Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (17): 4289-4298.doi: 10.12307/2026.195
Total flavonoids from Semen Cuscutae inhibits osteoblast apoptosis in hormone-induced femoral head avascular necrosis
Zhao Yu1, Xue Yun1, Huang Jiajun1, Wu Diyou1, Yang Bin2, Huang Junqing2
- 1College of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China; 2Department of Pain, Henan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2025-08-05Accepted:2025-08-28Online:2026-06-18Published:2025-11-26 -
Contact:Huang Junqing, MS, Chief physician, Department of Pain, Henan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China -
About author:Zhao Yu, MS candidate, College of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:National Project for the Inheritance of Distinctive Traditional Chinese Medicine Clinical Techniques, No. [2019]36 (to YB); Traditional Chinese Medicine Young Talent Cultivation Project of Henan Province, No. [2021] 16 (Mentor: HJQ); Henan Science and Technology Think Tank Traditional Chinese Medicine Strong Province Strategy Research Base 2024 Annual Special Project, No. 23104007-2024 (to HJQ); Traditional Chinese Medicine Scientific Research Special Project of Henan Province, No. 2023ZY3013 (to HJQ); 2024 Traditional Chinese Medicine Scientific Research Special Project of Henan Province, No. 2024ZY2066 (to YB); Traditional Chinese Medicine Culture and Management Research Project of Henan Province, No. TCM2024027 (to YB); Henan University of Chinese Medicine 2024 Annual Postgraduate Research and Innovation Capacity Enhancement Program Project, Nos. 2024KYCX075 (to ZY), 2024SHDY012 (to XY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhao Yu, Xue Yun, Huang Jiajun, Wu Diyou, Yang Bin, Huang Junqing. Total flavonoids from Semen Cuscutae inhibits osteoblast apoptosis in hormone-induced femoral head avascular necrosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4289-4298.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
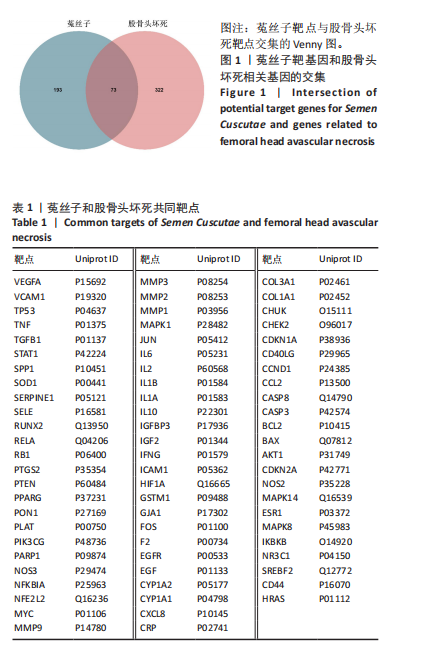
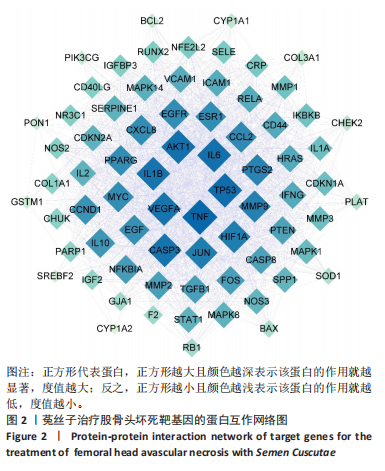
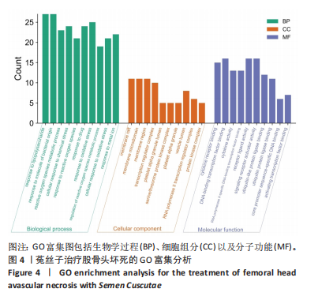
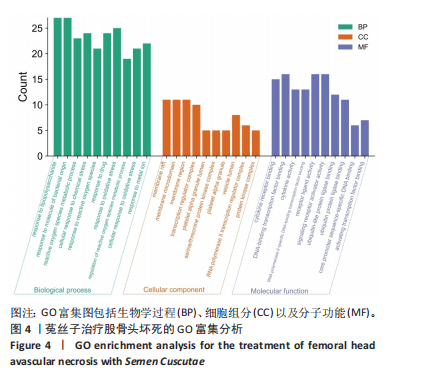
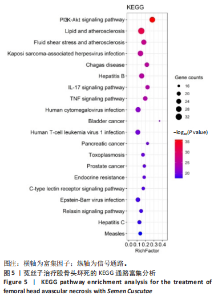
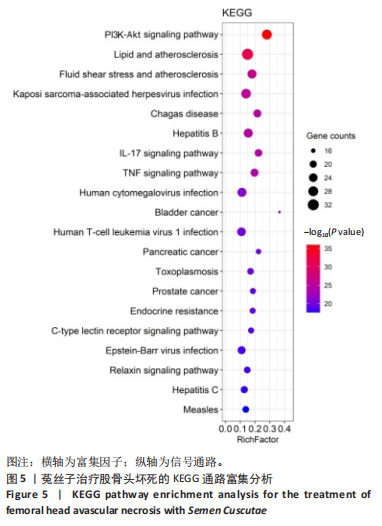
2.3 GO和KEGG的富集性分析 利用DAVID数据库得到GO功能1 731条(P < 0.05),其中生物过程(BP)1 633条、细胞组分(CC)22条,分子功能(76)条。分别从中选取排在前10位的条目进行可视化操作,见图4。运用R语言来进行有关KEGG信号通路的富集分析(绘制富集靶点数量最多的前20条通路)。结果发现,PI3K-Akt,AGE-RAGE信号以及白细胞介素17等信号通路是菟丝子治疗治疗股骨头坏死的潜在信号通路,见图5。 2.4 菟丝子总黄酮缓解了地塞米松对hFOB1.19细胞增殖的抑制作用 菟丝子总黄酮在一定范围内能促进hFOB1.19细胞的增殖,其质量浓度在100,200和400 μg/mL时促增殖效果与对照组(0 μg/mL)比较显"
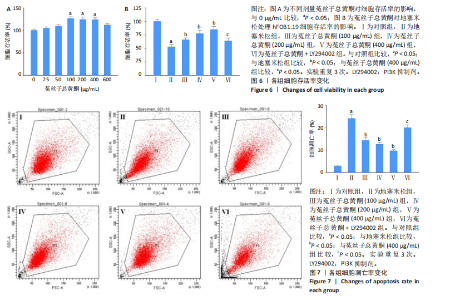
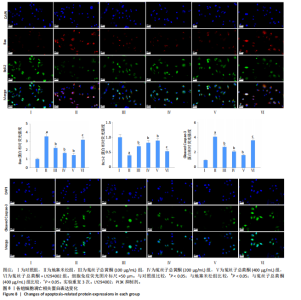
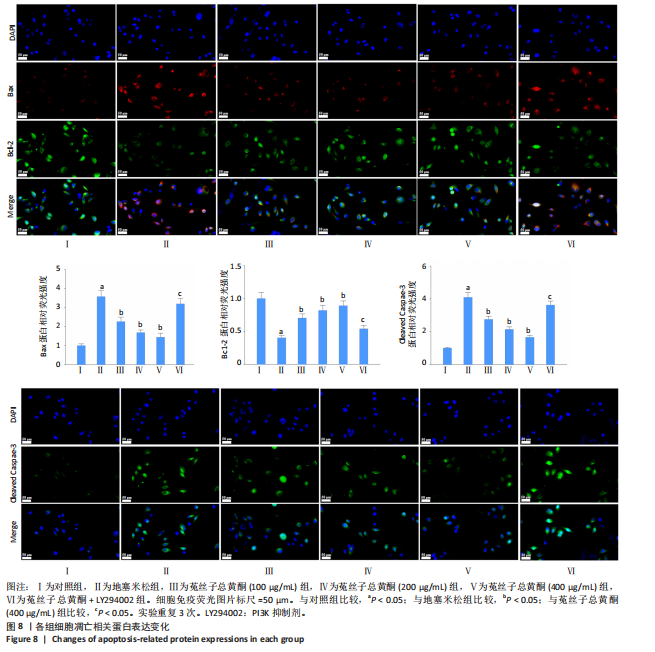
(P < 0.05);与菟丝子总黄酮(400 μg/mL)组比较,菟丝子总黄酮+LY294002组细胞存活率显著降低(P < 0.05),见图6B。 2.5 菟丝子总黄酮减弱了地塞米松诱导的hFOB1.19细胞凋亡 与对照组比较,地塞米松组细胞凋亡率显著升高(P < 0.05);与地塞米松组比较,菟丝子总黄酮各剂量组hFOB1.19细胞凋亡率显著降低(P < 0.05);与菟丝子总黄酮(400 μg/mL)组比较,菟丝子总黄酮+LY294002组细胞凋亡率显著升高(P < 0.05),见图7。 2.6 菟丝子总黄酮逆转了地塞米松对hFOB1.19细胞凋亡相关蛋白表达的作用 与对照组比较,地塞米松组细胞Bax和Cleaved-Caspase-3蛋白表达水平显著升高(P < 0.05),Bcl-2蛋白表达水平显著降低(P < 0.05);与地塞米松组比较,菟丝子总黄酮各剂量组hFOB1.19细胞Bax和Cleaved-Caspase-3蛋白表达水平显著降低(P < 0.05),Bcl-2蛋白表达水平显著升高(P < 0.05);与菟丝子总黄酮(400 μg/mL)组比较,菟丝子总黄酮+LY294002组细胞Bax和Cleaved-Caspase-3蛋白表达水平显著升高(P < 0.05),Bcl-2蛋白表达水平显著降低(P < 0.05),见图8。"

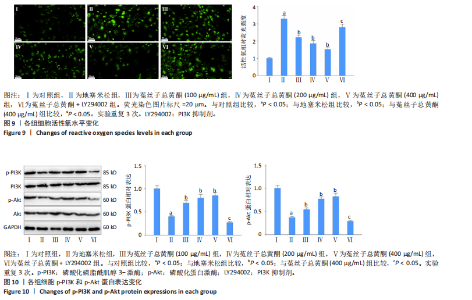
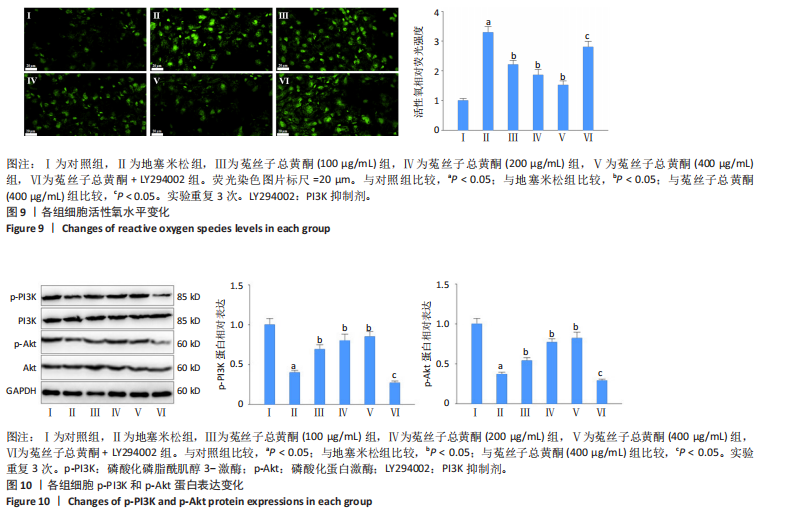
2.7 菟丝子总黄酮抑制了地塞米松诱导的hFOB1.19细胞活性氧水平升高 与对照组比较,地塞米松组细胞活性氧水平显著升高(P < 0.05);与地塞米松组比较,菟丝子总黄酮各剂量组细胞活性氧水平显著降低(P < 0.05);与菟丝子总黄酮(400 μg/mL)组比较,菟丝子总黄酮+LY294002组细胞活性氧水平显著升高(P < 0.05),结果见图9。 2.8 菟丝子总黄酮激活PI3K/Akt信号通路 与对照组比较,地塞米松组细胞中p-PI3K和p-Akt蛋白表达水平显著降低(P < 0.05);与地塞米松组比较,菟丝子总黄酮各剂量组hFOB1.19细胞中p-PI3K和p-Akt蛋白水平显著升高(P < 0.05);与菟丝子总黄酮 (400 μg/mL)组比较,菟丝子总黄酮+LY294002组细胞中p-PI3K和p-Akt蛋白水平显著降低(P < 0.05),见图10。"
| [1] 崔立强. 中国大陆地区股骨头坏死病因学调查及危险因素初步分析[D].北京:北京协和医学院,2014. [2] SONG L, ZHANG S.Anti-aging activity and modes of action of compounds from natural food sources. Biomolecules. 2023;13(11): 1600. [3] SHI T, LIU T, KOU Y, et al. The synergistic effect of Zuogui Pill and Eldecalcitol on improving bone mass and osteogenesis in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023;59(8):1414. [4] LI P, XU TY, YU AX, et al. The role of ferroptosis in osteoporosis and advances in Chinese herbal interventions. Biology. 2025;14(4):367. [5] LI Q, TIAN C, LIU X, et al. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant traditional Chinese medicine in treatment and prevention of osteoporosis. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1203767. [6] 卓小霞, 段宏婷, 闫媛聪, 等. 菟丝子中黄酮类成分的生物活性及体内代谢的研究进展[J]. 华西药学杂志,2023,38(6):705-710. [7] 陈鲁宁, 胡扬, 辛国松, 等. 菟丝子化学成分、药理作用研究进展及其质量标志物(Q-Marker)预测[J]. 中草药,2024,55(15):5298-5314. [8] WEI S, MA W, XIE S, et al. Hyperoside protects trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity via activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2025;39(3):481-490. [9] HE J, LI X, WANG Z, et al. Therapeutic anabolic and anticatabolic benefits of natural Chinese medicines for the treatment of osteoporosis. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:1344. [10] 李泰贤, 陈志伟, 王荣田, 等. 基于文献计量学分析中医药治疗股骨头坏死的研究现状[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2017,25(4):41-46. [11] 刘亚芳, 刘毅, 丁婉悦, 等. 菟丝子补肾药理作用研究进展[J]. 宜春学院学报,2021,43(9):22-25. [12] 王莹, 张婧如, 田伟, 等. 菟丝子及其提取物药理机制研究进展 [J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志,2023,29(11):1961-1964. [13] DUAN Y, SU YT, REN J, et al. Kidney tonifying traditional Chinese medicine: Potential implications for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosiss. Front Pharmacol. 2023;13:1063899. [14] 徐何方, 杨颂, 李莎莎,等. 菟丝子醇提物对肾阳虚证模型大鼠免疫功能的影响[J]. 中药材,2015,38(10):2163-2165. [15] 孟晓彤, 廖礼彬, 马伊萱, 等. 菟丝子黄酮对少弱精子症大鼠睾丸GM-CSF表达的影响[J]. 中华男科学杂志,2020,26(7):639-644. [16] 赵宝宝, 李兴勇, 董万涛, 等. 中药菟丝子防治骨质疏松症的研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(7):1089-1092. [17] FAN S, PAN H, HUANG J, et al. Hyperoside exerts osteoprotective effect on dexamethasone-induced osteoblasts by targeting NADPH Oxidase 4 (NOX4) to inhibit the reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation and activate c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway. Bioengineered. 2022;13(4):8657-8666. [18] CAO G, HU SQ, NING Y, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine in osteoporosis: from pathogenesis to potential activity. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15(000):18. [19] TAN M, LI Q, YANG B, et al. Insight of Chinese herbal medicine in treating osteoporosis: Achievements from 2013 to 2023. Am J Chin Med. 2024;52(5):26. [20] WANG G, ZHANG L, YAN C, et al. Upregulation of microRNA-576-5p protects from steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head by suppressing ANXA2. Cell Cycle. 2022;21(1):49-62. [21] CAI T, CHEN S, WU C, et al. Erythropoietin suppresses osteoblast apoptosis and ameliorates steroid-induced necrosis of the femoral head in rats by inhibition of STAT1-caspase 3 signaling pathway. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):894. [22] JIANG M, ZHANG K, HU Y, et al. The IFT80/Hedgehog pathway regulates the osteogenic-adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Curr Med Chem. 2024. doi: 10.2174/0109298673300113240418050128. [23] CAO J, LI Y, SI M, et al. Kaempferol combats the osteogenic differentiation damage of periodontal ligament stem cells in periodontitis via regulating EphrinB2-mediated PI3K/Akt and P38 pathways. Phytomedicine. 2025;141:157002. [24] 丘博元, 刘飞, 童思文, 等. 激素性股骨头坏死衰老关键基因的生物信息学鉴定和验证[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(26):5608-5620. [25] KUAI J, ZHENG J, KUMAR A, et al. Anti-inflammatory, antiosteoporotic, and bone protective effect of hydroxysafflor yellow A against glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024;38(9):e23797. [26] GAO Y, CHEN C, LIU R, et al. Research progress of connexin 43 mediated gap junction communication regulating bone metabolism in glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Exp Cell Res. 2025;449(1):114598. [27] YAN Z, ZHAN J, QI W, et al. The protective effect of luteolin in glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:1195. [28] HUANG C, JIN H, ZHANG Y, et al. Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. and its bioactive compounds: therapeutic potential in bone diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2025;16:1601537. [29] QIANG S, HAIMING Y, LVLIN Y, et al.Lycium barbarum polysaccharide protects against osteonecrosis of femoral head via regulating Runx2 expression. Injury. 2022;53(4):1361-1367. [30] 肖阳, 邢涛, 李向洲, 等. 外泌体在激素性股骨头坏死中的作用及中医药干预的研究进展[J]. 西部中医药,2025,38(7):96-102. [31] HE W, XU C, FAN Y, et al. Effects of the Chinese drugs for activating blood circulation on plasma TXB2 and 6-keto-PGF1alpha contents in rabbits with glucocorticoid-induced femoral head necrosis. J Tradit Chin Med. 2004;24(3):233-237. [32] 王克忠, 毛林中, 胡朝贵. 激素性股骨头坏死发病机制的实验研究[J].中华外科杂志,1994,32(9):515-517. [33] LI P, XIE C, LIU Y, et al. Quantitative analysis of local microcirculation changes in early osteonecrosis of femoral head: DCE-MRI findings. Front Surg. 2022;9:1003879. [34] 魏秋实, 何伟, 张庆文, 等. 股骨头坏死中医证型分布规律的文献研究和系统评价[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2013,7(3):369-372. [35] WANG WJ, ZHANG XH, WANG RX, et al. Observations on after-effect duration of kidney-nourishing and marrow-replenishing therapy on 58 cases of Mediterranean anemia. J Tradit Chin Med. 2009;29(4):258-262. [36] 孟娜, 徐双坤, 吕维瑶, 等. 菟丝子黄酮类化合物治疗不孕症的药理机制研究进展[J].环球中医药,2025,18(4):857-862. [37] 张雨婷, 杨之童, 刘子路, 等. UPLC-MS/MS测定菟丝子不同炮制品中3种黄酮类成分在大鼠体内的药物代谢动力学研究[J]. 安徽中医药大学学报,2025,44(2):100-107. [38] 马天宇, 史孟华, 林煦垚, 等. 菟丝子治疗男性不育症的作用机制研究进展[J]. 云南中医药大学学报,2025,48(1):106-112. [39] 刘海云, 纪玉龙, 何志坚. 菟丝子提取物对自然衰老小鼠学习记忆能力及肝和脑组织ATP酶活力的影响 [J]. 中国老年学杂志,2018, 38(23):5794-5796. [40] HONG XL, ZHAO Z, ZHAO YW, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosome mimetic vesicles regulation of the MAPK pathway and ROS levels inhibits glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis in osteoblasts. Stem Cells Int. 2023;2023:5537610. [41] 王翔宇, 冯晓云, 任红叶, 等. 菟丝子提取物通过BMP2/Smad4信号通路对MC3T3-E1细胞增殖的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2019, 34(6):2687-2689. [42] GUO S, MAO L, JI F, et al. Activating AMP-activated protein kinase by an α1 selective activator compound 13 attenuates dexamethasone-induced osteoblast cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016; 471(4):545-552. [43] JILKA RL, WEINSTEIN RS FAU - PARFITT AM, PARFITT AM FAU - MANOLAGAS SC, et al. Quantifying osteoblast and osteocyte apoptosis: challenges and rewards. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22(10): 1492-1501. [44] BAI L, WANG T, ZHENG J, et al. SIRT1 mediated by baicalein and GFI1 promotes osteogenic differentiation and ameliorates osteoporosis by inhibiting ferroptosis in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2025;39(7):e70368. [45] LIU S, FANG T, YANG L, et al. Gastrodin protects MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts from dexamethasone-induced cellular dysfunction and promotes bone formation via induction of the NRF2 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(4):2059-2069. [46] 陈晨, 郑润泉, 李宗玉. miR-218-5p通过靶向下调ANKRD1抑制地塞米松诱导的人成骨细胞HFOB1.19损伤[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2022,38(19):2325-2359+2335. [47] PENG P, WANG X, QIU C, et al. Extracellular vesicles from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells prevent steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head via the PI3K/AKT pathway. Food Chem Toxicol. 2023;180:114004. [48] LV W, YU M, YANG Q, et al. Total flavonoids of Rhizoma drynariae ameliorate steroid‑induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head via the PI3K/AKT pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(5):345. [49] XUE XH, FENG ZH, LI ZX, et al. Salidroside inhibits steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway: In vitro and in vivo studies. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(3):3751-3757. [50] YANG N, LI M, LI X, et al. MAGL blockade alleviates steroid-induced femoral head osteonecrosis by reprogramming BMSC fate in rat. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024;81(1):418. [51] DENG S, DAI G, CHEN S, et al. Dexamethasone induces osteoblast apoptosis through ROS-PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;110:602-608. [52] SUN F, ZHOU JL, WEI SX, et al. Glucocorticoids induce osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats via PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathway. PeerJ. 2022;10:e13319. |
| [1] | Yuan Xiaoshuang, Yang Xu, Yang Bo, Chen Xiaoxu, Tian Ting, Wang Feiqing, Li Yanju, Liu Yang, Yang Wenxiu. Effect of conditioned medium of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells on proliferation and apoptosis of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1632-1640. |
| [2] | He Jiale, Huang Xi, Dong Hongfei, Chen Lang, Zhong Fangyu, Li Xianhui. Acellular dermal matrix combined with adipose-derived stem cell exosomes promotes burn wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1699-1710. |
| [3] | Chen Yulin, He Yingying, Hu Kai, Chen Zhifan, Nie Sha Meng Yanhui, Li Runzhen, Zhang Xiaoduo , Li Yuxi, Tang Yaoping. Effect and mechanism of exosome-like vesicles derived from Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim. in preventing and treating atherosclerosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1768-1781. |
| [4] | Zhou Sirui, Xu Yukun, Zhao Kewei. Ideas and methods of anti-melanogenesis of Angelica dahurica extracellular vesicles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1747-1754. |
| [5] | Liu Anting, Lu Jiangtao, Zhang Wenjie, He Ling, Tang Zongsheng, Chen Xiaoling. Regulation of AMP-activated protein kinase by platelet lysate inhibits cadmium-induced neuronal apoptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1800-1807. |
| [6] | Peng Zhiwei, Chen Lei, Tong Lei. Luteolin promotes wound healing in diabetic mice: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1398-1406. |
| [7] | Jia Jinwen, Airefate·Ainiwaer, Zhang Juan. Effects of EP300 on autophagy and apoptosis related to allergic rhinitis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1439-1449. |
| [8] | Liu Yu, Lei Senlin, Zhou Jintao, Liu Hui, Li Xianhui. Mechanisms by which aerobic and resistance exercises improve obesity-related cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [9] | Wang Zhengye, Liu Wanlin, Zhao Zhenqun. Advance in the mechanisms underlying miRNAs in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1207-1214. |
| [10] | Chen Yixian, Chen Chen, Lu Liheng, Tang Jinpeng, Yu Xiaowei. Triptolide in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 805-815. |
| [11] | Bao Zhuoma, Hou Ziming, Jiang Lu, Li Weiyi, Zhang Zongxing, Liu Daozhong, Yuan Lin. Effect and mechanism by which Pterocarya hupehensis skan total flavonoids regulates the proliferation, migration and apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 816-823. |
| [12] | Yang Xiao, Bai Yuehui, Zhao Tiantian, Wang Donghao, Zhao Chen, Yuan Shuo. Cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: mechanisms and regenerative challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 926-935. |
| [13] | Wang Zhengye, Liu Wanlin, Zhao Zhenqun. Mechanism by which vascular endothelial growth factor A targets regulation of angiogenesis in the treatment of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 671-679. |
| [14] | Chen Ling, Mao Qiuhua, Xu Pu, Zhang Wenbo. Effect of water-soluble matrix of nano-pearl powder on proliferation, migration and apoptosis of mouse fibroblasts#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 338-344. |
| [15] | Wu Yilin, Tian Hongying, Sun Jiale, Jiao Jiajia, Zhao Zihan, Shao Jinhuan, Zhao Kaiyue, Zhou Min, Li Qian, Li Zexin, Yue Changwu. Intervention effect and mechanism of Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae in a mouse model of breast hyperplasia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4377-4389. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||