Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 2702-2711.doi: 10.12307/2026.095
Previous Articles Next Articles
Network pharmacological analysis and experimental verification of semen cuscutae in treating postmenopausal osteoporosis
Xu Sheng1, 2, Zhang Wenwen3, Zhang Weiwei1, 2, Wang Hongtao1, 2, Zhang Jun2, Yang Ruisheng2, Yuan Yuan4, Wang Li4, 5, Hao Haihu1, 2
- 1First Clinical College, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030600, Shanxi Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Bethune Hospital, Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences, Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China; 3School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Xinjiang Hetian College, Hetian 848000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 4Basic Medical Research Center, 5Department of Pathology, School of Basic Medicine, Shanxi Medical University, Jinzhong 030600, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2025-02-20Accepted:2025-06-13Online:2026-04-18Published:2025-09-02 -
Contact:Hao Haihu, MD, Chief physician, First Clinical College, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030600, Shanxi Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, Bethune Hospital, Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences, Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Xu Sheng, MS candidate, First Clinical College, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030600, Shanxi Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, Bethune Hospital, Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences, Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Scientific Research Project of Shanxi Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 2024ZYY2A020 (to HHH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Sheng, Zhang Wenwen, Zhang Weiwei, Wang Hongtao, Zhang Jun, Yang Ruisheng, Yuan Yuan, Wang Li, Hao Haihu. Network pharmacological analysis and experimental verification of semen cuscutae in treating postmenopausal osteoporosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2702-2711.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

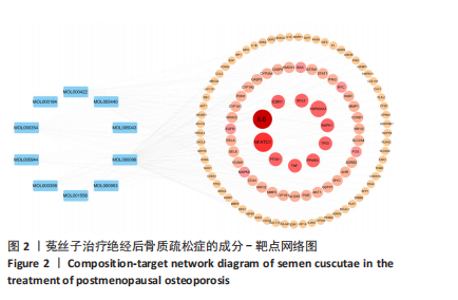
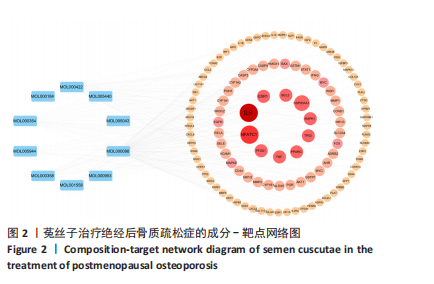
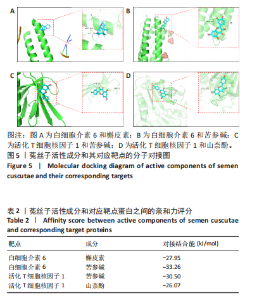
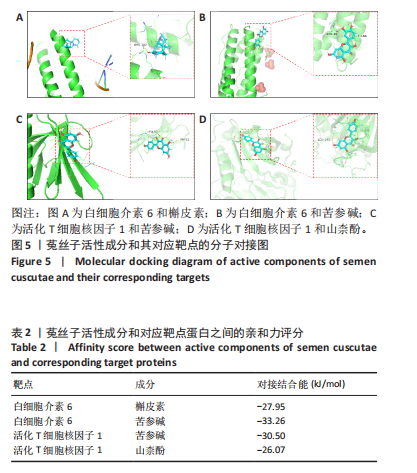
2.1 菟丝子主要活性成分和绝经后骨质疏松症的共同作用靶点 以生物利用度≥30% 、类药性≥0.18作为筛选标准,于TCMSP数据库内完成筛选,共获得菟丝子主要活性成分共11个,见表1;完成菟丝子潜在活性成分筛选后,在TCMSP数据库内整合各活性成分对应的靶点并整合去重,共获得靶点190个,使用UniProt数据库实现数据格式转换。基于OMIM、GeneCards和PharmGKB数据库获得绝经后骨质疏松症靶点并整合去重,共获得疾病靶点1 402个。通过R语言绘制韦恩图,筛选出两者的共同作用靶点110个,见图1。 2.2 菟丝子和绝经后骨质疏松症的共同作用靶点分析 将菟丝子11个主要活性成分和110个共同靶点信息添加到Cytoscape软件中,构建和绘制成分-靶"

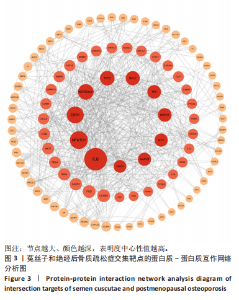
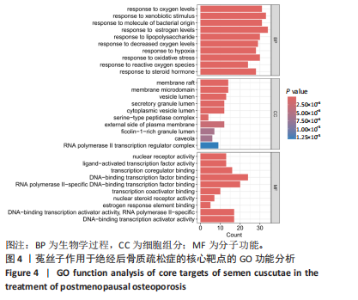
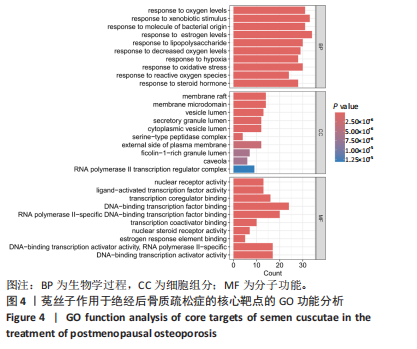
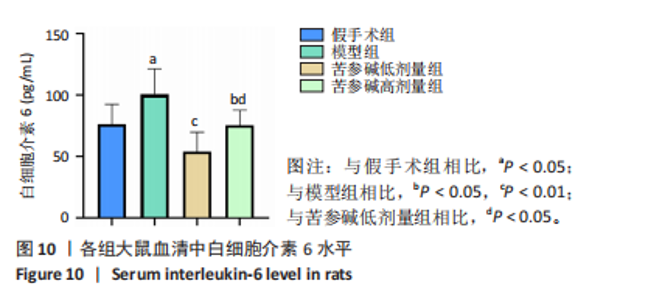
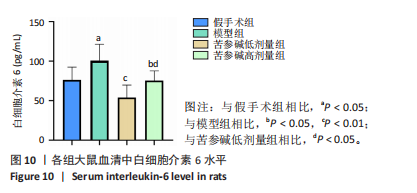
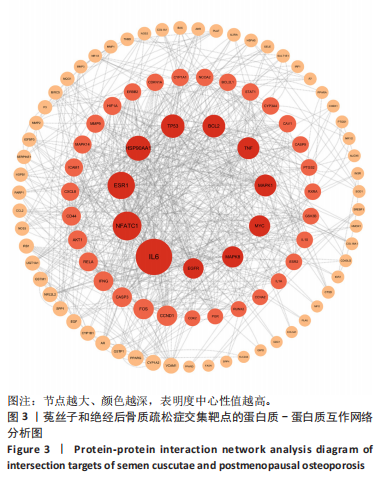
2.3 共同作用靶点的蛋白质-蛋白质互作网络分析 在String数据库中获取蛋白质间的互作关系,再将相关数据添加到Cytoscape软件中,完成对蛋白质-蛋白质互作网络图的绘制,并通过Cytoscape中的CytoNCA插件包含的度中心性值计算方法,计算得到中位数,筛选出度中心性值排名前10个作为核心靶点,分别为白细胞介素6、活化T细胞核因子1、雌激素受体1(ESR1)、热休克蛋白90 α家族A类成员1(HSP90AA1)、肿瘤蛋白p53(TP53)、B细胞淋巴瘤2(BCL2)、肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶1(MAPK1)、v-myc髓细胞组织增生病毒癌基因同源物(MYC)、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶8(MAPK8),见图3。"
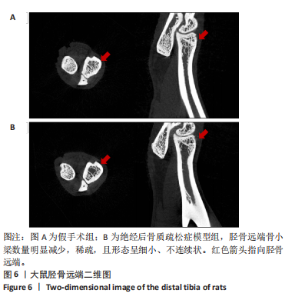
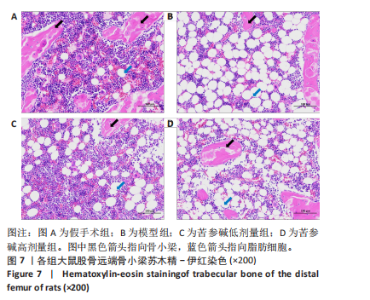
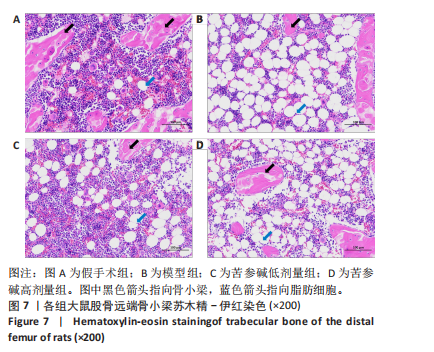
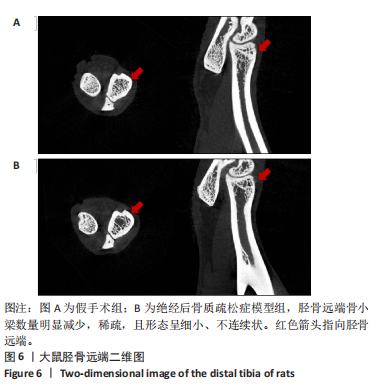
2.6 实验动物数量分析 实验共设计了4组,假手术组10只,模型组10只,苦参碱低剂量组10只,苦参碱高剂量组10只。实验结束后共有26只大鼠存活,分别为假手术组7只,模型组6只,苦参碱低剂量组7只,苦参碱高剂量组6只。在实验过程中,共有14只大鼠脱落,假手术组2只大鼠因感染死亡,1只大鼠因手术并发症死亡,具体表现为肠梗阻;模型组1只大鼠因感染死亡,3只大鼠因手术并发症死亡,具体表现为肠管坏死和肠梗阻;苦参碱低剂量组1只大鼠因感染死亡,2只大鼠因手术并发症死亡,具体表现为肠胀气和肠梗阻;苦参碱高剂量组1只大鼠因感染死亡,3只大鼠因手术并发症死亡,具体表现为肠胀气、肠梗阻和给药后出现抽搐。尽管有部分大鼠在实验过程中脱落,但最终进入结果分析的大鼠数量仍足以支持实验结果的可靠性。 2.7 验证模型的成功性 术后8周采用Micro-CT扫描胫骨远端作为观察区域,观察骨小梁密度及分布,并用Dataviewer软件截取胫骨远端二维图,可见模型组较假手术组的胫骨远端骨小梁数量明显减少,稀疏,且形态呈细小、不连续状,即证明造模成功,见图6。"
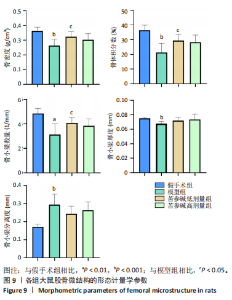
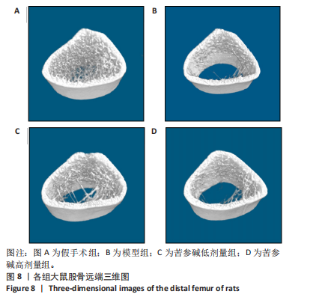
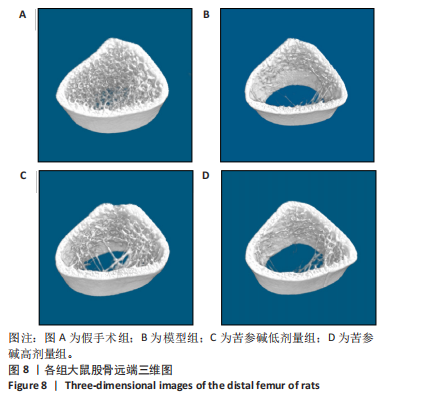
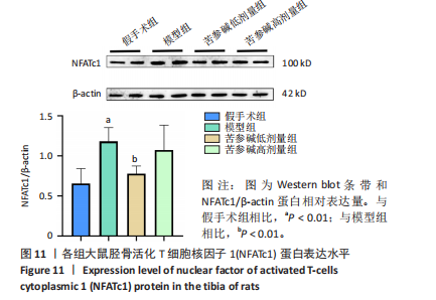
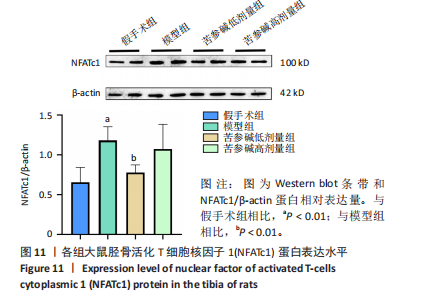
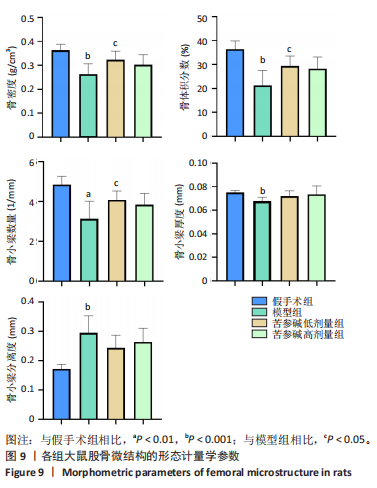
2.10 各组大鼠股骨微结构的形态计量学参数 与假手术组相比,模型组骨矿物质密度显著降低(P < 0.001);与模型组相比,苦参碱低剂量组骨矿物质密度显著升高(P < 0.05),而苦参碱高剂量组骨矿物质密度则无显著差异(P > 0.05);与假手术组相比,模型组相对骨体积显著降低(P < 0.001);与模型组相比,苦参碱低剂量组相对骨体积显著升高(P < 0.05),而苦参碱高剂量组骨矿物质密度则无显著差异(P > 0.05);与假手术组相比,模型组骨小梁数量显著降低(P < 0.01);与模型组相比,苦参碱低剂量组骨小梁数量显著升高(P < 0.05),而苦参碱高剂量组骨小梁数量则无显著差异(P > 0.05);与假手术组相比,模型组骨小梁厚度显著降低(P < 0.001);与模型组相比,苦参碱低剂量组、苦参碱高剂量组骨小梁厚度则无显著差异(P > 0.05);与假手术组相比,模型组骨小梁分离度显著升高(P < 0.001);与模型组相比,苦参碱低剂量组、苦参碱高剂量组骨小梁分离度则无显著差异(P > 0.05),见图9。"
| [1] RAMCHAND SK, LEDER BZ. Sequential Therapy for the Long-Term Treatment of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024;109(2):303-311. [2] SUBARAJAN P, ARCEO-MENDOZA RM, CAMACHO PM. Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: A Review of Latest Guidelines. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2024 Dec;53(4):497-512. [3] SALARI N, DARVISHI N, BARTINA Y, et al. Global prevalence of osteoporosis among the world older adults: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):669. [4] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会,章振林.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J].中国全科医学,2023,26(14):1671-1691. [5] YANG K, WANG X, ZHANG C, et al. Metformin improves HPRT1-targeted purine metabolism and repairs NR4A1-mediated autophagic flux by modulating FoxO1 nucleocytoplasmic shuttling to treat postmenopausal osteoporosis. Cell Death Dis. 2024;15(11):795. [6] AYERS C, KANSAGARA D, LAZUR B, et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Treatments to Prevent Fractures in People With Low Bone Mass or Primary Osteoporosis: A Living Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis for the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2023;176(2):182-195. [7] LEBOFF MS, GREENSPAN SL, INSOGNA KL, et al. The clinician’s guide to prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2022;33(10): 2049-2102. [8] FOESSL I, DIMAI HP, OBERMAYER-PIETSCH B. Long-term and sequential treatment for osteoporosis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2023;19(9):520-533. [9] SPÅNGEUS A, RYDETUN J, WOISETSCHLÄGER M. Prevalence of denosumab-induced hypocalcemia: a retrospective observational study of patients routinely monitored with ionized calcium post-injection. Osteoporos Int. 2024;35(1):173-180. [10] QI L, GUO WW, DONG HX, et al. Narrative Review of Traditional Chinese Medicine in the Treatment of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(15):2162-2169. [11] 陈鲁宁,胡扬,辛国松,等.菟丝子化学成分、药理作用研究进展及其质量标志物(Q-Marker)预测[J].中草药,2024,55(15):5298-5314. [12] 郭晓彤,宋俊丽,韦秋,等.菟丝子丸调控BMP2/RUNX2信号通路抗绝经后骨质疏松研究[J].天津中医药,2024,41(12):1599-1604. [13] 孟卓然,赵梓铭,贾壮壮,等.菟丝子乙醇提取物灌胃对大鼠绝经后骨质疏松症的改善作用及其机制[J].山东医药,2024,64(17):29-32. [14] SONG C, YAN Q, MA Y, et al. Modified Zuo Gui Wan Ameliorates Ovariectomy-Induced Osteoporosis in Rats by Regulating the SCFA-GPR41-p38MAPK Signaling Pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024;18:6359-6377. [15] 林楚彬,何兴鹏,丘育辉,等.病证结合骨质疏松模型大鼠骨骼的生物力学性能分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(23):3636-3641. [16] 赵琦明,龚婉,刘梦琴,等.三子丸有效成分群对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠骨代谢的影响[J].中国药学杂志,2021,56(8):640-646. [17] 贾艳萍,张国明.补肾壮骨汤联合西药治疗围绝经期骨质疏松症的临床疗效及对骨代谢、炎症因子的影响[J].中医研究,2021,34(12): 37-40. [18] 赵宝宝,李兴勇,董万涛,等.中药菟丝子防治骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(7):1089-1092. [19] HU X, WANG W, CHEN X, et al. Trehalose Rescues Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Induced by Ovariectomy through Alleviating Osteoblast Pyroptosis via Promoting Autophagy. Biomedicines. 2024;12(10):2224. [20] JIN J, FAN Z, LONG Y, et al. Matrine induces ferroptosis in cervical cancer through activation of piezo1 channel. Phytomedicine. 2024;122:155165. [21] SUN Z, WANG Y, PANG X, et al. Mechanisms of polydatin against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury based on network pharmacology, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation. Bioorg Chem. 2023;140:106840. [22] ZHANG C, LI H, LI J, et al. Oxidative stress: A common pathological state in a high-risk population for osteoporosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;163:114834. [23] ZOU J, CHEN H, FAN X, et al. Garcinol prevents oxidative stress-induced bone loss and dysfunction of BMSCs through NRF2-antioxidant signaling. Cell Death Discov. 2024;10(1):82. [24] WANG LT, CHEN LR, CHEN KH. Hormone-Related and Drug-Induced Osteoporosis: A Cellular and Molecular Overview. Int J Mol Sci. 2023; 24(6):5814. [25] CHEN X, ZHI X, PAN P, et al. Matrine prevents bone loss in ovariectomized mice by inhibiting RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis. FASEB J. 2017; 31(11):4855-4865. [26] XIN Z, JIN C, CHAO L, et al. A Matrine Derivative M54 Suppresses Osteoclastogenesis and Prevents Ovariectomy-Induced Bone Loss by Targeting Ribosomal Protein S5. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:22. [27] ZHOU P, XIA D, WANG Y, et al. Matrine derivate MASM protects murine MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells against dexamethasone-induced apoptosis via the regulation of USP14/p53. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019; 47(1):3720-3728. [28] HUANG X, NI B, LI Q, et al. Association between Postmenopausal Osteoporosis and IL-6、TNF-α: A Systematic Review and A Meta-analysis. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(15):2260-2266. [29] FISCHER V, HAFFNER-LUNTZER M. Interaction between bone and immune cells: Implications for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022;123:14-21. [30] YOKOTA K, SATO K, MIYAZAKI T, et al. Characterization and Function of Tumor Necrosis Factor and Interleukin-6-Induced Osteoclasts in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73(7):1145-1154. [31] CHEN Y, ZHENG J, MO L, et al. Oroxylin A suppresses breast cancer-induced osteoclastogenesis and osteolysis as a natural RON inhibitor. Phytomedicine. 2024;129:155688. [32] FENG W, LIU H, LUO T, et al. Combination of IL-6 and sIL-6R differentially regulate varying levels of RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis through NF-κB, ERK and JNK signaling pathways. Sci Rep. 2017;7:41411. [33] CHEN K, QIU P, YUAN Y, et al. Pseurotin A Inhibits Osteoclastogenesis and Prevents Ovariectomized-Induced Bone Loss by Suppressing Reactive Oxygen Species. Theranostics. 2019;9(6):1634-1650. [34] LIU T, JIANG L, XIANG Z, et al. Tereticornate A suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via the downregulation of c-Src and TRAF6 and the inhibition of RANK signaling pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;151:113140. [35] HUANG W, GONG Y, YAN L. ER Stress, the Unfolded Protein Response and Osteoclastogenesis: A Review. Biomolecules. 2023;13(7):1050. |
| [1] | Chen Yulin, He Yingying, Hu Kai, Chen Zhifan, Nie Sha Meng Yanhui, Li Runzhen, Zhang Xiaoduo , Li Yuxi, Tang Yaoping. Effect and mechanism of exosome-like vesicles derived from Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim. in preventing and treating atherosclerosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1768-1781. |
| [2] | Zhou Sirui, Xu Yukun, Zhao Kewei. Ideas and methods of anti-melanogenesis of Angelica dahurica extracellular vesicles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1747-1754. |
| [3] | Peng Zhiwei, Chen Lei, Tong Lei. Luteolin promotes wound healing in diabetic mice: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1398-1406. |
| [4] | Guo Ying, Tian Feng, Wang Chunfang. Potential drug targets for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: large sample analysis from European databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1549-1557. |
| [5] | Yang Zhijie, Zhao Rui, Yang Haolin, Li Xiaoyun, Li Yangbo, Huang Jiachun, Lin Yanping, Wan Lei, HuangHongxing. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: predictive values of muscle mass, grip strength, and appendicular skeletal muscle index [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1073-1080. |
| [6] | Chen Yixian, Chen Chen, Lu Liheng, Tang Jinpeng, Yu Xiaowei. Triptolide in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 805-815. |
| [7] | Chen Yueping, Chen Feng, Peng Qinglin, Chen Huiyi, Dong Panfeng . Based on UHPLC-QE-MS, network pharmacology, and molecular dynamics simulation to explore the mechanism of Panax notoginseng in treating osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1751-1760. |
| [8] |
Huang Xiaobin, Ge Jirong, Li Shengqiang, Xie Lihua, Huang Jingwen, He Yanyan, Xue Lipeng.
Mechanisms of different yin nourishing and kidney tonifying methods on osteoclastysis pathway in ovariectomized rats #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1214-1219.
|
| [9] | Jiang Qiyu, Zeng Huiyan. A novel analysis and prediction method for potential mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine based on artificial intelligence and omics data-driven approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7552-7561. |
| [10] | Yan Jing, Qin Qiujun, Li Fen, Zhou Jun, Ding Yuanyuan, Jin Chunlin. A systematic review of osteoporosis-specific quality-of-life scales [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7649-7655. |
| [11] | Wang Tong, Zheng Yu, Jia Chengming, Yang Hu, Zhang Guangfei, Ji Yaoyao. Action mechanism of Gegenmaqi prescription in treatment of periarthritis of shoulder combined with type 2 diabetes based on TCMSP database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7669-7678. |
| [12] | Fang Yuan, Qian Zhiyong, He Yuanhada, Wang Haiyan, Sha Lirong, Li Xiaohe, Liu Jing, He Yachao, Zhang Kai, Temribagen. Mechanism of Mongolian medicine Echinops sphaerocephalus L. in proliferation and angiogenesis of vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7519-7528. |
| [13] | Zhang Xin, Guo Baojuan, Xu Huixin, Shen Yuzhen, Yang Xiaofan, Yang Xufang, Chen Pei. Protective effects and mechanisms of 3-N-butylphthalide in Parkinson’s disease cell models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6466-6473. |
| [14] | Yu Bingbing, Wang Tingting, Fang Junlin, Guo Yun, Huang Yingru. Acupuncture for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis: meta-analysis, systematic evaluation and trial sequential analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6305-6316. |
| [15] | Liu Yuan, Qu Yuan, Wan Yakun, Guo Jingyu, Jiang Ping. Transcriptomic analysis and drug prediction of basement membrane-related genes in different traditional Chinese medicine patterns of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5486-5500. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||