Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (15): 2445-2451.doi: 10.12307/2024.246
Previous Articles Next Articles
Cerium and cerium-based materials in dental applications
Zhang Binjing, Wang Jian
- State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2023-02-28Accepted:2023-03-03Online:2024-05-28Published:2023-09-23 -
Contact:Wang Jian, MD, Professor, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Zhang Binjing, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82271034, No. 81970985 (to WJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Binjing, Wang Jian. Cerium and cerium-based materials in dental applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(15): 2445-2451.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
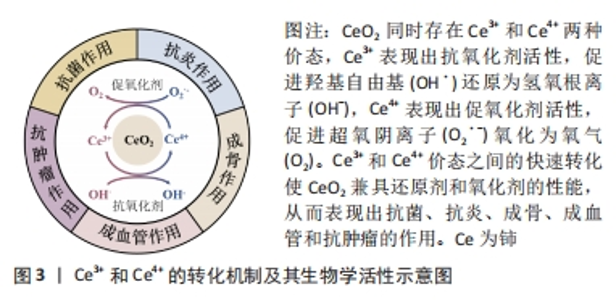
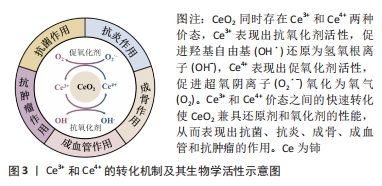
2.1 铈的生物学活性 2.1.1 抗菌作用 口腔众多疾病如龋病和牙周病等都与微生物感染有关。对于这些疾病的治疗,抑制微生物感染进而维持口腔微生态平衡是不可或缺的环节。感染的有效控制也为后续炎症的控制和组织再生提供良好的基础。铈的抗菌作用在19世纪末被发现。铈对金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌、铜绿假单胞菌、枯草芽孢杆菌、肺炎链球菌以及真菌如白色念珠菌均有良好的抗菌活性。一般认为,由于革兰阳性菌的肽聚糖阻碍了铈穿透细胞壁,铈对革兰阴性菌的抗菌活性强于革兰阳性菌[1-3]。铈的抗菌机制主要可以归纳为3类: 直接接触细菌:带正电的CeONP和带负电的细菌相结合,一方面阻碍了离子泵功能,使细菌细胞内外离子交换和营养物质转运受阻,影响DNA复制和细菌分裂[4];另一方面,释放的铈离子通过与巯基结合而吸附到转运蛋白上,抑制了细菌的电子流和细胞呼吸[5]。此外,CeONP不规则的表面形态可能对细菌细胞膜产生机械损伤[1]。 氧化应激:细菌表面Ce3+和Ce4+的可逆转化导致活性氧产生,活性氧可以破坏细菌核酸、蛋白质、多糖和脂质等其他生物分子[6]。 破坏细菌生物膜:细胞外DNA是生物膜的重要组成部分。基于CeONP的脱氧核糖核酸酶模拟活性,Ce4+可以诱导细胞外DNA水解成片段,进而破坏已形成细菌生物膜[7]。 2.1.2 抗炎作用 微生物感染引起的过度免疫炎症反应是造成组织损伤、疾病进展的重要因素,因此控制炎症反应也是口腔疾病治疗中需要关注的重点。活性氧是炎症进展中的关键信号分子,CeONP可通过Ce3+和Ce4+之间价态转化表现出来的超氧化物岐化酶和过氧化氢酶模拟酶活性清除活性氧[8]。此外,研究表明CeONP可以显著下调诱导型一氧化氮合酶、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素1β等促炎因子的表达表达[9],同时上调白细胞介素10、转化生成因子β和白细胞介素13等抗炎因子[3-9]。除此之外,CeONP还可以通过调控巨噬细胞极化而调节炎症反应。研究表明,高Ce4+/ Ce3+比例的CeONP相较于低Ce4+/ Ce3+比例的CeONP更有利于促进巨噬细胞向M2型极化,提高抗炎因子如白细胞介素10和白细胞介素1ra的表达,从而减轻炎症反应[10]。 2.1.3 成骨作用 口腔微生物感染和过度的免疫炎症反应常会引起牙槽骨破坏。有效实现骨再生有助于牙周重建和功能恢复。研究表明,铈通过激活转化生成因子β/骨形态发生蛋白信号通路促进Smad1/5/8蛋白的表达,最终上调了基质细胞衍生因子1和Runt相关转录因子2。基质细胞衍生因子1有利于间充质干细胞增殖和向骨损伤部位迁移,而Runt相关转录因子2促进成骨相关标志物如Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、碱性磷酸酶和骨钙素等的表达,从而促进间充质干细胞分化为成骨细胞[11]。此外,CeONP通过上调Fam53B蛋白而促进经典Wnt通路下游的β-连环蛋白的核易位,进而促进成骨相关基因的表达[12],同时也通过激活ERK通路增强骨再生[13]。进一步的研究表明高Ce4+/Ce3+比低Ce4+/Ce3+更有利于间充质干细胞成骨分化[10]。 2.1.4 成血管作用 良好的血供可为口腔软硬组织再生提供足够的氧气和营养物质。CeONP能增强血管内皮细胞的增殖和迁移能力,同时依靠其氧气缓冲能力提升低氧诱导因子1α的稳定性,上调血管内皮生长因子(血管生成的主要促进因子)的表达,诱导血管生成[14]。此外,最近的研究表明CeONP还通过Ref-1/APE1信号通路增加碱性成纤维细胞生长因子(参与血管生成过程中成纤维细胞的增殖迁移和细胞外基质的沉积)、血管内皮生长因子和肝细胞生长因子(抑制内皮细胞的凋亡)的表达,进而促进血管重建[15]。CHIGURUPATI等[14]的研究表明更大的表面积和更高的Ce3+/Ce4+比例使CeONP具有更强的细胞内氧气调节能力,从而更有利于血管的生成。但值得注意的是,CeONP的成血管作用受浓度和pH值等因素影响。例如,浓度高于8.6 μg/mL的CeONP会抑制人脐静脉内皮细胞的增殖[16]。在酸性pH值环境下,CeONP反而会诱导H2O2的产生和积累而抑制血管生成[17]。 2.1.5 抗肿瘤作用 一方面,CeONP在肿瘤特定微环境中表现出促氧化剂活性,上调活性氧水平对DNA造成损伤,同时通过激活p53依赖的线粒体信号通路诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡[18-19];另一方面,CeONP可调控肿瘤微环境,例如通过抑制肌成纤维细胞转化而降低肌成纤维细胞诱导的肿瘤细胞侵袭或通过抑制血管生成而抑制肿瘤生长[20]。此外,肿瘤微环境中过量累积的H2O2促进CeONP表现出过氧化氢酶活性而产生氧气以缓解肿瘤缺氧环境,有助于协同增强光动力治疗、光热治疗和放疗等疗效[21-22]。 综上,已有的研究证实铈具有广泛的生物学活性,为其在口腔医学领域的临床应用奠定了生物学基础。然而,目前对于抗菌机制的研究多局限于致病菌,而铈对口腔正常菌群及口腔微生态的影响尚无定论,进一步明确铈和口腔微生态的关系有助于对其抗菌作用的深入认识。在抗炎作用方面,相关研究多集中于调控活性氧生成和巨噬细胞极化方面,关于铈对单核细胞、肥大细胞、T细胞和B细胞等免疫炎症细胞影响的研究较为缺乏,有待未来进一步探索。此外,铈的抗肿瘤机制尚未完全明确,目前的观点更倾向于铈对肿瘤微环境的整体调控作用而非单一的活性氧对肿瘤细胞的毒性作用,更详细的机制需要深入地挖掘。Ce3+和Ce4+的转化机制及其生物学活性见图3。"
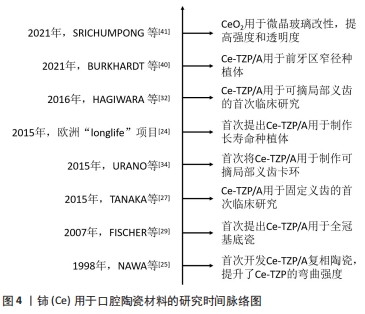
2.2 铈在口腔医学中的应用 2.2.1 铈在口腔陶瓷材料中的应用 氧化锆存在3种晶型:单斜晶相(m-ZrO2)、四方晶相(t-ZrO2)和立方晶相(c-ZrO2),具有优异的机械性能、美学性能和生物相容性,在修复和种植领域具有广泛的临床应用。但纯氧化锆难烧结致密,需要通过添加碱土氧化物或稀土氧化物使在中高温下才能存在的t相和c相在室温下稳定存在,所以称为稳定氧化锆陶瓷[23]。其中,氧化钇稳定的四方多晶氧化锆陶瓷有较高的弯曲强度(> 1 200 MPa)和断裂韧性(8-10 MPa·m1/2)[24],在临床中较为常用。然而,在潮湿的口腔环境中,氧化钇稳定的四方多晶氧化锆陶瓷容易发生低温老化而产生裂纹,最终可能导致修复体或种植体的失败。 为了解决此问题,氧化铈稳定的氧化锆(ceria-stabilized zirconia,Ce-TZP)陶瓷由于具有抗低温老化性和更好的相变诱导韧性(即在外力的作用下从t相转变为m相,产生体积膨胀和压应力以抵抗裂纹扩展),从1985年以来得到了广泛的研究。但Ce-TZP弯曲强度较低(约500 MPa),因此研究者开发了Ce-TZP/Al2O3复相陶瓷(Ce-TZP/A),Ce-TZP/A由摩尔分数10%的Ce-TZP和体积分数30%第二相Al2O3组成,纳米Al2O3颗粒和纳米ZrO2颗粒互相包裹在ZrO2晶粒和Al2O3晶粒中,Al2O3的引入使ZrO2晶粒显著细化,抑制了晶粒的生长,从而极大地提升了弯曲强度(1 400 MPa)和断裂韧性(19 MPa·m1/2)[25-26]。 尽管铈稳定的氧化锆/氧化铝纳米复合材料(ceria-stabilized zirconia/alumina nanocomposite,Ce-TZP/A)具有很高的机械强度,但Ce-TZP/A透光性低且呈白色,因此只适用于双层全瓷冠的基底瓷,表面需要制作饰面瓷,此外也可作为可摘局部义齿的支架和种植体材料。在实际的临床研究中,Ce-TZP/A已展现出良好的应用潜力。TANAKA等[27]对15例患者的22颗Ce-TZP/A制作的单冠和固定桥进行了3年的随访观察,结果发现探诊出血指数、牙周袋探诊深度和影像学未见明显改变,但有一颗基牙因牙根折裂而拔除,另有1例第一前磨牙修复体颈部饰面瓷轻微破碎。HUTTIG等[28]对57例患者的Ce-TZP/A制作的67颗单冠和40颗固定桥进行了为期3年的观察,结果出现10例饰面瓷的破损和断裂。饰面瓷破碎是其主要的并发症之一。 值得注意的是,Ce-TZP/A基底瓷和饰面瓷的匹配性是决定修复体成功与否的重要因素。已有研究证实不同饰面瓷的热膨胀系数和Ce-TZP/A双层陶瓷的断裂强度之间存在很强的相关性,饰面瓷的热膨胀系数略低于Ce-TZP/A基底瓷[热膨胀系数为(9.4±0.3)×10?6/℃]有利于在界面产生压缩应力而提升抗裂性[29-30]。例如,TERUI等[30]通过3点弯曲试验评估了Ce-TZP/A基底瓷和不同饰面瓷之间的粘接强度。结果显示,随饰面瓷的热膨胀系数的增高[(9.0,9.5,10)×10?6/℃],脱粘/裂纹起始强度从(30.5±1.5) MPa降低至(23.9±0.7) MPa。此外,饰面瓷厚度也会影响Ce-TZP/A双层陶瓷的断裂强度,0.8 mm的Ce-TZP/A基底瓷建议使用厚度为1.5-2.0 mm的饰面瓷[31]。除了在冠修复体中的应用,Ce-TZP/A还可用作全口义齿和可摘局部义齿的支架,研究表明Ce-TZP/A支架均未发生断裂或其他并发症,且患者对美观度和舒适度均较为满意[32-33]。上述结果表明,相较于传统的钴铬合金支架,Ce-TZP/A的机械力学性能与钴铬合金相当且优于氧化钇稳定的四方多晶氧化锆陶瓷,在提供足够的力学支撑的同时,其密度较小,舒适感更高,且能避免金属过敏等问题,在可摘局部义齿支架方面具有一定的应用潜力。URANO等[34]还发现2.0 mm宽度、1.0 mm厚度和0.6锥度比的Ce-TZP/A具有和钴铬合金相当的弯曲性能和抗疲劳性能,可用于卡环的制作。 在种植体方面,2015年欧洲项目“longlife”开发了一种新型的Ce-TZP,即在氧化锆中加入了等轴Al2O3和细长SrAl12O19,研究结果显示含摩尔分数10.5%CeO2的Ce-TZP具有优异的抗老化性能以及高的弯曲强度(> 1 GPa)和断裂韧性(> 10 MPa·m1/2)[35]。进一步研究证明Ce-TZP/A具有良好的生物相容性,能够通过促进集落刺激因子(CSF2/GM-CSF和CSF3/G-CSF)基因表达参与骨整合早期破骨细胞生成,通过调节骨形态发生蛋白和Runt相关转录因子2等成骨相关基因表达促进成骨向分化,还能直接与周围的骨样羟基磷灰石结合,从而实现良好的骨-种植体接触。数据表明,Ce-TZP/A植入后在髓质区和皮质区的骨种植体接触率持续上升,在第4-8周逐渐稳定,在第8周时分别达到56.81%和78.97%,其效果与氧化钇稳定的四方多晶氧化锆陶瓷基本相当。此外,Ce-TZP/A还可通过上调基质胶原、骨钙素、层粘连蛋白以及整合素β1和基质金属蛋白酶2等表达促进软组织整合[36-38]。LOPEZ-PIRIZ等[39]将Ce-TZP/A植入狗的上颌骨中,发现Ce-TZP/A展现出较好的骨和软组织整合,且没有观察到明显的炎症反应。BURKHARDT等[40]最近的研究表明Ce-TZP/A 3.4 mm窄直径种植体断裂载荷值为628 N,而单颗前牙咬合力为140-170 N,说明Ce-TZP/A在前牙区种植也有很好的应用潜力。 除此之外,CeO2还可以引入微晶玻璃中进行改性。在云母微晶玻璃中加入CeO2和氧化钇稳定的四方多晶氧化锆可提高云母微晶玻璃的强度、硬度和材料透明度,同时降低化学侵蚀性[41]。最近,GHAHSAREH等[42]发现CeO2通过提高残余玻璃相的化学稳定性提升了硅碱钙石微晶玻璃的化学稳定性,但会因为结晶度下降导致机械性能的降低。现将铈用于口腔陶瓷材料的研究总结于图4。"
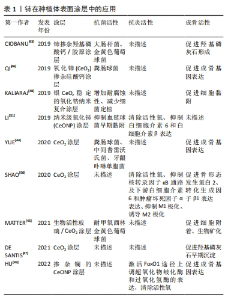
2.2.2 铈在种植体表面涂层中的应用 作为临床常用的种植材料,钛由于表面氧化物层呈生物惰性,其骨整合性较低。此外,种植体表面形成的细菌生物膜可能引起种植体周围炎,是导致种植体失败的主要原因。铈因其抗菌和抗炎活性可用于种植体表面改性,有效减少细菌生物膜形成而预防种植体周围炎的发生,促进骨和软组织整合。研究表明CeO2涂层或者掺杂铈的羟基磷灰石/硅酸钙涂层能有效抑制粪肠球菌、中间普雷沃氏菌、牙龈卟啉单胞菌、耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌等的生长繁殖[43-45],同时促进羟基磷灰石的早期沉淀,骨细胞黏附,显著上调碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素及骨唾液酸蛋白等成骨相关基因的表达,从而加速骨整合过程[46-47]。KALIARAJ等[48]在钛合金表面制备了银二氧化铈稳定的氧化锆纳米复合涂层,结果表明该涂层能增加钛合金的耐腐蚀性而减少细菌的定植。 尽管CeO2涂层抗氧化能力得到广泛的认可,但长期的氧化应激可能会削弱CeO2涂层的作用,适当地引入具有生物活性的离子有助于提升CeO2涂层的生物学功能。例如,Hu等[49]将镧掺杂到钛种植体表面的CeONP涂层中,发现30%镧掺杂的CeONP涂层能提高CeONP氧空位的数量从而提升其抗氧化能力,通过激活FoxO1通路上调超氧化物岐化酶和过氧化氢酶表达从而表现出最强的活性氧清除和促成骨活性。然而含有50%镧的CeONP涂层抗氧化能力反而更低,这可能归因于氧化镧的形成而没有形成更多的氧空位。 Ce3+/Ce4+比值是影响CeO2涂层的重要因素,有研究比较了AIII(低Ce4+/Ce3+)和B-IV(高Ce4+/Ce3+)两种CeO2涂层,发现B-IV涂层相较于AIII涂层具有更高的过氧化氢酶模拟活性,对活性氧生成和NF-κB信号通路的抑制作用更强,且能更好地抑制M1极化,诱导M2极化[50]。不同形状CeO2具有不同的Ce3+/Ce4+比值,LI等[51]评估了钛种植体表面不同形状的CeONP涂层(棒状、立方体和八面体)的抗菌和抗炎活性,结果显示八面体CeONP因尺寸最小和暴露的晶面更多,Ce3+/Ce4+比值更高,对血链球菌的早期黏附具有最强的抑制作用,活性氧清除能力也最强。因此通过调整CeO2纳米粒子的形状和Ce3+/Ce4+比值可实现CeO2种植体涂层的性能的调节和优化。现将上述铈在种植体表面涂层中的应用进展总结于表1中。"
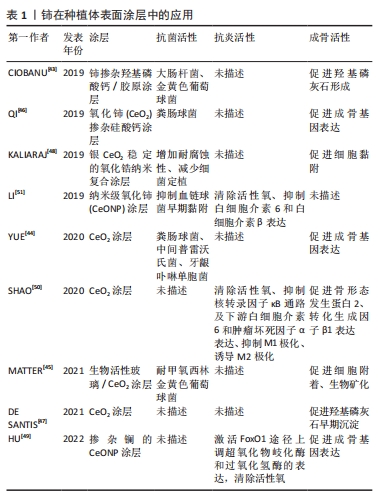
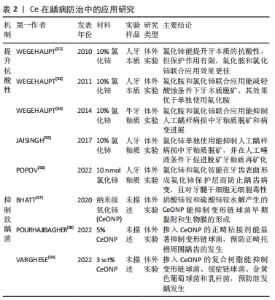
2.2.3 铈在龋病防治中的应用 龋病是由细菌生物膜介导的牙体硬组织脱矿的常见口腔疾病。氟化物防龋已被广泛应用于临床,但氟可导致氟牙症和氟骨症等不良反应。铈的防龋作用可分为两个方面:提升牙本质和牙釉质的抗酸性以及抑制致龋菌。在2010年,WEGEHAUPT等[52]发现氯化铈可增强牙本质的抗酸性,其团队后续的一系列的研究证明氯化铈和氟化物的联合使用能阻止酸蚀条件下牙釉质脱矿和根面龋病进展,其作用强于单独使用氟化物[53-54]。JAISINGH等[55]进一步研究表明单独使用10%的氯化铈也能在致龋条件减少牙釉质脱矿,在人工唾液的有利条件下促进脱矿牙釉质的再矿化,其作用可能归因于铈和钙的离子半径相似(分别为180 pm和185 pm),且铈的电荷价高于钙(分别为1.12和1.00鲍林电负性标度),所以Ce更易取代羟基磷灰石中的钙形成更稳定的铈磷灰石,从而提高牙釉质的抗酸能力。POPOV等[56]最新的研究还表明,氯化铈和氟化铵能在牙齿表面形成一层氟化铈保护层而起到保护牙釉质的作用,且未发现对牙髓干细胞明显的细胞毒性,显示出良好的生物相容性。由此可见,氯化铈可有效预防龋病发生并延缓龋病进展,氯化铈和氟化物的联合应用既能协同发挥最佳的龋病防治效果,又能降低氟化物用量从而减少不良反应,有望成为可替代的防龋方法。然而,目前的研究仅局限于体外实验,无法应对口腔复杂的实际的环境。此外,氯化铈的潜在毒性和合理用量尚未完全明确,限制了其在实际临床中的应用。未来应逐渐开展体内实验和临床试验,扩大氯化铈在龋病防治中的优势。 此外,铈强大的抗菌作用也可被用于抑制致龋菌。CeONP可减少变形链球菌早期黏附而抑制生物膜的形成(半抑制浓度为137 μmol/L)[57]。 POURHAJIBAGHER等[58]的研究发现掺杂体积分数5%的CeONP的正畸粘接剂能显著抑制变形链球菌而有效预防正畸托槽周围龋齿的发生。 VARGHESE等[59]将体积分数3%的CeONP作为抗菌填料添加到复合树脂中,发现该复合树脂材料对变形链球菌、缓症链球菌、金黄色葡萄球菌和乳杆菌都表现出明显的抑制作用,从而可有效防止继发龋的发生。除此之外,GARCIA等[60]还将CeO2掺入粘接剂中以提高黏接剂的阻射性,从而提升了对修复材料和相邻病变区域的鉴别和对继发龋的放射诊断。文章将铈在龋病防治中的应用进展研究总结于表2。"
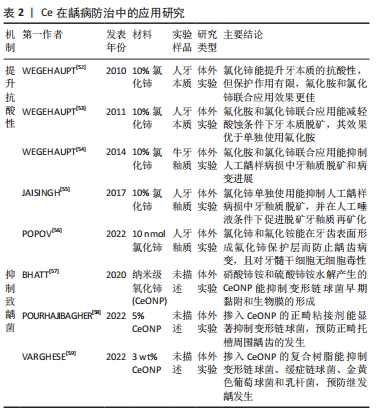
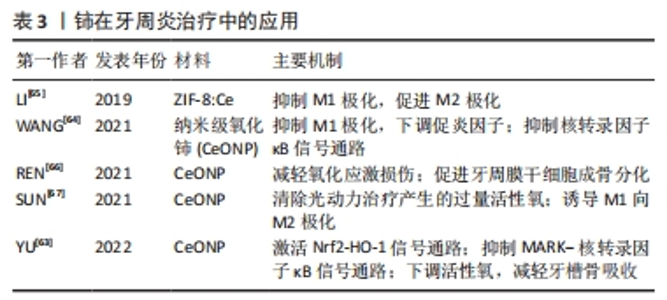
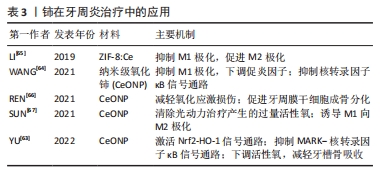
2.2.4 铈在牙髓治疗中的应用 牙本质牙髓复合体再生是牙髓治疗的趋势,对维护牙齿的完整性和耐久性至关重要。铈可作为市售三氧化矿物凝聚体的一种新型添加剂用于牙髓治疗。掺杂CeONP的市售三氧化矿物凝聚体可持续21 d通过下调活性氧水平促进牙髓干细胞向成牙本质细胞分化,增加钙沉积,同时不会降低MTA原本的抗压强度[61]。临床常用的Pro Root MTA中加入了氧化铋以增加阻射性,但会引起牙齿变色等问题。为解决此问题,DUMRONGVUTE等[62]合成了一种新型水门汀(2SrO·CeO2:S2Ce),结果显示Ce能有效吸收X射线中的较高能量成分,表现出比市售三氧化矿物凝聚体高3倍的阻射能力,同时还发现2SrO·CeO2:S2Ce具有更快的凝固速度和高的初始抗压强度,但在第28天后由于Sr离子的溶解,该水门汀抗压强度显著降低。这些结果说明Ce的引入不仅有效提升了水门汀初始强度并促进牙本质牙髓复合体再生,还能解决氧化铋引起的牙齿变色的问题,但需要关注离子溶解导致的水门汀抗压强度的长期变化。 2.2.5 铈在牙周炎治疗中的应用 牙周炎是由细菌诱发,宿主免疫调节失衡的氧化应激慢性炎症疾病。局部活性氧的大量产生导致牙周支持组织进行性破坏。铈在牙周炎治疗中的作用主要包括:减少活性氧生成,调节巨噬细胞极化和促进牙周组织愈合。一方面,CeONP依赖其超氧化物岐化酶和过氧化氢酶活性,通过激活Nrf2-HO-1信号通路(一种重要的抗氧化调节机制)和抑制MARK-NFκB信号通路下调由细菌内毒素刺激产生的活性氧,减轻牙周炎症反应,进而显著减轻牙槽骨吸收[63];另一方面,巨噬细胞是牙周炎发生发展的关键环节,牙周炎的进展与M1/M2巨噬细胞比例增高密切相关。WANG等[64]发现CeONP能抑制M1极化而抑制牙周炎破坏期的组织损伤。LI等[65]在类沸石咪唑酯骨架8(ZIF-8)中掺杂不同摩尔比的铈合成了ZIF-8:Ce纳米粒子,结果显示随着铈掺杂量的增加,ZIF-8:Ce的抗炎作用也随之增加,掺杂10%Ce的ZIF-8:Ce不仅抑制M1极化,还可诱导M2极化相关基因如Arg-1的表达,从而促进M1向M2表型的转化。在牙周组织再生方面,CeONP能保护牙周膜干细胞免受氧化应激损伤,诱导牙周膜干细胞成骨分化,从而促进牙周炎时牙周组织的愈合和骨再生[66]。 此外,抗菌光动力治疗是一种重要的牙周炎治疗方法,但光动力治疗产生的大量活性氧在杀菌的同时也会引起牙周组织的氧化应激,从而限制了其在临床中的应用。SUN等[67]将光敏剂涂覆在CeONP上,CeONP可有效且持续地清除光动力治疗后累积的大量残余活性氧,从而显著减轻了光动力治疗促炎症的不良反应,说明铈也可协同常规牙周炎治疗方法,在牙周炎治疗中具有广阔的应用前景。文章将上述铈在牙周炎治疗中的应用进展总结于表3。"

2.2.6 铈和口腔癌的联系 PACHAURI等[68]制备了基于CeONP-石墨烯复合纳米材料的电化学免疫传感器用于口腔癌标志物Cyfra-21-1蛋白早期检测(最佳线性范围为0.625 pg/mL-15 ng/mL),CeONP为电化学反应提供了更大的表面积从而显著提升了传感器的灵敏度。此外,最近的一项病例对照研究显示血清中高铈水平与口腔癌风险呈负相关,该结果有望促进铈在口腔癌预防和诊疗中的应用[69]。目前,CeONP在胃癌及卵巢癌等多种癌症治疗中已有广泛探索,但在颌面部肿瘤领域的应用仍存在大量空白,CeONP抗肿瘤活性有望为颌面部肿瘤的预防和治疗提供启发。 综上,关于Ce-TZP/A的研究已相对较为成熟,但远期疗效仍缺乏相关临床研究数据作为支撑。铈对口腔陶瓷材料的改性也不仅限于氧化锆陶瓷,对微晶玻璃等其他陶瓷材料的改性可能成为未来研究的方向之一。此外,目前大部分的研究多局限于CeONP,未来更多地关注铈和其他生物材料如金属有机骨架和生物活性玻璃等的联合应用有助于扩大对铈基材料的设计和探索。铈在种植体表面改性、龋病、牙髓炎及牙周炎等领域的研究也多停留在体外实验阶段,离实际的临床转化尚有一段距离,未来应在大量临床前研究数据的基础上,逐步推动临床前研究向临床试验过渡。 2.3 铈的生物安全性 尽管铈在大多数情况下具有良好的生物相容性,但也有研究报道了铈在高浓度和长时间给药的情况下存在潜在的细胞毒性和遗传毒性。例如,CeONP短期(24 h)作用于A549,CaCo2和 HepG2 细胞系均未观察到细胞毒性,但CeONP长期的作用(10 d)对所有细胞系均有细胞毒性[70]。铈的潜在毒性还与粒径和细胞类型等相关[70-71]。ARSLAN等[72]的研究显示氧化铈微粒(148.25 nm)的细胞毒性大于CeONP(25.30 nm)。STROBEL等[73]发现人脐静脉内皮细胞对CeONP的反应比人微血管内皮细胞更敏感。由此可见,不同的浓度、给药方式、粒径大小影响着铈基材料的生物安全性,更加长期和系统地探究潜在毒性,明确药代动力学途径,合理把控铈基材料的用法用量和适用范围,将是未来口腔应用中需要关注的重点。此外,未来也可更多地探索细胞和组织特异性靶向策略以及响应性释放策略(例如内部pH值、活性氧浓度、氧化还原电位等刺激或外界光、热、声及磁场等刺激)与铈基材料的开发和构建相结合,以提高生物相容性,扩大铈基材料在口腔医学乃至整个生物医学中的应用优势。"

| [1] BARKER E, SHEPHERD J, ASENCIO IO. The use of cerium compounds as antimicrobials for biomedical applications. Molecules. 2022;27(9):2678. [2] LI H, XIA P, PAN S, et al. The advances of ceria nanoparticles for biomedical applications in orthopaedics. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15: 7199-7214. [3] KARGOZAR S, BAINO F, HOSEINI SJ, et al. Biomedical applications of nanoceria: new roles for an old player. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2018; 13(23):3051-3069. [4] THILL A, ZEYONS O, SPALLA O, et al. Cytotoxicity of CeO2 nanoparticles for escherichia coli. physico-chemical insight of the cytotoxicity mechanism. Environ Sci Technol. 2006;40(19):6151-6156. [5] PELLETIER DA, SURESH AK, HOLTON GA, et al. Effects of engineered cerium oxide nanoparticles on bacterial growth and viability. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010;76(24):7981-7989. [6] ZHANG M, ZHANG C, ZHAI X, et al. Antibacterial mechanism and activity of cerium oxide nanoparticles. Sci China Mater. 2019;62(11):1727-1739. [7] LIU Z, WANG F, REN J, et al. A series of MOF/Ce-based nanozymes with dual enzyme-like activity disrupting biofilms and hindering recolonization of bacteria. Biomaterials. 2019;208:21-31. [8] STEPHEN INBARAJ B, CHEN BH. An overview on recent in vivo biological application of cerium oxide nanoparticles. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2020;15(5):558-575. [9] WEI F, NEAL CJ, SAKTHIVEL TS, et al. Multi-functional cerium oxide nanoparticles regulate inflammation and enhance osteogenesis. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;124:112041. [10] LI J, WEN J, LI B, et al. Valence state manipulation of cerium oxide nanoparticles on a titanium surface for modulating cell fate and bone formation. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018;5(2):1700678. [11] HU Y, DU Y, JIANG H, et al. Cerium promotes bone marrow stromal cells migration and osteogenic differentiation via Smad1/5/8 signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(8):5369-5378. [12] LUO J, ZHU S, TONG Y, et al. Cerium oxide nanoparticles promote osteoplastic precursor differentiation by activating the Wnt pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022;201(2):865-873. [13] LU B, ZHU DY, YIN JH, et al. Incorporation of cerium oxide in hollow mesoporous bioglass scaffolds for enhanced bone regeneration by activating the ERK signaling pathway. Biofabrication. 2019;11(2):025012. [14] CHIGURUPATI S, MUGHAL MR, OKUN E, et al. Effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles on the growth of keratinocytes, fibroblasts and vascular endothelial cells in cutaneous wound healing. Biomaterials. 2013;34(9): 2194-2201. [15] PARK IS, MAHAPATRA C, PARK JS, et al. Revascularization and limb salvage following critical limb ischemia by nanoceria-induced Ref-1/APE1-dependent angiogenesis. Biomaterials. 2020;242:119919. [16] DOWDING JM, DAS S, KUMAR A, et al. Cellular interaction and toxicity depend on physicochemical properties and surface modification of redox-active nanomaterials. ACS Nano. 2013;7(6):4855-4868. [17] WASON MS, COLON J, DAS S, et al. Sensitization of pancreatic cancer cells to radiation by cerium oxide nanoparticle-induced ROS production. Nanomedicine. 2013;9(4):558-569. [18] TIAN Z, LIU H, GUO Z, et al. A pH-responsive polymer-CeO2 hybrid to catalytically generate oxidative stress for tumor therapy. Small. 2020;16(47):e2004654. [19] DATTA A, MISHRA S, MANNA K, et al. Pro-oxidant therapeutic activities of cerium oxide nanoparticles in colorectal carcinoma cells. ACS Omega. 2020;5(17):9714-9723. [20] CORSI F, CAPUTO F, TRAVERSA E, et al. Not Only Redox: The multifaceted activity of cerium oxide nanoparticles in cancer prevention and therapy. Front Oncol. 2018;8:309. [21] ZENG L, CHENG H, DAI Y, et al. In vivo regenerable cerium oxide nanozyme-Loaded pH/H2O2-responsive nanovesicle for tumor-targeted photothermal and photodynamic therapies. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(1):233-244. [22] ZHOU X, YOU M, WANG F, et al. Multifunctional graphdiyne-cerium oxide nanozymes facilitate microRNA delivery and attenuate tumor hypoxia for highly efficient radiotherapy of esophageal cancer. Adv Mater. 2021;33(24):e2100556. [23] 李楠,谢志鹏,易中周,等. CeO2稳定ZrO2陶瓷材料的研究进展[J].陶瓷学报,2020,41(6):835-848. [24] PALMERO P, FORNABAIO M, MONTANARO L, et al. Towards long lasting zirconia-based composites for dental implants. Part I: innovative synthesis, microstructural characterization and in vitro stability. Biomaterials. 2015; 50:38-46. [25] NAWA M, NAKAMOTO S, SEKINO T, et al. Tough and strong Ce-TZP/alumina nanocomposites doped with titania. Ceram Int. 1998;24(7):497-506. [26] TANAKA K, TAMURA J, KAWANABE K, et al. Ce-TZP/Al2O3 nanocomposite as a bearing material in total joint replacement. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002; 63(3):262-270. [27] TANAKA S, TAKABA M, ISHIURA Y, et al. A 3-year follow-up of ceria-stabilized zirconia/alumina nanocomposite (Ce-TZP/A) frameworks for fixed dental prostheses. J Prosthodont Res. 2015;59(1):55-61. [28] HUTTIG F, KEITEL JP, PRUTSCHER A, et al. Fixed dental prostheses and single-tooth crowns based on ceria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia/alumina nanocomposite frameworks: outcome after 2 years in a clinical trial. Int J Prosthodont. 2017;30(5):461-464. [29] FISCHER J, STAWARCZYK B. Compatibility of machined Ce-TZP/Al2O3 nanocomposite and a veneering ceramic. Dent Mater. 2007;23(12): 1500-1505. [30] TERUI Y, SATO K, GOTO D, et al. Compatibility of Ce-TZP/Al2O3 nanocomposite frameworks and veneering porcelains. Dent Mater J. 2013;32(5):839-846. [31] SAWADA T, SCHILLE C, WAGNER V, et al. Biaxial flexural strength of the bilayered disk composed of ceria-stabilized zirconia/alumina nanocomposite (Ce-TZP/A) and veneering porcelain. Dent Mater. 2018;34(8):1199-1210. [32] HAGIWARA Y, NAKAJIMA K. Application of Ce-TZP/Al2O3 nanocomposite to the framework of an implant-fixed complete dental prosthesis and a complete denture. J Prosthodont Res. 2016;60(4):337-343. [33] HAGIWARA Y, NAKABAYASHI S, IKEDA T, et al. Ceria-stabilized zirconia/alumina nanocomposite for fabricating the framework of removable dental prostheses: preliminary results from a 4-year follow-up. Int J Prosthodont. 2019;32(3):254-256. [34] URANO S, HOTTA Y, MIYAZAKI T, et al. Bending properties of Ce-TZP/A nanocomposite clasps for removable partial dentures. Int J Prosthodont. 2015;28(2):191-197. [35] REVERON H, FORNABAIO M, PALMERO P, et al. Towards long lasting zirconia-based composites for dental implants: transformation induced plasticity and its consequence on ceramic reliability. Acta Biomater. 2017;48:423-432. [36] ALTMANN B, RABEL K, KOHAL RJ, et al. Cellular transcriptional response to zirconia-based implant materials. Dent Mater. 2017;33(2):241-255. [37] ALTMANN B, KARYGIANNI L, AL-AHMAD A, et al. Assessment of novel long-lasting ceria-stabilized zirconia-based ceramics with different surface topographies as implant materials. Adv Funct Mater. 2017;27(40):1702512. [38] SAITO MM, ONUMA K, YAMAMOTO R, et al. New insights into bioactivity of ceria-stabilized zirconia: direct bonding to bone-like hydroxyapatite at nanoscale. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021; 121:111665. [39] LOPEZ-PIRIZ R, FERNANDEZ A, GOYOS-BALL L, et al. Performance of a new Al2O3/Ce-TZP ceramic nanocomposite dental implant: a pilot study in dogs. Materials (Basel). 2017;10(6):614. [40] BURKHARDT F, HARLASS M, ADOLFSSON E, et al. A novel zirconia-based composite presents an aging resistant material for narrow-diameter ceramic implants. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(9):2151. [41] SRICHUMPONG T, PINTASIRI S, HENESS G, et al. The influence of yttria-stabilised zirconia and cerium oxide on the microstructural morphology and properties of a mica glass-ceramic for restorative dental materials. J Asian Ceram Soc. 2021;9(3):926-933. [42] GHAHSAREH ZS, BANIJAMALI S, AGHAEI A. Cerium oxide containing canasite based glass-ceramics for dental applications: crystallization behavior, mechanical and chemical properties. ceram Int. 2022;48(6): 8489-8501. [43] CIOBANU G, HARJA M. Cerium-doped hydroxyapatite/collagen coatings on titanium for bone implants. Ceram Int. 2019;45(2):2852-2857. [44] YUE J, JIN Z, POON HLE, et al. Osteogenic and antibacterial activity of a plasma-sprayed CeO2 coating on a titanium (Ti)-based dental implant. Coatings. 2020;10(10):1007. [45] MATTER MT, MALIQI L, KEEVEND K, et al. One-step synthesis of versatile antimicrobial nano-architected implant coatings for hard and soft tissue healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(28):33300-33310. [46] QI S, WU J, XU Y, et al. Chemical stability and antimicrobial activity of plasma-sprayed cerium oxide-incorporated calcium silicate coating in dental implants. Implant Dent. 2019;28(6):564-570. [47] DE SANTIS S, SOTGIU G, PORCELLI F, et al. A simple cerium coating strategy for titanium oxide nano-tubes’ bioactivity enhancement. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021;11(2):445. [48] KALIARAJ GS, KIRUBAHARAN AMK, ALAGARSAMY K, et al. Silver-ceria stabilized zirconia composite coatings on titanium for potential implant applications. Surf Coat Tech. 2019;368:224-231. [49] HU W, YIE KHR, LIU C, et al. Improving the valence self-reversible conversion of cerium nanoparticles on titanium implants by lanthanum doping to enhance ROS elimination and osteogenesis. Dent Mater. 2022;38(8):1362-1375. [50] SHAO D, LI K, YOU M, et al. Macrophage polarization by plasma sprayed ceria coatings on titanium-based implants: cerium valence state matters. Appl Surf Sci. 2020;504:144070. [51] LI X, QI M, SUN X, et al. Surface treatments on titanium implants via nanostructured ceria for antibacterial and anti-inflammatory capabilities. Acta Biomater. 2019;94:627-643. [52] WEGEHAUPT FJ, SENER B, ATTIN T, et al. Application of cerium chloride to improve the acid resistance of dentine. Arch Oral Biol. 2010;55(6): 441-446. [53] WEGEHAUPT FJ, SENER B, ATTIN T, et al. Anti-erosive potential of amine fluoride, cerium chloride and laser irradiation application on dentine. Arch Oral Biol. 2011;56(12):1541-1547. [54] WEGEHAUPT FJ, BUCHALLA W, SENER B, et al. Cerium chloride reduces enamel lesion initiation and progression in vitro. Caries Res. 2014;48(1):45-50. [55] JAISINGH R, SHANBHOG R, NANDLAL B, et al. Effect of 10% cerium chloride on artificial caries lesions of human enamel evaluated using quantitative light-induced fluorescence: an in vitro study. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2017;18(3):163-169. [56] POPOV AL, ZHOLOBAK NM, SHCHERBAKOV AB, et al. The strong protective action of Ce3+/F- combined treatment on tooth enamel and epithelial cells. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022;12(17):3034. [57] BHATT L, CHEN L, GUO J, et al. Hydrolyzed Ce(IV) salts limit sucrose-dependent biofilm formation by Streptococcus mutans. J Inorg Biochem. 2020;206:110997. [58] POURHAJIBAGHER M, BAHADOR A. Physico-mechanical properties, antimicrobial activities, and anti-biofilm potencies of orthodontic adhesive containing cerium oxide nanoparticles against Streptococcus mutans. Folia Med (Plovdiv). 2022;64(2):252-259. [59] VARGHESE EJ, SIHIVAHANAN D, VENKATESH KV. Development of novel antimicrobial dental composite resin with nano cerium oxide fillers. Int J Biomater. 2022;2022:3912290. [60] GARCIA IM, LEITUNE VCB, TAKIMI AS, et al. Cerium dioxide particles to tune radiopacity of dental adhesives: microstructural and physico-chemical evaluation. J Funct Biomater. 2020;11(1):7. [61] JUN SK, YOON JY, MAHAPATRA C, et al. Ceria-incorporated MTA for accelerating odontoblastic differentiation via ROS downregulation. Dent Mater. 2019;35(9):1291-1299. [62] DUMRONGVUTE K, ADEL S, WADA T, et al. Distrontium cerate as a radiopaque component of hydraulic endodontic cement. Materials (Basel). 2021;15(1):284. [63] YU Y, ZHAO S, GU D, et al. Cerium oxide nanozyme attenuates periodontal bone destruction by inhibiting the ROS-NFκB pathway. Nanoscale. 2022;14(7):2628-2637. [64] WANG Y, LI C, WAN Y, et al. Quercetin-loaded ceria nanocomposite potentiate dual-directional immunoregulation via macrophage polarization against periodontal inflammation. Small. 2021;17(41): e2101505. [65] LI X, QI M, LI C, et al. Novel nanoparticles of cerium-doped zeolitic imidazolate frameworks with dual benefits of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory functions against periodontitis. J Mater Chem B. 2019;7(44):6955-6971. [66] REN S, ZHOU Y, FAN R, et al. Constructing biocompatible MSN@Ce@PEG nanoplatform for enhancing regenerative capability of stem cell via ROS-scavenging in periodontitis. Chem Eng J. 2021;423:130207. [67] SUN Y, SUN X, LI X, et al. A versatile nanocomposite based on nanoceria for antibacterial enhancement and protection from aPDT-aggravated inflammation via modulation of macrophage polarization. Biomaterials. 2021;268:120614. [68] PACHAURI N, DAVE K, DINDA A, et al. Cubic CeO2 implanted reduced graphene oxide-based highly sensitive biosensor for non-invasive oral cancer biomarker detection. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6(19):3000-3012. [69] HE B, WANG J, LIN J, et al. Association between rare earth element cerium and the risk of oral cancer: a case-control study in southeast china. Front Public Health. 2021;9:647120. [70] DE MARZI L, MONACO A, DE LAPUENTE J, et al. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of ceria nanoparticles on different cell lines in vitro. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(2):3065-3077. [71] GAGNON J, FROMM KM. Toxicity and Protective Effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles (nanoceria) depending on their preparation method, particle size, cell type, and exposure route. Eur J Inorg Chem. 2015;2015(27):4510-4517. [72] ARSLAN K, AKBABA GB. In vitro genotoxicity assessment and comparison of cerium (IV) oxide micro- and nanoparticles. Toxicol Ind Health. 2020;36(2):76-83. [73] STROBEL C, FORSTER M, HILGER I. Biocompatibility of cerium dioxide and silicon dioxide nanoparticles with endothelial cells. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2014;5:1795-1807. |
| [1] | Xu Yinghua, Liu Jing, You Quan, Wen Zhihao, Gao Lu. Effect of neodymium-doped:yttrium aluminum perovskite laser combined with two kinds of remineralizers on remineralization of early enamel caries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 360-365. |
| [2] | Han Yue, Wang Yufei, Liu Wanqing, Dong Ming, Niu Weidong. Effects of icariin on proliferation and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells in an inflammatory environment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3709-3714. |
| [3] | Ge Ruiyang, Ni Can, Yang Kun, Yan Fuhua. The role of macrophage polarization in the pathogenesis and treatment of periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(20): 3246-3251. |
| [4] | Xiao Ziteng, Wang Tingyu, Zhang Wenwen, Tan Fengyi, Su Haiwei, Li Siting, Wu Yahui, Zhou Yanfang, Peng Xinsheng. Exosomes and skin wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(19): 3104-3110. |
| [5] | Wang Yuxue, Zhou Xin, Zheng Junyuan, Zhou Yongqing. Human beta-defensin 3 hydrogel for treatment of periodontitis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(17): 2690-2695. |
| [6] | Bian Zhihong, Zhang Yuntao, Li Zeming, Hou Yudong. Potential of shikonin and its derivatives in oral soft and hard tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(17): 2747-2752. |
| [7] | Cheng Weilu, Liu Yinghui. Clinical application of additive manufacturing technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(17): 2782-2788. |
| [8] | He Wei, Zhou Zheng, Wu Lingling, Wang Kai, Mu Caiyun. Moxibustion and reduced graphene oxide/cerium dioxide nanocomposites for repairing infectious wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(15): 2307-2314. |
| [9] | Zhai Haoyan, Zhao Yuan, Fan Dengying, Liu Chunyan. The role of reactive oxygen species in periodontitis and periodontal tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2254-2260. |
| [10] | Tong Tong, Liu Chunyan, Liu Bing, Zhao Fei. Long non-coding RNA and periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2267-2273. |
| [11] | Sun Jinyi, Wang Qinying, Li Ying, Meng Maohua, Chen Helin, Zeng Xiao, Shu Jiayu, Li Wenjie, Luo Yuncai, Dong Qiang. The role of silent information regulator in periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1737-1742. |
| [12] | Lang Yaoling, Wang Qian, Chen Bin, Bai Guohui, Guan Xiaoyan, Liu Jianguo. Removal of the selective marker gene in the fusion gene expression vector of plant anti-caries vaccine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 7-11. |
| [13] | Li Mengfei, Zhang Hong, Zhao Shaojian, Yin Guanghao, Wang Qibao. Expression of forkhead box protein 3 in refractory periapical periodontitis in rats with Enterococcus faecalis infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1187-1192. |
| [14] | Xu Xingxing, Wen Chaoju, Meng Maohua, Wang Qinying, Chen Jingqiao, Dong Qiang. Carbon nanomaterials in oral implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1062-1070. |
| [15] | Li Hao, Ye Zhimao, Luo Yicai, Li Kongmei, Mai Yuying, Wang Qi. Enhanced miR-185-5p expression attenuates inflammatory responses in a mouse model of experimental periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(35): 5676-5680. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||