Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (19): 3090-3096.doi: 10.12307/2024.145
Previous Articles Next Articles
Strategies and advance on stem cell transplantation for repair of spinal cord injury
He Wanyu1, Cheng Leping1, 2
- 1Institute of Neuroscience and Guangxi Key Laboratory of Brain Science, Guangxi Health Commission Key Laboratory of Basic Research on Brain Function and Disease, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Key Laboratory of Longevity and Aging-Related Diseases of Chinese Ministry of Education, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-03-16Accepted:2023-04-28Online:2024-07-08Published:2023-09-26 -
Contact:Cheng Leping, PhD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Doctoral supervisor, Institute of Neuroscience and Guangxi Key Laboratory of Brain Science, Guangxi Health Commission Key Laboratory of Basic Research on Brain Function and Disease, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Key Laboratory of Longevity and Aging-Related Diseases of Chinese Ministry of Education, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:He Wanyu, Master candidate, Institute of Neuroscience and Guangxi Key Laboratory of Brain Science, Guangxi Health Commission Key Laboratory of Basic Research on Brain Function and Disease, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 32070976 (to CLP); Science and Technology Program of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. AD21075052 (to CLP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
He Wanyu, Cheng Leping. Strategies and advance on stem cell transplantation for repair of spinal cord injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(19): 3090-3096.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
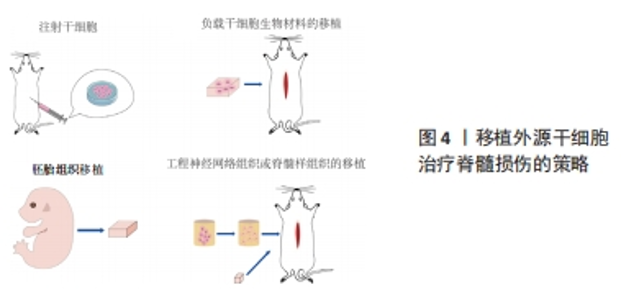
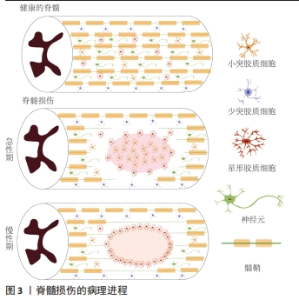
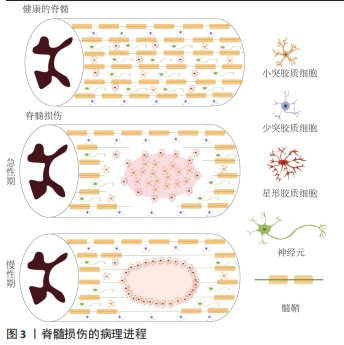
2.1.1 原发性损伤 原发性损伤是由于机械外力作用于脊髓而引起,从而导致脊髓组织挫伤和出血,损伤部位神经元轴突损伤和神经元死亡,这是一个不可逆的过程[5]。原发性损伤持续时间很短。原发性损伤会导致炎症因子上调以及小胶质细胞和中性粒细胞等免疫细胞浸润[7]。这些细胞将继续产生更多的炎症递质,过度的炎症反应会导致细胞死亡[7]。损伤部位的免疫细胞外渗对受伤的脊柱组织施加压力,进一步阻碍血液的流动,引起血管痉挛[8]。血-脊髓屏障是血液和脊髓之间的物理屏障,它能够阻止毒素、血细胞和病原体进入脊髓,以维持脊髓内环境的平衡状态[9]。在脊髓损伤发生后,这种平衡状态被破坏[9]。研究表明,保持血-脊髓屏障的完整性可以促进脊髓损伤后损伤部位的恢复和功能改善[9]。常规的核磁共振成像在脊髓损伤的诊断检查中起着至关重要的作用,该技术可以揭示原发性脊髓损伤的宏观结构证据,如出血、水肿、创伤后囊肿腔和组织桥等[10]。 2.1.2 继发性损伤 继发性损伤根据损伤时间及病理生理表现分为3个阶段,即急性期、亚急性期和慢性期。急性期在脊髓损伤发生后立即开始,包括血管损伤、离子失衡、神经递质积累(兴奋性毒性)、自由基形成、钙内流、脂质过氧化、炎症、水肿和坏死的细胞死亡[11],其中兴奋性毒性是由于谷氨酸浓度过高、离子型谷氨酸受体过度激活、Ca2+和Na+内流增加、神经元去极化所致。激活电压门控钙离子通道后,Ca2+进一步流入,结果细胞质中的Ca2+过多,Ca2+稳态被打破,最终导致细胞凋亡[12]。此外,各种细胞因子和趋化因子参与其中,导致严重的炎性反应。亚急性期发生在损伤后第2天至2周。在此阶段,受损的星形胶质细胞发生细胞水肿和坏死,而受损组织周围的星形胶质细胞增殖则起到止血、重建血脑屏障以及限制免疫细胞流入的作用[13]。慢性期从脊髓损伤后3个月开始,其特征是囊肿腔形成、轴突坏死和瘢痕成熟[6]。 髓鞘对维持轴突的完整性至关重要,其可以促进轴突信号传导[14-17]。在中枢神经系统中,少突胶质细胞负责生成和维持不同轴突的髓鞘段[18-19]。 在脊髓损伤后1周内,损伤区域的少突胶质细胞凋亡水平达到峰值,少突胶质细胞的坏死和凋亡是轴突脱髓鞘的主要原因[16,20]。新生的少突胶质细胞来源有祖少突胶质细胞和内源性神经干细胞[21]。祖少突胶质细胞被激活后分化为未成熟的状态,随着其不断增殖,这些细胞分化为可髓鞘化的少突胶质细胞,从而使轴突再髓鞘化[21]。 在脊髓损伤发生后,反应性星形胶质细胞在损伤部位增殖并紧密交织,参与形成抑制性网状阵列——胶质瘢痕[22]。除了反应性星形胶质细胞,胶质瘢痕中的细胞还包括少突胶质细胞的祖细胞、巨噬细胞、室管膜细胞、成纤维细胞、小胶质细胞[23]。胶质细胞瘢痕可以防止炎症反应在受损区域的扩散,保护周围组织不受损伤,但其形成的密集的物理屏障也会抑制轴突的再生[24-25]。因此,为了促进脊髓损伤后轴突再生、突触形成和神经元存活,抑制过度的炎症反应及胶质瘢痕的形成十分重要[23,26]。在脊髓损伤发生后,形成瘢痕的星形胶质细胞为内源性神经干细胞产生,该细胞具有保护组织完整性和为存活神经元提供营养支持的作用。此外,这类星形胶质细胞可以被重编程,这为获得神经元用于脊髓损伤治疗提供了新的细胞来源[27]。 硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖(chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans,CSPG)是一种细胞外基质组分[28],在脊髓损伤的早期,硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖由反应性星形胶质细胞分泌,它通过黏附和固定再生的轴突,发挥抑制因子的作用,阻碍神经元轴突的再生[28-30]。硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖的表达水平在病变区域呈梯度分布:在病变中心最高,从病变中心到周围损伤区域逐渐降低[28]。然而,形成瘢痕的星形胶质细胞是否为硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖的主要来源细胞尚存在争议[22]。 目前,大量的单细胞测序结果表明,脊髓损伤后的前3 d,神经元功能迅速丧失,星形胶质细胞、少突胶质细胞的祖细胞和小胶质细胞被激活,并伴有免疫细胞浸润;在损伤后的3-14 d,包括神经元在内的许多细胞类型都出现了恢复的趋势,同时伴随免疫细胞浸润和胶质瘢痕形成;但是在脊髓损伤14 d后,小胶质细胞重新激活,神经元和星形胶质细胞的数量进一步减少,免疫细胞数量持续增加[31]。这些结果提示,脊髓损伤早期(前3 d)抗炎处理可能为减少后续链式不良反应的关键。同时,避免脊髓损伤早期神经元休克也可能有助于维持功能性神经元的数量。此外,脊髓损伤2周后小胶质细胞的激活也值得关注,因为它们在后续脊髓长期持续损伤及降低再生潜能中发挥关键作用[31]。 2.2 脊髓损伤的干细胞移植治疗 干细胞具有自我更新和分化的能 力[32]。细胞移植有益于脊髓损伤的治疗,其中的细胞分子机制包括分泌生物活性分子促进神经保护、防止血管进一步损伤、促进血管再生、免疫调节、促进轴突再生、形成神经元中继和促进髓鞘再生等[33]。目前,很多干细胞移植的临床试验已处于早期阶段(Ⅰ/Ⅱ期),其有效性和安全性已得到初步的证实[34]。该综述将干细胞移植修复脊髓损伤的策略分为外源性干细胞移植与内源性干细胞的移植。 2.2.1 外源性干细胞的移植 移植外源性干细胞的策略主要分为4种:①注射间充质干细胞或神经干细胞(neural stem cells,NSCs)到损伤部位;②负载NSCs生物材料的移植;③胚胎组织移植;④工程神经网络组织或脊髓样组织的移植。见图4。"
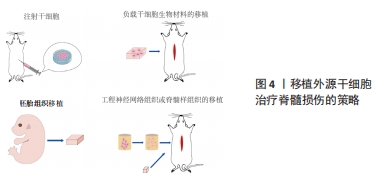
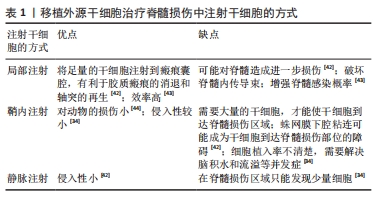
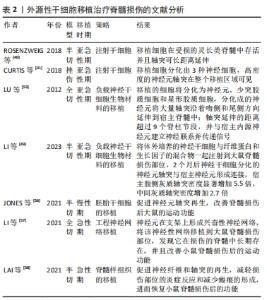
(1)注射间充质干细胞和NSCs到损伤部位[35-37]。在该种策略中,间充质干细胞表现出显著的自分泌和旁分泌活性,并参与脊髓损伤后的组织再生和功能恢复[38]。移植到脊髓损伤区域的间充质干细胞可以在损伤部位释放营养因子来维持损伤区域细胞的活性,并且释放抑炎因子,进一步促进血管再生、血-脊髓屏障的修复和神经再生[36,38-39]。间充质干细胞还可以通过调节巨噬细胞、星形胶质细胞和T细胞的状态,使炎症细胞因子的平衡向抗炎方向倾斜[36,38]。间充质干细胞调节神经炎症的能力是抑制继发性损伤的有力工具,这对脊髓损伤患者是非常有效的治疗“工具”[36-37,39]。此外,将人脊髓源性神经前体细胞直接通过注射方式移植到恒河猴的脊髓内,这些前体细胞在受损的灵长类脊髓中存活并且轴突可向长距离延伸[40]。还有,NSI-566是一种人类脊髓源性NSCs,将其注射到脊髓损伤区域外围与边界,移植细胞分化出3种神经细胞,包括神经元、少突胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞[41]。同时,高密度的神经元轴突在整个移植区域可见[41]。 在注射干细胞时,需要考虑到注射方式、注射剂量和注射时间等影响因素。干细胞的注射方式主要有以下3种,见表1。 "
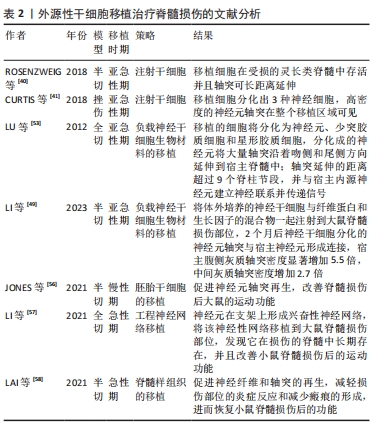
细胞剂量是进行干细胞移植的影响因素之一。由于体质量和脊髓大小的差异,很难从动物实验的结果中确定人体的最佳剂量,不同试验的细胞剂量差异很大,从106到1010个细胞不等[34,45]。在慢性期移植NSCs,细胞分布受到神经胶质瘢痕的限制,亚急性期移植比慢性期移植更能促进脊髓损伤后功能的恢复[46]。然而,在临床试验中,治疗一般在慢性期进行[46]。 (2)负载NSCs生物材料的移植[36,47-54]。将NSCs嵌入到含有生长因子的纤维蛋白基质中,并移植到严重的脊髓损伤部位,移植的细胞将分化为神经元、少突胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞,分化的神经元将大量轴突沿着吻侧和尾侧方向延伸到宿主脊髓中;轴突延伸的距离超过9个脊柱节段,同时分化的神经元与宿主内源神经元建立神经联系并传递信号[53]。此外,将体外培养的NSCs与纤维蛋白和生长因子的混合物一起注射到大鼠脊髓损伤部位,2个月后NSCs分化出的神经元轴突与宿主神经元形成连接,宿主腹侧灰质轴突密度显著增加5.5倍,中间灰质轴突密度增加2.7倍[49]。 (3)胚胎组织移植。胚胎组织移植的研究始于19世纪70年代中期。有研究将大鼠胚胎的大脑皮质和脑干的神经细胞移植到脊髓受损区域中,发现这些移植神经元的轴突可以在宿主脊髓白质和灰质中延伸[55]。新近的研究表明,在体外诱导人胚胎干细胞分化,再将分化出的神经嵴细胞移植到大鼠脊髓损伤部位,可促进神经元轴突再生,改善脊髓损伤后大鼠的运动功能[56]。 (4)工程神经网络组织或脊髓样组织的移植。有文献报道,将NSCs种植到神经营养因子3/丝素涂层明胶海绵(NT-3/ fibroin-coated gelatin sponge,NF-GS)的3D工程支架中,让NSCs在支架上生长。支架释放的神经营养因子3促进NSCs分化为神经元,这些神经元在支架上形成兴奋性神经网络。将该神经性网络移植到大鼠脊髓损伤部位,发现它在损伤的脊髓中长期存在,并且改善小鼠脊髓损伤后的运动功能[57]。此外,在支架上可构建特异性脊髓白质样组织,再将支架填充到脊髓损伤的缝隙中,可促进神经纤维和轴突的再生,减轻损伤部位的炎症反应和减少瘢痕的形成,进而恢复小鼠脊髓损伤后的功能[58]。 外源性干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤文献分析,见表2。"
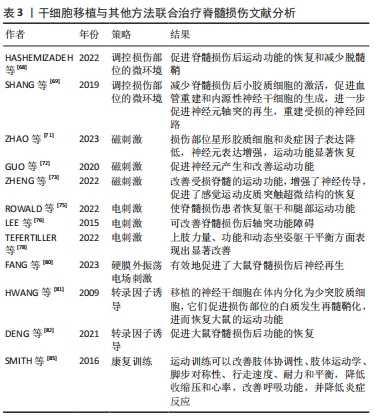
2.2.2 内源性干细胞移植 脊髓损伤发生后,内源性脊髓神经干细胞要经历3个阶段,分别是激活、迁移和分化[59]。在健康的脊髓中,神经干细胞分布于脊髓中央管周围,并保持静止或缓慢的增殖状态[60],脊髓损伤会诱导脊髓神经干细胞的激活,活化的神经干细胞会在脊髓损伤后3 d从中央管向病变部位迁移,最后在损伤部位募集和分化,其主要分化为星形胶质细胞[59,61-62]。室管膜细胞被认为是内源性脊髓干细胞[63],其排列在脊髓的中央管内[59,64]。内源性干细胞修复脊髓损伤的策略为重新编程室管膜细胞分化为少突胶质细胞和神经元谱系,这可减少瘢痕形成、生成新的神经元以及诱发再髓鞘化[65]。有文献报道,从脊髓损伤大鼠中分离室管膜细胞,再将其移植到脊髓损伤模型中,结果发现这些移植的细胞分化出的神经元轴突会长距离迁移[66]。 2.2.3 干细胞移植的联合治疗 联合治疗比单一的治疗方式将使脊髓功能恢复得更好,同时使治疗具有一定的安全性[67-68]。目前干细胞移植的联合治疗方式主要有:调控损伤部位的微环境、磁刺激、电刺激、振荡电场刺激、转录因子诱导、康复治疗。 (1)调控损伤部位的微环境。为干细胞的存活准备适宜的环境,同时控制干细胞增殖和分化,引导其分化为神经元,以防止其形成恶性肿瘤。这可通过纳米材料将干细胞输送到作用靶区、控制诱导化合物的释放以及去除炎性物质来解决[54]。有文献报道,使用亚毒性剂量的脂多糖(0.5 mg/kg)可以将病变部位的促炎性环境转变为抗炎性环境,为间充质干细胞移植提供有益的微环境,进而促进脊髓损伤后运动功能的恢复和减少脱髓鞘[68]。此外,将碱性成纤维细胞生长因子控释系统(bFGF-controlled releasing system,bFGF-CRS)支架植入到脊髓损伤大鼠,可减少脊髓损伤后小胶质细胞的激活,促进血管重建和内源性神经干细胞的生成[69],进一步促进神经元轴突的再生,重建受损的神经回路[69]。在继发性损伤不同阶段,调控损伤部位的微环境进行干细胞移植治疗的方式不同。在急性期,移植策略侧重于止血和血管再生,同时应对各种后续反应;进入亚急性期后,抑制炎症和保护神经元的存活为主要问题;而在慢性期,减少瘢痕形成和检测产生的神经元是否传递信号为神经再生的关键[46]。调节损伤部位微环境的方式有限制缺血缺氧、抑制炎症和免疫反应、限制和缩小瘢痕以及促进内源细胞分化[46]。 (2)磁刺激。磁刺激可分为经颅磁刺激和神经根磁刺激。经颅磁刺激是一种对人脑进行非侵入性刺激的技术,该技术使短暂的电流通过磁线圈产生短暂的高强度磁场来产生刺激,磁场可以刺激或抑制线圈下方的一小块大脑的区域[70]。有文献报道,脊髓损伤发生后进行经颅磁刺激,损伤部位星形胶质细胞和炎症因子表达降低,神经元表达增强,运动功能显著恢复[71]。还有文献报道,重复经颅磁刺激与人脐血间充质干细胞移植联合治疗脊髓损伤,可促进神经元产生和改善运动功能[72]。另外,有一种新的磁刺激方法——神经根磁刺激,该刺激可以靶向刺激运动皮质和脊神经根,改善受损脊髓的运动功能,增强神经传导,促进感觉运动皮质突触超微结构的恢复[73]。 (3)电刺激可分为硬膜外电刺激、外周神经刺激和功能性电刺激[74]。硬膜外刺激是通过植入的桨状电极阵列在腰骶脊髓处施加电刺激以促进运动功能的恢复[74]。有文献报道,硬膜外电刺激可以使脊髓损伤患者恢复躯干和腿部运动功能[75]。外周神经刺激是通过刺激脊髓损伤下方的外周神经来达到治疗脊髓损伤的目的[74]。有文献报道,脊髓损伤患者进行短期外周神经刺激后,可改善脊髓损伤后轴突功能障碍[76]。功能性电刺激是通过对肌肉施加电刺激来实现功能性和有目的的运动,功能性动作包括从桌子上拿起一本书、把一瓶水送到嘴里以及拿着笔写字等[77]。有文献报道,四肢瘫痪患者在接受宽脉冲/高频功能性电刺激和上肢训练后,上肢力量、功能和动态坐姿躯干平衡方面表现出显著改善[78]。 (4)振荡电场刺激。振荡电场刺激是使直流电场的极性每隔15 min 反转1次,在阳极造成脊髓轴突退化之前将其电极转化成阴极,从而促进脊髓轴突的双向生长[79]。振荡电场刺激可作为药物和非药物干预的联合治疗的一部分,促进脊髓损伤的恢复[67]。硬膜外振荡电场刺激可以促进脊髓损伤后神经再生和功能恢复[67]。有文献报道,硬膜外振荡电场刺激与NSCs移植联合治疗脊髓损伤,有效地促进了大鼠脊髓损伤后神经再生[80]。 (5)转录因子可使干细胞高效分化为神经元和少突胶质细胞,它们可促进脊髓损伤后脊髓功能的恢复。有研究表明,在人源NSCs中过表达转录因子Olig2,并将这些细胞移植进大鼠脊髓损伤部位,移植的NSCs在体内分化为少突胶质细胞,它们促进损伤部位的白质发生再髓鞘化,进而恢复了大鼠的运动功能[81]。还有研究表明,在建立大鼠脊髓损伤模型后,使转录因子Mash-1在NSCs内过量表达,促进NSCs向神经元分化,再将这些细胞移植到大鼠脊髓损伤部位,可促进大鼠脊髓损伤后功能的恢复[82]。 (6)康复治疗。脊髓损伤发生后的运动训练有助于运动功能的恢复[83-84]。在脊髓损伤患者中,运动训练可以改善肢体协调性、肢体运动学、脚步对称性、行走速度、耐力和平衡,降低收缩压和心率,改善呼吸功能,并降低炎症反应[85]。另外,在脊髓损伤发生后开始进行运动训练的时间尤为重要,早开始的运动训练不利于脊髓损伤后运动功能的恢复[84]。 干细胞移植与其他方法联合治疗脊髓损伤文献分析,见表3。"
| [1] GBD 2016 Traumatic Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(1):56-87. [2] BADHIWALA JH, WILSON JR, FEHLINGS MG. Global burden of traumatic brain and spinal cord injury. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(1):24-25. [3] SUZUKI H, IMAJO Y, FUNABA M, et al. Current Concepts of Biomaterial Scaffolds and Regenerative Therapy for Spinal Cord Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(3):2528. [4] FIANI B, ARSHAD MA, SHAIKH ES, et al. Current updates on various treatment approaches in the early management of acute spinal cord injury. Rev Neurosci. 2021;32(5):513-530. [5] CHAUDHARI LR, KAWALE AA, DESAI SS, et al. Pathophysiology of Spinal Cord Injury and Tissue Engineering Approach for Its Neuronal Regeneration: Current Status and Future Prospects. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1409:51-81. [6] ANJUM A, YAZID MD, FAUZI DAUD M, et al. Spinal Cord Injury: Pathophysiology, Multimolecular Interactions, and Underlying Recovery Mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7533. [7] HELLENBRAND DJ, QUINN CM, PIPER ZJ, et al. Inflammation after spinal cord injury: a review of the critical timeline of signaling cues and cellular infiltration. J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18(1):284. [8] LI S, DINH HTP, MATSUYAMA Y, et al. Molecular Mechanisms in the Vascular and Nervous Systems following Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. Life (Basel). 2022;13(1):9. [9] JIN LY, LI J, WANG KF, et al. Blood-Spinal Cord Barrier in Spinal Cord Injury: A Review. J Neurotrauma. 2021;38(9):1203-1224. [10] PFYFFER D, FREUND P. Spinal cord pathology revealed by MRI in traumatic spinal cord injury. Curr Opin Neurol. 2021;34(6):789-795. [11] ALIZADEH A, DYCK SM, KARIMI-ABDOLREZAEE S. Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury: An Overview of Pathophysiology, Models and Acute Injury Mechanisms. Front Neurol. 2019;10:282. [12] MOMENI HR, JARAHZADEH M, FARJAD E. Glutamate excitotoxicity; a possible mechanism for apoptosis of motoneurons in adult mouse spinal cord slices. Neurophysiology. 2020;52(6):408-414. [13] ELI I, LERNER DP, GHOGAWALA Z. Acute Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. Neurol Clin. 2021;39(2):471-488. [14] DE FARIA O JR, PIVONKOVA H, VARGA B, et al. Periods of synchronized myelin changes shape brain function and plasticity. Nat Neurosci. 2021; 24(11):1508-1521. [15] DUNCAN GJ, SIMKINS TJ, EMERY B. Neuron-Oligodendrocyte Interactions in the Structure and Integrity of Axons. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:653101. [16] FAN B, WEI Z, FENG S. Progression in translational research on spinal cord injury based on microenvironment imbalance. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):35. [17] RAFFAELE S, BOCCAZZI M, FUMAGALLI M. Oligodendrocyte Dysfunction in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cells. 2021;10(3):565. [18] XIN W, CHAN JR. Myelin plasticity: sculpting circuits in learning and memory. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020;21(12):682-694. [19] SPAAS J, VAN VEGGEL L, SCHEPERS M, et al. Oxidative stress and impaired oligodendrocyte precursor cell differentiation in neurological disorders. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021;78(10):4615-4637. [20] HUNTEMER-SILVEIRA A, PATIL N, BRICKNER MA, et al. Strategies for Oligodendrocyte and Myelin Repair in Traumatic CNS Injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021;14:619707. [21] DUNCAN GJ, MANESH SB, HILTON BJ, et al. The fate and function of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells after traumatic spinal cord injury. Glia. 2020;68(2):227-245. [22] YANG T, DAI Y, CHEN G, et al. Dissecting the Dual Role of the Glial Scar and Scar-Forming Astrocytes in Spinal Cord Injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020; 14:78. [23] ZHANG Y, YANG S, LIU C, et al. Deciphering glial scar after spinal cord injury. Burns Trauma. 2021;9:tkab035. [24] YANG B, ZHANG F, CHENG F, et al. Strategies and prospects of effective neural circuits reconstruction after spinal cord injury. Cell Death Dis. 2020; 11(6):439. [25] LINNERBAUER M, ROTHHAMMER V. Protective Functions of Reactive Astrocytes Following Central Nervous System Insult. Front Immunol. 2020; 11:573256. [26] HE Y, LIU X, CHEN Z. Glial Scar-a Promising Target for Improving Outcomes After CNS Injury. J Mol Neurosci. 2020;70(3):340-352. [27] WU Y, TANG Z, ZHANG J, et al. Restoration of spinal cord injury: From endogenous repairing process to cellular therapy. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022;16:1077441. [28] YIU G, HE Z. Glial inhibition of CNS axon regeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7(8):617-627. [29] VARADARAJAN SG, HUNYARA JL, HAMILTON NR, et al. Central nervous system regeneration. Cell. 2022;185(1):77-94. [30] TRAN AP, WARREN PM, SILVER J. New insights into glial scar formation after spinal cord injury. Cell Tissue Res. 2022;387(3):319-336. [31] LI C, WU Z, ZHOU L, et al. Temporal and spatial cellular and molecular pathological alterations with single-cell resolution in the adult spinal cord after injury. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):65. [32] ZAKRZEWSKI W, DOBRZYŃSKI M, SZYMONOWICZ M, et al. Stem cells: past, present, and future. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):68. [33] ASSINCK P, DUNCAN GJ, HILTON BJ, et al. Cell transplantation therapy for spinal cord injury. Nat Neurosci. 2017;20(5):637-647. [34] YAMAZAKI K, KAWABORI M, SEKI T, et al. Clinical Trials of Stem Cell Treatment for Spinal Cord Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(11):3994. [35] SUN X, HUANG LY, PAN HX, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and exercise restore motor function following spinal cord injury by activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(5):1067-1075. [36] PANG QM, CHEN SY, FU SP, et al. Regulatory Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Secondary Inflammation in Spinal Cord Injury. J Inflamm Res. 2022;15:573-593. [37] ABDOLMOHAMMADI K, MAHMOUDI T, ALIMOHAMMADI M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy as a new therapeutic approach for acute inflammation. Life Sci. 2023;312:121206. [38] LV B, ZHANG X, YUAN J, et al. Biomaterial-supported MSC transplantation enhances cell-cell communication for spinal cord injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):36. [39] PANG QM, DENG KQ, ZHANG M, et al. Multiple strategies enhance the efficacy of MSCs transplantation for spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;157:114011. [40] ROSENZWEIG ES, BROCK JH, LU P, et al. Restorative effects of human neural stem cell grafts on the primate spinal cord. Nat Med. 2018;24(4):484-490. [41] CURTIS E, MARTIN JR, GABEL B, et al. A First-in-Human, Phase I Study of Neural Stem Cell Transplantation for Chronic Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;22(6):941-950. [42] OH SK, JEON SR. Current Concept of Stem Cell Therapy for Spinal Cord Injury: A Review. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2016;12(2):40-46. [43] 张达,屠冠军. 骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤的途径及联合方式[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012,16(49):9265-9270. [44] BAKSHI A, HUNTER C, SWANGER S, et al. Minimally invasive delivery of stem cells for spinal cord injury: advantages of the lumbar puncture technique. J Neurosurg Spine. 2004;1(3):330-337. [45] TAHMASEBI F, BARATI S. Effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury patients. Cell Tissue Res. 2022;389(3):373-384. [46] SHU J, CHENG F, GONG Z, et al. Transplantation Strategies for Spinal Cord Injury Based on Microenvironment Modulation. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;15(6):522-530. [47] LI Z, ZHAO T, DING J, et al. A reactive oxygen species-responsive hydrogel encapsulated with bone marrow derived stem cells promotes repair and regeneration of spinal cord injury. Bioact Mater. 2022;19:550-568. [48] YING Y, HUANG Z, TU Y, et al. A shear-thinning, ROS-scavenging hydrogel combined with dental pulp stem cells promotes spinal cord repair by inhibiting ferroptosis. Bioact Mater. 2022;22:274-290. [49] LI Y, TRAN A, GRAHAM L, et al. BDNF guides neural stem cell-derived axons to ventral interneurons and motor neurons after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2023;359:114259. [50] WANG Z, DUAN H, HAO F, et al. Circuit reconstruction of newborn neurons after spinal cord injury in adult rats via an NT3-chitosan scaffold. Prog Neurobiol. 2023;220:102375. [51] NEW LE, YANAGAWA Y, MCCONKEY GA, et al. GABAergic regulation of cell proliferation within the adult mouse spinal cord. Neuropharmacology. 2023;223:109326. [52] GAO X, YOU Z, LI Y, et al. Multifunctional hydrogel modulates the immune microenvironment to improve allogeneic spinal cord tissue survival for complete spinal cord injury repair. Acta Biomater. 2023;155:235-246. [53] LU P, WANG Y, GRAHAM L, et al. Long-distance growth and connectivity of neural stem cells after severe spinal cord injury. Cell. 2012;150(6):1264-1273. [54] ZAREPOUR A, BAL ÖZTÜRK A, KOYUNCU IRMAK D, et al. Combination therapy using nanomaterials and stem cells to treat spinal cord injuries. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2022;177:224-240. [55] JAKEMAN LB, REIER PJ. Fetal spinal cord transplantation after spinal cord injury: around and back again. Oxford: Academic Press, 2015: 351-365. [56] JONES I, NOVIKOVA LN, WIBERG M, et al. Human Embryonic Stem Cell-derived Neural Crest Cells Promote Sprouting and Motor Recovery Following Spinal Cord Injury in Adult Rats. Cell Transplant. 2021;30: 963689720988245. [57] LI G, ZHANG B, SUN JH, et al. An NT-3-releasing bioscaffold supports the formation of TrkC-modified neural stem cell-derived neural network tissue with efficacy in repairing spinal cord injury. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(11): 3766-3781. [58] LAI BQ, BAI YR, HAN WT, et al. Construction of a niche-specific spinal white matter-like tissue to promote directional axon regeneration and myelination for rat spinal cord injury repair. Bioact Mater. 2021;11:15-31. [59] LIU S, CHEN Z. Employing Endogenous NSCs to Promote Recovery of Spinal Cord Injury. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:1958631. [60] 张浩,肖世宁,张钰,等. 内源性神经干细胞在脊髓损伤修复的研究进展[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(24):2250-2254. [61] MYCKATYN TM, MACKINNON SE, MCDONALD JW. Stem cell transplantation and other novel techniques for promoting recovery from spinal cord injury. Transpl Immunol. 2004;12(3-4):343-358. [62] 张正丰. 内源性神经干细胞与脊髓损伤的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2010,16(4):344-346. [63] 范一鸣,刘方煜,张洪宇,等.脊髓损伤后室管膜区内源性神经干细胞反应的系列问题[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(7):1137-1142. [64] LI X, FLORIDDIA EM, TOSKAS K, et al. Regenerative Potential of Ependymal Cells for Spinal Cord Injuries Over Time. EBioMedicine. 2016;13:55-65. [65] QIN Y, ZHANG W, YANG P. Current states of endogenous stem cells in adult spinal cord. J Neurosci Res. 2015;93(3):391-398. [66] MORENO-MANZANO V, RODRÍGUEZ-JIMÉNEZ FJ, GARCÍA-ROSELLÓ M, et al. Activated spinal cord ependymal stem cells rescue neurological function. Stem Cells. 2009;27(3):733-743. [67] BACOVA M, BIMBOVA K, KISUCKA A, et al. Epidural oscillating field stimulation increases axonal regenerative capacity and myelination after spinal cord trauma. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(12):2730-2736. [68] HASHEMIZADEH S, HOSSEINDOOST S, OMIDI A, et al. Novel therapeutic approach to slow down the inflammatory cascade in acute/subacute spinal cord injury: Early immune therapy with lipopolysaccharide enhanced neuroprotective effect of combinational therapy of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and bone-marrow mesenchymal stem cell in spinal cord injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022;16:993019. [69] SHANG J, QIAO H, HAO P, et al. bFGF-Sodium Hyaluronate Collagen Scaffolds Enable the Formation of Nascent Neural Networks After Adult Spinal Cord Injury. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2019;15(4):703-716. [70] HALLETT M. Transcranial magnetic stimulation: a primer. Neuron. 2007; 55(2):187-199. [71] ZHAO D, ZHANG Y, ZHENG Y, et al. Double-target neural circuit-magnetic stimulation improves motor function in spinal cord injury by attenuating astrocyte activation. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(5):1062-1066. [72] GUO M, WU L, SONG Z, et al. Enhancement of Neural Stem Cell Proliferation in Rats with Spinal Cord Injury by a Combination of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS) and Human Umbilical Cord Blood Mesenchymal Stem Cells (hUCB-MSCs). Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e924445. [73] ZHENG Y, ZHAO D, XUE DD, et al. Nerve root magnetic stimulation improves locomotor function following spinal cord injury with electrophysiological improvements and cortical synaptic reconstruction. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(9):2036-2042. [74] DORRIAN RM, BERRYMAN CF, LAUTO A, et al. Electrical stimulation for the treatment of spinal cord injuries: A review of the cellular and molecular mechanisms that drive functional improvements. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023;17:1095259. [75] ROWALD A, KOMI S, DEMESMAEKER R, et al. Activity-dependent spinal cord neuromodulation rapidly restores trunk and leg motor functions after complete paralysis. Nat Med. 2022;28(2):260-271. [76] LEE M, KIERNAN MC, MACEFIELD VG, et al. Short-term peripheral nerve stimulation ameliorates axonal dysfunction after spinal cord injury. J Neurophysiol. 2015;113(9):3209-3218. [77] MARQUEZ-CHIN C, POPOVIC MR. Functional electrical stimulation therapy for restoration of motor function after spinal cord injury and stroke: a review. Biomed Eng Online. 2020;19(1):34. [78] TEFERTILLER C, BARTELT P, STOBELAAR M, et al. Improving Upper Extremity Strength, Function, and Trunk Stability Using Wide-Pulse Functional Electrical Stimulation in Combination With Functional Task-Specific Practice. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil. 2022;28(2):139-152. [79] 黄先甲,张坤坤,钱军,等. 振荡电场刺激治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J]. 安徽医科大学学报,2016,51(11):1710-1712. [80] FANG C, SUN J, QIAN J, et al. Oscillating field stimulation promotes neurogenesis of neural stem cells through miR-124/Tal1 axis to repair spinal cord injury in rats. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(4):895-900. [81] HWANG DH, KIM BG, KIM EJ, et al. Transplantation of human neural stem cells transduced with Olig2 transcription factor improves locomotor recovery and enhances myelination in the white matter of rat spinal cord following contusive injury. BMC Neurosci. 2009;10:117. [82] DENG M, XIE P, CHEN Z, et al. Mash-1 modified neural stem cells transplantation promotes neural stem cells differentiation into neurons to further improve locomotor functional recovery in spinal cord injury rats. Gene. 2021;781:145528. [83] ZHAO B, ZHOU X, LIU C, et al. The effects of walking training onset on motor evoked potentials after acute spinal cord injury. Neurosci Lett. 2020; 739:135338. [84] MARQUES MR, NICOLA FC, SANCHES EF, et al. Locomotor Training Promotes Time-dependent Functional Recovery after Experimental Spinal Cord Contusion. Neuroscience. 2018;392:258-269. [85] SMITH AC, KNIKOU M. A Review on Locomotor Training after Spinal Cord Injury: Reorganization of Spinal Neuronal Circuits and Recovery of Motor Function. Neural Plast. 2016;2016:1216258. [86] XU B, YIN M, YANG Y, et al. Transplantation of neural stem progenitor cells from different sources for severe spinal cord injury repair in rat. Bioact Mater. 2022;23:300-313. [87] ZIPSER CM, CRAGG JJ, GUEST JD, et al. Cell-based and stem-cell-based treatments for spinal cord injury: evidence from clinical trials. Lancet Neurol. 2022;21(7):659-670. [88] GUO W, ZHANG X, ZHAI J, et al. The roles and applications of neural stem cells in spinal cord injury repair. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:966866. [89] PAREDES-ESPINOSA MB, PALUH JL. Human stem cell-derived neurons and neural circuitry therapeutics: Next frontier in spinal cord injury repair. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022;247(23):2142-2151. [90] SZYMONIUK M, LITAK J, SAKWA L, et al. Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Application of Multipotent Stem Cells for Spinal Cord Injury. Cells. 2022;12(1):120. [91] 吕谨南, 谭伟,杨磊落,等. 干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J]. 当代医药论丛,2018,16(9):45-47. |
| [1] | Chen Kaijia, Liu Jingyun, Cao Ning, Sun Jianbo, Zhou Yan, Mei Jianguo, Ren Qiang. Application and prospect of tissue engineering in treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1450-1456. |
| [2] | Bai Chen, Yang Wenqian, Meng Zhichao, Wang Yuze. Strategies for repairing injured anterior cruciate ligament and promoting graft healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1457-1463. |
| [3] | Zhou Bangyu, Li Jie, Ruan Yushang, Geng Funeng, Li Shaobo. Effects of Periplaneta americana powder on motor function and autophagic protein Beclin-1 in rats undergoing spinal cord hemisection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1223-1228. |
| [4] | Ma Shuwei, He Sheng, Han Bing, Zhang Liaoyun. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of animals with acute liver failure: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1137-1142. |
| [5] | Feng Ruiqin, Han Na, Zhang Meng, Gu Xinyi, Zhang Fengshi. Combination of 1% platelet-rich plasma and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves the recovery of peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 985-992. |
| [6] | Qiu Xiaoyan, Li Bixin, Li Jingdi, Fan Chuiqin, Ma Lian, Wang Hongwu. Differentiation of insulin-producing cells from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells infected by MAFA-PDX1 overexpressed lentivirus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1000-1006. |
| [7] | Zeng Fanzhuo, Li Yuxin, Sun Jiachen, Gu Xinyang, Wen Shan, Tian He, Mei Xifan. Efficient strategies for microglia replacement in spinal cord injury models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1007-1014. |
| [8] | Liu Qiwei, Zhang Junhui, Yang Yuan, Wang Jinjuan. Role and mechanism of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on polycystic ovary syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1015-1020. |
| [9] | Liu Tao, Zhang Wenkai, Ma Ziqian, Zhang Yan, Chen Xueming. Riluzole interferes with the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in microglia of rats with spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1036-1042. |
| [10] | Pan Xiaolong, Fan Feiyan, Ying Chunmiao, Liu Feixiang, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine on inhibiting the aging of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1091-1098. |
| [11] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [12] | Chen Zepeng, Hou Yonghui, Chen Shudong, Hou Yu, Lin Dingkun. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid treats spinal cord injury by reducing apoptosis of spinal cord neurons under glucose and oxygen deprivation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 528-534. |
| [13] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| [14] | Lin Feng, Cheng Ling, Gao Yong, Zhou Jianye, Shang Qingqing. Hyaluronic acid hydrogel-encapsulated bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote cardiac function in myocardial infarction rats (III) [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 355-359. |
| [15] | Xu Yinghua, Liu Jing, You Quan, Wen Zhihao, Gao Lu. Effect of neodymium-doped:yttrium aluminum perovskite laser combined with two kinds of remineralizers on remineralization of early enamel caries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 360-365. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||