Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (34): 5544-5551.doi: 10.12307/2024.810
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role of inflammatory factors in diabetic ulcers and prospects of traditional Chinese medicine intervention
Zhang Yuchang1, Chen Xiang1, He Bo2, Li Shenghua1, Mu Xiangqian1, Sun Weiqiang1, Zhang Li1, Chen Jie1
- 1Gansu Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China; 2Nanyang Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanyang 473007, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2023-11-30Accepted:2023-12-24Online:2024-12-08Published:2024-03-15 -
Contact:He Bo, Master, Physician, Nanyang Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanyang 473007, Henan Province, China Chen Xiang, Master, Attending physician, Gansu Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China -
About author:Zhang Yuchang, Master, Associate chief physician, Gansu Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province, No. 22JR5RA620 (to CJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Yuchang, Chen Xiang, He Bo, Li Shenghua, Mu Xiangqian, Sun Weiqiang, Zhang Li, Chen Jie. Role of inflammatory factors in diabetic ulcers and prospects of traditional Chinese medicine intervention[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5544-5551.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

2.1 中医对糖尿病溃疡的认识 中医对糖尿病溃疡的认识和治疗的历史非常悠久,中医虽然无溃疡之名,但把糖尿病溃疡归于“消渴”和“脱疽”的范畴。《灵枢·痈疽》“发于足指,名曰脱痈。其状赤黑,死不治;不赤黑,不死,不衰,急斩之,不则死矣”,最早记录糖尿病溃疡的临床表现、治疗措施和严重后果。认为“气虚血瘀”是其基本病机,因此,在治疗上重视“益气活血,通经活络”[8-9]。中医学认为,皮肤创面的修复和皮肤、肌肉、骨骼关系密切,又与气血津液、脏腑经络相关。若气虚血瘀,皮肉之间热胜肉腐,则易蒸酿成“脓”,即炎症反应的病理产物。若扶助正气,托里透脓,正气载毒流出,毒随浓泄,疾病可愈。在《河间六书》和《外科启玄·明内托法论》建议在疮疡的早中期也就是西医所指的炎症期使用补气活血和托里透脓的药物,托毒外出,这与西医中的炎症期的治疗要求相一致。 针对糖尿病溃疡,西医多以调控血糖、抗感染、局部清创、消毒换药等方式对症处理,虽有疗效,但存在一定的不良反应。相对于西医而言,中药具有“安全、有效、不良反应低”等显著优势。现代药理学显示,中药具有抗氧化、抗炎以及调节免疫力等作用,其中治疗疮疡的中药不仅具有抗菌抑菌作用,而且具有较强的抗耐药性,可以显著促进糖尿病溃疡创面的愈合。中医药在与糖尿病溃疡长期的斗争中积累了丰富的经验,建立了完整的理论体系,不仅将糖尿病溃疡分为初、中、后三期,还将糖尿病溃疡分为湿热毒盛证、血脉瘀阻证、热毒伤阴证和气血两虚4个证型,并对四妙勇安汤、桃红四物汤、血府逐瘀汤及顾步汤等多种方剂进行加减用于糖尿病溃疡治疗并取得显著疗效。而且随着中医药的发展,中医药对糖尿病溃疡的认识和治疗也在不断更新和完善,根据糖尿病溃疡 的特点对糖尿病溃疡进行分期并提出“清法”“温清并用”与“养法”的治疗方案,此外还先后创立了疮疡Ⅰ号、Ⅱ号和三黄血竭方等多种方剂,临床效果显著。文章总结了中医药认识和治疗糖尿病溃疡的时间脉络图[10-14],见图3。"

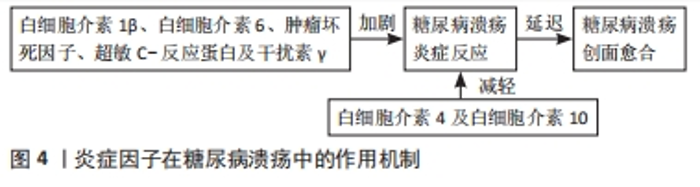
2.2 慢性炎症反应是糖尿病溃疡愈合障碍的重要致病因素 糖尿病溃疡主要表现为慢性难愈性溃疡,发病机制十分复杂,与氧化应激水平升高、慢性炎症反应及血管新生障碍等有关,其中慢性炎症反应是导致糖尿病溃疡创面迁延不愈的重要因素。原因如下,①人体的高血糖可以提高促炎细胞因子水平,降低生长因子水平,并降低组织的血液循环和细胞的增殖、迁移,阻碍糖尿病溃疡创面愈合[15-16]。②人体的高糖环境会影响巨噬细胞和中性粒细胞等功能。首先,中性粒细胞数量和功能出现异常,中性粒细胞数量增加会导致炎症浸润时间延长,中性粒细胞的迁移、吞噬和细胞内杀伤能力降低,无法及时有效清除细菌,机体长期处于炎症状态。此外,中性粒细胞数量的增加会导致基质金属蛋白酶分泌过多,分解细胞外基质中的多种蛋白质,抑制肉芽组织的形成和成熟[17]。 巨噬细胞的表型变化异常,炎症后期促炎因子数量的递减和抗炎因子的递增是炎症向修复过渡的正常过程,然而机体的高糖状态会导致巨噬细胞表型异常,体现在M1型和M2型巨噬细胞比例异常,表现为M1型分泌的白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α及超敏C-反应蛋白等促炎因子增多,而M2型分泌的白细胞介素4及白细胞介素10抗炎因子减少,导致促炎因子和抗炎因子质检的平衡失调,使糖尿病溃疡创面长期处于促炎状态,难以消退。如果促炎因子分泌持续增多,会降低转化生长因子β(TGF-β)等生长因子的表达[18],进一步阻碍糖尿病溃疡创面愈合甚至无法愈合,最终形成慢性溃疡[19]。因此,与正常伤口的愈合相比,糖尿病溃疡创面炎性反应持续时间较长且消退障碍,创面长期处于慢性炎性反应状态,而难以向伤口愈合的后两期过渡,故糖尿病溃疡创面愈合过程被持续的炎症反应所延迟。方金赢[20]在对120例糖尿病溃疡患者进行炎症反应抑制的对照研究中发现,炎症反应抑制干预后,患者血清中促炎因子白细胞介素6、C-反应蛋白及肿瘤坏死因子α的水平均明显降低,而血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)和碱性成纤维细胞生长因子(bFGF)等促生长因子明显升高,溃疡面愈合时间明显缩短。表明通过炎症反应抑制干预可以有效减轻糖尿病溃疡创面的炎症反应并提高生长因子的表达,加快愈合速度。因此,调控炎症因子的表达,抑制过度的炎症反应可能是促进糖尿病溃疡创面愈合的重要举措。 2.3 炎症反应相关因子 炎症因子介导的炎症反应是组织损伤后创面愈合的一个重要环节,炎症因子众多,分为促炎细胞因子和抗炎细胞因子,促炎细胞因子具有促进炎症反应的作用,抗炎细胞因子具有拮抗炎症反应的作用,二者的动态平衡维持了创面的正常炎症反应,保证了创面的正常愈合。作用机制见图4。"
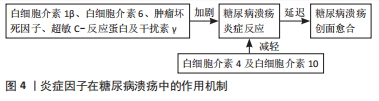
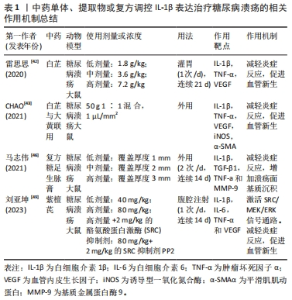
2.3.1 促炎细胞因子 促炎细胞因子在创面愈合中扮演重要角色,炎症早期,适量的促炎因子可以有效促进创面的愈合,而糖尿病溃疡患者机体的高糖环境会导致促炎细胞因子的分泌异常增多,引发过度的炎症反应,延迟创面的愈合。促炎因子很多,包括白细胞介素家族中的白细胞介素α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素18以及肿瘤坏死因子α、超敏C-反应蛋白及干扰素γ等,其中白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、超敏C-反应蛋白和干扰素γ等在糖尿病溃疡起主要作用。 白细胞介素1β:白细胞介素1β在许多炎症反应中发挥重要作用,在糖尿病溃疡中,白细胞介素1β被大量持续释放,加剧糖尿病溃疡创面炎症反应,延缓创面愈合速度。机制如下:①升高患者血糖,研究发现,白细胞介素1β可以导致糖尿病患者胰岛细胞损伤[21],导致胰岛素分泌减少。②白细胞介素1β受体在巨噬细胞和胰岛β细胞表面高表达,他们在与白细胞介素1β结合后会激活核转录因子κB通路,刺激白细胞介素1β进一步产生,加剧炎症反应。③抑制成纤维细胞的增殖,研究发现,不同的浓度的白细胞介素1β在不同的条件下对不同的细胞的作用可能会不同,甚至完全相反。肖正华等[22]研究发现,低浓度的白细胞介素1β对成纤维细胞的增殖有促进作用,当浓度增到50 ng/mL时对细胞增殖没有刺激作用,而当浓度进一步升高到500 ng/mL时对细胞增殖有明显抑制作用;研究还发现,黄芪多糖可能通过抑制白细胞介素1β浓度显著刺激糖尿病足部溃疡部位成纤维细胞的增殖进而促进糖尿病溃疡的愈合。白细胞介素1β可以促进炎症反应,研究发现,阻断白细胞介素1β不仅抑制促炎巨噬细胞的活化,还能上调促进创面修复因子的表达[23],因此,白细胞介素1β可能为治疗糖尿病溃疡创面的一个新的思路。 白细胞介素6:白细胞介素6具有很强的促炎作用,它的过度表达可引起组织的修复能力下降。当组织炎症时,白细胞介素6的反应和升高速度比其它炎症细胞因子更早,而且持续时间长,是细胞因子级联反应活化的重要指标。所以早期其常被用于急性感染的辅助诊断,中期白细胞介素6的水平还常被用于反映机体的炎症反应程度和疾病的严重程度[24],后期白细胞介素6可以被用于评价炎症反应程度和疾病预后的判断。范世珍等[25]研究发现,白细胞介素6与急性感染的病程相关性很大,对疾病的治疗的指导具有很大的指导意义。研究发现,在糖尿病溃疡创面中,白细胞介素6的表达水平和胰岛素抵抗呈负相关关系[26]。因此白细胞介素6的水平对糖尿病溃疡创面的治疗具有重要的指导意义。 肿瘤坏死因子α:肿瘤坏死因子α在抗感染及促进损伤组织的修复中具有重要作用。肿瘤坏死因子α正常表达可以调节人体的免疫系统,发挥免疫作用。而高水平的肿瘤坏死因子α会导致机体发生病理性损害,破坏机体的免疫平衡。糖尿病患者的皮肤未溃破前,肿瘤坏死因子α高表达会刺激血管内皮细胞产生血小板生长因子,增加血管通透性[27],引起血栓。肿瘤坏死因子α还会刺激血管内皮细胞分泌多种细胞因子,诱发内皮细胞、T细胞及单核巨噬细胞释放白细胞介素2、白细胞介素8 等炎性递质,引起炎症反应,导致组织损伤甚至破溃[28]。皮肤发生破溃后,外周血的单核细胞相对活跃,促炎因子分泌增加,抗炎因子分泌减少,加剧炎症反应。且活化的单核细胞能够分泌肿瘤坏死因子α,导致肿瘤坏死因子α水平进一步升高,进一步加剧炎症反应。所以,肿瘤坏死因子α的升高与糖尿病溃疡的发生和发展密切相关,且其水平与糖尿病溃疡的严重程度成正相关关系。 超敏C-反应蛋白:超敏C-反应蛋白是一种肝细胞合成的全身性炎症反应急性期的非特异性标志物。当机体未发生炎症时,超敏C-反应蛋白表达水平较低甚至不表达,炎症发生后,其表达水平在炎症早期便可迅速升高,参与机体的早期免疫[29],而且超敏C-反应蛋白的升高幅度和感染程度呈正相关关系,因此超敏C-反应蛋白能够准确反映炎症反应的程度,故近年来超敏C-反应蛋白被广泛应用到急性炎症的判断以及感染性疾病诊断和预后评价[30-31]。陈向红等[32]研究发现,糖尿病足多重耐药菌感染患者的超敏C-反应蛋白水平高。糖尿病溃疡可诱导大量炎症细胞因子释放,致使超敏C-反应蛋白水平呈异常升高表达,而超敏C-反应蛋白又可激活多种炎性细胞因子,引起炎症级联反应,加重炎症活动度[33-34]。 干扰素γ:干扰素γ是由多种免疫细胞产生的具有免疫调节特性、抗病毒和抗肿瘤特性的多效性细胞因子,人类先天性免疫与获得性免疫中的重要分子,主要参与刺激巨噬细胞和白细胞的非特异性防御机制。在急性炎症期,干扰素γ的激活会刺激巨噬细胞产生肿瘤坏死因子α,加剧炎症反应,此外,干扰素γ还会抑制血管生成及胶原沉积,最终阻碍创面愈合。HAMMAD等[35]研究发现,干扰素γ的表达水平和糖尿病溃疡的发生和发展密切相关。 2.3.2 抗炎细胞因子 抗炎细胞因子拮抗的作用在炎症的转归和创面的愈合发挥重要作用,在炎症中后期,抗炎细胞因子拮抗促炎因子介导的炎症反应,促使炎症反应消退,使创面愈合进入增殖期,加速创面的愈合速度。在糖尿病溃疡起主要作用的抗炎因子有白细胞介素4和白细胞介素10。 白细胞介素4:白细胞介素4是一种重要的抗炎细胞因子,具有较强的抗炎作用[36]。它能促进以Th2型细胞为特征的免疫应答反应过程,白细胞介素4可以通过刺激B细胞分化成浆细胞、刺激嗜酸性粒细胞和肥大细胞的活化和生长以及Ig类别的转换等促进体液免疫,这些细胞因子能够削弱T细胞增殖、巨噬细胞激活和促炎因子产生[37],从而发挥抗炎作用。ZHENG 等[38]研究表明,白细胞介素4在炎症早期可以抑制M1型巨噬细胞的激活并促进M2型巨噬细胞的激活,发挥抗炎作用。张洁等[39]在体外实验证明了白细胞介素4可以促进M2型巨噬细胞活化而抑制M1型巨噬细胞活化;她还发现白细胞介素4的干预不仅能够降低肿瘤坏死因子α的分泌,还能够提高白细胞介素10的水平。研究还发现,白细胞介素4还能明显抑制白细胞介素1β、NOD样受体热蛋白结构域相关蛋白3(NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain associated protein 3,NLRP3)以及Caspase-1的mRNA 表达,继而抑制炎症反应。 白细胞介素10:白细胞介素10是一种抗炎细胞因子,参与免疫反应和炎性反应。白细胞介素10既能抑制促炎细胞因子的释放,又能抑制炎性细胞激活、迁移和黏附[40],还能抑制多种趋化因子的合成,在一定程度上抑制白细胞向炎症部位的迁移。在创面愈合中,白细胞介素10在中后期的水平逐渐上升,因为M2型巨噬细胞促进其高分泌,减弱巨噬细胞和单核细胞的活化,从而降低促炎细胞因子的分泌,继而抑制创面的炎症反应[41]。在糖尿病溃疡的进程中,血清白细胞介素10水平会明显降低,糖尿病溃疡创面的抗炎能力减弱,机体一直处于炎症状态。 2.4 中医药调控促炎因子表达治疗糖尿病溃疡 近年来,随着对糖尿病溃疡的研究不断深入,中药单体、提取物和中药复方通过调控促炎因子的表达,抑制糖尿病溃疡创面炎症反应,显著促进了糖尿病溃疡的愈合,中医药在治疗糖尿病溃疡方面取得了显著的成果。然而,促炎因子众多,文章总结了在糖尿病溃疡发挥关键作用的促炎因子白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、超敏C-反应蛋白和干扰素γ。 2.4.1 中药调控白细胞介素1β表达抑制糖尿病溃疡创面炎症反应 白芷祛风除湿、消肿排脓及燥湿止带等功效显著,是治疗痈疽疮疡的常用药。雷思思[42]通过将1.8,3.6和7.2 g/kg的白芷在糖尿病溃疡大鼠灌胃的研究中发现,白芷可以降低糖尿病溃疡大鼠血清中促炎细胞因子白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α表达,并提高了血管内皮生长因子的表达,加速糖尿病溃疡创面的愈合,且低剂量的效果最好。表明白芷可以通过抑制糖尿病溃疡创面的炎症反应和促进糖尿病溃疡创面血管新生来提高糖尿病溃疡创面的愈合速度和愈合质量。此外,CHAO等[43]以 50 g,1∶1浓度混合的白芷、大黄粉末制作混合物,按照1 μL/mm2用量在糖尿病溃疡大鼠创面的局部外用,结果发现,白芷和大黄的联用显著抑制了核转录因子κB活性,降低了促炎因子白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α的水平,同时还增强了糖尿病溃疡创面组织中血管内皮生长因子、α-平滑肌肌动蛋白及诱导型一氧化氮合酶的表达,促进了血管生成。表明,白芷与大黄联用可减轻创面炎症反应,促进血管生成,进而促进 糖尿病溃疡大鼠创面愈合。 基质金属蛋白酶是一组由巨噬细胞等分泌的内肽酶家族,在创面愈合中发挥重要作用,其活性增强或表达增高会阻碍创面的愈合。既往研究表明,基质金属蛋白酶及其活性酶的水平在糖尿病溃疡中会显著升高,并且基质金属蛋白酶9与糖尿病并发症的发生和发展也有非常密切的关系[44],抑制基质金属蛋白酶的活性可以促进创面的愈合[45]。复方糖足生脉膏具有清热解毒、益气活血、消肿止痛、祛腐生肌之功效。马志伟等[46]利用低、中、高3种剂量的复方糖足生脉膏干预糖尿病溃疡大鼠,结果发现复方糖足生脉膏显著降低了糖尿病溃疡大鼠创面促炎因子白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达,提高了转化生长因子β1的表达,同时降低基质金属蛋白酶9的表达,增加溃疡面基质沉积。表明,复方糖足生脉膏可以通过抑制炎症反应及增加基质沉积等作用加速糖尿病溃疡大鼠创面的愈合。 紫檀芪是白藜芦醇的甲氧基化衍生物,不仅具有抗炎、抗氧化和抗糖尿病活性的作用,既往研究发现,紫檀芪能够通过抑制炎症反应和控制血糖等作用促进糖尿病合并烧伤的大鼠的创面愈合[47]。SRC是Ras/Raf/胞外信号调节激酶(ERK)信号通路的中枢,对细胞的增殖、迁移以及血管生成等有调节作用。Ras/Raf/促分裂原活化的蛋白激酶激酶(MEK)/ERK信号通路是促分裂原活化的蛋白激酶(MAPK)通路中研究较为充分的级联反应通路,能够调节细胞的存活、分化和生长。既往研究发现,SRC和MEK/ERK信号通路可促进皮肤的水合作用及改善皮肤的屏障功能[48],而通过激活SRC/MEK/ERK信号通路能够促进皮肤缺损大鼠的血管生成,进而促进创面愈合。刘亚坤等[49]通过在腹腔注射紫檀芪糖尿病溃疡大鼠的研究中发现,紫檀芪可以降低血清中白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α含量,提高血管内皮生长因子含量和创面肉芽组织中SRC,MEK1/2及ERK1/2的磷酸化水平,减轻创面炎症反应,促进血管生成;而在加入SRC抑制剂PP2后发现,PP2可逆转紫檀芪大鼠创面的上述作用,并抑制了紫檀芪对SRC/MEK/ERK信号通路相关蛋白表达的激活,表明紫檀芪可以通过抑制糖尿病溃疡大鼠创面炎症反应及促进血管生成等作用加速糖尿病溃疡大鼠创面的愈合速度,其机制可能与SRC/MEK/ERK信号通路被激活有关。中药单体、提取物或复方调控白细胞介素1β表达治疗糖尿病溃疡的相关作用机制见表1。"
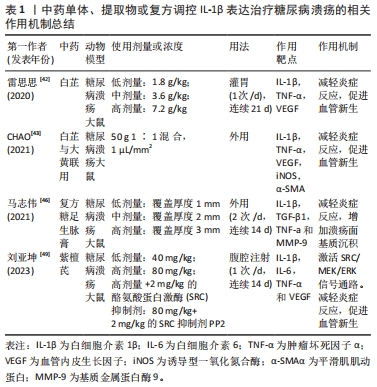
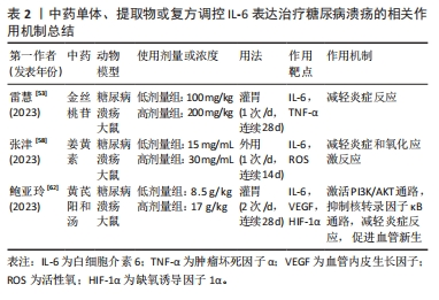
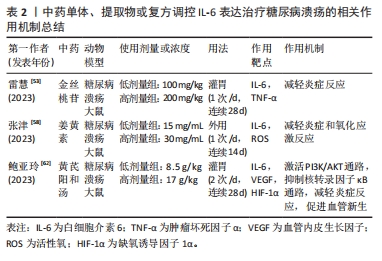
2.4.2 中药调控白细胞介素6表达抑制糖尿病溃疡创面炎症反应 金丝桃苷具有显著的抗氧化、抑制炎症反应以及保护血管等作用[50]。腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶(AMPK)/沉默信息调节因子1(SIRT1)信号通路参与炎症反应过程,在糖尿病中也有调控作用[51]。既往研究发现,激活 AMPK/SIRT1信号通路可抑制糖尿病心肌病小鼠的炎症和心肌细胞凋亡,从而减轻糖尿病心肌病症状[52]。雷慧等[53]在金丝桃苷干预糖尿病溃疡大鼠中发现低、高剂量的金丝桃苷均可以价降低糖尿病溃疡大鼠血清中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平,提高创面肉芽组织中AMPK、SIRT1 mRNA表达水平,大鼠创面肉芽组织炎性细胞浸润减少,成纤维细胞及毛细血管坏死减少,且高剂量的金丝桃苷的作用效果优于低剂量的金丝桃苷,表明金丝桃苷可减轻糖尿病溃疡大鼠炎症反应,加快创面愈合,其机制可能与激活AMPK/SIRT1信号通路有关。姜黄素是从姜黄中提取的多酚化合物,既往研究发现,姜黄素具有抑制体内和体外的氧化应激反应和炎症反应的作用[54-55],还能促进肉芽组织的形成,加速伤口的收缩和上皮化[56-57],因此已被用于治疗多种疾病。张津等[58]研究发现,低剂量和高剂量的姜黄素均可以降低脂多糖诱导的RAW264.7巨噬细胞CD86和白细胞介素6 mRNA表达,增加CD206和ARG1 mRNA的表达。同时降低活性氧水平,且高剂量的姜黄素组伤口中平滑肌α-肌动蛋白表达量较低剂量姜黄素组明显增加,结果显示,低剂量和高剂量的姜黄素组糖尿病溃疡大鼠的新生血管、胶原蛋白沉积和肉芽组织均明显增加,胶原纤维排列整齐致密,愈合速度加快,愈合效果更好,且高剂量作用效果优于低剂量。结果表明,姜黄素通过姜降低促炎因子表达,增加抗炎因子的释放来发挥抗炎作用,同时通过清除活性氧减少氧化应激,发挥抗氧化作用,进而促进糖尿病溃疡 大鼠创面的肉芽组织增生和胶原沉积,进而加快糖尿病溃疡大鼠创面的愈合。 阳和汤临床上被广泛应用于治疗糖尿病溃疡[59]。黄芪及以黄芪为主药的方剂可明显促进创面愈合,降低高血糖,提升早期糖尿病溃疡的治疗效果[60-61]。鲍亚玲等[62]在以阳和汤为主方,加入生黄芪的研究中发现,8.5 g/kg的低剂量和17 g/kg的高剂量黄芪阳和汤均可以降低血清炎性因子白细胞介素6水平,提高血管内皮生长因子、缺氧诱导因子1α水平,从而抑制炎症反应,促进血管生成,加速糖尿病溃疡大鼠创面愈合。PI3K/AKT 和核转录因子κB信号在炎症及血管生成中起关键作用。同时,该研究还发现,黄芪阳和汤还能提高糖尿病溃疡大鼠创面组织中p-PI3K,p-AKT及IκB-α蛋白表达,降低磷酸化核转录因子κB p65蛋白表达。表明,黄芪阳和汤的降低炎症反应,促进血管新生及加速糖尿病溃疡大鼠创面愈合的作用可能与PI3K/AKT通路的激活及核转录因子κB通路的抑制有关。中药单体、提取物或复方调控白细胞介素6治疗糖尿病溃疡的相关作用机制见表2。"
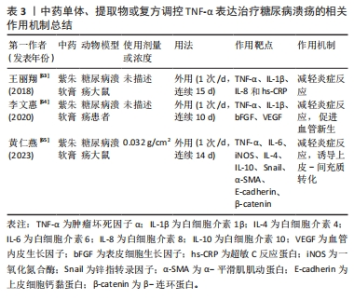
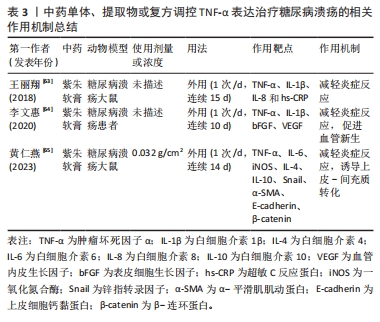
2.4.3 中药调控肿瘤坏死因子α表达抑制糖尿病溃疡创面炎症反应 紫朱软膏以紫草和朱砂为君,具有去腐生肌和补血益气功效,王丽翔等[63]研究发现,紫朱软膏能够降低糖尿病非缺血型溃疡中促炎因子肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素8、超敏C-反应蛋白表达,抑制创面炎症反应。李文惠等[64]在临床上观察紫朱软膏干预糖尿病溃疡患者愈合过程中细胞因子表达,发现紫朱软膏干预后,患者血清中促炎因子肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和终末糖基化产物(AGEs)表达明显降低,且其表达量差值与溃疡愈合率呈负相关,同时表皮细胞生长因子(bFGF)、血管内皮生长因子表达明显升高,表明紫朱软膏不仅能够抑制炎症反应,还能通过提高表皮细胞生长因子、血管内皮生长因子的表达,诱导糖尿病溃疡创面血管新生,促进糖尿病溃疡创面愈合。此外,紫朱软膏还能下调溃疡组织肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、诱导性一氧化氮合成酶 mRNA和上皮细胞钙黏蛋白(E-cadherin)表达,上调白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10 RNA和锌指转录因子(Snail)、β-连环蛋白(β-catenin)、α-平滑肌肌动蛋白(α-SMA)的表达,表明紫朱软膏不仅能下调促炎因子的表达,还能上调抗炎因子的表达,进而抑制炎症反应,同时还能通过促进上皮-间充质转化,促进糖尿病溃疡愈合,其机制可能与Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路的激活有关[65]。中药单体、提取物或复方调控肿瘤坏死因子α治疗糖尿病溃疡的相关作用机制见表3。"
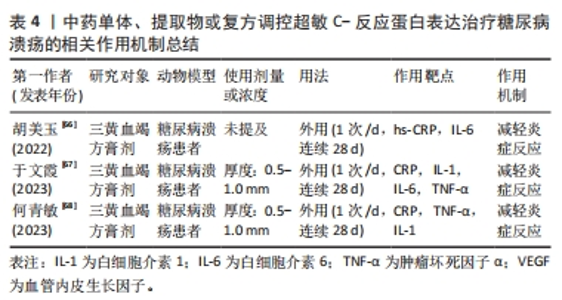
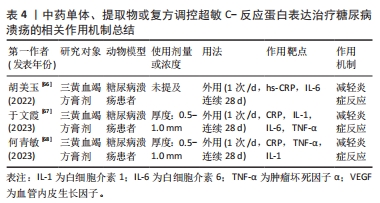
2.4.4 中药调控超敏C-反应蛋白表达抑制糖尿病溃疡创面炎症反应 三黄血竭方由黄连、黄柏、大黄、血竭和紫草等组成,具有活血散瘀、敛疮生肌之功。胡美玉[66]在临床中观察60例湿热毒盛证糖尿病溃疡患者发现,糖尿病溃疡患者在三黄血竭方膏剂干预后,超敏C-反应蛋白、血沉及白细胞介素6 等炎症指标水平显著降低,中医证候积分均降低,且治疗组疗效优于对照组,创面愈合面积和创面愈合率均显著提高。于文霞等[67]在临床中对120例湿热毒盛型糖尿病足患者用三黄血竭方膏剂治疗4周后发现,患者血清C-反应蛋白、白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6及肿瘤坏死因子α水平均降低,中医症状评分及总分均也降低,创面面积均也缩小,结果表明,三黄血竭方膏剂外敷治疗可通过抑制炎症反应,促进糖尿病溃疡创面愈合。何青敏等[68]在临床中也证实三黄血竭方能有效降低湿热毒盛证糖尿病溃疡患者血清C-反应蛋白、白细胞介素1、肿瘤坏死因子α水平,进而抑制炎症反应和感染,促进创面的组织修复,且治疗的患者总有效率高达94.74%。上述研究表明,三黄血竭方主要通过抑制炎症反应促进糖尿病溃疡愈合,已被广泛运用于临床,且有确切的疗效,对于湿热毒盛证糖尿病溃疡的治疗具有中药的指导意义。中药单体、提取物或复方调控超敏C-反应蛋白治疗糖尿病溃疡的相关作用机制见表4。"
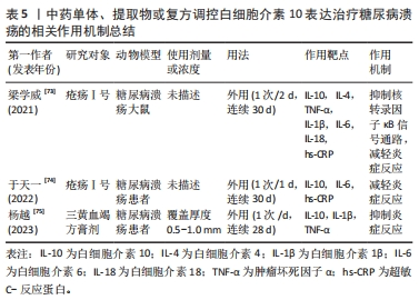
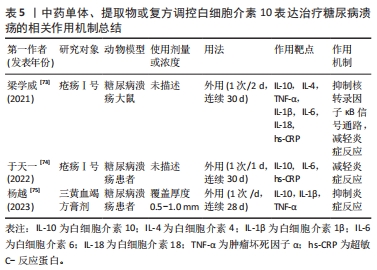
2.4.5 中药调控干扰素γ表达抑制糖尿病溃疡创面炎症反应 冲和膏具有行气活血、散瘀消肿之功,是治疗疮疡半阴半阳证的代表方。李月炜等[69]在利用冲和膏及改良冲和膏方Ⅰ和改良冲和膏方Ⅱ连续外用8周治疗糖尿病溃疡大鼠后发现,治疗后大鼠创面组织干扰素γ水平和髓过氧化物酶的表达明显降低,M1和M2型巨噬细胞均减少,而白细胞介素4的水平明显提高,创面炎性浸润减轻。表明冲和膏及其2个改良方均可有效调节促炎因子干扰素γ和抗炎因子白细胞介素4的水平,恢复Th1与Th2细胞动态平衡,进而抑制炎症反应,加速糖尿病溃疡的愈合,且改良冲和膏方Ⅰ作用优于冲和膏和改良冲和膏方Ⅱ。 解毒化瘀丸由大黄、黄连及当归等组成,具有清热解毒、除淤血等功能,专为热毒型脱疽而设。张箐鸿等[70]在解毒化瘀丸治疗60例非缺血性糖尿病溃疡患者的临床中发现,解毒化瘀丸干预治疗后,患者外周血干扰素γ、白细胞、血清降钙素原、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α及环氧化酶2水平均降低,血管内皮细胞和血清胰岛素样生长因子1的水平均升高,创面肉芽组织形成和愈合时间均缩短,目测类比评分均降低。表明解毒化瘀丸可以有效抑制糖尿病溃疡患者炎症反应,促进血管生成,并减轻患者的疼痛症状,最终促进糖尿病溃疡患者的创面愈合。 综上,通过对上述中医药抑制促炎因子的表达治疗糖尿病溃疡进行归纳和总结后发现,目前治疗糖尿病溃疡的中药单体、提取物和复方众多,分为外用和内服方剂,大多以中药复方为主,中药复方作用靶点也多于中药单体、提取物,提示多种药物的联用可能会增强疗效[71-75]。同时中药的使用剂量在一定程度上与糖尿病溃疡的治疗效果也呈正相关关系。目前最常用也是最新研制的中药是三黄血竭方和紫朱软膏,分别是治疗湿热毒盛型和非缺血型糖尿病溃疡的代表方剂,对多种促炎因子的表达均具有抑制作用,也有一定的促进血管生成作用。其中现已常用于临床的只有三黄血竭方,其他大部分治疗糖尿病溃疡的中药还处于动物实验阶段,因此研究者们应亟需进一步扩展中医药治疗糖尿病溃疡的临床使用。 2.5 中医药调控抗炎因子表达治疗糖尿病溃疡 炎症反应是促炎因子与抗炎因子两者相互协调下的的复杂过程,二者的动态平衡在炎症反应和创面愈合中起着关键作用。中药单体、提取物和中药复方不仅能下调促炎因子的表达,还能上调抗炎因子的表达,通过拮抗促炎因子介导的炎症反应,促使炎症反应消退。抗炎因子众多,在糖尿病溃疡发挥关键作用的促炎因子主要是白细胞介素4和白细胞介素10。 2.5.1 中药调控白细胞介素4表达抑制糖尿病溃疡创面炎症反应 温经通络方具有祛风除湿、活血通络、温经散寒之功。徐秀娟等[71]在临床中运用温经通络熏洗方外用治疗188例糖尿病溃疡患者3个月后发现,经温经通络熏洗方干预后,患者白细胞介素4、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α水平明显降低,胰岛素敏感指数、胰岛素抵抗指数以及胫后动脉和足背动脉的血管内径、血流速峰值均明显改善,溃疡面积明显缩小。表明温经通络熏洗方可以有效控制患者血糖、抑制创面炎症反应、改善足背动脉血流动力学,进而加速糖尿病溃疡创面的愈合。 ALI等[72]在利用丁香花提取物水凝胶治疗糖尿病溃疡大鼠,结果发现,香花提取物提高了抗炎因子白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10和促凋亡标志物p53,BAX及caspase-3的释放和表达,并抑制促炎因子 肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β分泌和表达,减少创面肉芽组织大量炎性细胞的浸润。同时上调了血管内皮生长因子、表皮生长因子(EGF)和成纤维细胞生长因子的水平及生长因子信号通路过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体 γ 辅激活因子1α(PGC-1α) 、过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体α(PPARα)、成纤维细胞生长因子β和血管内皮生长因子β mRNA的表达,促进血管生成。该实验还发现,丁香花提取物上调了创面愈合标志物基质金属蛋白酶 9、转化生长因子β、胶原蛋白和纤维连接蛋白表达。表明丁香花提取物通过调控炎症因子、促凋亡因子、血管生成因子以及创面愈合因子的表达,发挥抑制炎症反应、促进血管生成、促进内皮细胞和成纤维细胞等相关细胞增殖与凋亡的作用,促进糖尿病溃疡创面的愈合。 2.5.2 中药调控白细胞介素10表达抑制糖尿病溃疡创面炎症反应 疮疡Ⅰ号方由连翘、黄芩、苦参、赤芍、当归组成。梁学威等[73]研究发现,疮疡Ⅰ号外敷治疗后,大鼠创面中抗炎因子白细胞介素10和白细胞介素4的水平明显上升,而促炎因子肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素18、超敏C-反应蛋白及核转录因子κB-p65蛋白表达的水平明显下降,创面面积缩小,结果表明,疮疡Ⅰ号外敷通过提高抗炎因子水平,降低促炎因子水平,抑制炎症反应,加速糖尿病溃疡创面愈合,其机制可能与抑制核转录因子κB信号通路有关。随后,其课题组又将疮疡Ⅰ号应用于临床,在疮疡Ⅰ号外敷治疗30例湿热毒盛型糖尿病足部溃疡的临床观察中发现,经疮疡Ⅰ号治疗后,糖尿病溃疡患者创面的抗炎因子白细胞介素10水平显著上升,而促炎因子白细胞介素6、超敏C反应蛋白及中性粒细胞的水平明显下降,创面渗出减少,愈合速度和面积均显著提升,且疼痛症状减轻,表明疮疡Ⅰ号方通过调节炎症因子水平,抑制创面的炎症反应,进而促进糖尿病溃疡患者创面的愈合[74]。如前所述,三黄血竭方不仅能够降低超敏C-反应蛋白的表达,杨越等[75]研究发现,三黄血竭方外敷还能提高糖尿病溃疡创面分泌物中白细胞介素10的表达并降低肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β的表达,抑制炎症反应,有效改善糖尿病溃疡患者症状,缩小创面面积,改善溃疡深度,促进糖尿病溃疡愈合。 中药单体、提取物或复方调控白细胞介素10治疗糖尿病溃疡的相关作用机制[73-75],见表5。"
| [1] NATHAN DM. Long-term complications of diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993; 328(23):1676-1685. [2] MELONI M, IZZO V, GIURATO L, et al. Prevalence, clinical aspects and outcomes in a large cohort of persons with diabetic foot disease: comparison between neuropathic and ischemic ulcers. J Clin Med. 2020;9(6):1780. [3] SHOFLER D, RAI V, MANSAGER S, et al. Impact of resolvin mediators in the immunopathology of diabetes and wound healing. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2021;17(6):681-690. [4] BUEGESS JL, WYANT WA, ABDO AB, et al. Diabetic wound-healing science. Medicina. 2021;57(10):1072. [5] JIAO Y, CHEN Xl, NIU YX, et al. Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cells embedded in PF-127 hydrogel plus sodium ascorbyl phosphate combination promote diabetic wound healing in type 2 diabetic rat. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):559. [6] 杨博华,鞠上.中西医结合防治糖尿病足中国专家共识(精简版)[J].北京中医药,2019,38(11):1078-1087. [7] AWASTHI A, SINGH SK, KUMAR B, et al. Treatment strategies against diabetic foot ulcer: success so far and the road ahead. Curr Diabetesn Rev. 2021;17(4):421-436. [8] 刘佳莅,姜伟华,夏成勇,等.生肌玉红膏联合封闭负压引流术对糖尿病足患者溃疡创面血管新生及氧化应激指标的影响[J].湖南中医药大学学报, 2019,39(2):257-261. [9] 周丽俊,叶企兵,叶泽宇.中医综合疗法治疗糖尿病足溃疡的临床疗效观察[J].中华中医药杂志,2022,37(6):3613-3616. [10] 章威.中华图书集成:第十八册[M].北京:中医古籍出版社,1999:119. [11] 罗恩艳,杨九一,文奕舒,等.张嗣兰辨治脱疽经验[J].山东中医杂志,2023, 42(9):991-994. [12] 陆灏,倪青,柳国斌,等.糖尿病足病中医病证结合诊疗指南[J].中医杂志, 2021,62(12):1099-1104. [13] 王军,徐军.糖尿病足溃疡中医循证临床实践指南[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2015,21(5):540-543. [14] 徐洪涛,曹烨民.曹烨民教授分期辨证治疗糖尿病足筋疽经验[J].西部中医药,2021,34(5):61-64. [15] AITCHESON SM, FRENTIU FD, HURN SE, et al. Skin wound healing: normal macrophage function and macrophage dysfunction in diabetic woundss. Molecules. 2021;26(16):4917. [16] WAN G, CHEN Y, CHEN J, et al. Regulation of endothelial progenitor cell functions during hyperglycemia: new therapeutic targets in diabetic wound healings. J Mol Med (Berl). 2022;100(4):485-498. [17] MARÔNEK M, MARAFINI I, GARDLÍK R, et al. Metalloproteinases in inflammatory bowel diseasess. J Inflamm Res. 2021;14(1):1029-1041. [18] BREM H, TOMIC-CANIC M. Cellular and molecular basis of wound healing in diabetes. J Clin invest. 2007;117(5):1219-1222. [19] 金剑虹,洪郁芝,徐新鹏.感染性糖尿病足患者血清白细胞介素表达与感染的关系[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2015,25(4):747-749. [20] 方金赢.炎症反应抑制对糖尿病足溃疡患者血清血管生长因子、炎症因子的影响研究[J].数理医药学杂志,2021,34(11):1700-1702. [21] DINARELLO CA, DONATH MY, MANDRUP-POULSEN T. Role of IL-1beta in type 2 diabetes. Curr Opin Endocrinol. 2010,17(4):314-321. [22] 肖正华,张正军,陈定宇,等.黄芪多糖对糖尿病足部溃疡成纤维细胞增殖功能的影响[J].中国糖尿病杂志,2010,18(12):913-916. [23] MIRZA RE, FANG MM, ENNIS WJ, et al. Blocking interleukin-1beta induces a healing-associated wound macrophage phenotype and improves healing in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2013;62(7):2579-2587. [24] GMEZ-ZORRILLA S, MORANDEIRA F, CASTRO MJ, et al. Acute inflammatoryresp onse of patients with pseudomonas aeruginosa infections: a prospective study. Microb Drug Resist. 2017;23(4):523-530. [25] 范世珍,于波海.动态监测CRP、SAA和IL-6在儿童甲型流感诊断和治疗中的价值[J].中国实验诊断学,2021,25(1):9-12. [26] KARMAKER M, SANYAL SK, SULTANA M, et al. Association of bacteria in diabetic and non-diabetic foot infection - An investigation in patients from Bangladesh. J Infect Public Heal. 2016;9(3):267-277. [27] ASIF M, YOUSAF HM, SALEEM M, et al. Raphanus sativus seeds oilarrested in vivo inflammation and angiogenesis through down-regulation of TNF-a. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2022;23(5):728-739. [28] WNG T, HE R, ZHAO J, et al. Negative pressure wound therapy inhibits inflammation and upregulates activating transcription factor-3 and downregulates nuclear factor-κB in diabetic patients with foot ulcerations. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2017. doi:10.1002/dmrr.2871. [29] JETHANI S, BHUTANI N, YADAV A. Diagnostic utility of combined immature and total neutrophil counts along with C-reactive protein in early detection of neonatal sepsis: a cross-sectional study. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022;77(9): 103589. [30] SUN JT, LIU Y, LU L, et al. Diabetes-invoked high-density lipoprotein and its association with coronary artery disease in patients with type2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Cardiol. 2016;118(11):1674-1679. [31] 余成强,王启明,何家花,等.陕西省商洛市儿童呼吸道感染病原体血清流行病学研究[J].现代检验医学杂志,2019,34(6):142-144. [32] 陈向红,何红梅,赵娜,等.糖尿病足感染病原菌分布及多重耐药菌感染相关因素分析[J].中国消毒学杂志,2023,40(10):757-759, 763. [33] XU L, GONG C, LI G, et al. Ebselen suppresses inflammation induced by Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide via the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(5):6847-6851. [34] ALTUN E, YILDIZ A, CEVIK C, et al. The role of high sensitive C-reactive protein and histopathological evaluation in chronic gastritis patients with or without Helicobacter pylori infection. Acta Cir Bras. 2019;34(3):e201900310. [35] HAMMAD R, ELMADBOULY AA, AHMAD IH, et al. T-natural killers and interferon gamma/interleukin 4 in augmentation of infection in foot ulcer in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes metab Synbr Obes. 2021;14:1897-1908. [36] 谭强,肖敏,余倩颖,等.四川文氏皮外科协定方马齿苋汤加减治疗慢性湿疹疗效及对IL-4、IL-22、IFN-γ的影响[J].中国皮肤性病学杂志,2019,33(7): 824-827. [37] SCHULTEN V, TRIPPLE V, SIDNEY J, et al. Association between specific timothy grass antigens and changes in TH1-and TH2-cell responses following specific immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134(5):1076-1083. [38] ZHENG ZW, CHEN YH, WU DY, et al. Development of an accurate and proactive immunomodulatory strategy to improve bone substitute material-mediated osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Theranostics. 2018;8(19):5482-5500. [39] 张洁,肖天骄,李丽等.白细胞介素4调控巨噬细胞极化及骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(25):3960-3966. [40] NAGATA K, NISHIYAMA C. IL-10 in mast cell-mediated immune responses:anti-inflammatory and proinflammatory roles. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(9):4972-4975. [41] MOTWANI MP, GILROY DW. Macrophage development and polarization in chronic inflammation. Semin Immunol. 2015;27(4):257-266. [42] 雷思思.白芷对2型糖尿病小鼠皮肤溃疡促愈的作用机制的研究[D].天津:天津医科大学,2020. [43] CHAO YH, YANG WT, LI MC, et al. Angelica dahurica and Rheum officinale facilitated diabetic wound healing by elevating vascular endothelial growth factor. Am J Chin Med. 2021;49(6):1515. [44] MISHRA M, FLAGA J, KOWLURU RA. Molecular mechanism of transcriptional regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in diabetic retinopathy. J Cell Physiol. 2016;231(8):1709-1718. [45] LOBMANN R, AMBROSCH A, SCHULTZ G, et al. Expression of matrixmetalloproteinases and their inhibitors in the wounds of diabetic and non-diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 2002;45(7):1011-1016. [46] 马志伟,马晓蓉,张甜.复方糖足生脉膏对糖尿病大鼠创面炎症消散的影响[J].中国冶金工业医学杂志,2021,38(2):142-143. [47] HU W, YU H, ZHOU X, et al. Topical administration of pterostilbene accelerates burn wound healing in diabetes through activation of the HIF1α signaling pathway. Burns. 2022;48(6):1452-1461. [48] LEE JO, HWANG SH, SHEN T, et al. Enhancement of skin barrier and hydration-related molecules by protopanaxatriol in human keratinocytes. J Ginseng Res. 2021;45(2):354-360. [49] 刘亚坤,李刚,颜娟,等.紫檀芪对糖尿病性皮肤溃疡模型大鼠创面愈合的影响及机制[J].中国药房,2023,34(16):1967-1971. [50] 曹明明,车琳琳,朱路文.金丝桃苷药理作用及机制研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2022,24(6):150-155. [51] 邓九红,郑超,王声遥,等.醋酸泼尼松对糖尿病肾病模型大鼠肾功能、肾脏炎性反应及AMPK/SIRT1信号通路的影响[J].基础医学与临床,2022,42(2): 243-248. [52] JIA W, BAI T, ZENG J, et al. Combined administration of metformin and atorvastatin attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy by inhibiting inflammation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetic mice. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:634900. [53] 雷慧,鲍亚玲,鲍喜静,等.金丝桃苷对糖尿病足溃疡大鼠炎症反应、创面愈合及AMPK/SIRT1信号通路的影响[J].天津医药,2023,51(11):1205-1210. [54] FEREDOUNI N, DARROUNDI M, MOVAFFAGH J, et al. Curcumin nanofibers for the purpose of wound healing. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(5):5537-5554. [55] MOKHTARI M, RAZZAGHI R, MOMEN-HERAVI M. The effects of curcumin intake on wound healing and metabolic status in patients with diabetic foot ulcer: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Phytother Res. 2021;35(4): 2099-2107. [56] LIU X, ZHANG R, SHI H, et al. Protective effect of curcumin against ultraviolet a irradiation-induced photoaging in human dermal fibroblasts. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(5):7227-7237. [57] LENG QQ, LI Y, PANG XL, et al. Curcumin nanoparticles incorporated in PVA/collagen composite films promote wound healing. Drug Deliv. 2020;27(1):1676-1685. [58] 张津,崔新刚,朱彦兆,等.姜黄素对糖尿病小鼠皮肤创面愈合的影响[J].医药导报,2024,43(2):167-174. [59] 陈晶,刘欣欣.阳和汤的临床应用和基础研究进展[J].中华中医药学刊, 2022,40(8):10-13. [60] 牛文晶,刘鹏,王军.基于网络药理学探讨黄芪-当归治疗糖尿病足的作用机制[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2022,28(2):252-257. [61] 马艳春,段莹,胡建辉,等.黄芪治疗糖尿病及其并发症研究进展[J].中医药学报,2022,50(6):103-107. [62] 鲍亚玲,雷慧,马君,等.黄芪阳和汤调控PI3K/AKT/NF-κB信号通路促进糖尿病足溃疡大鼠创面愈合[J/OL].天津医药,1-8[2024-01-16]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/12.1116.R.20231019.1758.002.html. [63] 王丽翔,李文惠,柳国斌.紫朱软膏对糖尿病非缺血型溃疡愈合及相关炎性因子的干预作用[J].四川中医,2018,36(6):69-71. [64] 李文惠,杨晓,闫少庆,等.紫朱软膏干预糖尿病足愈合过程中细胞因子表达[J].中国老年学杂志,2020,40(6):1159-1161. [65] 黄仁燕,王宏飞,王徐红,等.紫朱软膏对糖尿病溃疡小鼠创面炎症反应及上皮-间充质转化的影响[J].陕西中医,2023,44(12):1673-1677. [66] 胡美玉.三黄血竭方膏剂治疗湿热毒盛证糖尿病足的临床疗效观察[D].唐山:华北理工大学,2022. [67] 于文霞,何青敏,姚彬,等.三黄血竭方对糖尿病足患者感染创面愈合及血清炎症因子水平的影响[J].广西医学,2023,45(2):157-161. [68] 何青敏,于文霞,王猛,等.三黄血竭方外敷治疗糖尿病足湿热毒盛证的疗效及对感染创面的影响[J].河北中医药学报,2023,38(4):43-46. [69] 李月炜,师建平,刘钰,等.改良冲和膏对糖尿病溃疡大鼠皮肤致敏性的研究[J].广州中医药大学学报,2023,40(4):955-964. [70] 张箐鸿,李宇宏,刘辉,等.解毒化瘀丸对非缺血性糖尿病足溃疡患者实验室指标及创面愈合情况的影响[J].河南医学研究,2023,32(14):2612-2616. [71] 徐秀娟,严小丽.温经通络熏洗方对糖尿病足患者血糖、足背动脉血流动力学和炎症因子的影响[J]. 浙江中医杂志,2022,57(7):493-494. [72] ALI R, KHAMIS T, ENAN G, et al. The healing capability of clove flower extract (CFE) in streptozotocin-induced (STZ induced) diabetic rat wounds infected with multidrug resistant bacteria. Molecules. 2022;27(7):2270. [73] 梁学威,苑海刚,于天一.疮疡Ⅰ号外敷对大鼠糖尿病性溃疡的影响[J].中医药信息,2021,38(4):37-41. [74] 于天一,梁学威,赵钢.疮疡I号外敷治疗湿热毒盛型糖尿病足部溃疡的临床观察[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2022,28(2):248-251. [75] 杨越,于文霞,何青敏,等.三黄血竭方外敷治疗糖尿病足溃疡疗效研究[J].陕西中医,2023,44(12):1740-1744. |
| [1] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [2] | Wang Weiqing, Zhou Yue. Chronic inflammation regulates adipose tissue fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1307-1312. |
| [3] | Zhang Xiaoyun, Liu Hua, Chai Yuan, Chen Feng, Zeng Hao, Gao Zhengang, Huang Yourong. Effect of Yishen Gushu Formula on bone metabolic markers and clinical efficacyn in patients with osteoporosis of kidney deficiency and blood stasis type [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1155-1160. |
| [4] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Li Wenbo, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. Effect of aerobic exercise on glycolipid metabolism, skeletal muscle inflammation and autophagy in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1200-1205. |
| [5] | Mu Bingtao, Yu Jingwen, Liu Chunyun, Guo Minfang, Meng Tao, Yang Pengwei, Wei Wenyue, Song Lijuan, Yu Jiezhong, Ma Cungen. Immunomodulatory effect of astragaloside IV on T cells of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1057-1062. |
| [6] | Pan Xiaolong, Fan Feiyan, Ying Chunmiao, Liu Feixiang, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine on inhibiting the aging of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1091-1098. |
| [7] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [8] | Zhang Ya, Mu Qiuju, Wang Zilin, Liu Hongjie, Zhu Lili. Hydrogel loaded with platelet-rich plasma promotes wound healing in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 690-696. |
| [9] | Qiao Hujun, Wang Guoxiang. Evaluation of rat osteoarthritis chondrocyte models induced by interleukin-1beta [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 516-521. |
| [10] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| [11] | Liu Luxing, Di Mingyuan, Yang Qiang. Signaling pathways in the mechanism underlying active ingredients of Chinese medicine in the treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 609-614. |
| [12] | Li Yuxuan, Yuan Lingli, Xu Zhiyuan, Yan Tao, Zhang Zhongchuan, Xu Wendi, Zhu Xunbing. Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of medial compartment osteoarthritis of knee joint: joint function and changes in inflammatory cytokines [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5828-5832. |
| [13] | Pan Shihong, Liu Ruiduan. Mitophagy and intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5872-5876. |
| [14] | Huang Keqi, Li Jiagen, Chen Shangtong, Rong Xiangbin. Mechanisms of long non-coding RNA in osteoarthritis and traditional Chinese medicine intervention [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5571-5576. |
| [15] | Ying Pu, Xu Yue, Lu Tong, Xue Yi, Miao Yiming. Mechanism by which miR-34a-5p/PLCD3 axis regulates osteoarthritis progression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(33): 5320-5325. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

