Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (6): 939-944.doi: 10.12307/2023.736
Previous Articles Next Articles
Imaging landmarks of one-hole split endoscope in the treatment of upper lumbar intervertebral disc herniation under the guidance of three-dimensional reconstruction
Liu Changzhen, Liu Xin, Li Yuefei, Wang Jianye, Feng Zhimeng, Sun Zhaozhong
- Department of Spine Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256603, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2022-10-17Accepted:2022-11-30Online:2024-02-28Published:2023-07-12 -
Contact:Sun Zhaozhong, Chief physician, Department of Spine Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256603, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Liu Changzhen, Master candidate, Department of Spine Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256603, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:National Key Research & Development Program, No. 2017YFC0114002 (to SZZ); Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, No. 2R2017LH021 (to SZZ); “Clinic+X” Project of Binzhou Medical University, No. BY2021LCX17 (to SZZ); Science and Technology Plan Project of Binzhou Medical University, No. BY2018KJ03 (to LX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Changzhen, Liu Xin, Li Yuefei, Wang Jianye, Feng Zhimeng, Sun Zhaozhong. Imaging landmarks of one-hole split endoscope in the treatment of upper lumbar intervertebral disc herniation under the guidance of three-dimensional reconstruction[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 939-944.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
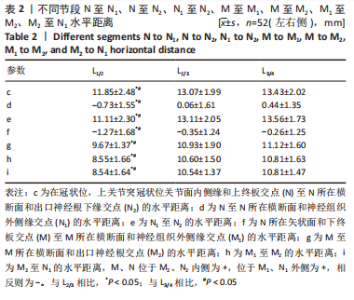
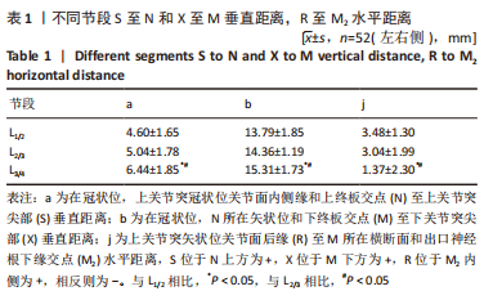
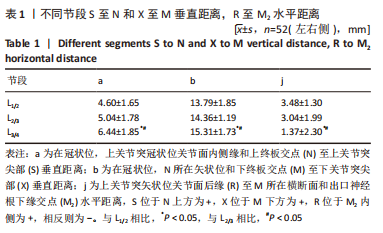
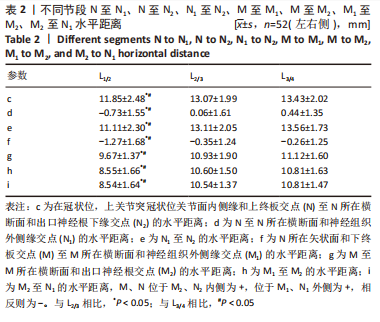
在L1/2-L3/4节段,在冠状位,上关节突冠状位关节面内侧缘和上终板交点(N)至N所在横断面和神经组织外侧缘交点(N1)水平距离(d),随着节段的降低距离先减小后增大;N所在矢状面和下终板交点(M)至M所在横断面和神经组织外侧缘交点(M1)水平距离(f),随着节段的降低距离逐渐减小;N至N所在横断面和出口神经根下缘交点(N2)水平距离(c)、N1至N2水平距离(e)、M至M所在横断面和出口神经根交点(M2)水平距离(g)、M1至M2水平距离(h)、M2至N1水平距离(i),均随着节段的降低距离逐渐增大,但c、d、e、f、g、h、i距离在L2/3节段和L3/4节段相比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表2。"
| [1] LIU C, XUE J, LIU J, et al. Is there a correlation between upper lumbar disc herniation and multifidus muscle degeneration? A retrospective study of MRI morphology. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):92. [2] XU W, YANG B, LAI X, et al. Comparison of microendoscopic discectomy and percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy for upper lumbar disc herniation: A protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(46):e27914. [3] HUET T, COHEN-SOLAL M, LAREDO JD, et al. Lumbar spinal stenosis and disc alterations affect the upper lumbar spine in adults with achondroplasia. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):4699. [4] PARK JH, CHUNG SG, KIM K. Electrodiagnostic characteristics of upper lumbar stenosis: Discrepancy between neurological and structural levels. Muscle Nerve. 2020;61(5):580-586. [5] KARAASLAN B, ASLAN A, BÖRCEK AÖ, et al. Clinical and surgical outcomes of upper lumbar disc herniations: a retrospective study. Turk J Med Sci. 2017;47(4):1157-1160. [6] LEE DS, PARK KS, PARK MS. The Comparative Analysis of Clinical Characteristics and Surgical Results between the Upper and Lower Lumbar Disc Herniations. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2013;54(5):379-383. [7] LI Z, ZHANG C, CHEN W, et al. Percutaneous Endoscopic Transforaminal Discectomy versus Conventional Open Lumbar Discectomy for Upper Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Comparative Cohort Study. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:1852070. [8] YÜCE I, KAHYAOĞLU O, MERTAN P, et al. Analysis of clinical characteristics and surgical results of upper lumbar disc herniations. Neurochirurgie. 2019;65(4):158-163. [9] SHIN MH, BAE JS, CHO HL, et al. Extradiscal Epiduroscopic Percutaneous Endoscopic Discectomy for Upper Lumbar Disc Herniation A Technical Note. Clin Spine Surg. 2019;32(3):98-103. [10] HERRING E, KASLIWAL MK. Commentary: Novel Transdural Epiarachnoid Approach for Large Central Disk Herniation in Upper Lumbar Spine. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown). 2022;22(2):e111-e112. [11] VIRK S, VAISHNAV AS, SHEHA E, et al. Combining Expandable Interbody Cage Technology With a Minimally Invasive Technique to Harvest Iliac Crest Autograft Bone to Optimize Fusion Outcomes in Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery. Clin Spine Surg. 2021;34(9):E522-E530. [12] ZHAO J, ZHANG S, LI X, et al. Comparison of Minimally Invasive and Open Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24: 8693-8698. [13] XUE J, SONG Y, LIU H, et al. Minimally invasive versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for single segmental lumbar disc herniation: A meta-analysis. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2022; 35(3):505-516. [14] XIAO C, YIN W, ZHAO K, et al. Early Clinical Efficacy of Endo-TLIF in the Treatment of Lumbar Disc Herniation [published online ahead of print, 2022 Apr 25]. Frühe klinische Wirksamkeit von Endo-TLIF bei der Behandlung von lumbalen Bandscheibenvorfällen - Bandscheibenvorfall und lumbale Instabilität: eine vergleichende Studie mit der traditionellen Methode der Behandlung [published online ahead of print, 2022 Apr 25]. Z Orthop Unfall. 2022;10.1055/a-1795-4038. [15] YANG Y, YAN X, LI W, et al. Long-Term Clinical Outcomes and Pain Assessment after Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Recurrent Lumbar Disc Herniation. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(3):907-916. [16] 杨福生,王文,康宁超,等 .腰椎脊柱内镜微创手术中区域定位原则[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志,2017,23(8):619-621. [17] 王建业,刘鑫,田霖,等.构建腰椎三维模型测量腰椎管减压术区神经组织及骨性结构的位置关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(4): 539-546. [18] 王建业,刘鑫,任佳彬,等.单侧双通道脊柱内镜技术对侧入路治疗上腰椎椎间盘突出症的影像学研究及临床应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2022,36(10):1213-1220. [19] 毕经纬,任佳彬,刘鑫,等.单侧双通道内镜的上段腰椎影像解剖测量[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(14):1293-1298. [20] ERDOĞAN U. The Results of Using a Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Cage at the Upper Lumbar Level. Cureus. 2021;13(6):e15496. [21] KANG J, CHANG Z, HUANG W, et al. The posterior approach operation to treat thoracolumbar disc herniation: A minimal 2-year follow-up study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(16):e0458. [22] WU J, ZHANG C, ZHENG W, et al. Analysis of the Characteristics and Clinical Outcomes of Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy for Upper Lumbar Disc Herniation. World Neurosurg. 2016;92:142-147. [23] BAE J, LEE SH, SHIN SH, et al. Radiological analysis of upper lumbar disc herniation and spinopelvic sagittal alignment. Eur Spine J. 2016; 25(5):1382-1388. [24] NISHIKAWA H, FUJIMOTO M, TANIOKA S, et al. Novel Transdural Epiarachnoid Approach for Large Central Disk Herniation in Upper Lumbar Spine. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown). 2022;22(1):e58-e61. [25] JHA RT, SYED HR, CATALINO M, et al. Contralateral Approach for Minimally Invasive Treatment of Upper Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Herniation: Technical Note and Case Series. World Neurosurg. 2017; 100:583-589. [26] SON S, LEE SG, KIM WK, et al. Advantages of a Microsurgical Translaminar Approach (Keyhole Laminotomy) for Upper Lumbar Disc Herniation. World Neurosurg. 2018;119:e16-e22. [27] MCCARTHY M, SWIATEK PR, ROUMELIOTIS AG, et al. Comparison of Lumbar Fusion With and Without Interbody Fusion for Lumbar Stenosis Using Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) Computer Adaptive Testing (CAT). Cureus. 2022; 14(3):e23467. [28] YUAN C, WANG J, ZHOU Y, et al. Endoscopic lumbar discectomy and minimally invasive lumbar interbody fusion: a contrastive review. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2018;13(4):429-434. [29] LIU C, ZHOU Y. Comparison Between Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy and Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Lumbar Disc Herniation with Biradicular Symptoms. World Neurosurg. 2018;120:e72-e79. [30] CASTILLO H, CHINTAPALLI RTV, BOYAJIAN HH, et al. Lumbar discectomy is associated with higher rates of lumbar fusion. Spine J. 2019;19(3): 487-492. [31] 李瑞,孙兆忠,房清敏,等.椎间孔镜TESSYS技术上关节突磨削程度对腰椎稳定性的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(10):898-903. [32] SORIANO-SÁNCHEZ JA, QUILLO-OLVERA J, SORIANO-SOLIS S, et al. Microscopy-assisted interspinous tubular approach for lumbar spinal stenosis. J Spine Surg. 2017;3(1):64-70. [33] 吐尔洪江·阿布都热西提,孟祥玉,买合木提·亚库甫,等.椎间孔镜下腰椎间盘髓核摘除治疗腰椎间盘突出症的生物力学优势[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(36):5768-5773. [34] 余洋,谢一舟,石银,等.三维有限元法分析腰椎不同尺寸关节突成形后相关节段的生物力学特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(33):5288-5293. [35] 朱爱国,张烽,朱建炜,等.腰骶丛神经根的应用解剖及临床意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(4):573-577. [36] ZHANG L, YANG J, HAI Y, et al. Relationship of the Exiting Nerve Root and Superior Articular Process in Kambin’s Triangle: Assessment of Lumbar Anatomy Using Cadavers and Computed Tomography Imaging. World Neurosurg. 2020;137:e336-e342. [37] CAN H, UNAL TC, DOLAS I, et al. Comprehensive Anatomic and Morphometric Analyses of Triangular Working Zone for Transforaminal Endoscopic Approach in Lumbar Spine: A Fresh Cadaveric Study. World Neurosurg. 2020;138:e486-e491. [38] YAMADA K, NAGAHAMA K, ABE Y, et al. Morphological analysis of Kambin’s triangle using 3D CT/MRI fusion imaging of lumbar nerve root created automatically with artificial intelligence. Eur Spine J. 2021; 30(8):2191-2199. [39] ZHAO X, ZHAO J, GUAN J, et al. Measurement of the nerve root of the lower lumbar region using digital images. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(8):e9848. [40] ZHANG KH, ZHANG WH, XU BS, et al. CT-based Morphometric Analysis of Approach of Percutaneous Transforaminal Endoscopic Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(2):212-220. |
| [1] | Zhang Rui, Wang Kun, Shen Zicong, Mao Lu, Wu Xiaotao. Effects of endoscopic foraminoplasty and laminoplasty on biomechanical properties of intervertebral disc and isthmus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 833-839. |
| [2] | Zhang Zhidong, Qi Jialong, Pei Shaobao, Ma Li, Wang Shansong, Liu Yiming. 3D printed guide template technique combined with multiple derotation for severe rigid scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 922-926. |
| [3] | . Changes in Lumbosacral Sagittal Plane Parameters of L5/S1 Disc Herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-6. |
| [4] | You Zhengqiu, Zhang Zhongzu, Wang Qunbo. Early symptomatic intervertebral disc pseudocysts after discectomy detected on MRI [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1403-1409. |
| [5] | Cai Zhihao, Xie Zhaoyong. Femoral neck anteversion measurement assessment: how to establish a unified method and standard [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1448-1454. |
| [6] | Zhan Hongqi, Ma Jianxiong, Cui Shuangshuang, Sun Lei, Wang Ying, Bai Haohao, Ma Xinlong. Correlation between three-dimensional measurement of posterior tilt of impacted femoral neck fracture and femoral head necrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5747-5752. |
| [7] | Yan Ruizhong, Li Jiahui, Lin Shuzhong, Wu Xiaogang, Guo Zhijian, Liu Wenqi, Liu Qiang. Effect of pelvic tilt on the stress at the acetabular side in standing position after total hip arthroplasty: finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5795-5800. |
| [8] | Yuan Haibo, Li Dongya, Pan Bin, Guan Kai, Chen Feng, Yuan Feng, Wu Jibin. Sagittal related factors of upper lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 4984-4989. |
| [9] | Li Daen, Wu Yafei, Qiu Shang, Wang Gang, Gao Xuren, Chen Xiangyang. Factors associated with subscapularis injury and predictive efficacy based on three-dimensional CT reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4351-4356. |
| [10] | Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Yang Junliang, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the stress of the patellofemoral joint after medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction by different femoral reconstruction insertion points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(22): 3463-3468. |
| [11] | Wang Jian, Wang Xing, Li Kun, Gao Shang, Wang Chaoqun, Zhang Shaojie, Li Zhijun. Digital morphology of foramen magnum and occipital condyle: an observation based on three-dimensional reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3117-3122. |
| [12] | Jiang Daixiang, Lu Hui, Ma Ling, Zhang Hua, Liu Dingxi, Sheng Zhaoyou, Wu Qimei, Liu Rong. Study on the distribution of calcaneal fracture line based on three-dimensional fracture map technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(18): 2842-2847. |
| [13] | Liu Changzhen, Sun Ning, Zhu Kai, Liu Xin, Dou Yongfeng, Wang Jianye, Bi Jingwei, Zhu Tengyue, Sun Zhaozhong. Safety of interbody fusion with one-hole split endoscope for L4/5 spondylolisthesis evaluated by three-dimensional CT [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(18): 2884-2891. |
| [14] | Wang Chunyu, Chen Zhigang, Zhang Jianli. Effects of mecobalamin on neuropathic pain and acid-sensing ion channels in a rat model of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(17): 2658-2663. |
| [15] | Li Xin, Luo Mingran, Li Gen, Cheng Lin, Pan Bin, Yuan Feng. Establishment and validation of a prognostic model for the recurrence risk after percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(13): 2087-2092. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||