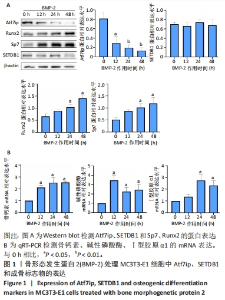
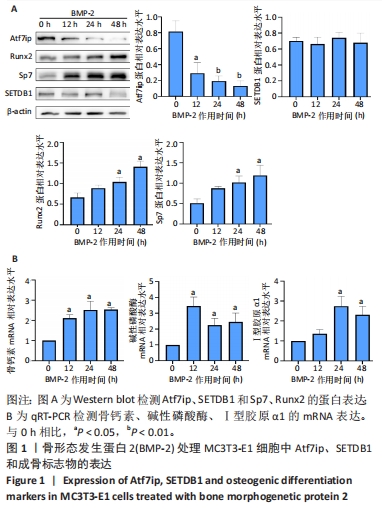
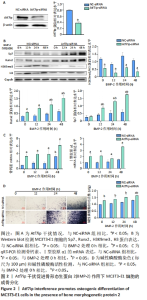
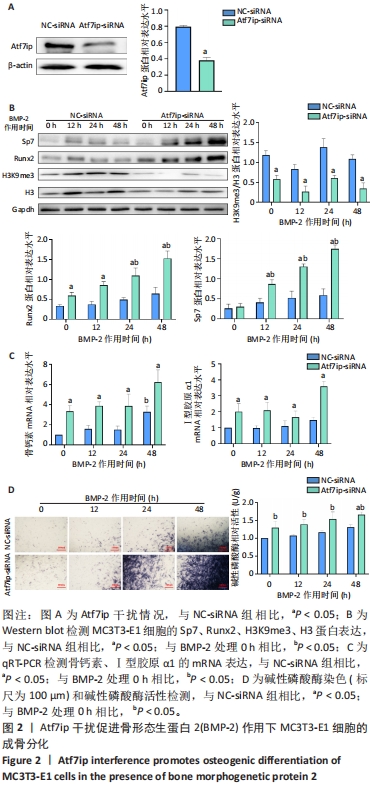
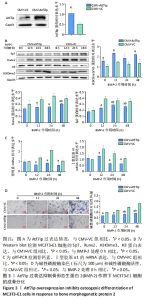
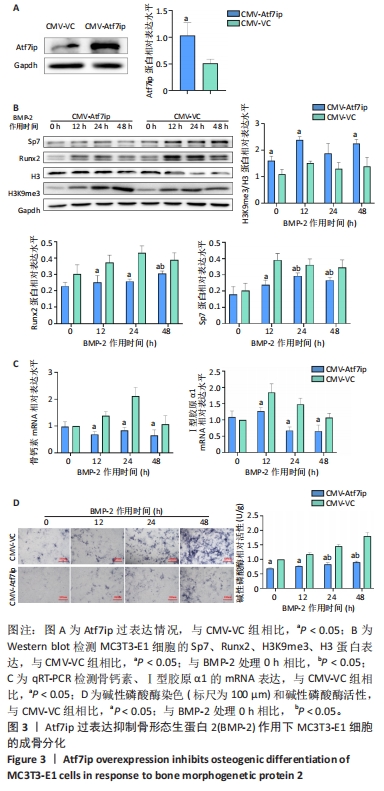
[1] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会,章振林.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J].中国全科医学,2023,26(14):1671-1691.
[2] 周倩,杨胜慧.积极应对人口老龄化政策背景下我国老年人口健康状况分析——基于第六次、第七次全国人口普查数据的比较分析[J].人口与健康,2023(7):49-53.
[3] WANG W, MAO J, CHEN Y, et al. Naringin promotes osteogenesis and ameliorates osteoporosis development by targeting JAK2/STAT3 signalling. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2022;49(1):113-121.
[4] ANAGNOSTIS P, PASCHOU SA, MINTZIORI G, et al. Drug holidays from bisphosphonates and denosumab in postmenopausal osteoporosis: EMAS position statement. Maturitas. 2017;101:23-30.
[5] 刘晖,李熙,吴学军,等.miR-21通过调节TGF-β/activin信号通路影响人骨髓间质干细胞向成骨细胞分化的机制[J].中国老年学杂志,2023,43(5):1211-1214.
[6] HOJO H, SAITO T, HE X, et al. Runx2 regulates chromatin accessibility to direct the osteoblast program at neonatal stages. Cell Rep. 2022; 40(10):111315.
[7] MORGAN MAJ, SHILATIFARD A. Reevaluating the roles of histone-modifying enzymes and their associated chromatin modifications in transcriptional regulation. Nat Genet. 2020;52(12):1271-1281.
[8] GOU LT, LIM DH, MA W, et al. Initiation of Parental Genome Reprogramming in Fertilized Oocyte by Splicing Kinase SRPK1-Catalyzed Protamine Phosphorylation. Cell. 2020;180(6):1212-1227.e14.
[9] WU J, LI J, CHEN K, et al. Atf7ip and SETDB1 interaction orchestrates the hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell state with diverse lineage differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023;120(1):e2209062120.
[10] SIN JH, ZUCKERMAN C, CORTEZ JT, et al. The epigenetic regulator ATF7ip inhibits Il2 expression, regulating Th17 responses. J Exp Med. 2019;216(9):2024-2037.
[11] TANJAYA J, HA P, ZHANG Y, et al. Genetic and pharmacologic suppression of PPARγ enhances NELL-1-stimulated bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2022;287:121609.
[12] YANG P, TRONCONE L, AUGUR ZM, et al. The role of bone morphogenetic protein signaling in vascular calcification. Bone. 2020; 141:115542.
[13] CHEN Y, ZHAO X, WU H. Transcriptional Programming in Arteriosclerotic Disease: A Multifaceted Function of the Runx2 (Runt-Related Transcription Factor 2). Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021;41(1): 20-34.
[14] HU G, SHI X, QU X, et al. Atf7ip Inhibits Osteoblast Differentiation via Negative Regulation of the Sp7 Transcription Factor. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(5):4305.
[15] QASEEM A, HICKS LA, ETXEANDIA-IKOBALTZETA I, et al. Pharmacologic Treatment of Primary Osteoporosis or Low Bone Mass to Prevent Fractures in Adults: A Living Clinical Guideline From the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2023;176(2):224-238.
[16] BEREBICHEZ-FRIDMAN R, MONTERO-OLVERA PR. Sources and Clinical Applications of Mesenchymal Stem Cells: State-of-the-art review. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2018;18(3):e264-e277.
[17] IZUMIYA M, HANIU M, UEDA K, et al. Evaluation of MC3T3-E1 Cell Osteogenesis in Different Cell Culture Media. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(14): 7752.
[18] 刘晖,李熙,吴学军,等.miR-21通过调节TGF-β/activin信号通路影响人骨髓间质干细胞向成骨细胞分化的机制[J].中国老年学杂志,2023,43(5):1211-1214.
[19] ZHANG L, XU L, ZHANG X, et al. Methyltransferase SETDB1 Promotes Osteoblast Proliferation by Epigenetically Silencing Macrod2 with the Assistance of Atf7ip. Cells. 2022;11(16):2580.
[20] FIDDES IT, LODEWIJK GA, MOORING M, et al. Human-Specific NOTCH2NL Genes Affect Notch Signaling and Cortical Neurogenesis. Cell. 2018;173(6):1356-1369.e22.
[21] CARBALLO GB, HONORATO JR, DE LOPES GPF, et al. A highlight on Sonic hedgehog pathway. Cell Commun Signal. 2018;16(1):11.
[22] 安小宁. PNS介导BMP-Smad信号通路调控BMSCs成骨分化的机制研究[D].南宁:广西医科大学,2019.
[23] OH WT, YANG YS, XIE J, et al. WNT-modulating gene silencers as a gene therapy for osteoporosis, bone fracture, and critical-sized bone defects. Mol Ther. 2023;31(2):435-453.
[24] PARK I, HWANG YJ, KIM T, et al. In silico probing and biological evaluation of SETDB1/ESET-targeted novel compounds that reduce tri-methylated histone H3K9 (H3K9me3) level. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2017;31(10):877-889.
[25] GUO Y, MAO X, XIONG L, et al. Structure-Guided Discovery of a Potent and Selective Cell-Active Inhibitor of SETDB1 Tudor Domain. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021;60(16):8760-8765. |