Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (17): 4529-4541.doi: 10.12307/2026.139
Previous Articles Next Articles
Visual analysis of cuproptosis research: global landscape of hotspots and frontiers
Li Ruiying1, Xia Hong2
- 1Forth Clinical School, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100176, China; 2School of Biomedical Engineering, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100069, China
-
Received:2025-04-24Accepted:2025-08-10Online:2026-06-18Published:2025-12-05 -
Contact:Xia Hong, PhD, Associate professor, School of Biomedical Engineering, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100069, China -
About author:Li Ruiying, Forth Clinical School, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100176, China -
Supported by:the National Research Association of Computer Basic Education in Colleges and Universities of China, No. 2024-AFCEC-105 (to XH); the Scientific Research and Innovation Project of Capital Medical University, No. XSKY2024160 (to XH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Ruiying, Xia Hong. Visual analysis of cuproptosis research: global landscape of hotspots and frontiers[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4529-4541.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
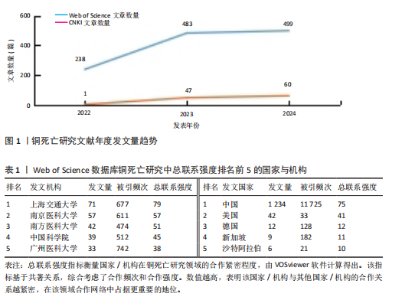
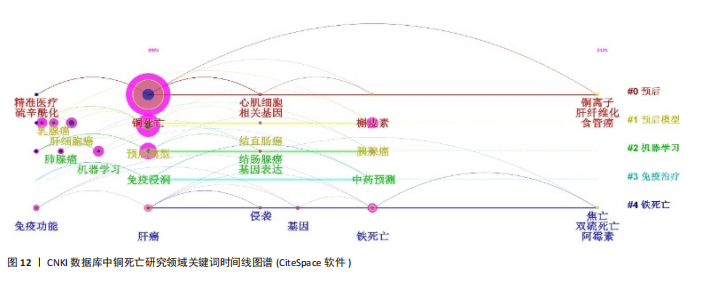
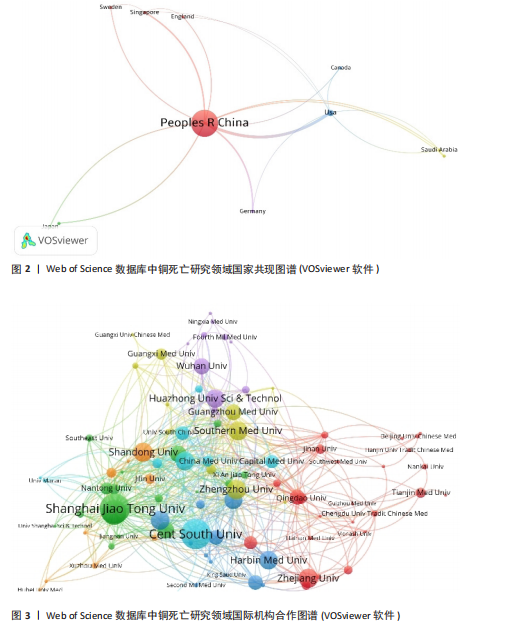
2.1 文献发表量年度变化趋势分析 结合铜死亡研究年度发文趋势(图1),Web of Science核心合集数据库文献量从2022年的238篇增至2023年的483篇(+103%),2024年达499篇,显示该领域在2023年进入爆发期后仍保持强劲增速。CNKI数据库文献量则从2022年的1篇骤增至2023年47篇(47倍),2024年升至60篇,反映中文研究快速跟进。截至2025年1月,Web of Science(43篇)、CNKI(7篇)单月发文量仍处高位,印证铜死亡作为新型细胞死亡机制的研究热度在全球持续攀升。 2.2 国际与国内机构合作格局分析 为深入探究铜死亡研究领域的国际合作态势及国内机构的合作特点,分别基于Web of Science和CNKI数据库,运用VOSviewer和CiteSpace软件,构建并解读了国家共现网络、国际机构合作网络及国内机构合作网络。 2.2.1 Web of Science数据库国家合作网络分析 国家合作图谱(图2、表1)定量揭示了全球铜死亡研究的空间分布特征。中国以1 234篇发文量(占比68.3%)、总联系强度75和极高被引频次(11 725)的绝对优势占据网络枢纽地位,节点辐射范围覆盖德国、新加坡等主要合作伙伴,形成以中国为核心的合作网络。对比特征显示,美国虽以42篇发文量位居第二,但其文章数量少,且与中国直接合作稀疏(连线权重< 5),提示两国在该领域的合作还有较大的空间。 2.2.2 Web of Science数据库机构合作网络分析 国际机构合作图谱(图3)呈现出全球铜死亡研究机构间复杂的合作网络。图中节点代表机构,节点大小与机构发文量呈正比,线条连接代表机构间存在合作关系,线条粗细与机构合作强度呈正比,线条颜色用于区分不同机构之间的合作关系。在全球机构合作网络中,中国的研究机构占据了主导地位。上海交通大学和中南大学是图中最为突出的两个节点,节点体积显著偏大,表明这两所大学在全球铜死亡研究机构中具有极高的发文量和影响力。同时,图中也显示上海交通大学和中南大学与诸多其他机构存在合作连线,例如浙江大学、复旦大学、南京医科大学等中国顶尖高校,以及部分国外机构,预示着中国机构在铜死亡研究领域的强大实力和广泛的合作网络。结合表1的数据进一步验证了这一结论:上海交"
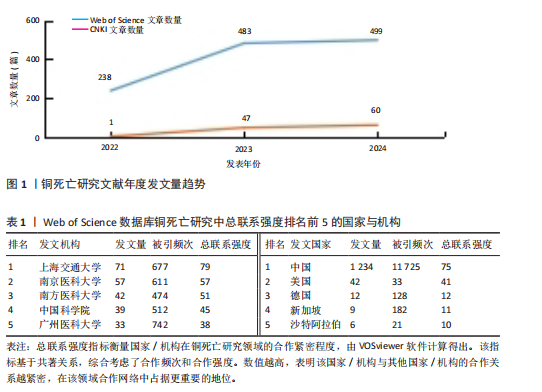
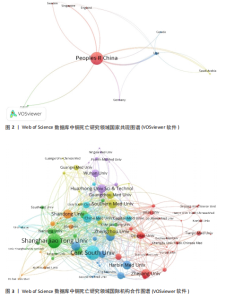
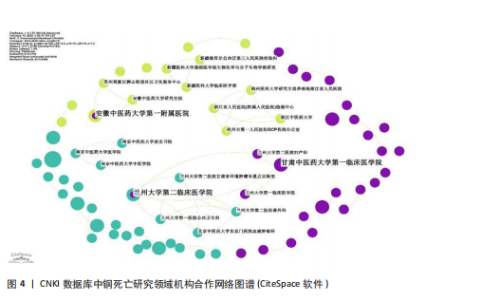
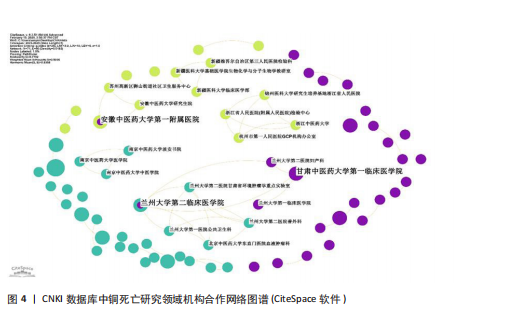
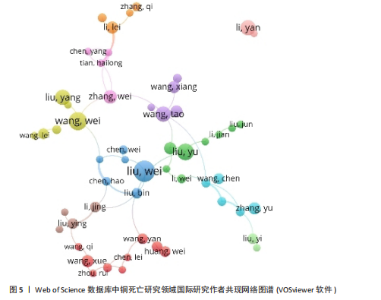
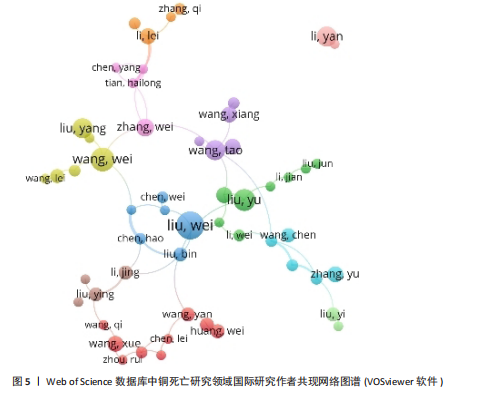
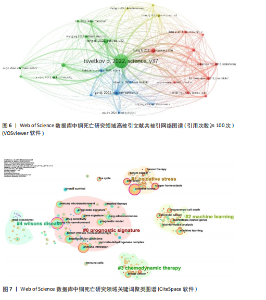
通大学的发文量为71篇,总联系强度高达79,中南大学的发文量同样为71篇,被引频次更是达到了984次,总联系强度为30。这些数据均表明,中国顶尖高校在全球铜死亡研究领域中扮演着至关重要的角色,并构建了以中国机构为核心的国际合作网络。 2.2.3 CNKI机构合作网络分析 机构合作网络图谱(图4)展现了CNKI数据库中中国机构在“铜死亡”研究领域的合作态势。与VOSviewer类似,CiteSpace的节点也代表发文机构,节点大小都与机构发文量呈正比,连线的线条粗细都与机构合作强度呈正比。与全球合作图谱有所区别的是,CNKI图谱中节点体积最大的机构并非上海交通大学或中南大学等顶尖高校,而是安徽中医药大学第一附属医院和甘肃中医药大学第一临床医学院。这两个机构的节点颜色也显著区别于其他机构,呈现出相对独立的紫色,表明这两所中医药大学附属医院可能更侧重于探索中医药在铜死亡研究中的应用,并初步形成了自身的研究特色与机构合作网络。从CNKI发文机构前5的数据来看,也印证了中医药大学在该领域占有一定席位,但各机构的发文量均相对有限。发文量排名前5的机构中,发文量最高的广西中医药大学仅为3篇,其余如广西中医药大学第一附属医院、黑龙江中医药大学、贵州中医药大学药学院、广西中医药大学附属瑞康医院等均为2篇。然而,结合Web of Science的分析结果可以发现,国内顶尖高校在铜死亡研究的国际合作网络中已占据核心地位,并与众多国内机构开展了合作。这实际上反映了国内机构在铜死亡研究领域的广泛参与和合作,尽管这些合作成果更多地体现在被Web of Science数据库收录的英文文献中,而非主要收录中文文献的CNKI数据库。 2.3 Web of Science数据库国际研究作者共现网络分析 国际研究作者合作共现网络图谱(图5)显示中国作者在铜死亡领域国际合作网络中占主导地位。为识别核心作者,基于普莱斯"
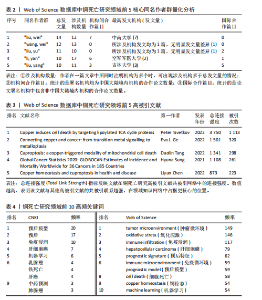
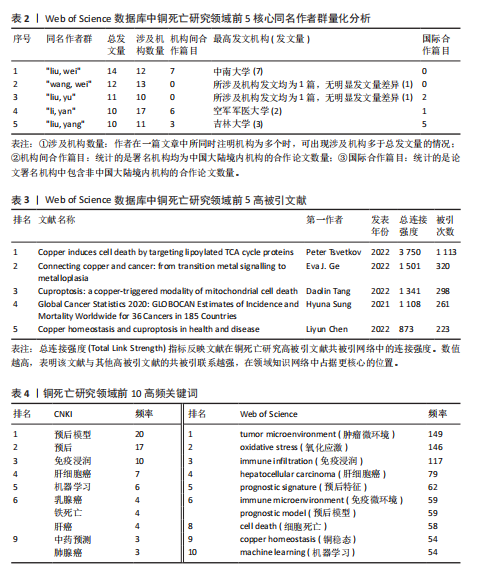
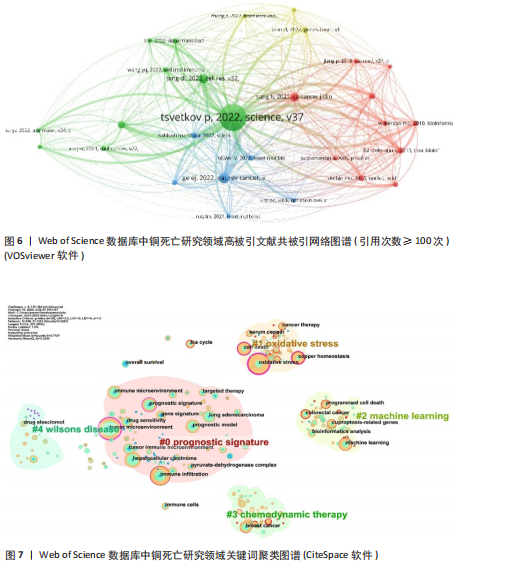
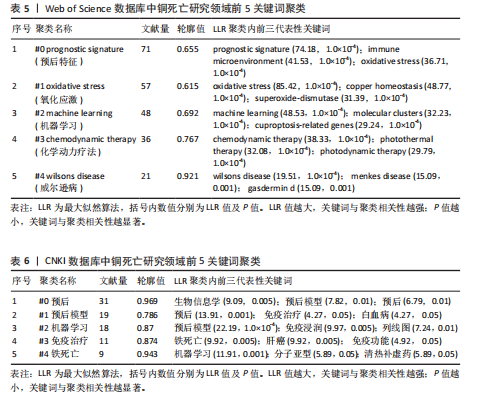
定律和发文量阈值(≥3篇),识别出349位核心作者。基于姓名聚合,可能包含同名研究者。Web of Science数据库中铜死亡文献前5同名作者群量化分析(表2)总结了发文特征。国际作者共现综合体现了各“同名作者群”的分散性、中国科研机构的广泛参与及部分合作性、研究主题高度聚焦于铜死亡在肿瘤领域的重要性,以及铜死亡研究的综合交叉性。 2.4 高被引文献共被引网络分析 以引证次数为100进行数据筛选,从38 692个参考文献中挑选出满足阈值的28条文献记录,生成高被引文献共被引网络图谱(引用次数≥100次)(图6)。从图谱中可以看到,节点体积最大的文献是Tsvetkov P等于2022年发表在《Science》上的文章[2],位于整个共被引网络的核心位置,被引频次也遥遥领先于其他文献,总连接强度也高达3 750,表明其在铜死亡研究领域中具有奠基性和核心地位。 表3为铜死亡领域被引次数前5的高被引文献。2022年发表于《Nature Reviews Cancer》的综述和2022年发表于《Cell Research》的文章分别位列共被引频次第2名和第3名[28-29],其节点在图谱中也相对较大,并与发表于《Science》的文章存在强连接[2],表明这些高被引文献之间存在紧密的学术关联,共同构筑了铜死亡研究领域的核心知识框架。此外,2021年发表的全球癌症统计报告[30]、2015年发表的免疫浸润分析方法学文章[31],以及2013年发表的基因集变异分析方法学文章等[32],虽并非直接聚焦于铜死亡机制,但因其在肿瘤研究领域或生物信息学分析方法学上的广泛影响力,同样被铜死亡研究领域的高被引文献网络所引用,并在图谱中占据了一席之地。 2.5 铜死亡关键词分析 2.5.1 关键词词频分析 关键词词频的多维对比(表4)清晰刻画了铜死亡研究的中外协同与分异特征。共性层面,CNKI与Web of Science高频词共现“预后模型/预后”“机器学习”“肝细胞癌/乳腺癌”等关键词,初步体"
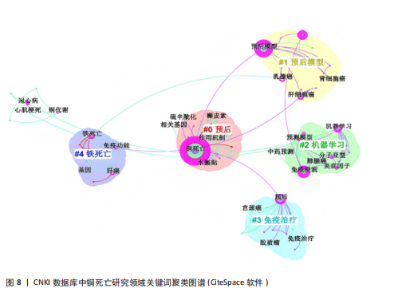
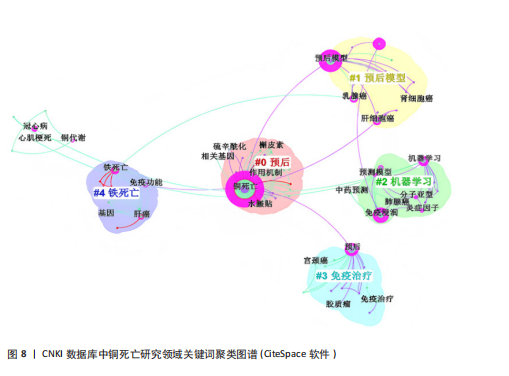
现了预后、机器学习与肿瘤研究为全球的核心主题,反映铜死亡研究临床转化导向与计算生物学方法的高度融合趋势。差异层面,Web of Science以“tumor microenvironment(肿瘤微环境)”“oxidative stress(氧化应激)”及“immune infiltration(免疫浸润)”凸显铜死亡分子机制解析(如铜稳态失衡诱导氧化损伤)与靶向治疗(如纳米催化疗法)的创新优势;而CNKI以“中药预测”(频次第9)等关键词,可反映出中医药在铜死亡研究中的潜在特色和本土化路径,尤其是在铜死亡相关免疫微环境重塑及中药活性成分(如肝豆扶木颗粒)的预后预测价值方面。 2.5.2 关键词聚类与共现分析 Web of Science关键词聚类图谱(图7)显示七大核心聚类(Q=0.419 2,S=0.718 7),其结构与铜死亡前5关键词聚类(表5)高度契合。最大聚类#0“prognostic signature(预后特征)”(Size=71)聚焦铜死亡相关预后生物标志物研究,关键词如tumor microenvironment (肿瘤微环境)、hepatocellular carcinoma (肝细胞癌)揭示铜死亡与疾病关联的核心地位。聚类#1“oxidative stress (氧化应激)”(Size=57)以oxidative stress (氧化应激)、copper homeostasis (铜稳态)等为关键词。方法学与应用方向分别由聚类#2“machine learning (机器学习)”(Size=48,含machine learning、bioinformatics analysis等)和#3“chemodynamic therapy (化学动力疗法,CDT)”(Size=36,含breast cancer、immune cells等)体现,显示机器学习在标志物筛选与CDT等化学疗法在乳腺癌免疫调控中的研究热点。值得注意的是,聚类#4“wilson’s disease (威尔逊病)”(Size=21,S=0.921)以铜代谢疾病模型为特色,关联drug elesclomol (药物艾司氯胺酮)与immune microenvironment (免疫微环境),反映药物干预铜死亡的临床探索。 CNKI聚类图谱(图8)呈现四大主题(Q=0.779 2,S=0.869 3),与Web"
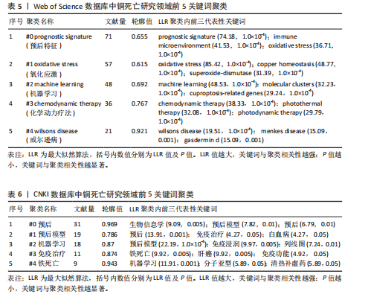
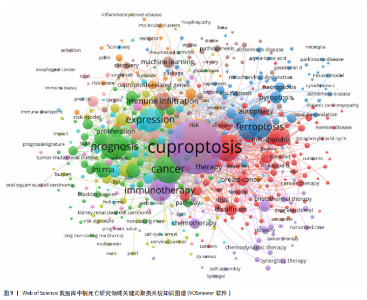
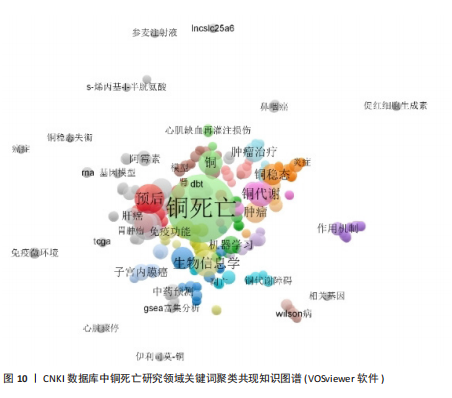
of Science形成互补。结合表6分析,核心聚类#0“预后应用机制”(Size=31,S=0.969)以“铜死亡”“预后”“肿瘤”为关键词,与Web of Science预后主题呼应,聚焦肝癌等肿瘤研究。聚类#1“预后模型”(Size=19)和#2“机器学习”(Size=18,S=0.87)细化研究方法,印证机器学习在预后模型构建中的跨平台重要性。特色聚类#3“免疫治疗”(Size=11,S=0.874)通过“免疫治疗”“铁死亡”等关键词,凸显对铜死亡联合免疫治疗及死亡方式互作的深度探索,尤其在肝癌领域形成研究侧重。 VOSviewer共现图谱(图9,10)进一步印证CiteSpace的分析结果,以“cuproptosis/铜死亡”为核心,通过网络结构直观呈现五大研究主题。Web of Science图谱(图9)聚焦"
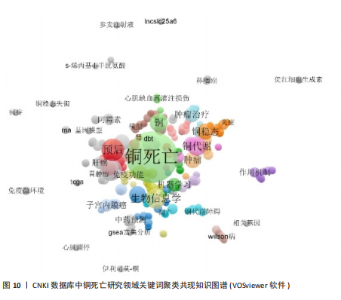
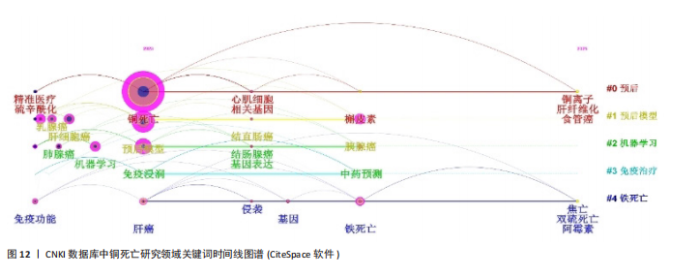
肿瘤预后与关联、死亡方式互作、免疫治疗与耐药机制、机器学习模型构建及肿瘤疾病研究,系统覆盖机制、治疗与方法。CNKI图谱(图10)在共性主题外,强化预后模型构建、中医药预测及心脏疾病探索,并以威尔逊病与铜代谢研究形成特色,展现跨学科整合潜力。 2.5.3 关键词时间线与突现分析 Web of Science时间线图谱(图11)显示,#0“prognostic signature(预后标志物)”研究持续至2025年且突现于2022年,印证其作为持续热点的核心地位;#1“oxidative stress(氧化应激)”、#2“machine learning(机器学习)”、#3“chemodynamic therapy(化学动力疗法)”均突现于2023年并延伸至2025年,揭示氧化应激机制、机器学习方法及化学疗法应用为新兴研究热点;#4“wilsons disease(威尔逊病)”虽时间线较短但突现于2022年,凸显铜代谢疾病模型的基础价值。在CNKI时间线图谱(图12)中,#0“预后”、#1“预后模型”、#2“机器学习”同步延伸至2025年(突现于2023年),与英文文献方向一致;#3“免疫治疗”"
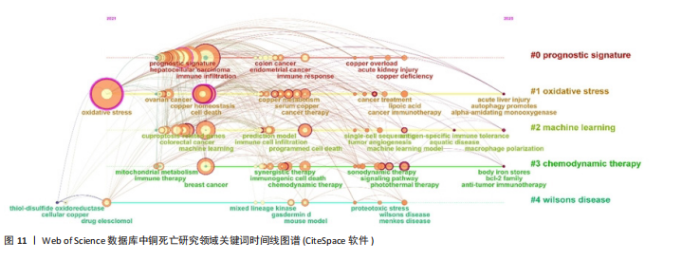
突现于2024年,反映治疗策略的快速迭代;#4“铁死亡”(突现于2023年)则体现在中文文献对铜死亡与铁死亡互作的特色关注,拓展细胞死亡机制交叉研究边界。 Web of Science数据库的铜死亡突现关键词图谱(图13)可以更直观地观察到不同时期英文研究热点的变迁。2022年是研究突现关键词最为集中的年份,包括“overall survival (总生存期)”“risk score(风险评分)”“tumor microenvironment(肿瘤微环境)”“gene signature(基因特征)”和“tumor immune microenvironment(肿瘤免疫微环境)”,这些关键词的突现强度较高,均超过3.0,特别是“overall survival(总生存期)”和“risk score(风险评分)”强度分别达到5.09和4.08,显示出极高的突现强度,然而这些突现关键词的持续时间较短,仅为1年,集中在2022年,表明2022年铜死亡研究领域在肿瘤预后预测、风险评估以及肿瘤微环境和基因特征的关联研究方面受到了高度关注,并迅速成为研究热点。2023年突现的关键词为“regulatory t-cells (调节性T细胞)”和“immunogenic cell death(免疫原性细胞死亡)”,突现强度相对降低,但提示铜死亡与免疫调节和免疫原性细胞死亡的关联性开始受到重视。2024年开始突现的关键词包括“photothermal therapy (光热疗法)”“signaling pathway (信"
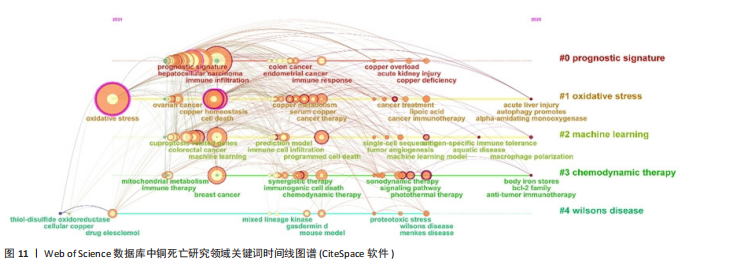

号通路)”和“regulated cell death (调节性细胞死亡)”,突现强度中等,且持续时间相对较长,为2年(2024-2025年),预示着光热疗法等新型治疗策略与铜死亡的结合、铜死亡的信号通路机制研究,以及作为一种受调控的细胞死亡形式的深入探索,可能成为未来一段时间内铜死亡研究的重点方向。 同样分析CNKI的突现关键词图谱(图14),2023年突现的中文关键词包括“胃癌”“免疫”和“肝细胞癌”,但其突现持续时间较短,仅为1年,暗示这些主题在2023年成为研究关注的焦点,但可能热度持续时间相对有限,或已被后续更受关注的方向所取代。相比之下,2024年开始突现的关键词,如“铁死亡”“中药预测”“基因”“冠心病”“铜代谢”“胰腺癌”和“心肌梗死”,其突现时间跨度为2024-2025年,表明这些方向代表了更近期且持续的研究兴趣点。虽然所有关键词的突现强度均相对温和,强度值均低于0.5,其中“胃癌”和“免疫”以0.49的强度并列最高,但整体趋势显示,铜死亡研究在2024年之后呈现出与铁死亡等其他细胞死亡方式的交叉研究、疾病预后的预测分析以及在更广泛疾病领域如心血管疾病和胰腺癌中探索应用潜力的趋势。"

| [1] CHEN Q, KANG J, FU C. The independence of and associations among apoptosis, autophagy, and necrosis. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2018;3:18. [2] TSVETKOV P, COY S, PETROVA B, et al. Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science. 2022;375(6586):1254-1261. [3] LI Y, HAN Y, SHU Q, et al. Cuproptosis and copper as potential mechanisms and intervention targets in Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Pharmacother. 2025;183:117814. [4] WANG S, LIU X, WEI D, et al. Polyvalent Aptamer Nanodrug Conjugates Enable Efficient Tumor Cuproptosis Therapy Through Copper Overload and Glutathione Depletion. J Am Chem Soc. 2024;146(44):30033-30045. [5] NOH D, LEE H, LEE S, et al. Copper-Based Nanomedicines for Cuproptosis-Mediated Effective Cancer Treatment. Biomater Res. 2024;28:0094. [6] ZHAO P, WANG H, ZHAO H, et al. Tumor microenvironment-reprogrammable CpG-templated copper sulfide loaded with disulfiram for sensitized cuproptosis immunotherapy. Chem Eng J. 2024;487:150524. [7] ZHANG J, ZHANG A, GUO Y, et al. Nanoparticle-Mediated Cuproptosis and Photodynamic Synergistic Strategy: A Novel Horizon for Cancer Therapy. Cancer Med. 2025;14(3):e70599. [8] SPRINGER C, HUMAYUN D, SKOUTA R. Cuproptosis: Unraveling the Mechanisms of Copper-Induced Cell Death and Its Implication in Cancer Therapy. Cancers (Basel). 2024;16(3):647. [9] XIAO C, WANG X, LI S, et al. A cuproptosis-based nanomedicine suppresses triple negative breast cancers by regulating tumor microenvironment and eliminating cancer stem cells. Biomaterials. 2025;313:122763. [10] 宋一博,郑才仕,周树锋.铜死亡在肿瘤治疗方面的研究进展[J].华侨大学学报(自然科学版),2023,44(6):671-675. [11] 高亚婷,曹泽如,郭秀丽,等.铜死亡在妇科恶性肿瘤中的研究进展[J].国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志,2024,43(1):74-78. [12] 要甜,马宇锋.铜死亡在口腔鳞状细胞癌治疗及预后中的研究进展[J].口腔医学, 2024,44(11):871-875. [13] 王俊峰,包仕廷.铜死亡在肝细胞癌中的作用机制及诊疗研究进展[J].肝胆胰外科杂志,2024,36(10):634-640. [14] 曾丹,孙晓杰,贾伟涛,等.铜死亡与肾细胞癌关系的研究进展[J].山东医药, 2023,63(31):107-111. [15] 张雅浏,敖经盛,张晓东.铜死亡机制及其在动脉硬化中的研究进展[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2024,32(10):890-898. [16] 张纪萌,谢昌材,罗耀文,等.铜死亡及铜代谢紊乱与神经退行性疾病的关系研究进展[J].空军军医大学学报,2025, 46(3):401-407. [17] 刘骏达,梁志超,王倩,等.铜死亡与铜代谢相关疾病研究进展[J].江苏大学学报(医学版),2022,32(4):318-325. [18] 叶涛,郑冀鲁,宋欣怡,等.基于铜死亡的癌症纳米疗法研究进展[J].生命科学, 2025,37(2):147-157. [19] 蔡林峻,彭婷,陈俊杰,等.铜死亡与铜载体药物抗肿瘤机制的研究进展[J].世界临床药物,2024,45(2):181-186. [20] REN X, ZHAO L, HAO Y, et al. Copper-instigated modulatory cell mortality mechanisms and progress in kidney diseases. Ren Fail. 2025;47(1):2431142. [21] SU Y, LIU B, WANG B, et al. Progress and Challenges in Tumor Ferroptosis Treatment Strategies: A Comprehensive Review of Metal Complexes and Nanomedicine. Small. 2024;20(25):e2310342. [22] XIONG F, ZHANG Y, LI T, et al. A detailed overview of quercetin: implications for cell death and liver fibrosis mechanisms. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15:1389179. [23] LI X, ZHU D. Role of disulfide death in cancer (Review). Oncol Lett. 2024;29(1):55. [24] CHEN L, SHEN Q, LIU Y, et al. Homeostasis and metabolism of iron and other metal ions in neurodegenerative diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025;10(1):31. [25] ZHANG L, DENG R, GUO R, et al. Recent progress of methods for cuproptosis detection. Front Mol Biosci. 2024;11:1460987. [26] CHEN C. Searching for intellectual turning points: progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004; 101 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):5303-5310. [27] VAN ECK NJ, WALTMAN L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. 2010;84(2):523-538. [28] GE EJ, BUSH AI, CASINI A, et al. Connecting copper and cancer: from transition metal signalling to metalloplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022;22(2):102-113. [29] TANG D, CHEN X, KROEMER G. Cuproptosis: a copper-triggered modality of mitochondrial cell death. Cell Res. 2022; 32(5):417-418. [30] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. [31] NEWMAN AM, LIU CL, GREEN MR, et al. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods. 2015;12(5):453-457. [32] HÄNZELMANN S, CASTELO R, GUINNEY J. GSVA: gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013;14:7. [33] LI D, JIN S, CHEN P, et al. Comprehensive analysis of cuproptosis-related lncRNAs for prognostic significance and immune microenvironment characterization in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Immunol. 2023;13:991604. [34] WANG X, JING H, LI H. A novel cuproptosis-related lncRNA signature to predict prognosis and immune landscape of lung adenocarcinoma. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023;12(2):230-246. [35] YAN JN, GUO LH, ZHU DP, et al. Clinical significance and potential application of cuproptosis-related genes in gastric cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023; 15(7):1200-1214. [36] ZHANG S, ZHANG L, LU H, et al. A cuproptosis and copper metabolism-related gene prognostic index for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Front Oncol. 2022;12:955336. [37] HUANG X, ZHOU S, TÓTH J, et al. Cuproptosis-related gene index: A predictor for pancreatic cancer prognosis, immunotherapy efficacy, and chemosensitivity. Front Immunol. 2022; 13:978865. [38] ZHOU C, JIN L, YU J, et al. Integrated analysis identifies cuproptosis-related gene DLAT and its competing endogenous RNAs network to predict the prognosis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024;103(9):e37322. [39] 安梦霞,王萍玉.基于铜死亡相关 LncRNAs 构建肺鳞癌预后预测模型[J]. 肿瘤防治研究,2023,50(11):1084-1090. [40] BHAT AA, AFZAL M, MOGLAD E, et al. lncRNAs as prognostic markers and therapeutic targets in cuproptosis-mediated cancer. Clin Exp Med. 2024; 24(1):226. [41] QIN Y, PU X, HU D, et al. Machine learning-based biomarker screening for acute myeloid leukemia prognosis and therapy from diverse cell-death patterns. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):17874. [42] LI C, ZHANG K, GONG Y, et al. Based on cuproptosis-related lncRNAs, a novel prognostic signature for colon adenocarcinoma prognosis, immunotherapy, and chemotherapy response. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14: 1200054. [43] ZHANG S, YU S, DUAN H, et al. Revealing prognostic and tumor microenvironment characteristics of cuproptosis in bladder cancer by genomic analysis. Front Genet. 2022;13:997573. [44] 孟云,李想,潘凯,等.铜死亡相关基因在肝细胞癌中的表达及其临床意义[J].中国普通外科杂志,2023,32(1):74-86. [45] LI W, XIAO Y, GUO G, et al. Cuprous oxide nanocomposites with photothermal (PTT) and chemical dynamics (CDT) effects induce cuproptosis in breast cancer using the strategy of increasing inflow and reducing outflow. Nano Today. 2024;56:102223. [46] TIAN Y, HE X, YUAN Y, et al. TME-Responsive Nanoplatform with Glutathione Depletion for Enhanced Tumor-Specific Mild Photothermal/Gene/Ferroptosis Synergistic Therapy. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19:9145-9160. [47] XIE D, HU C, ZHU Y, et al. Sequential Therapy for Osteosarcoma and Bone Regeneration via Chemodynamic Effect and Cuproptosis Using a 3D-Printed Scaffold with TME-Responsive Hydrogel. Small. 2025;21(5): e2406639. [48] 张保朝,罗超,彭涛,等.基于铜死亡相关基因的肾透明细胞癌中预后模型的构建与应用[J].临床泌尿外科杂志,2023, 38(12):934-941. [49] WU H, ZHANG Z, CAO Y, et al. A Self-Amplifying ROS-Responsive Nanoplatform for Simultaneous Cuproptosis and Cancer Immunotherapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(23):e2401047. [50] HUANG H, GUO H, LIU J, et al. Dendrimer/metal-phenolic nanocomplexes encapsulating CuO2 for targeted magnetic resonance imaging and enhanced ferroptosis/cuproptosis/chemodynamic therapy by regulating the tumor microenvironment. Acta Biomater. 2024;183:252-263. [51] 徐森磊,刘超,潘慧,等.瘤周围刺电针调控三阴性乳腺癌铜死亡增敏化疗疗效的作用研究[J].针刺研究,2024,49(11): 1153-1159. [52] 王飞,王春艳,郭晓燕,等.基于Fibro Touch技术探讨肝豆扶木颗粒干预痰瘀互结型WD患者肝纤维化及铜死亡相关指标的临床疗效[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2025,31(4):174-181. [53] CAO F, QI Y, WU W, et al. Single-cell and genetic multi-omics analysis combined with experiments confirmed the signature and potential targets of cuproptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11:1240390. [54] CHEN F, WEN X, WU J, et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Characteristics of Cuproptosis-Related LncRNAs Associated with Prognosis of Lung Adenocarcinoma and Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024;17(9):1244. [55] LIU T, WEI J. Validation of a Novel Cuproptosis-Related Prognostic Gene Marker and Differential Expression Associated with Lung Adenocarcinoma. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023;45(10):8502-8518. [56] 房慧琴,王静,郭晓慧,等.基于生物信息学探讨与铜死亡相关的早、晚期动脉粥样硬化的差异基因及潜在标志物[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2023,31(11):938-944. [57] 贺天文,朱浩彦,鲁志兵.不稳定动脉粥样硬化斑块中铜死亡相关特征基因的鉴定[J].武汉大学学报(医学版),2024, 45(6):681-687. [58] 张玉俊,李盼,姜苗苗,等.基于铜死亡相关长链非编码RNA的子宫颈癌预后模型构建及药物敏感性分析[J].实用肿瘤杂志,2024,39(2):111-123. [59] CHEN W, HU K, LIU Y, et al. Comprehensive analysis of cuproptosis-related genes involved in prognosis and tumor microenvironment infiltration of colorectal cancer. Transl Cancer Res. 2024;13(9):4555-4573. [60] CHEN K, ZHOU A, ZHOU X, et al. Cellular Trojan Horse initiates bimetallic Fe-Cu MOF-mediated synergistic cuproptosis and ferroptosis against malignancies. Sci Adv. 2024;10(15):eadk3201. [61] 具星,李丽,郑磊,等.基于生物信息学及单细胞测序构建心肌梗死与铜死亡相关基因的风险模型并探究其免疫机制[J].中国免疫学杂志,2024,40(11):2247-2256. [62] 农琛,韦春旭,覃智,等.铜死亡相关性lncRNA在甲状腺癌中的表达模式以及预后价值[J].右江民族医学院学报, 2023,45(3):384-395. [63] GONG H, LIU Z, YUAN C, et al. Identification of cuproptosis-related lncRNAs with the significance in prognosis and immunotherapy of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Comput Biol Med. 2024;171: 108198. [64] LIU S, GE J, CHU Y, et al. Identification of hub cuproptosis related genes and immune cell infiltration characteristics in periodontitis. Front Immunol. 2023;14: 1164667. [65] JIANG J, ZHAN X, WEI J, et al. Artificial intelligence reveals dysregulation of osteosarcoma and cuproptosis-related biomarkers, PDHA1, CDKN2A and neutrophils. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):4927. [66] ABADIN X, DE DIOS C, ZUBILLAGA M, et al. Neuroinflammation in Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases: Role of Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024;13(12):1440. [67] LI B, LI Z, QIAN Y, et al. The Convergence of Sonodynamic Therapy and Cuproptosis in the Dual-Responsive Biomimetic CytoNano for Precision Mitochondrial Intervention in Cancer Treatment. Nano Lett. 2024;24(26):8107-8116. [68] YU X, LI B, YAN J, et al. Cuproptotic nanoinducer-driven proteotoxic stress potentiates cancer immunotherapy by activating the mtDNA-cGAS-STING signaling. Biomaterials. 2024;307:122512. [69] NING S, LYU M, ZHU D, et al. Type-I AIE Photosensitizer Loaded Biomimetic System Boosting Cuproptosis to Inhibit Breast Cancer Metastasis and Rechallenge. ACS Nano. 2023;17(11):10206-10217. [70] LI J, TUO D, GUO G, et al. Aberrant expression of cuproptosisrelated gene LIPT1 is associated with metabolic dysregulation of fatty acid and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023; 149(17):15763-15779. [71] XUE Y, JIANG X, WANG J, et al. Effect of regulatory cell death on the occurrence and development of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Biomark Res. 2023;11(1):2. [72] TAPIERO H, TOWNSEND DM, TEW KD. Trace elements in human physiology and pathology. Copper. Biomed Pharmacother. 2003;57(9):386-398. [73] XU C, WEN S, DU X, et al. Targeting regulated cell death (RCD) with naturally derived sesquiterpene lactones in cancer therapy. Pharmacol Res. 2025;211:107553. [74] GAO L, ZHANG A. Copper-instigated modulatory cell mortality mechanisms and progress in oncological treatment investigations. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1236063. [75] LI J, CAO F, YIN HL, et al. Ferroptosis: past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(2):88. [76] XUE Q, KANG R, KLIONSKY DJ, et al. Copper metabolism in cell death and autophagy. Autophagy. 2023;19(8):2175-2195. [77] LI Y, DU Y, ZHOU Y, et al. Iron and copper: critical executioners of ferroptosis, cuproptosis and other forms of cell death. Cell Commun Signal. 2023;21(1):327. [78] OVERCHUK M, WEERSINK RA, WILSON BC, et al. Photodynamic and Photothermal Therapies: Synergy Opportunities for Nanomedicine. ACS Nano. 2023;17(9):7979-8003. [79] PASHOOTAN P, SAADATI F, FAHIMI H, et al. Metal-based nanoparticles in cancer therapy: Exploring photodynamic therapy and its interplay with regulated cell death pathways. Int J Pharm. 2024;649:123622. [80] XIA J, HU C, JI Y, et al. Copper-Loaded Nanoheterojunction Enables Superb Orthotopic Osteosarcoma Therapy via Oxidative Stress and Cell Cuproptosis. ACS Nano. 2023;17(21):21134-21152. [81] SONG S, QIU X, HUANG S, et al. Cystine-Modified Lignin-Copper Coordination Nanocarriers Improve the Therapeutic Efficacy of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition via Cuproptosis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025;17(6):9074-9086. [82] ZHANG H, DONG K, CHEN M, et al. Self-Boosting Cuproptosis-Based Synergistic Antitumor Therapy by GSH-Enhanced Cocatalysis and Copper Efflux Inhibition. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2024;7(16):19341-19354. [83] WU L, PI W, HUANG X, et al. Orchestrated metal-coordinated carrier-free celastrol hydrogel intensifies T cell activation and regulates response to immune checkpoint blockade for synergistic chemo-immunotherapy. Biomaterials. 2025;312:122723. [84] LI T, WANG D, MENG M, et al. Copper-Coordinated Covalent Organic Framework Produced a Robust Fenton-Like Effect Inducing Immunogenic Cell Death of Tumors. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2023; 44(11):e2200929. [85] PI W, WU L, LU J, et al. A metal ions-mediated natural small molecules carrier-free injectable hydrogel achieving laser-mediated photo-Fenton-like anticancer therapy by synergy apoptosis/cuproptosis/anti-inflammation. Bioact Mater. 2023;29: 98-115. [86] YANG P, YANG W, WEI Z, et al. Novel targets for gastric cancer: The tumor microenvironment (TME), N6-methyladenosine (m6A), pyroptosis, autophagy, ferroptosis and cuproptosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;163:114883. [87] CHENG Q, WANG W, LV Z, et al. Construction and validation of a prognostic and therapeutic cuproptosis- and immune-related gene signature in hepatocellular carcinoma. Transl Cancer Res. 2024;13(6):2629-2646. [88] SUN Z, CHEN X, HUANG X, et al. Cuproptosis and Immune-Related Gene Signature Predicts Immunotherapy Response and Prognosis in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Life (Basel). 2023;13(7):1583. [89] GAO X, HUANG H, PAN C, et al. Disulfiram/Copper Induces Immunogenic Cell Death and Enhances CD47 Blockade in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(19):4715. [90] 牙秋艳,曾文婷,韦云丽,等.糖尿病肾病中铜死亡相关基因的生物信息学分析及靶向中药预测[J].广西医学,2024, 46(8):1226-1235. [91] 卓桂锋,罗敏,姚晓燕,等.血管性痴呆铜死亡关键差异基因的生物信息学分析及防治中药筛选[J].中草药,2023, 54(21):7120-7129. |
| [1] | Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Yuping, Ba Yinying, Chi Li, Wang Wenjuan, Wang Jiajia. Research context and trend of TBK1 in autoimmunity, signaling pathways, gene expression, tumor prevention and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-11. |
| [2] | Zhu Xiaolong, Zhang Wei, Yang Yang. Visualization analysis of research hotspots and cutting-edge information in the field of intervertebral disc regeneration and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2391-2402. |
| [3] | Wen Fayan, Li Yan, Qiang Tianming, Yang Chen, Shen Linming, Li Yadong, Liu Yongming. Unilateral biportal endoscopic technology for treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases: global research status and changing trends [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2380-2390. |
| [4] | Huang Jie, Zeng Hao, Wang Wenchi, Lyu Zhucheng, Cui Wei. Visualization analysis of literature on the effect of lipid metabolism on osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1558-1568. |
| [5] | Zhang Haiwen, Zhang Xian, Xu Taichuan, Li Chao. Bibliometric and visual analysis of the research status and trends of senescence in osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1580-1591. |
| [6] | Yang Zeyu, Zhi Liang, Wang Jia, Zhang Jingyi, Zhang Qingfang, Wang Yulong, Long Jianjun. A visualized analysis of research hotspots in high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation from the macroscopic perspective [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1320-1330. |
| [7] | Peng Hao, Chen Qigang, Shen Zhen. A visual analysis of research hotspots of H-type vessels in various bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 760-769. |
| [8] | Zhang Anqi, Hua Haotian, Cai Tianyuan, Wang Zicheng, Meng Zhuo, Zhan Xiaoqian, Chen Guoqian . Pain after total knee arthroplasty: current status and trend analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 795-804. |
| [9] | Jiang Kan, Alimujiang·Abudourousuli, Shalayiding·Aierxiding, Aikebaierjiang·Aisaiti, Kutiluke·Shoukeer, Aikeremujiang·Muheremu. Biomaterials and bone regeneration: research hotspots and analysis of 500 influential papers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 528-536. |
| [10] | Wei Jingyi, Wang Xiaojing, Liu Xihua. Application trends of eye-tracking technology in rehabilitation: a visualization analysis based on CiteSpace and VOSviewer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4265-4277. |
| [11] | Liu Annan, Li Jianhui, Gao Wei, Li Xue, Song Jing, Xing Liping, Li Honglin. Bibliometric analysis of ferroptosis and Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4278-4288. |
| [12] | Zou Shunyi, Yi Jin, Zeng Hao, Li Jianqi, Wu Zhongping. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: visualization analysis of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4229-4239. |
| [13] | Wang Jingyi, An Shuai, Li Daoqin, He Tao, Feng Mingli, La Gaoyan, Li Zheng, Cheng Jingbo. Stepwise surgical treatment of knee osteoarthritis and the application trends of three surgical procedures: a bibliometric analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(15): 4010-4020. |
| [14] | Li Kanglin, Jiang Yongdong, Wu Yufeng. Visualization analysis of piriformis syndrome: research trends and hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2886-2895. |
| [15] | Xiao Meina, Jiang Chuanyin. Visualization analysis of whole-body vibration training: research progress, hotspots, and future trends [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2896-2908. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||