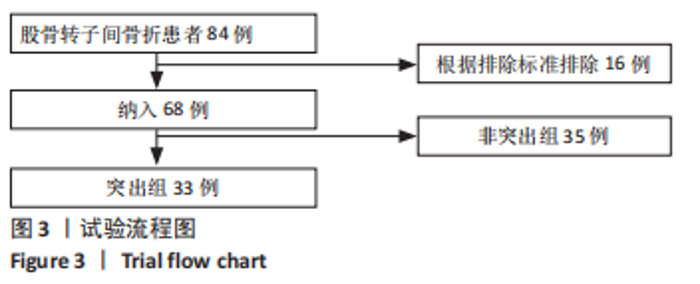
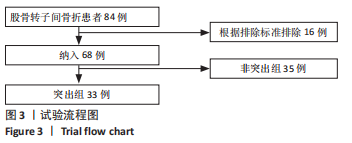
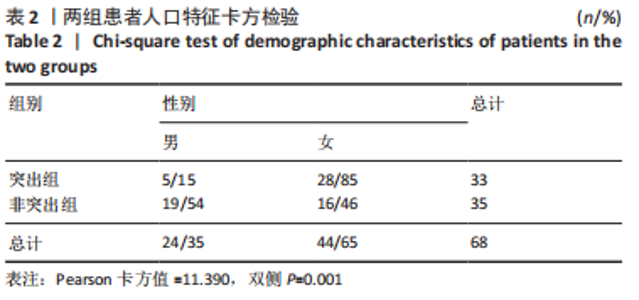
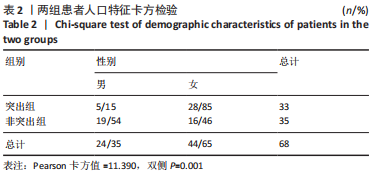
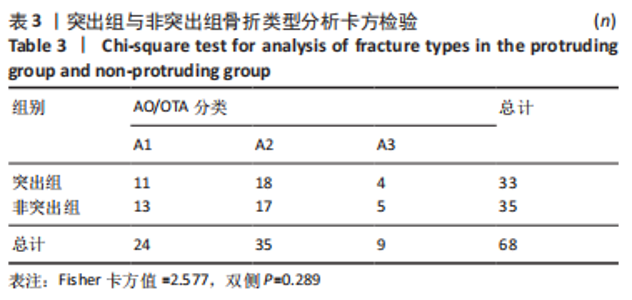
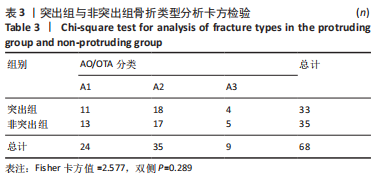
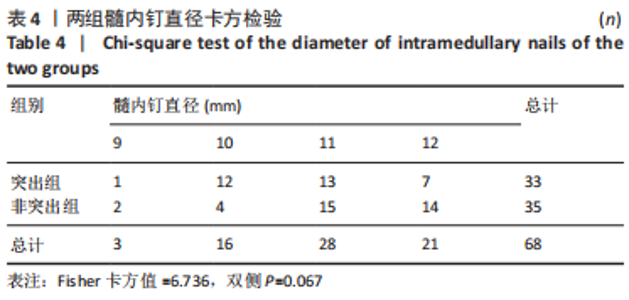
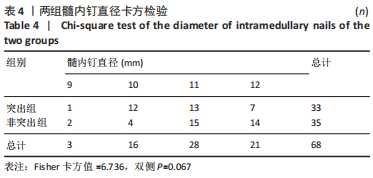
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (12): 1901-1906.doi: 10.12307/2024.016
Previous Articles Next Articles
Proximal femoral nail antirotation Asian version for treating femoral intertrochanteric fractures: comparison of the protruding degree of intramedullary nails in Asian population
Wang Anquan, Chen Hao, Hua Xingyi, Lu Xiaolin, Zhou Jian, Cui Yiliang, Li Guangyu, Yin Zongsheng
- Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230022, Anhui Province, China
-
Received:2022-12-06Accepted:2023-01-29Online:2024-04-28Published:2023-08-22 -
Contact:Yin Zongsheng, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230022, Anhui Province, China -
About author:Wang Anquan, MD, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230022, Anhui Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Anquan, Chen Hao, Hua Xingyi, Lu Xiaolin, Zhou Jian, Cui Yiliang, Li Guangyu, Yin Zongsheng. Proximal femoral nail antirotation Asian version for treating femoral intertrochanteric fractures: comparison of the protruding degree of intramedullary nails in Asian population[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(12): 1901-1906.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] CHANG SM, HOU ZY, HU SJ, et al. Intertrochanteric Femur Fracture Treatment in Asia: What We Know and What the World Can Learn. Orthop Clin North Am. 2020;51(2):189-205. [2] 殷健,伍徐范. 亚洲型股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定治疗老年骨质疏松性股骨粗隆间骨折[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(10): 1058-1060. [3] LI XP, ZHANG P, ZHU SW, et al. All-cause mortality risk in aged femoral intertrochanteric fracture patients. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):727. [4] MASCOE JE, HERICKHOFF PK. Conservative Treatment of a Nondisplaced Intertrochanteric Femur Fracture: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Iowa Orthop J. 2021;41(2):91-94. [5] SU Z, YANG M, LUO G, et al. Treatment of Elderly Femoral Intertrochanteric Fracture by InterTan Intramedullary Nail and PFNA. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:5020960. [6] MU W, ZHOU J. PFNA-II Internal Fixation Helps Hip Joint Recovery and Improves Quality of Life of Patients with Lateral-Wall Dangerous Type of Intertrochanteric Fracture. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:5911868. [7] WANG D, ZHANG K, QIANG M, et al. Computer-assisted preoperative planning improves the learning curve of PFNA-II in the treatment of intertrochanteric femoral fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):34. [8] SHIN WC, SEO JD, LEE SM, et al. Radiographic Outcomes of Osteosynthesis Using Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA) System in Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture: Has PFNA II Solved All the Problems? Hip Pelvis. 2017;29(2):104-112. [9] KIM SS, KIM HJ, LEE CS. Clinical outcomes of PFNA-II in the Asian intertrochanteric fracture patients: Comparison of clinical results according to proximal nail protrusion. Injury. 2020;51(2):361-366. [10] CHANG SM, HU SJ, MA Z, et al. Femoral intertrochanteric nail (fitn): a new short version design with an anterior curvature and a geometric match study using post-operative radiographs. Injury. 2018;49(2):328-333. [11] BEDRETTIN A, SAHIN F, YUCEL MO. Treatment of intertrochanteric femur fracture with closed external fixation in high-risk geriatric patients: can it be the most reliable method that reduces mortality to minimum compared to proximal femoral nail and hemiarthroplasty? Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(1):e28369. [12] HIRAO M, MIYATAKE K, TAKADA R, et al. Periprosthetic fragility fracture of the femur after primary cementless total hip arthroplasty. Mod Rheumatol. 2022;32(3):626-633. [13] SINGH NK, SHARMA V, TRIKHA V, et al. Is PFNA-II a better implant for stable intertrochanteric fractures in elderly population ? A prospective randomized study. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2019;10(Suppl 1):S71-S76. [14] KUMAR GN, SHARMA G, KHATRI K, et al. Treatment of Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractureswith Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation II: Our Experience in Indian Patients. Open Orthop J. 2015;9:456-459. [15] 胡靖, 王林, 陈义, 等. 防旋股骨近端髓内钉治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折的效果及对髋关节功能、生活质量和日常生活能力的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2022,42(12):2918-2920. [16] MACHERAS GA, KOUTSOSTATHIS SD, GALANAKOS SP, et al. Reply to letter to the editor: Does PFNA II avoid lateral cortex impingement for unstable peritrochanteric fractures? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013; 471(4):1395-1396. [17] TAO YL, MA Z, CHANG SM. Does PFNA II avoid lateral cortex impingement for unstable peritrochanteric fractures? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(4):1393-1394. [18] YU Y, PAN K, WANG G. Femoral trochanteric fracture: PFNA spiral blade placement with the aid of an angler. J Int Med Res. 2020;48(3): 300060519890782. [19] SHON OJ, CHOI CH, PARK CH. Factors Associated with Mechanical Complications in Intertrochanteric Fracture Treated with Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation. Hip Pelvis. 2021;33(3):154-161. [20] ZENG J, YE J, XIE Y, et al. Effect of screw blade position on proximal femoral nail anti-rotation internal fixation for unstable intertrochanteric fractures in the elderly. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020;34(5):569-573. [21] CHO HM, PARK JY, KWON KH, et al. Is it advantageous to use the intraoperative compression option of proximal femoral nail antirotation in the treatment of osteoporotic intertrochanteric fractures? A retrospective comparative study. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2021; 55(4):285-292. [22] QUENTAL C, VASCONCELOS S, FOLGADO J, et al. Influence of the PFNA screw position on the risk of cut-out in an unstable intertrochanteric fracture: a computational analysis. Med Eng Phys. 2021;97:70-76. [23] JUNG EY, OH IT, SHIM SY, et al. The Effect of Valgus Reduction on the Position of the Blade of the Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation in Intertrochanteric Hip Fractures. Clin Orthop Surg. 2019;11(1):36-42. [24] HU SJ, CHANG SM, MA Z, et al. PFNA-II protrusion over the greater trochanter in the Asian population used in proximal femoral fractures. Indian J Orthop. 2016;50(6):641-646. [25] CHRISTENSEN AM, LESLIE WD, BAIM S. Ancestral differences in femoral neck axis length: possible implications for forensic anthropological analyses. Forensic Sci Int. 2014;236:193.e191-194. [26] PU JS, LIU L, WANG GL, et al. Results of the proximal femoral nail anti-rotation (PFNA) in elderly Chinese patients. Int Orthop. 2009;33(5): 1441-1444. [27] 张世民, 祝晓忠, 黄轶刚, 等. 外侧壁危险型股骨粗隆间骨折DHS与PFNA治疗的对比研究[C]. 第20届中国康协肢残康复学术年会. 2011.广州. [28] TAKAI H, KITAJIMA M, TAKAI S, et al. Delayed hematoma in gluteus medius caused by Gamma nail protrusion over the greater trochanter. Trauma Case Rep. 2021;36:100542. [29] YOON PW, KWON JE, YOO JJ, et al. Femoral neck fracture after removal of the compression hip screw from healed intertrochanteric fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;27(12):696-701. [30] TOBIN MK, GRAGNANIELLO C, HORWITZ J, et al. Generational Changes in Lumbar Spinal Canal Dimensions: Findings from a Sample U.S. Population. World Neurosurg. 2021;146:e902-e916. [31] WELLS JC, TRELEAVEN P, CHAROENSIRIWATH S. Body shape by 3-D photonic scanning in Thai and UK adults: comparison of national sizing surveys. Int J Obes (Lond). 2012;36(1):148-154. [32] CHANG SM, SONG DL, MA Z, et al. Mismatch of the short straight cephalomedullary nail (PFNA-II) with the anterior bow of the Femur in an Asian population. J Orthop Trauma. 2014;28(1):17-22. [33] ZHANG W, ANTONY XAVIER RP, DECRUZ J, et al. Risk factors for mechanical failure of intertrochanteric fractures after fixation with proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA II): a study in a Southeast Asian population. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141(4):569-575. |
| [1] | Ouyang Beiping, Ma Xiangyang, Luo Chunshan, Zou Xiaobao, Lu Tingsheng, Chen Qiling. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new horizontal screw-screw crosslink in posterior atlantoaxial internal fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1320-1324. |
| [2] | Wu Jing, Yao Yingce, Yang Xiaowei, Xue Boshi, Zhao Jianbin, Yang Chen, Luan Tianfeng, Zhou Zhipeng. Intervention of muscle strength training combined with neuromuscular electrical stimulation on lower limb function and biomechanical changes in patients with patellofemoral pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1365-1371. |
| [3] | Shan Jiaxin, Zhang Yilong, Wu Hongtao, Zhang Jiayuan, Li Anan, Liu Wengang, Xu Xuemeng, Zhao Chuanxi. Changes in muscle strength and pain in patients receiving Jianpi Yiqi Huoxue Formula after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1378-1382. |
| [4] | Li Xiaoqiang, Chen Wei, Li Mingyue, Shan Tianchi, Shen Wen. Value of preoperative quantitative ultrasound analysis of quadriceps femoris in predicting chronic post-surgical pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1388-1393. |
| [5] | Niu Hegang, Yang Kun, Zhang Jingjing, Yan Yizhu, Zhang Yinshun. Design of a new posterior atlas fracture reduction and internal fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1399-1402. |
| [6] | Wang Menghan, Qi Han, Zhang Yuan, Chen Yanzhi. Three kinds of 3D printed models assisted in treatment of Robinson type II B2 clavicle fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1403-1408. |
| [7] | Feng Tianxiao, Bu Hanmei, Wang Xu, Zhu Liguo, Wei Xu. Interpretation of key points of International Framework for Examination of the Cervical Region for potential of vascular pathologies of the neck prior to Orthopaedic Manual Therapy (OMT) Intervention: International IFOMPT Cervical Framework [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1420-1425. |
| [8] | Chen Zhiling, Huang Xuecheng, Pan Min, Huang Ying, Wu Yuntian. Evaluation of the relationship between neck and shoulder pain and scalene muscles based on shear wave elastography [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1265-1270. |
| [9] | Han Bing, Liu Hongbin, Wang Hehong, Zhao Hanqing, Zhao Riguang, Sun Yiyan, Zhang Yu. Correlation between lower limb alignment and risk factors of patellofemoral pain syndrome in young men [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1211-1216. |
| [10] | Wang Qiang, Li Shiyun, Xiong Ying, Li Tiantian. Biomechanical changes of the cervical spine in internal fixation with different anterior cervical interbody fusion systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 821-826. |
| [11] | Xue Xiaofeng, Wei Yongkang, Qiao Xiaohong, Du Yuyong, Niu Jianjun, Ren Lixin, Yang Huifeng, Zhang Zhimin, Guo Yuan, Chen Weiyi. Finite element analysis of osteoporosis in proximal femur after cannulated screw fixation for femoral neck fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 862-867. |
| [12] | Wu Zhonghan, Wang Jingkun, Li Tao, Xu Xinzhong, Yu Shuisheng, Cheng Li, Tian Dasheng, Tang Jian, Jing Juehua. Proximal femoral nail antirotation for femoral intertrochanteric fractures with lateral wall integrity and lateral wall risk [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 911-916. |
| [13] | Zheng Jiafa, Song Xiufeng, Li Hongzhi, Zhou Jinming, Guan Shengyi, Yu He. Open reduction and internal fixation via the para-Achilles tendon approach for the treatment of posterior malleolus sandwich fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 934-938. |
| [14] | Yu Zhaoyu, Tan Lixin, Sun Kai, Lu Yao, Li Yong. Meta-analysis of cement-augmented pedicle screw for thoracolumbar degenerative diseases with osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 813-820. |
| [15] | Wang Juan, Wang Ling, Zuo Huiwu, Zheng Cheng, Wang Guanglan, Chen Peng. Rehabilitative efficacy of kinesio taping following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 651-656. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||