其核心机制在于,当不同RNA分子通过微小RNA反应元件竞争结合有限的微小RNA时,会削弱微小RNA对靶基因的抑制作用,形成复杂的调控网络,最终影响细胞的生理或病理过程[25]。当微小RNA通过结合微小RNA反应元件抑制靶mRNA稳定性或翻译时,富含微小RNA反应元件的竞争性内源性RNA(长链非编码 RNA、环状 RNA等)可通过“吸附”微小RNA分子,间接解除其对mRNA的靶向抑制,从而调控蛋白质的转录后翻译,见图4。目前已有大量研究表明在骨关节炎疾病的发展进程中,存在许多不同的长链非编码 RNA/环状 RNA-微小RNA-mRNA轴,其影响相关蛋白质的表达以及关键信号通路,进而参与骨关节炎的病理过程[26]。 综上,竞争性内源性RNA机制构成了非编码RNA调控基因表达的核心模式之一,在骨关节炎病理进程中扮演关键角色。值得深入探讨的是,在铁死亡这一特定背景下,网络如何特异性地整合和传递氧化还原信号?不同非编码RNA构成的竞争性内源性RNA模块之间是否存在协同或拮抗效应?这些问题的解答将有助于构建更精细的骨关节炎铁死亡调控图谱。 2.2 铁死亡分子机制及在骨关节炎中的作用 铁死亡作为一种新型的程序性细胞死亡方式,其核心特征在于铁依赖性脂质过氧化的异常累积。在形态学、生化特征及遗传调控层面,铁死亡均显著区别于凋亡、自噬等其他细胞死亡途径,其发生机制错综复杂,主要涉及铁代谢紊乱、脂质过氧化及抗氧化系统崩溃[9-10]。近年来,越来越多的研究发现,铁死亡在骨关节炎的病理进程中扮演着不可忽视的驱动角色,骨关节炎关节微环境中的铁离子过载、炎症刺激及机械应力均可触发软骨细胞铁死亡,最终导致软骨细胞外基质破坏和滑膜组织炎症加剧[15,27]。 2.2.1 铁代谢紊乱 细胞内铁过载是铁死亡的关键驱动因素,细胞通过转铁蛋白受体1识别并结合血液中的转铁蛋白-铁复合物(Fe3+),经内吞作用进入细胞后,Fe3+在酸性内体中还原为Fe2+,随后通过二价金属转运蛋白释放到细胞质中,形成不稳定的游离铁池[28]。这一过程增强了细胞内铁的可利用性,过量Fe2+可通过与过氧化氢反应生成羟基自由基(此过程被称为芬顿反应[29]),进而攻击含多不饱和脂肪酸的磷脂,形成脂质过氧化物并导致铁死亡的发生[17]。"
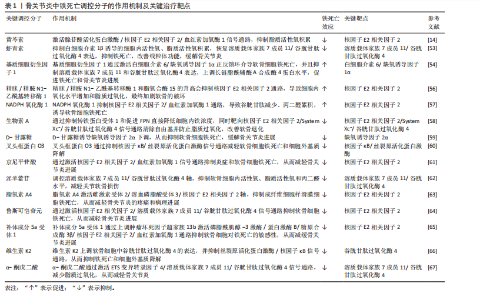
核受体辅激活因子4通过选择性自噬途径靶向铁蛋白,将其降解并释放游离铁至胞质[30],显著提升游离铁池水平,从而促进芬顿反应和脂质过氧化,促进铁死亡发生。有研究表明核受体辅激活因子4介导的铁蛋白自噬可导致软骨细胞铁死亡和加重创伤后骨关节炎,并且c-Jun氨基末端激酶-JUN轴直接调控核受体辅激活因子4表达,在白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞铁死亡和骨关节炎发病机制中发挥重要作用[31]。因此针对铁代谢过程中的转铁蛋白受体1、核受体辅激活因子4等关键分子的干预策略可以为治疗铁死亡相关疾病提供新方向。血红素加氧酶1可以通过从血红素中释放亚铁来发挥促铁死亡作用,但也有研究表明敲低或敲除血红素加氧酶1后会加剧铁死亡的发生[32],因此其在铁死亡中的作用尚未清楚。 2.2.2 脂质过氧化 铁死亡中的脂质过氧化是铁依赖性细胞死亡的核心生化特征。长链脂酰辅酶A合成酶4通过将多不饱和脂肪酸连接辅酶A,随后由溶血磷脂酰胆碱酰基转移酶3将其酯化至膜磷脂中,形成易被氧化的多不饱和脂肪酸磷脂结构。此步骤显著增加细胞膜对脂质过氧化的敏感性[33]。 活性氧是一类含氧的高活性分子,包括过氧化氢(H2O2)、超氧阴离子(O2-)、次氯酸(HOCl)、单线态氧(1O2)和羟基自由基(·OH)等,其可参与细胞信号传导、免疫防御和基因表达调控,过量活性氧导致氧化应激,损伤脂质、蛋白质和DNA,与肿瘤疾病的发展密切相关[34]。在铁死亡发生过程中,过量Fe2?通过芬顿反应生成高反应性羟基自由基,直接攻击多不饱和脂肪酸的亚甲基位点,引发脂质自由基链式反应,其过程产生脂质活性氧以及丙二醛、4-羟基壬烯醛等氧化产物,最终破坏膜完整性并诱导跨膜蛋白失活[35]。 脂氧合酶可以调节铁死亡中脂质过氧化过程,人类有6个脂氧合酶基因[36](即脂氧合酶5、脂氧合酶12、脂氧合酶12B、脂氧合酶15、脂氧合酶15B和脂氧合酶E3)。其中,脂氧合酶15 可与磷脂酰乙醇胺结合蛋白1结合,促进脂质过氧化物的产生,介导RSL3诱导的铁死亡[37]。脂氧合酶12是p53依赖性铁死亡的重要因子,其可调控p53介导的铁死亡,在一些肿瘤疾病中发挥重要作用[38]。此外,氧化还原酶在促进铁死亡中发挥协同作用,细胞色素P450还原酶和细胞色素b5还原酶将电子从NAD(P)H转移到氧气中产生过氧化氢,以促进芬顿反应,最终导致脂质过氧化和铁死亡发生[39]。 2.2.3 抗氧化系统崩溃 铁死亡中抗氧化系统的崩溃是推动脂质过氧化不可逆增长的核心机制,其过程涉及谷胱甘肽耗竭、谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4失活、辅酶Q10抗氧化功能受损等多重环节。两种经典铁死亡激活剂erastin和RSL3可以通过不同途径导致细胞内抗氧化系统崩溃,诱导铁死亡[40]。 胱氨酸/谷氨酸逆向转运体(System Xc?)是一种广泛分布在磷脂双层中的氨基酸抗转运蛋白,由溶质载体家族7成员11和溶质载体家族3成员2两个亚基组成。胱氨酸和谷氨酸通过System Xc?以1∶1的比例进出细胞。被细胞摄取的胱氨酸在胞内首先被还原为半胱氨酸,后者参与谷胱甘肽的合成,谷胱甘肽在谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶的作用下可清除活性氧和活性氮[41]。影响谷胱甘肽合成的主要决定因素是半胱氨酸的可用性以及限速酶谷氨酸半胱氨酸连接酶的活性[42], 其中谷氨酸半胱氨酸连接酶的活性受氧化应激和转录途径所影响,当核因子E2相关因子2通路失活时,谷氨酸半胱氨酸连接酶活性下调,从而进一步加剧谷胱甘肽耗竭[43]。Erastin作为一种经典铁死亡激活剂,其可以通过抑制System Xc?诱导铁死亡发生,当System Xc?被抑制或表达下调时,细胞内胱氨酸供应不足,直接导致谷胱甘肽水平下降,从而引起谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶活性下降、细胞抗氧化能力减弱、脂质活性氧积累[10,44]。 谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4利用还原型谷胱甘肽将脂质过氧化物(PL-OOH)转化为无毒的脂醇(PL-OH),其表达或活性受硒和谷胱甘肽控制[9]。当谷胱甘肽水平不足时,谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4的催化活性丧失,无法清除脂质过氧化物,导致其在膜内积累并引发氧化链式反应。而铁死亡激活剂RSL3可与谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4结合并使其活性丧失,直接诱导铁死亡发生[45]。谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4活性中心的硒代半胱氨酸(Sec)是其发挥抗氧化功能的核心,动物实验研究发现将硒代半胱氨酸替换为普通半胱氨酸(Cys)的谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4突变体(谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4-普通半胱氨酸)完全丧失了其催化活性,无法还原脂质过氧化物,导致细胞抗过氧化能力显著降低[46]。因此在缺乏硒的环境下谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4的活性降低,抗氧化能力下降,从而触发铁死亡。 铁死亡抑制蛋白1是一种不依赖于谷胱甘肽系统的铁死亡关键调控分子,可发挥与谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4平行的铁死亡抑制作用[47]。铁死亡抑制蛋白1通过催化还原辅酶Q10和维生素K,分别生成具有强效自由基清除能力的辅酶Q10H2和VKH2。这些还原型分子能够直接中和脂质过氧化自由基,从而发挥与谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4平行的细胞保护作用。若铁死亡抑制蛋白1表达水平下降或辅酶Q10合成过程受阻,该通路将失去代偿能力,从而加速脂质过氧化物的积累。此外,铁死亡抑制蛋白1还能通过ESCRT-Ⅲ依赖的膜修复途径抑制铁死亡发生[48]。在线粒体层面,二氢乳清酸脱氢酶(DHODH)定位于内膜,其功能是将泛醌(CoQ)还原为泛醇(CoQH2),泛醇作为一种具有抗铁死亡活性的自由基捕获抗氧化剂,能够阻止脂质过氧化,从而发挥抑制线粒体内膜铁死亡的作用[49]。四氢生物蝶呤同样也是细胞内一类重要的自由基捕获抗氧化剂,其可显著保护脂质免受氧化损伤,而GTP环水解酶1可以通过调控四氢生物蝶呤的生成水平影响细胞铁死亡的发生。因此靶向激活GTP环水解酶1/四氢生物蝶呤信号通路可能作为一种有效干预铁死亡的治疗策 略[15,50]。 核因子E2相关因子2是抗氧化应答主调控因子,可调节溶质载体家族7成员11、血红素加氧酶1、重组人铁蛋白重链1及谷氨酸半胱氨酸连接酶等一系列关键靶基因的表达,在协调细胞对抗铁死亡的多层面防御程序中发挥着不可或缺的作用[51]。值得注意的是,近期一项研究揭示了核因子E2相关因子2在特定肿瘤微环境中的独特调控机制:在Kelch样环氧氯丙烷相关蛋白1功能缺失性突变或Kelch样环氧氯丙烷相关蛋白1蛋白失活的肿瘤细胞中,核因子E2相关因子2信号通路被异常激活,从而诱导铁死亡抑制蛋白1的表达上调。这一发现表明,除了经典的抗氧化基因调控外,核因子E2相关因子2还可通过激活铁死亡抑制蛋白1-辅酶Q10通路,协同强化细胞对铁死亡应激的抵抗能力[52]。 2.2.4 骨关节炎中铁死亡的调控与治疗靶点 软骨细胞损伤是骨关节炎进展过程中的一个主要事件,不同的细胞死亡形式如凋亡、坏死性凋亡、焦亡等能够导致细胞外基质降解、软骨退变,加剧骨关节炎进展。铁死亡作为一种新型的程序性细胞死亡形式,从被提出至今已逐渐成为研究焦点,近年来,多项研究证实促炎因子或铁过载模型通过增加活性氧、脂质活性氧和铁离子水平,同时下调谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4、溶质载体家族7成员11等抗氧化蛋白,诱导软骨细胞铁死亡[13,53-54],并且铁死亡抑制剂Fer-1以及铁螯合剂去铁胺可逆转这些效应,减轻软骨退变[13,55]。如表1所示,近年来涌现出大量调控骨关节炎软骨细胞铁死亡的关键分子及潜在治疗靶点。深入分析这些分子及其通路可发现几个显著特征:①核因子E2相关因子2通路是核心的抗氧化防御节点,被多种保护性分子(如黄芩素、生物素A等)激活,其提示核因子E2相关因子2是骨关节炎中关键的治疗靶点;②System Xc?/谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4轴是铁死亡的核心执行通路,是众多调控因子的共同靶点;③炎症"
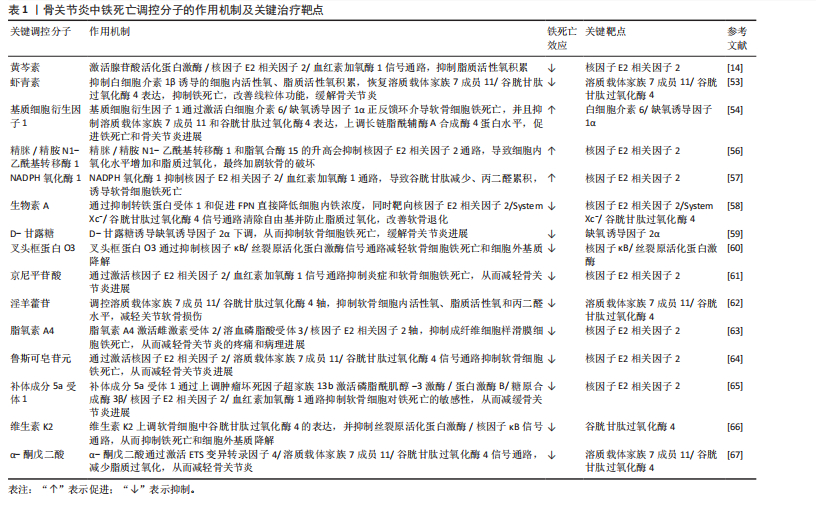
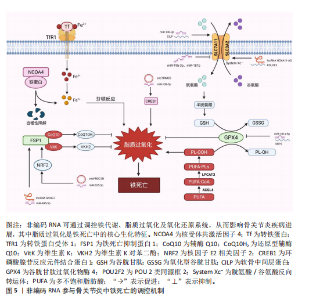
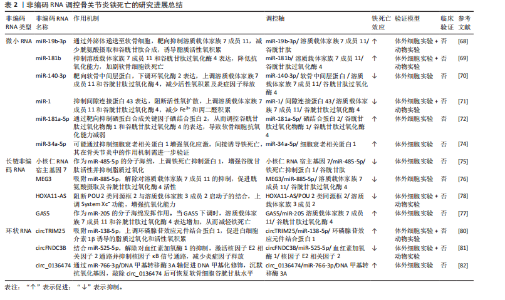
信号(如白细胞介素6/缺氧诱导因子1α、核因子κB/丝裂原活化蛋白激酶)与铁死亡进程紧密交织,形成恶性循环。这提示骨关节炎中的铁死亡并非孤立事件,而是嵌入在复杂的炎症-代谢-细胞死亡网络中的关键环节。未来研究需致力于解析这些通路间的交互关系及其在非编码RNA调控下的整合机制。 2.3 非编码RNA调控铁死亡参与骨关节炎疾病进展 目前有研究表明非编码RNA可以通过靶向铁死亡相关基因或信号通路调控铁死亡的发生,在骨关节炎的软骨退变、滑膜炎症及细胞代谢失衡中发挥重要作用。 2.3.1 微小RNA调控骨关节炎中的铁死亡 在骨关节炎的发病机制中,微小RNA扮演着重要角色,其能够调节软骨细胞的凋亡与增殖、细胞外基质的代谢以及炎症反应等生物学过程,且有研究指出,微小RNA还可通过铁死亡机制发挥调控效应。 在铁死亡发生过程中,溶质载体家族7成员11和谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4是重要的抗氧化蛋白,其在骨关节炎软骨细胞中受到微小RNA的调控。KONG等[68]研究发现,在骨关节炎的发病进程中,成纤维样滑膜细胞扮演着关键角色,其能够分泌含有 miR-19b-3p的外泌体。当成纤维样滑膜细胞外泌体与软骨细胞接触时,miR-19b-3p靶向结合溶质载体家族7成员11的3’UTR,抑制其转录翻译,导致溶质载体家族7成员11蛋白的合成显著减少,从而影响谷胱甘肽合成以及谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4活性,诱导软骨细胞铁死亡。根据WANG等[69]的研究发现,miR-181b在erastin诱导的骨关节炎细胞模型中呈现异常升高的特征,并且双荧光素酶报告基因试验证实了miR-181b与溶质载体家族7成员11具有靶向调控关系。功能验证实验表明,抑制miR-181b表达可增加溶质载体家族7成员11、谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4和FTH1的蛋白水平,有效降低丙二醛以及Fe2?水平,从而抑制铁死亡相关的软骨细胞损伤。该研究不仅为骨关节炎发病的分子机制提供了新视角,也为靶向miR-181b/溶质载体家族7成员11轴干预软骨细胞铁死亡提供了潜在治疗策略。 此外,软骨中间层蛋白可介导骨关节炎中铁死亡相关基因的调控,研究发现在脂多糖诱导下,软骨细胞中的软骨中间层蛋白水平显著增加,miR-140-3p通过靶向软骨中间层蛋白抑制铁死亡发生[70]。miR-140-3p的过表达会下调软骨中间层蛋白,同时上调溶质载体家族7成员11和谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4,进而降低氧化应激标志物超氧化物歧化酶、丙二醛及Fe2+的表达水平。该研究结果提示,miR-140-3p作为骨关节炎进展的关键调节因子,其通过靶向结合软骨中间层蛋白并调控炎症、氧化应激通路及铁死亡过程,从而影响骨关节炎的发生与发展。ZHOU等[71]研究发现miR-1可以通过靶向间隙连接蛋白43抑制软骨细胞的铁死亡并减轻骨关节炎进展。在炎症因子白细胞介素1β刺激下的骨关节炎软骨细胞中间隙连接蛋白43表达升高,并且谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4和溶质载体家族7成员11降低,当过表达miR-1时表现出间隙连接蛋白43的下调,并且可以减弱细胞内活性氧和脂质活性氧的积累。这些研究结果表明miR-1可以通过靶向间隙连接蛋白43并减弱炎症反应和维持软骨细胞的稳态来调节软骨细胞铁死亡。XUE等[72]研究揭示了miR-181a-5p通过靶向抑制硒蛋白合成关键因子硒结合蛋白2,从而调控谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶编码基因谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶1和谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4的表达,最终导致软骨细胞的氧化应激抵抗能力减弱。其结果提示miR-181a-5p可能在骨关节炎中发挥抑制硒结合蛋白2表达的作用,从而间接调控软骨细胞铁死亡发生,加剧软骨氧化损伤。此外,miR-34a-5p在晚期骨关节炎滑膜组织中显著上调,并且已被证实在神经细胞中可以通过靶向和抑制细胞衰老相关蛋白1来诱导铁死亡,提示其可能通过调控铁死亡影响骨关节炎进展,但miR-34a-5p在骨关节炎中的作用靶点与铁死亡的直接关系需要进一步研究确认[73-74]。 当前研究证据不断积累,证实了微小RNA在骨关节炎进程中扮演着关键的调控角色,其作用机制部分通过调控软骨细胞铁死亡过程得以实现。多种微小RNA分子被证实能够靶向作用于铁死亡核心调控分子或其上游关键信号通路,进而直接或间接地影响软骨细胞内氧化还原稳态以及脂质过氧化进程。这些发现不仅揭示了微小RNA参与骨关节炎中铁死亡调控的复杂分子互作网络,更奠定了重要的理论基础:一方面,特定微小RNA的表达谱变化有望成为骨关节炎早期诊断的新型生物标志物;另一方面,靶向干预关键微小RNA,以重建抗氧化防御体系或阻断促铁死亡信号通路,代表了极具前景的、旨在延缓甚至阻断骨关节炎病理进展的疾病修饰治疗策略。 2.3.2 长链非编码 RNA调控骨关节炎中的铁死亡 长链非编码 RNA在骨关节炎中可通过海绵作用竞争性结合微小RNA,释放靶mRNA表达,从而发挥调控铁死亡作用。研究发现,骨髓间充质干细胞分泌外泌体传递长链非编码 RNA 小核仁RNA宿主基因7至骨关节炎软骨细胞,小核仁RNA宿主基因7作为miR-485-5p的分子海绵,上调铁死亡抑制蛋白1表达,提高谷胱甘肽活性并抑制活性氧累积,降低丙二醛水平,从而延缓软骨降解[75]。该研究结果显示,骨髓间充质干细胞释放的外泌体中的小核仁RNA宿主基因7通过调节miR-485-3p/铁死亡抑制蛋白1轴,有效抑制软骨细胞的铁死亡和炎症反应,从而缓解骨关节炎症状,显示出潜在的治疗价值。ZHU等[76]研究发现长链非编码 RNA MEG3在骨关节炎软骨细胞中低表达,其过表达可通过吸附miR-885-5p解除其对溶质载体家族7成员11的抑制,增强胱氨酸摄取和谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4活性,减少脂质过氧化,恢复软骨细胞活力,减轻软骨细胞铁死亡。GU等[77]发现长链非编码 RNA GAS5作为竞争性内源性RNA结合并抑制miR-205,从而调节骨关节炎患者成纤维样滑膜细胞中的炎症和氧化应激。当长链非编码 RNA GAS5的表达下调时,展现出对细胞的显著保护效应,具体表现为肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6的分泌减少,而溶质载体家族7成员11和谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4的表达水平上升,进而有效缓解了铁死亡现象,增强了细胞的活力并提升了其生长速率。另一项研究发现,长链非编码 RNA HOXA11-AS可直接结合转录抑制因子POU 2类同源框2,阻止其与溶质载体家族3成员2启动子区域的结合,从而上调溶质载体家族3成员2表达,促进System Xc?功能,增强抗氧化能力,从而抑制软骨细胞铁死亡[78]。值得注意的是,长链非编码 RNA HOXA11-AS的作用机制区别于经典的竞争性内源性RNA模式,它并非通过吸附微小RNA来间接调控靶基因,而是直接与转录因子相互作用,实现对溶质载体家族3成员2的直接转录调控。 这一发现揭示了长链非编码 RNA调控基因表达和细胞命运的一种新型且更为直接的分子机制。鉴于其在抵抗铁死亡等关键病理生理过程中的重要作用,继续深入探索长链非编码 RNA HOXA11-AS以及具有同类直接作用模式的长链非编码 RNA的功能和机制,对于全面理解疾病发生发展、发现新的治疗靶点具有重要的科学意义和潜在的应用价值。 YANG等[79]运用生物信息学方法,系统性构建了骨关节炎软骨细胞中铁死亡相关基因所介导的全景竞争性内源性RNA调控网络。该网络涉及氧化应激反应、氧稳态平衡以及细胞铁死亡的调控,其中成功鉴定出3种关键长链非编码 RNA(AC011511.5、C9orf139、AL358072.1),参与下游多种关键铁死亡基因的调控,并初步揭示了其潜在的分子互作机制。长链非编码 RNA AC011511.5被预测可通过竞争性结合4种微小RNA(hsa-miR-520c-5p、hsa-miR-518d-5p、hsa-miR-518f-5p、hsa-miR-665),进而解除这些微小RNA对下游关键铁死亡相关基因(GABARAPL2、HMOX1、NOX4、STMN1和TXNIP)的转录后抑制作用。而分析预测结果显示长链非编码 RNA AL358072.1可通过竞争性结合hsa-miR-138-5p和hsa-miR-122-5p,从而调控SQSTM1、JDP2、HERPUD1、SLC38A1、AGPAT3和UBC等下游关键铁死亡相关基因。同样地,hsa-miR-138-5p和hsa-miR-490-3p被长链非编码 RNA C9orf139竞争性结合,进而调控SQSTM1、JDP2、HERPUD1、SLC38A1、PROM2和AGPAT3铁死亡相关基因。并且该研究通过体外细胞实验验证了AC011511.5、C9orf139及AL358072.1在骨关节炎软骨细胞中的表达水平存在显著差异。这一发现初步支持了该生物信息学预测的可靠性,并提示这3种长链非编码 RNA在骨关节炎病理微环境中可能具有潜在功能活性。然而,它们参与调控骨关节炎软骨细胞铁死亡进程的具体分子机制仍属未知领域,因此需要进一步研究探讨它们在骨关节炎中的分子调控机制。 长链非编码 RNA在骨关节炎铁死亡调控中主要扮演“分子海绵”角色,通过竞争性内源性RNA机制竞争性结合微小RNA,间接调控下游铁死亡相关基因。相较于微小RNA,长链非编码 RNA的调控更具网络性和间接性,其研究仍处于发展阶段,多数机制源于生物信息学预测或初步功能验证。关键挑战在于:①验证预测的竞争性内源性RNA调控轴在体内的真实性和贡献度;②探索长链非编码 RNA除竞争性内源性RNA外的其他调控功能(如转录调控、蛋白互作)在铁死亡中的作用;③阐明不同长链非编码 RNA模块间的协同与层级关系。未来还需结合多组学技术及临床验证进一步挖掘其转化潜力。 2.3.3 环状 RNA调控骨关节炎中的铁死亡 随着非编码RNA研究的不断深入,环状 RNA通过竞争性内源性RNA机制调控骨关节炎铁死亡的作用逐渐被揭示。凭借独特的闭合环状结构,环状 RNA展现出优异的稳定性,能够高效充当特定微小RNA的“分子海绵”,从而解除其对下游靶基因的抑制作用,在氧化应激、脂质过氧化及铁代谢失衡等病理过程中发挥核心调控功能。例如,circTRIM25被证实通过海绵吸附作用结合miR-138-5p,显著解除miR-138-5p对其靶基因环磷腺苷效应元件结合蛋白1的转录抑制,导致环磷腺苷效应元件结合蛋白1蛋白水平升高。功能研究表明,环磷腺苷效应元件结合蛋白1的积累会加剧白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞内脂质过氧化,进而触发铁死亡。功能拯救实验证实,沉默circTRIM25不仅能够有效抑制活性氧和丙二醛的生成,还能显著减少白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α等炎症因子的释放,同时延缓细胞外基质中胶原蛋白和蛋白聚糖的降解。这些研究为靶向调控circTRIM25/miR-138-5p/环磷腺苷效应元件结合蛋白1轴以治疗骨关节炎提供了可靠的实验依据[80]。另一项研究聚焦于circFNDC3B(hsa_circ_0001361),该环状 RNA在白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞中异常低表达,过表达circFNDC3B可通过竞争性结合miR-525-5p解除对血红素加氧酶1的抑制作用,功能验证实验表明血红素加氧酶1可以减轻细胞外基质降解并促进细胞增殖,进而缓解骨关节炎病理进程[81]。鉴于血红素加氧酶1本身是铁死亡调控网络中的核心分子,该研究结果强烈提示circFNDC3B可能通过激活miR-525-5p/血红素加氧酶1通路,间接抑制软骨细胞的铁死亡进程。相反地,circ_0136474则可能具有促铁死亡效应,其可通过吸附miR-766-3p上调DNA甲基转移酶3A,加剧白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞氧化损伤。而敲除该环状 RNA可提高谷胱甘肽水平,减少活性氧、丙二醛的积累,从而恢复细胞活力,缓解骨关节炎进展[82],提示circ_0136474/miR-766-3p/DNA甲基转移酶3A轴作为干预靶点的潜力。 目前聚焦于环状 RNA调控骨关节炎软骨细胞铁死亡的直接证据相对有限,但基于其独特分子特性以及已报道的环状 RNA在骨关节炎病理进程中的调控作用,环状 RNA具有作为更稳定的潜在生物标志物及治疗靶点的独特价值,未来需重点解决的难题有:①筛选和验证具有骨关节炎铁死亡调控特异性的关键环状 RNA;②深入解析其竞争性内源性RNA网络的具体效应以及与长链非编码 RNA的协同或拮抗作用;③探索其环状结构赋予的特殊功能。 综上,近年来非编码RNA调控骨关节炎铁死亡的作用机制及研究进展汇总可见表2及图5,通过对现有文献的系统梳理,作者发现当前关于非编码RNA调控骨关节炎铁死亡的研究领域存在关键性挑战与局限:①绝大多数研究聚焦于非编码RNA通过调控经典抗氧化防御系统(特别是SLC97A11/谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4轴)来影响铁死亡敏感性。相比之下,非编码RNA对铁代谢相关蛋白(如核受体辅激活因子4、转铁蛋白受体1)的调控则鲜有深入探讨。②现有成果几乎完全来源于体外细胞模型和动物模型的实验数据。虽然这些研究为机制探索提供了重要基础,但非编码RNA作为铁死亡调控因子在骨关节炎患者"
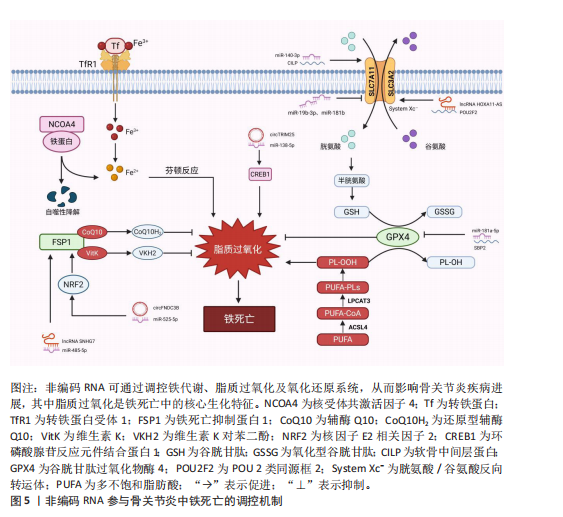

体内的表达谱、特异性、作用机制及其作为诊断标志物或治疗靶点的临床可行性尚未得到充分验证。 2.4 靶向非编码RNA与铁死亡的治疗策略 随着非编码RNA在调控骨关节炎铁死亡中核心作用的明确,靶向这些非编码RNA以干预铁死亡进程,进而缓解骨关节炎病理进展,已成为极具前景的治疗策略。 2.4.1 抑制促铁死亡非编码RNA 针对在骨关节炎中发挥促铁死亡作用的非编码RNA,如miR-19b-3p、miR-181b、miR-181a-5p、miR-34a-5p、circTRIM25和circ_0136474等,核心策略是抑制其表达或功能。主要手段包括设计特异性的反义寡核苷酸靶向降解或封闭促铁死亡微小RNA[83],使其无法结合下游靶标(如溶质载体家族7成员11、谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4、硒结合蛋白2、细胞衰老相关蛋白1);利用小干扰RNA或短发夹RNA技术沉默促铁死亡的长链非编码 RNA或环状 RNA[84-85]。目标在于解除这些非编码RNA对关键铁死亡抑制因子(如System Xc?、谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4、硒蛋白合成)的负向调控,从而减轻软骨细胞脂质过氧化和死亡。 2.4.2 增强抑铁死亡非编码RNA 对于具有抑制骨关节炎软骨细胞铁死亡功能的非编码RNA,如miR-140-3p、miR-1、长链非编码 RNA 小核仁RNA宿主基因7、长链非编码 RNA MEG3、长链非编码 RNA HOXA11-AS和circFNDC3B等,策略侧重于提升其表达水平或增强其活性,这可通过合成并递送微小RNA模拟物来实现,模拟内源性抑铁死亡微小RNA的功能,从而上调保护性基因(如溶质载体家族7成员11、谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4、铁死亡抑制蛋白1)或抑制有害因子(如软骨中间层蛋白、间隙连接蛋白43);或通过病毒/非病毒载体介导的基因过表达技术[86],在软骨细胞中稳定高表达抑铁死亡的长链非编码 RNA或环状 RNA,使其更有效地发挥“分子海绵”作用(如吸附miR-485-5p、miR-885-5p)或直接调控基因表达(如HOXA11-AS上调溶质载体家族3成员2表达),最终增强细胞抗氧化能力。 2.4.3 干预竞争性内源性RNA调控网络 鉴于长链非编码 RNA和环状 RNA主要通过竞争性内源性RNA机制吸附微小RNA来调控铁死亡,直接干预该网络的节点是另一重要策略。这包括:①利用反义寡核苷酸或小干扰RNA特异性敲低充当“促铁死亡海绵”的长链非编码 RNA/环状 RNA,如沉默circTRIM25释放miR-138-5p,抑制环磷腺苷效应元件结合蛋白1表达;②调控网络中关键微小RNA的表达;③在明确调控轴的前提下,直接靶向下游关键的效应mRNA,如使用小分子激活剂增强核因子E2相关因子2活性以及谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4功能。目标是精细调节复杂的竞争性内源性RNA网络,恢复其对铁死亡进程的平衡控制。 2.4.4 挑战与未来方向 尽管前景广阔,靶向非编码RNA调控铁死亡治疗骨关节炎仍面临显著挑战。首要难题是高效、特异性的关节腔递送,需要开发安全可靠的纳米载体或工程化外泌体,将反义寡核苷酸、小干扰RNA、微小RNA模拟物或过表达载体精准送达软骨细胞,潜在的脱靶效应和安全性问题需通过严谨评估来解决。其次,非编码RNA表达的时空特异性及其在骨关节炎不同阶段的动态变化尚不明确,且其作用机制复杂,可能涉及多通路调控并产生截然不同的效应,亟待深入研究。此外,当前研究多基于细胞和动物模型,亟需推进临床前安全性和有效性验证,并最终迈向临床试验。未来探索将靶向非编码RNA策略与直接铁死亡抑制剂(如铁抑素1、铁螯合剂)或抗炎药物联合应用,可能产生协同效应,是开发有效延缓甚至逆转骨关节炎软骨退化疾病修饰疗法的关键方向。"

| [1] SHIH PC, LEE YH, TSOU HK, et al. Recent targets of osteoarthritis research. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2023;37(2):101851. [2] LEIFER VP, KATZ JN, LOSINA E. The burden of OA-health services and economics. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(1):10-16. [3] COURTIES A, KOUKI I, SOLIMAN N, et al. Osteoarthritis year in review 2024: Epidemiology and therapy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2024;32(11):1397-1404. [4] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, diagnosis, and treatment options. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2): 293-311. [5] DI FRANCESCO M, FRAGASSI A, PANNUZZO M, et al. Management of osteoarthritis: From drug molecules to nano/micromedicines. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2022;14(3): e1780. [6] ROEMER FW, GUERMAZI A, DEMEHRI S, et al. Imaging in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(7):913-934. [7] CHO Y, JEONG S, KIM H, et al. Disease-modifying therapeutic strategies in osteoarthritis: Current status and future directions. Exp Mol Med. 2021;53(11): 1689-1696. [8] JIANG X, STOCKWELL BR, CONRAD M. Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021; 22(4):266-282. [9] TANG D, CHEN X, KANG R, et al. Ferroptosis: Molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res. 2021;31(2):107-125. [10] DIXON SJ, LEMBERG KM, LAMPRECHT MR, et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012; 149(5):1060-1072. [11] CHEN H, HAN Z, WANG Y, et al. Targeting ferroptosis in bone-related diseases: Facts and perspectives. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16: 4661-4677. [12] ZHU R, WANG Y, OUYANG Z, et al. Targeting regulated chondrocyte death in osteoarthritis therapy. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023;215:115707. [13] YAO X, SUN K, YU S, et al. Chondrocyte ferroptosis contribute to the progression of osteoarthritis. J Orthop Transl. 2021;27: 33-43. [14] WAN Y, SHEN K, YU H, et al. Baicalein limits osteoarthritis development by inhibiting chondrocyte ferroptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2023;196:108-120. [15] LIU Y, ZHANG Z, FANG Y, et al. Ferroptosis in osteoarthritis: Current understanding. J Inflamm Res. 2024;17:8471-8486. [16] ZHANG Y, LI J, LIU J, et al. Ferroptosis in osteoarthritis: Towards novel therapeutic strategy. Cell Prolif. 2025;58(3):e13779. [17] ZHANG S, XU J, SI H, et al. The role played by ferroptosis in osteoarthritis: Evidence based on iron dyshomeostasis and lipid peroxidation. Antioxid Basel Switz. 2022; 11(9):1668. [18] ZHENG X, ZHANG C. The regulation of ferroptosis by noncoding RNAs. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(17):13336. [19] LUO Y, HUANG Q, HE B, et al. Regulation of ferroptosis by non‑coding RNAs in the development and treatment of cancer (review). Oncol Rep. 2021;45(1):29-48. [20] JIANG M, JIKE Y, LIU K, et al. Exosome-mediated miR-144-3p promotes ferroptosis to inhibit osteosarcoma proliferation, migration, and invasion through regulating ZEB1. Mol Cancer. 2023;22(1):113. [21] ZHANG R, PAN T, XIANG Y, et al. Curcumenol triggered ferroptosis in lung cancer cells via lncRNA H19/miR-19b-3p/FTH1 axis. Bioact Mater. 2022;13:23-36. [22] SEAL RL, CHEN L, GRIFFITHS‐JONES S, et al. A guide to naming human non‐coding RNA genes. EMBO J. 2020;39(6):e103777. [23] LOGANATHAN T, DOSS C GP. Non-coding RNAs in human health and disease: Potential function as biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023;23(1):33. [24] SALMENA L, POLISENO L, TAY Y, et al. A ceRNA hypothesis: The rosetta stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell. 2011;146(3): 353-358. [25] THOMSON DW, DINGER ME. Endogenous microRNA sponges: Evidence and controversy. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17(5): 272-283. [26] H K, ML S, XA Z, et al. Crosstalk among circRNA/lncRNA, miRNA, and mRNA in osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 773140. [27] LU S, LIU Z, QI M, et al. Ferroptosis and its role in osteoarthritis: Mechanisms, biomarkers, and therapeutic perspectives. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024;12:1510390. [28] ROCHETTE L, DOGON G, RIGAL E, et al. Lipid peroxidation and iron metabolism: Two corner stones in the homeostasis control of ferroptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):449. [29] LIU Y, ZHANG Z, FANG Y, et al. Ferroptosis in osteoarthritis: Current understanding. J Inflamm Res. 2024;17:8471-8486. [30] DOWDLE WE, NYFELER B, NAGEL J, et al. Selective VPS34 inhibitor blocks autophagy and uncovers a role for NCOA4 in ferritin degradation and iron homeostasis in vivo. Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16(11):1069-1079. [31] SUN K, HOU L, GUO Z, et al. JNK-JUN-NCOA4 axis contributes to chondrocyte ferroptosis and aggravates osteoarthritis via ferritinophagy. Free Radic Biol Med. 2023; 200:87-101. [32] ZHENG J, CONRAD M. The metabolic underpinnings of ferroptosis. Cell Metab. 2020;32(6):920-937. [33] LIANG D, MINIKES AM, JIANG X. Ferroptosis at the intersection of lipid metabolism and cellular signaling. Mol Cell. 2022;82(12): 2215-2227. [34] NAKAMURA H, TAKADA K. Reactive oxygen species in cancer: Current findings and future directions. Cancer Sci. 2021;112(10): 3945-3952. [35] CHEN X, LI J, KANG R, et al. Ferroptosis: Machinery and regulation. Autophagy. 2021;17(9):2054-2081. [36] LIU J, KANG R, TANG D. Signaling pathways and defense mechanisms of ferroptosis. FEBS J. 2022;289(22):7038-7050. [37] WENZEL SE, TYURINA YY, ZHAO J, et al. PEBP1 wardens ferroptosis by enabling lipoxygenase generation of lipid death signals. Cell. 2017;171(3):628-641.e26. [38] CHU B, KON N, CHEN D, et al. ALOX12 is required for p53-mediated tumour suppression through a distinct ferroptosis pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(5):579-591. [39] YAN B, AI Y, SUN Q, et al. Membrane damage during ferroptosis is caused by oxidation of phospholipids catalyzed by the oxidoreductases POR and CYB5R1. Mol Cell. 2021;81(2):355-369.e10. [40] COSTA I, BARBOSA DJ, BENFEITO S, et al. Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and their involvement in brain diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 2023; 244: 108373. [41] LI J, CAO F, YIN HL, et al. Ferroptosis: Past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(2):88. [42] ZHANG LH, TANG M, TAO X, et al. Covalent targeting of glutamate cysteine ligase to inhibit glutathione synthesis. ChemBioChem. 2023;24(23):e202300371. [43] LIU Z, LV X, SONG E, et al. Fostered Nrf2 expression antagonizes iron overload and glutathione depletion to promote resistance of neuron-like cells to ferroptosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020;407:115241. [44] YANG WS, STOCKWELL BR. Ferroptosis: Death by lipid peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol. 2016;26(3):165-176. [45] VUČKOVIĆ A, BOSELLO TRAVAIN V, BORDIN L, et al. Inactivation of the glutathione peroxidase GPx4 by the ferroptosis‐inducing molecule RSL3 requires the adaptor protein 14‐3‐3ε. FEBS Lett. 2020;594(4):611-624. [46] INGOLD I, BERNDT C, SCHMITT S, et al. Selenium utilization by GPX4 is required to prevent hydroperoxide-induced ferroptosis. Cell. 2018;172(3):409-422.e21. [47] LI W, LIANG L, LIU S, et al. FSP1: A key regulator of ferroptosis. Trends Mol Med. 2023;29(9):753-764. [48] YOSHIOKA H, KAWAMURA T, MUROI M, et al. Identification of a small molecule that enhances ferroptosis via inhibition of ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (FSP1). ACS Chem Biol. 2022;17(2):483-491. [49] MAO C, LIU X, ZHANG Y, et al. DHODH-mediated ferroptosis defence is a targetable vulnerability in cancer. Nature. 2021; 593(7860):586-590. [50] SOULA M, WEBER RA, ZILKA O, et al. Metabolic determinants of cancer cell sensitivity to canonical ferroptosis inducers. Nat Chem Biol. 2020;16(12):1351-1360. [51] YAN R, LIN B, JIN W, et al. NRF2, a superstar of ferroptosis. Antioxid Basel Switz. 2023; 12(9):1739. [52] KOPPULA P, LEI G, ZHANG Y, et al. A targetable CoQ-FSP1 axis drives ferroptosis- and radiation-resistance in KEAP1 inactive lung cancers. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1): 2206. [53] WANG X, LIU Z, PENG P, et al. Astaxanthin attenuates osteoarthritis progression via inhibiting ferroptosis and regulating mitochondrial function in chondrocytes. Chem Biol Interact. 2022;366:110148. [54] YANG T, YANG X, WANG G, et al. Unraveling the crucial role of SDF-1 in osteoarthritis progression: IL6/HIF-1α positive feedback and chondrocyte ferroptosis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025;152:114400. [55] GUO Z, LIN J, SUN K, et al. Deferoxamine alleviates osteoarthritis by inhibiting chondrocyte ferroptosis and activating the Nrf2 pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13: 791376. [56] XU J, RUAN Z, GUO Z, et al. Inhibition of SAT1 alleviates chondrocyte inflammation and ferroptosis by repressing ALOX15 expression and activating the Nrf2 pathway. Bone Jt Res. 2024;13(3):110-123. [57] TAO L, YANG K, WANG K, et al. NOX1-mediated oxidative stress induces chondrocyte ferroptosis by inhibiting the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1): 19877. [58] HE Q, YANG J, PAN Z, et al. Biochanin a protects against iron overload associated knee osteoarthritis via regulating iron levels and NRF2/system xc-/GPX4 axis. Biomed Pharmacother. Biomedecine Pharmacother. 2023;157:113915. [59] ZHOU X, ZHENG Y, SUN W, et al. D-mannose alleviates osteoarthritis progression by inhibiting chondrocyte ferroptosis in a HIF-2α-dependent manner. Cell Prolif. 2021; 54(11):e13134. [60] ZHAO C, SUN G, LI Y, et al. Forkhead box O3 attenuates osteoarthritis by suppressing ferroptosis through inactivation of NF-κB/MAPK signaling. J Orthop Transl. 2023;39: 147-162. [61] SUN J, SONG X, WANG C, et al. Geniposidic acid alleviates osteoarthritis progression through inhibiting inflammation and chondrocytes ferroptosis. J Cell Mol Med. 2024;28(8):e18228. [62] XIAO J, LUO C, LI A, et al. Icariin inhibits chondrocyte ferroptosis and alleviates osteoarthritis by enhancing the SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;133:112010. [63] HU Z, CHEN L, ZHAO J, et al. Lipoxin A4 ameliorates knee osteoarthritis progression in rats by antagonizing ferroptosis through activation of the ESR2/LPAR3/Nrf2 axis in synovial fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Redox Biol. 2024;73:103143. [64] RUAN Q, WANG C, ZHANG Y, et al. Ruscogenin attenuates cartilage destruction in osteoarthritis through suppressing chondrocyte ferroptosis via Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 2024;388:110835. [65] LV M, CAI Y, HOU W, et al. The C5AR1/TNFSF13B axis alleviates osteoarthritis by activating the PI3K/akt/GSK3β/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway to inhibit ferroptosis. Exp Cell Res. 2024;441(2):114195. [66] HE Q, LIN Y, CHEN B, et al. Vitamin K2 ameliorates osteoarthritis by suppressing ferroptosis and extracellular matrix degradation through activation GPX4’s dual functions. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomedecine Pharmacother. 2024;175: 116697. [67] HE R, WEI Y, PENG Z, et al. α-ketoglutarate alleviates osteoarthritis by inhibiting ferroptosis via the ETV4/SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling pathway. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024; 29(1):88. [68] KONG R, JI L, PANG Y, et al. Exosomes from osteoarthritic fibroblast-like synoviocytes promote cartilage ferroptosis and damage via delivering microRNA-19b-3p to target SLC7A11 in osteoarthritis. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1181156. [69] WANG D, FANG Y, LIN L, et al. Upregulating miR-181b promotes ferroptosis in osteoarthritic chondrocytes by inhibiting SLC7A11. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023; 24(1):862. [70] MA F, WANG L, CHI H, et al. Exploring the therapeutic potential of MIR-140-3p in osteoarthritis: Targeting CILP and ferroptosis for novel treatment strategies. Cell Prolif. 2025;58(11):e70018. [71] ZHOU M, ZHAI C, SHEN K, et al. miR-1 inhibits the ferroptosis of chondrocyte by targeting CX43 and alleviates osteoarthritis progression. J Immunol Res. 2023;2023: 2061071. [72] XUE J, MIN Z, XIA Z, et al. The hsa-miR-181a-5p reduces oxidation resistance by controlling SECISBP2 in osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):355. [73] YU Q, XIAO Y, GUAN M, et al. Regulation of ferroptosis in osteoarthritis and osteoarthritic chondrocytes by typical MicroRNAs in chondrocytes. Front Med. 2024;11:1478153. [74] HAO R, GE J, SONG X, et al. Cadmium induces ferroptosis and apoptosis by modulating miR-34a-5p/Sirt1axis in PC12 cells. Environ Toxicol. 2022;37(1):41-51. [75] WANG Y, HU K, LIAO C, et al. Exosomes-shuttled lncRNA SNHG7 by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells alleviates osteoarthritis through targeting miR-485-5p/FSP1 axis-mediated chondrocytes ferroptosis and inflammation. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2024;21(8):1203-1216. [76] ZHU C, CHEN B, HE X, et al. LncRNA MEG3 suppresses erastin-induced ferroptosis of chondrocytes via regulating miR-885-5p/SLC7A11 axis. Mol Biol Rep. 2024;51(1):139. [77] GU Y, WANG G, CHEN P. GAS5 long non-coding RNA interacts with microRNA-205 to relieve fibroblast-like synoviocyte inflammation and ferroptosis in osteoarthritis. Apoptosis. 2025;30(1-2): 320-333. [78] YU B, ZENG A, LIU H, et al. LncRNA HOXA11-AS intercepts the POU2F2-mediated downregulation of SLC3A2 in osteoarthritis to suppress ferroptosis. Cell Signal. 2024; 124: 111399. [79] YANG T, YANG G, WANG G, et al. Bioinformatics identification and integrative analysis of ferroptosis-related key lncRNAs in patients with osteoarthritis. Biosci Rep. 2023;43(9):BSR20230255. [80] HE C, ZENG Z, YANG Y, et al. Silencing of CircTRIM25/miR-138-5p/CREB1 axis promotes chondrogenesis in osteoarthritis. Autoimmunity. 2024;57(1):2361749. [81] CHEN Z, HUANG Y, CHEN Y, et al. CircFNDC3B regulates osteoarthritis and oxidative stress by targeting miR-525-5p/HO-1 axis. Commun Biol. 2023;6(1):200. [82] ZHU H, ZHU S, SHANG X, et al. Exhausting circ_0136474 and restoring miR-766-3p attenuate chondrocyte oxidative injury in IL-1β-induced osteoarthritis progression through regulating DNMT3A. Front Genet. 2021;12:648709. [83] NAKAMURA A, ALI SA, KAPOOR M. Antisense oligonucleotide-based therapies for the treatment of osteoarthritis: Opportunities and roadblocks. Bone. 2020; 138:115461. [84] LI Y, ZHAO J, GUO S, et al. siRNA therapy in osteoarthritis: Targeting cellular pathways for advanced treatment approaches. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1382689. [85] ZHU W, YANG X, LIU S, et al. Lentivirus‐based shRNA of caspase‐3 gene silencing inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis and delays the progression of surgically induced osteoarthritis. Biotechnol J. 2024;19(1): 2300031. [86] CHEN H, LI Z, LI X, et al. Biomaterial-based gene delivery: Advanced tools for enhanced cartilage regeneration. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023;17:3605-3624. |
| [1] |
Dong Chunyang, Zhou Tianen, Mo Mengxue, Lyu Wenquan, Gao Ming, Zhu Ruikai, Gao Zhiwei.
Action mechanism of metformin combined with Eomecon chionantha Hance dressing in treatment of deep second-degree burn wounds#br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2001-2013.
|
| [2] | Yang Xuetao, Zhu Menghan, Zhang Chenxi, Sun Yimin, Ye Ling. Applications and limitations of antioxidant nanomaterials in oral cavity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2044-2053. |
| [3] | Tao Daiju, Su Haiyu, Wang Yuqi, Shen Zhiqiang, He Bo . Construction and identification of stable PC12 cell lines with high/low expression of miR-122-5p [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1790-1799. |
| [4] | Liu Anting, Lu Jiangtao, Zhang Wenjie, He Ling, Tang Zongsheng, Chen Xiaoling. Regulation of AMP-activated protein kinase by platelet lysate inhibits cadmium-induced neuronal apoptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1800-1807. |
| [5] | Lyu Guoqing, Aizimaitijiang·Rouzi, Xiong Daohai. Irisin inhibits ferroptosis in human articular chondrocytes: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1359-1367. |
| [6] | Zhang Qian, Huang Dongfeng. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis combined with machine learning to screen and validate biomarkers for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1096-1105. |
| [7] | Bu Yangyang, Ning Xinli, Zhao Chen. Intra-articular injections for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the temporomandibular joint: different drugs with multiple combined treatment options [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1215-1224. |
| [8] | Zou Rongji, Yu Fangfang, Wang Maolin, Jia Zhuopeng. Triptolide inhibits ferroptosis and improves cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat model of cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 873-881. |
| [9] | Yang Xiao, Bai Yuehui, Zhao Tiantian, Wang Donghao, Zhao Chen, Yuan Shuo. Cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: mechanisms and regenerative challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 926-935. |
| [10] | Dong Chao, Zhao Mohan, Liu Yunan, Yang Zeli, Chen Leqin, Wang Lanfang. Effects of magnetic nano-drug carriers on exercise-induced muscle injury and inflammatory response in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 345-353. |
| [11] | Li Jiayin, Sui Lei, Li Yanjing. microRNA-146a regulates bone metabolism and its application in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(18): 4702-4712. |
| [12] | Yu Le, Nan Songhua, Shi Zijian, He Qiqi, Li Zhenjia, Cui Yinglin. Mechanisms underlying mitophagy, ferroptosis, cuproptosis, and disulfidptosis in Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4446-4456. |
| [13] | Liu Annan, Li Jianhui, Gao Wei, Li Xue, Song Jing, Xing Liping, Li Honglin. Bibliometric analysis of ferroptosis and Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4278-4288. |
| [14] | Chen Xinlong, Meng Tao, Wang Yaomin, Zhang Kefan, Li Jian, Shi Hui, Zhang Chenchen. Ferroptosis inhibitors in the treatment of osteoarthritis: diversity and multitarget characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4166-4179. |
| [15] | Huang Lei, Wang Xianghong, Zhang Xianxu, Li Shicheng, Luo Zhiqiang. Mechanism and therapeutic potential of nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 in regulating non-infectious spinal diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(15): 3971-3982. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||