Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (17): 4517-4528.doi: 10.12307/2026.100
Previous Articles Next Articles
Dandeng Tongnao soft capsules against ischemic stroke: fingerprinting and network pharmacological analysis of efficacy and mechanism of action
Wu Xue1, Zhang Linao1, Luo Shifang1, Liu Feifan1, Wan Yan1, Bai Yuanmei1, Cao Julin2, Xie Yuhuan1, Guo Peixin1
- 1Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China; 2China Shineway Pharmaceutical Group Limited, Shijiazhuang 051430, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2025-03-19Accepted:2025-06-24Online:2026-06-18Published:2025-12-04 -
Contact:Xie Yuhuan, PhD, Professor, Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Wu Xue, MS candidate, Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:Key Laboratory of Formulated Granules of Yunnan Province, No. 202105AG070014 (to XYH [project participant]); State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine High-level Construction Discipline of Dai Medicine, No. zyzdxk-2023192 (to GPX [project participant]); Yunnan Provincial Department of Education Scientific Research Fund Project, No. 2024Y359 (to WX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Xue, Zhang Linao, Luo Shifang, Liu Feifan, Wan Yan, Bai Yuanmei, Cao Julin, Xie Yuhuan, Guo Peixin. Dandeng Tongnao soft capsules against ischemic stroke: fingerprinting and network pharmacological analysis of efficacy and mechanism of action[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4517-4528.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
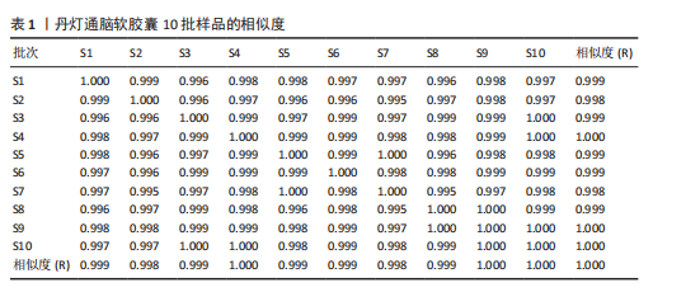
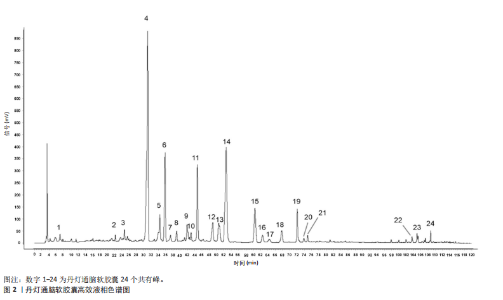
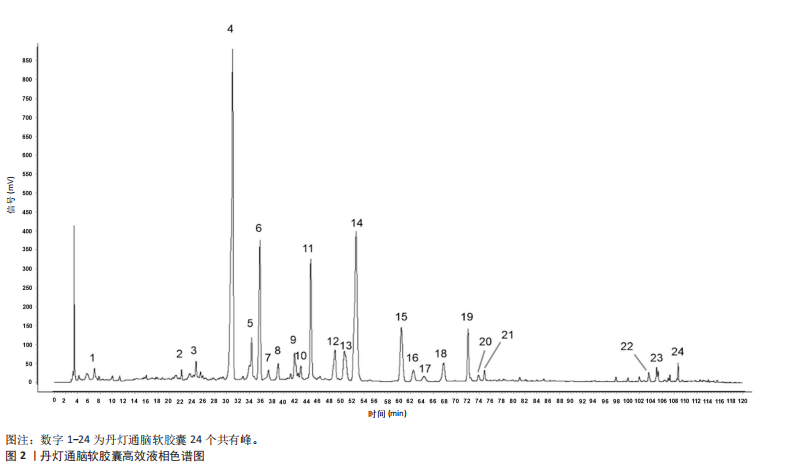
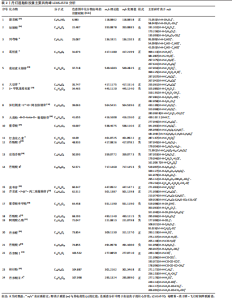
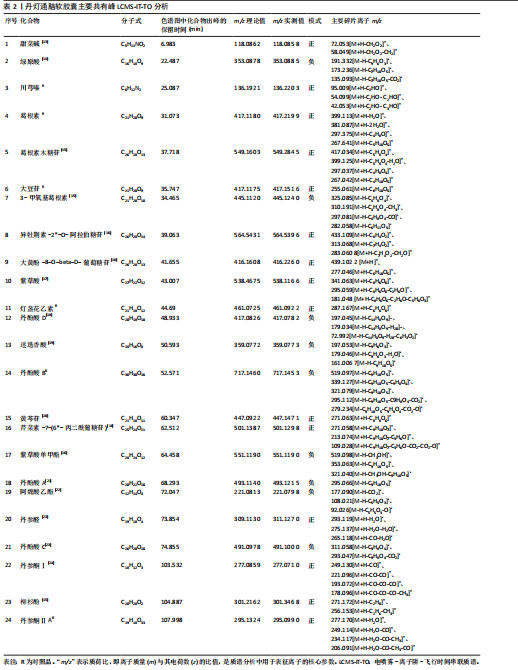
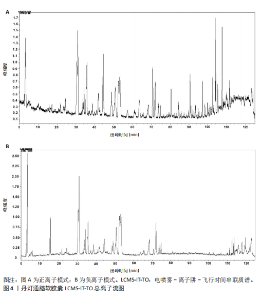
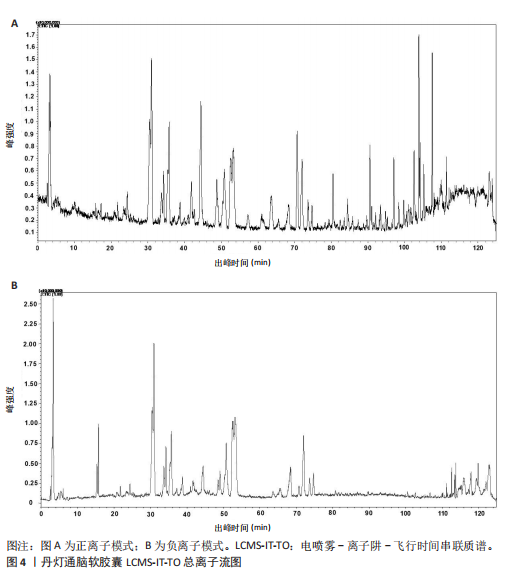
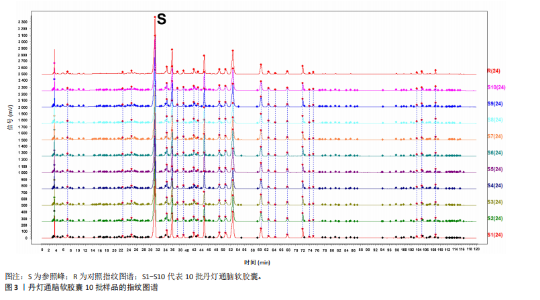
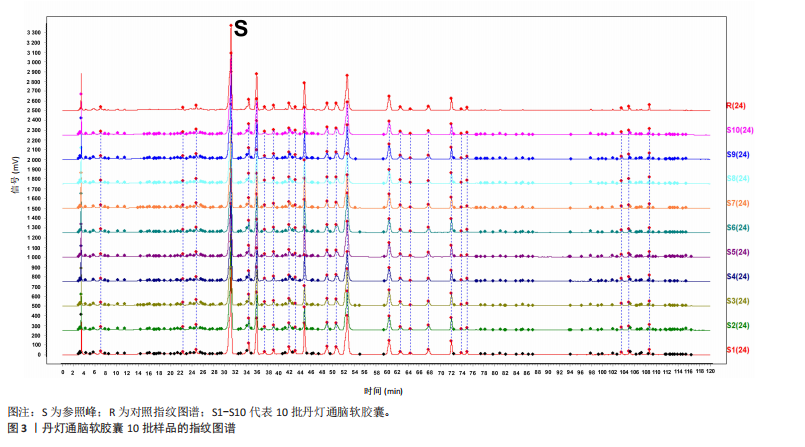
2.1 指纹图谱结果 2.1.1 指纹图谱建立和共有峰标定 指纹图谱共生成24个共有峰,通过混合对照品的色谱采集结果(图1),确定峰3,4,6,11,14,24分别为川芎嗪、葛根素、大豆苷、灯盏花乙素、丹酚酸B、丹参酮ⅡA(图2)。 2.1.2 相似度评价 将10批DDTN 胶囊品与对照指纹图谱进行相似度评价分析,结果显示10批基准样品相似度评价结果均> 0.9,这说明不同批次DDTN样品具有较好的一致性(表1、图3)。 2.1.3 LCMS-IT-TO鉴定丹灯通脑软胶囊指纹图谱共有峰化学成分 丹灯通脑软胶囊复方的已知活性成分包含川芎中的川芎嗪,葛根中的葛根素和大豆苷,丹参中的丹参酮ⅡA和丹酚酸B,以及灯盏细辛中的灯盏花乙素。上述成分具有明确的抗缺血性脑卒中活性。 文章除通过混合对照品色谱采集确定的共有峰3,4,6,11,14,24分别为川芎嗪、葛根素、大豆苷、灯盏花乙素、丹酚酸B、丹参酮ⅡA外,通过LCMS-IT-TOF法对DDTN样品指纹图谱共有峰进行指认,根据色谱峰保留行为、特征碎片峰、精确分子质量,参考已有文献报道的处方中单味药材化学成分数据和在线数据库[13-24],鉴定共有峰1,2,5,7,8,9,10,12,13,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23分别为甜菜碱、绿原酸、葛根素木糖苷、3’-羟基葛根素、异牡荆素-2’’-O-阿拉伯糖苷、大黄酚-8-O-beta-D-葡萄糖苷、紫草酸、丹酚酸D、迷迭香酸、黄芩苷、芹菜素-7-(6’’-丙二酰葡糖苷)、紫草酸单甲酯、丹酚酸A、阿魏酸乙酯、丹参醛、丹酚酸C、丹参酮Ⅰ、柳杉酚,见表2,图4。"
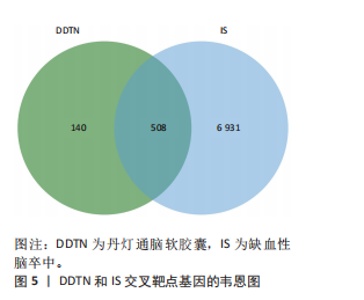
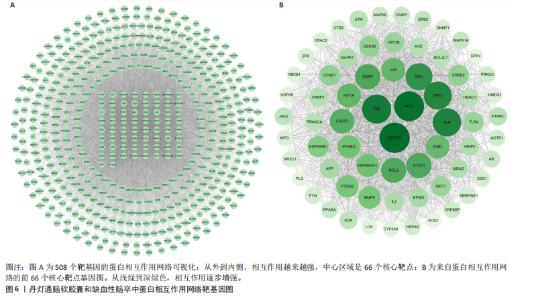
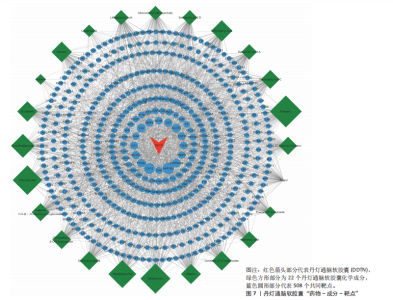
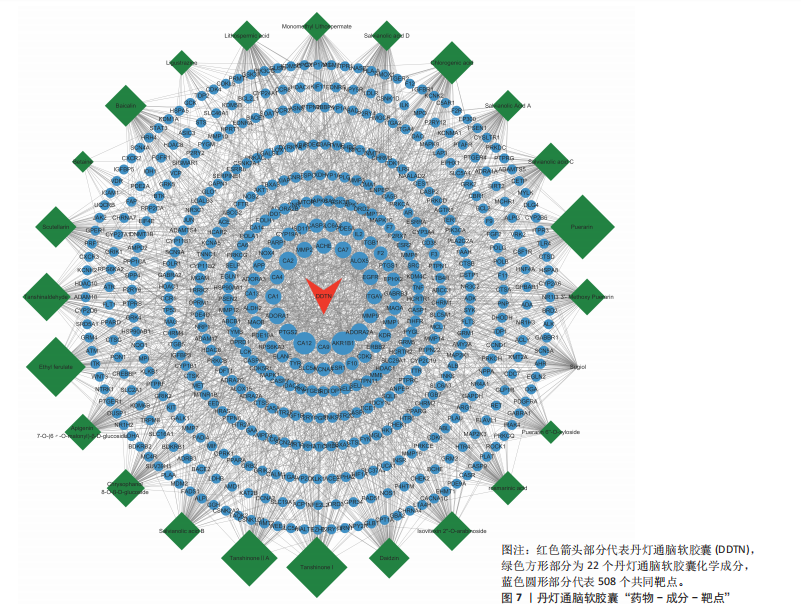
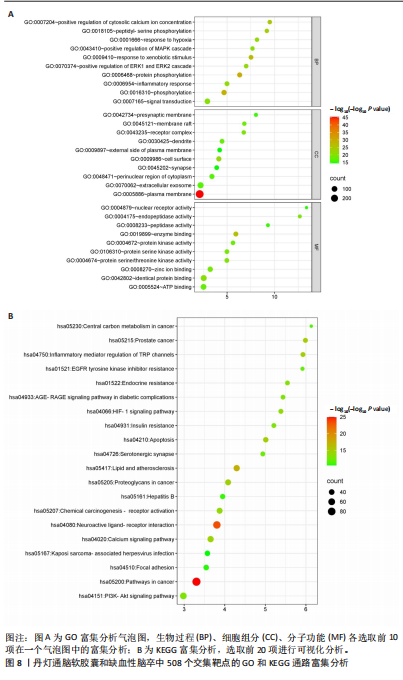
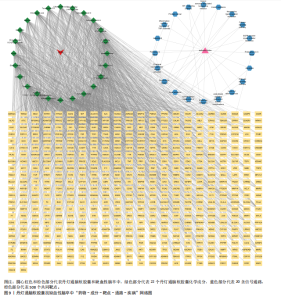
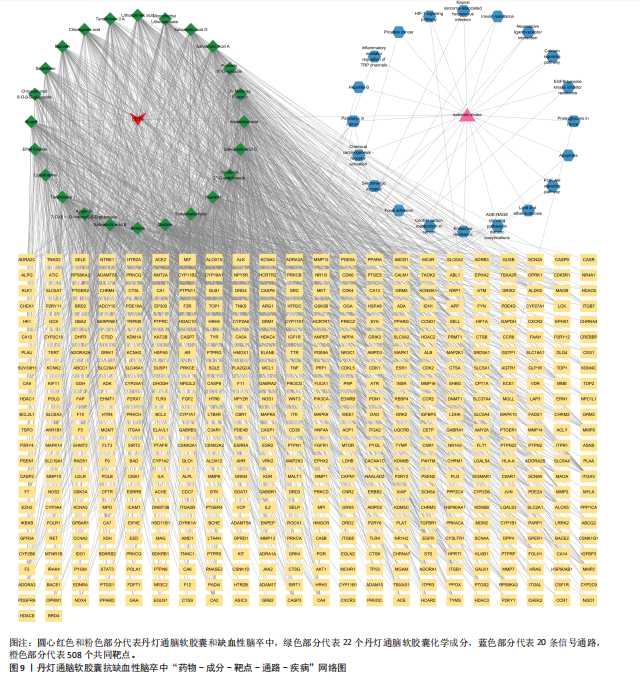
2.2 网络药理学结果 2.2.1 DDTN共有峰成分靶点和疾病靶点 将24个共有峰成分的648个靶点与缺血性脑卒中的7 440个靶点取交集,构建韦恩图,见图5,结果得到508个共同靶点。 2.2.2 蛋白相互作用网络分析 将韦恩绘图平台获得的508个潜在作用靶点导入到String数据库当中,设置蛋白物种为“Homo sapiens”进行检索,点击“Continue”,将最小相互作用阈值设置为Highest Confidence(0.4),隐藏彼此间无连接的蛋白,其余设置均为默认,之后将网络数据以TSV文件格式进行下载,之后导入Cytoscape 3.10.1软件中构建蛋白相互作用网络,见图6A。通过Centiscape 2.2插件中的度中心性、中介中心性、接近中心性值来评估其拓扑特征,以中位数为标准,即度中心性≥66.78、中介中心性≥591.765 407、接近中心性≥0.000 928,筛选得到66个关键靶点,见图6B。结果显示,甘油醛-3-磷酸脱氢酶(GAPDH)、丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶1(AKT1)、肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)、肿瘤蛋白 p53(TP53)、白蛋白(ALB)和非受体酪氨酸激酶(SCR)等靶点为核心靶点。 2.2.3 “药物-成分-靶点”网络的构建 通过Cytoscape 3.10.1软件构建“药物-成分-靶点”网络图,见图7。该网络包含533个节点和1 888条边。其中葛根素、丹参酮Ⅰ、阿魏酸乙酯、丹参酮ⅡA、丹参醛的Betweennss值排名前5,分别为32 849,30 803,30 027,28 063,23 100,这些化合物可能是DDTN抗缺血性脑卒中的关键成分。 2.2.4 富集分析 GO富集共筛选出1 680个条目,生物过程、细胞组分、分子功能条目分别为1 196、169、315条。将所得的GO条目根据P值进行降序排列,生物过程、细胞组分、分子功能分别选取前10个条目,导入微生信网站作图,绘制成富集气泡图,见图8A。其中生物过程主要包括蛋白质磷酸化、对异生物刺激的反应、细胞膜钙离子浓度的正向调节等;细胞组分主要包括质膜、细胞表面、受体复合物等;分子功能主要涉及酶结合、同种蛋白结合、蛋白丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶活性等。KEGG通路富集分析筛选出201个KEGG富集条目,根据P值筛选出前20条密切相关的通路,见图8B。结果显示,DDTN抗缺血性脑卒中的主要富集通路为低氧诱导因子1(hypoxia inducible factor-1,HIF-1)信号通路、高级糖基化终末产物-受体(advanced glycation end products-receptor for advanced glycation end products,AGE-RAGE)信号通路、磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B(phosphoinositide 3 kinase/protein kinase B,PI3K/AKT)信号通路。 取显著性前20条的KEGG通路构建“药物-成分-靶点-通路-疾病”网络,见图9。其中圆心红色部分代表DDTN,圆心粉色部分代表缺血性脑卒中,绿色部分代表22个DDTN化学成分,蓝色部分代表20条信号通路,橙色部分代表508个共同靶点。说明DDTN抗缺血性脑卒中的药理过程涉及多成分、多靶点以及多途径。"
| [1] RANDOLPH SA. Ischemic Stroke. Workplace Health Saf. 2016;64(9):444. [2] 柴高峰,张青萍.活血化瘀法治疗缺血性卒中临床研究进展[J].中医药临床杂志, 2018,30(8):1397-1400. [3] 冯桂丽. “丹灯通脑软胶囊”的临床应用[J].中国实用医药,2014,9(4):177. [4] 李菲,郑国成,屈云萍,等.丹灯通脑胶囊剂的临床应用概况[J].中国民族民间医药,2016,25(13):35-37+41. [5] 吴文玉,陈浩,焦欣,等.丹灯通脑软胶囊及其组方化学成分与分析方法研究进展[J].药学研究,2024,43(7): 677-683. [6] ZHANG Q, YAO M, QI J, et al. Puerarin inhibited oxidative stress and alleviated cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1134380. [7] LIN YL, TSAY HJ, LAI TH, et al. Lithospermic acid attenuates 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridine-induced neurotoxicity by blocking neuronal apoptotic and neuroinflammatory pathways. J Biomed Sci. 2015;22(1):37. [8] KUMAR G, MUKHERJEE S, PALIWAL P, et al. Neuroprotective effect of chlorogenic acid in global cerebral ischemia-reperfusion rat model. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2019;392(10):1293-1309. [9] LEE JC, PARK JH, PARK OK, et al. Neuroprotective effects of tanshinone I from Danshen extract in a mouse model of hypoxia-ischemia. Anat Cell Biol. 2013; 46(3):183-190. [10] AREFNEZHAD R, NEJABAT A, BEHJATI F, et al. Tanshinone IIA Against Cerebral Ischemic Stroke and Ischemia- Reperfusion Injury: A Review of the Current Documents. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024;24(18):1701-1709. [11] 赵丽萍,张琳成,陈冰,等.丹参酮ⅡA对脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠神经保护作用的研究[J].中华中医药学刊,2019,37(9): 2082-2085. [12] 李岩.灯盏花乙素调控NOX2治疗脑缺血再灌注损伤的作用机制研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2017. [13] MIKOŁAJCZYK-BATOR K, BŁASZCZYK A, CZYŻNIEJEWSKI M, et al. Identification of saponins from sugar beet (Beta vulgaris) by low and high-resolution HPLC-MS/MS. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2016;1029-1030:36-47. [14] YANG J, YAO L, GONG K, et al. Identification and Quantification of Chlorogenic Acids from the Root Bark of Acanthopanax gracilistylus by UHPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry. ACS Omega. 2022;7(29):25675-25685. [15] 孙志,赵灵灵,左莉华,等.UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS鉴定丹灯通脑软胶囊中多种化学成分[J].中国现代应用药学,2019, 36(2):191-199. [16] KIM S, CHEN J, CHENG T, et al. PubChem 2023 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023; 51(D1):D1373-D1380. [17] LIN LZ, HARNLY J. Identification of the phenolic components of arnica flowers (Arnica montana L.) by LC‐DAD‐ESI/MS. FASEB J. 2007;21(5):AQ316. [18] LIU AH, GUO H, YE M, et al. Detection, characterization and identification of phenolic acids in Danshen using high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2007;1161(1-2):170-182. [19] 刘静,霍志鹏,田介峰,等.迷迭香酸及咖啡酸的ESI四级杆飞行时间高分辨质谱裂解规律研究[J].化工与医药工程,2023, 44(3):29-34. [20] HAN YK, KIM H, SHIN H, et al. Characterization of Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Constituents from Scutellaria baicalensis Using LC-MS Coupled with a Bioassay Method. Molecules. 2020; 25(16):3617. [21] 谢家丽,黄艳萍,孙佳,等.蓖麻叶HPLC指纹图谱建立及化学成分鉴定[J].中药材,2022,45(9):2170-2176. [22] 蔡嵘鑫.基于UPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS/MS技术研究中药酚酸RAF抗氧化机制[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2020. [23] ZHAO X, YANG DH, XU F, et al. The in vivo absorbed constituents and metabolites of Danshen decoction in rats identified by HPLC with electrospray ionization tandem ion trap and time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Biomed Chromatogr. 2015; 29(2):285-304. [24] 戴海学,李晓蓉,李宇航,等.丹参酮ⅡA和丹参酮Ⅰ的电子轰击与电喷雾电离质谱分析[J].分析试验室,2008,27(5):24-29. [25] CAO Y, LI Y, HE C, et al. Selective Ferroptosis Inhibitor Liproxstatin-1 Attenuates Neurological Deficits and Neuroinflammation After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurosci Bull. 2021;37(4): 535-549. [26] LIU J, WANG F, SHENG P, et al. A network-based method for mechanistic investigation and neuroprotective effect on treatment of tanshinone Ⅰ against ischemic stroke in mouse. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;272: 113923. [27] ZOU X, GAO S, LI J, et al. A monoamine oxidase B inhibitor ethyl ferulate suppresses microglia-mediated neuroinflammation and alleviates ischemic brain injury. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1004215. [28] CHEN B, CHEN Z, LIU M, et al. Inhibition of neuronal ferroptosis in the acute phase of intracerebral hemorrhage shows long-term cerebroprotective effects. Brain Res Bull. 2019;153:122-132. [29] FEI YX, WANG SQ, YANG LJ, et al. Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (Danshen) extract attenuates permanent cerebral ischemia through inhibiting platelet activation in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017;207:57-66. [30] LI Y, LIU Y, WU P, et al. Inhibition of Ferroptosis Alleviates Early Brain Injury After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage In Vitro and In Vivo via Reduction of Lipid Peroxidation. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021;41(2):263-278. [31] NAKAJIMA H, KUBO T, IHARA H, et al. Nuclear-translocated Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase Promotes Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase-1 Activation during Oxidative/Nitrosative Stress in Stroke. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(23): 14493-14503. [32] TAO J, CUI Y, DUAN Y, et al. Puerarin attenuates locomotor and cognitive deficits as well as hippocampal neuronal injury through the PI3K/Akt1/GSK-3β signaling pathway in an in vivo model of cerebral ischemia. Oncotarget. 2017;8(63): 106283-106295. [33] QIU J, WANG YH, WANG XM, et al. PI3Kδ inhibition alleviates the brain injury during cerebral ischemia reperfusion via suppressing pericyte contraction in a TNF-α dependent manner. Exp Neurol. 2024;375:114728. [34] CHEN J, ZHANG DM, FENG X, et al. TIGAR inhibits ischemia/reperfusion-induced inflammatory response of astrocytes. Neuropharmacology. 2018;131:377-388. [35] MAO S, HU Y, ZHENG X, et al. Correlation Analysis of Neutrophil/Albumin Ratio and Leukocyte Count/Albumin Ratio with Ischemic Stroke Severity. Cardiol Cardiovasc Med. 2023;7(1):32-38. [36] IDICULA TT, WAJE-ANDREASSEN U, BROGGER J, et al. Serum albumin in ischemic stroke patients: the higher the better. The Bergen Stroke Study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2009;28(1):13-17. [37] WU Y, SPAN LM, NYGREN P, et al. The Tyrosine Kinase c-Src Specifically Binds to the Active Integrin αIIbβ3 to Initiate Outside-in Signaling in Platelets. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(25):15825-15834. [38] WANG XY, WANG YJ, HOU ZL, et al. Ingenane-type diterpenoids inhibit non-small cell lung cancer cells by regulating SRC/PI3K/Akt pathway. Nat Prod Res. 2024;38(19):3460-3465. [39] LEY K. Fueling the fire: Src family kinases drive inflammation. J Exp Med. 2014; 211(10):1922. [40] LIU XS, CHOPP M, ZHANG RL, et al. MicroRNA profiling in subventricular zone after stroke: MiR-124a regulates proliferation of neural progenitor cells through Notch signaling pathway. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23461. [41] 朱迎春.基于PI3K/Akt/mT0R信号通路研究丹参酮ⅡA对脑梗死后的神经保护调控机制[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2017. [42] FENG C, WAN H, ZHANG Y, et al. Neuroprotective Effect of Danhong Injection on Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats by Activation of the PI3K-Akt Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:298. [43] XIA T, ZHANG Z, ZHAO Y, et al. The anti-diabetic activity of polyphenols-rich vinegar extract in mice via regulating gut microbiota and liver inflammation. Food Chem. 2022; 393:133443. [44] 张娟利,李骅,王文军,等.基于网络药理学探讨丹参-丹皮配伍抗脑缺血损伤的作用机制[J].天然产物研究与开发, 2021,33(1):103-113+149. [45] LIU M, ZHAO X, MA Z, et al. Discovery of potential Q-marker of traditional Chinese medicine based on chemical profiling, chemometrics, network pharmacology, and molecular docking: Centipeda minima as an example. Phytochem Anal. 2022; 33(8):1225-1234. |
| [1] | Jiang Xianglong, Li Zhongshan, Che Tongtong. Application effects and mechanisms of low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields in muscle repair and growth [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2350-2360. |
| [2] | Wang Zheng, Cheng Ji, Yu Jinlong, Liu Wenhong, Wang Zhaohong, Zhou Luxing. Progress and future perspectives on the application of hydrogel materials in stroke therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2081-2090. |
| [3] | Chen Yulin, He Yingying, Hu Kai, Chen Zhifan, Nie Sha Meng Yanhui, Li Runzhen, Zhang Xiaoduo , Li Yuxi, Tang Yaoping. Effect and mechanism of exosome-like vesicles derived from Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim. in preventing and treating atherosclerosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1768-1781. |
| [4] | Zhou Sirui, Xu Yukun, Zhao Kewei. Ideas and methods of anti-melanogenesis of Angelica dahurica extracellular vesicles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1747-1754. |
| [5] | Tao Daiju, Su Haiyu, Wang Yuqi, Shen Zhiqiang, He Bo . Construction and identification of stable PC12 cell lines with high/low expression of miR-122-5p [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1790-1799. |
| [6] | Peng Zhiwei, Chen Lei, Tong Lei. Luteolin promotes wound healing in diabetic mice: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1398-1406. |
| [7] | Chen Yixian, Chen Chen, Lu Liheng, Tang Jinpeng, Yu Xiaowei. Triptolide in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 805-815. |
| [8] | Zhao Yu, Xue Yun, Huang Jiajun, Wu Diyou, Yang Bin, Huang Junqing. Total flavonoids from Semen Cuscutae inhibits osteoblast apoptosis in hormone-induced femoral head avascular necrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4289-4298. |
| [9] | Wu Yilin, Tian Hongying, Sun Jiale, Jiao Jiajia, Zhao Zihan, Shao Jinhuan, Zhao Kaiyue, Zhou Min, Li Qian, Li Zexin, Yue Changwu. Intervention effect and mechanism of Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae in a mouse model of breast hyperplasia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4377-4389. |
| [10] | Zhou Wu, Zhang Jingxin, Liu Yuancheng, Hu Chenglong, Wang Siqi, Xu Jianxia, Huang Hai, Wei Sixi. Treatment of acute myeloid leukemia with corynoline: network pharmacology analysis of potential mechanisms and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4088-4104. |
| [11] | Jiang Huanhuan, Mu Sheng, Ma Wenxin, Liu Chang, Liu Ziyu, Pu Jing, Zhu Xiangdong, Hui Hong, Ma Huiming. Mechanism of multi-target intervention of the active ingredient of Allii Tuberosi Semen in rats with oligoasthenozoospermia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 3044-3057. |
| [12] | Xu Sheng, Zhang Wenwen, Zhang Weiwei, Wang Hongtao, Zhang Jun, Yang Ruisheng, Yuan Yuan, Wang Li, Hao Haihu. Network pharmacological analysis and experimental verification of semen cuscutae in treating postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2702-2711. |
| [13] |
Zhang Yueting, Li Jinglin, Fu Zhenyi, Yan Fei, Gao Yu, Liu Jiaxin.
Endoplasmic reticulum stress promotes ferroptosis and aggravates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury#br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2806-2813.
|
| [14] | Zhou Xinying, Sun Xinyue, Zhu Wenhao. Insulin-like growth factors and ischemic stroke: a genome-wide association analysis in European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2909-2919. |
| [15] | Wang Zheng, Cheng Ji, Yu Jinlong, Liu Wenhong, Wang Zhaohong, Zhou Luxing. Progress and future perspectives on the application of hydrogel materials in stroke therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-10. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||