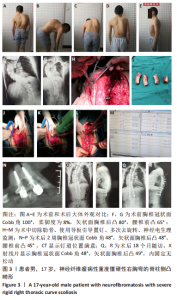
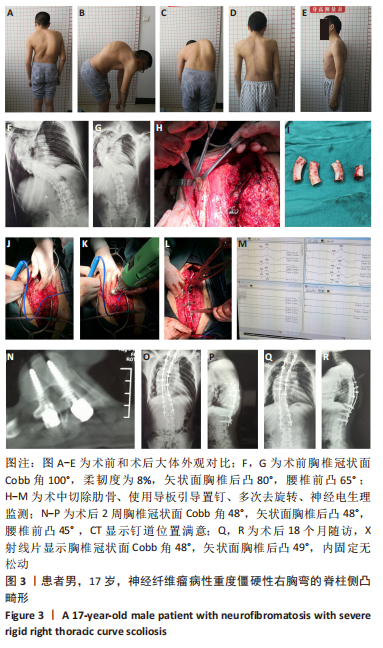
[1] 周春光,宋跃明.重度僵硬性脊柱侧凸矫正技术进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(2):238-243.
[2] 谭海涛,谢兆林,江建中,等.数字化导航模板在颈椎椎弓根螺钉置入中的应用[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,25(6):497-502.
[3] 陈毅,王利民,王卫东,等.3D打印辅助 SRS-Schwab Ⅳ级截骨术治疗老年性脊柱后凸畸形[J].中华实验外科杂志,2020,37(12): 2337-2340.
[4] 张同同,王中华,文杰,等.3D打印模型在颈椎肿瘤手术切除与重建中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(9):1335-1339.
[5] 吴荣海,周俊德,陈培友,等.3D打印技术辅助后路截骨治疗脊柱畸形的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(36):5880-5885.
[6] 蒋维利,牛国旗,周功,等.3D打印技术辅助成人脊柱侧后凸畸形的术前规划及应用价值[J].中国骨伤,2020,33(2):99-105.
[7] 金国鑫,郭文力,李雷,等.二次测量三维CT重建数据在脊柱侧弯矫形术中的应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(1):45-48.
[8] 刘忠军.3D打印技术在脊柱外科中的应用价值[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2020,30(9):321-323.
[9] 卢志军,陈荣春,郭朝阳,等.3D 打印定向截骨导板治疗脊柱畸形的临床效果[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(17):1574-1579.
[10] 董骐源,曾岩,陈仲强,等.脊柱侧凸手术中徒手置钉、3D打印导板和导航技术辅助置钉的准确性对比[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2021, 31(8):683-692.
[11] PUTZIER M, STRUBE P, CECCHINATO R, et al. A New Navigational Tool for Pedicle Screw Placement in Patients With Severe Scoliosis: A Pilot Study to Prove Feasibility, Accuracy, and Identify Operative Challenges. Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30(4):E430-E439.
[12] 李路,唐文.下颈椎后路椎弓根钉置钉:人工智能发展将如何提高治疗效果[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(3):474-479.
[13] QIU Y, WANG S, WANG B, et al. Incidence and risk factors of neurological deficits of surgical correction for scoliosis: analysis of 1373 cases at one Chinese institution. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(5):519-526.
[14] 丁江平,翁习生,唐国柱,等.重度僵硬性脊柱畸形后路三柱截骨矫形67例疗效及并发症分析[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2020,9(4): 246-254.
[15] 史本龙,刘万友,李洋,等.术前磁共振不同脊髓形态分型脊柱畸形三柱截骨矫形术后神经并发症的发生情况[J].中华医学杂志, 2022,102(5):344-349.
[16] ZHANG BB, ZHANG T, TAO HR, et al. Neurological complications of thoracic posterior vertebral column resection for severe congenital deformities. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(7):1871-1877.
[17] 陆晓生,黄湄景.脊柱畸形手术治疗现状与方向[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(3):239-241.
[18] CHEN J, SHAO XX, SUI WY, et al. Risk factors for neurological complications in severe and rigid spinal deformity correction of 177 cases. BMC Neur. 2020;20(1):433-451.
[19] 张之栋,刘艺明,杜怡斌.反复多次去旋转治疗重度僵硬性脊柱侧凸[J].中华医学杂志,2015,95(23):1811-1814.
[20] 曹硕,陈欣,周非非,等.凹侧撑开术或凸侧切除术治疗先天性颈胸段侧凸畸形的对比研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2022,42(7):413-425.
[21] 王超,石志才.腰椎间盘蠕变特性研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(12):1624-1629.
[22] 史本龙,邱俊荫,毛赛虎,等.严重脊柱畸形全脊椎截骨术中神经电生理监测严重不良事件的危险因素及转归[J].中华骨科杂志, 2016,36(24):1545-1550.
|