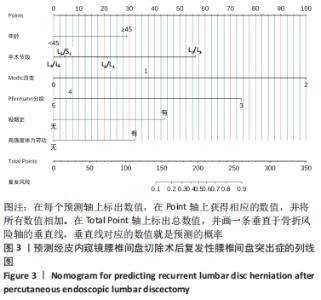
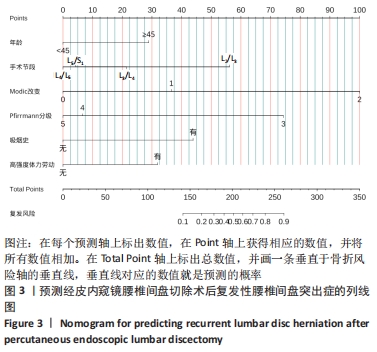
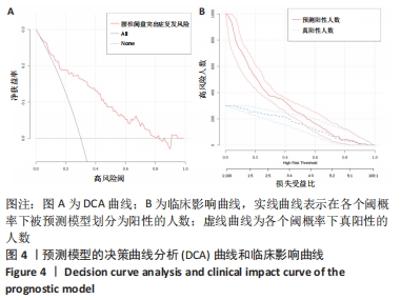
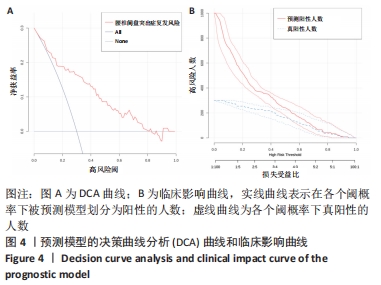
[1] BAI X, LIAN Y, WANG J, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy compared with other surgeries for lumbar disc herniation: A meta-analysis. Medicine. 2021;100(9):e24747.
[2] KIM HS, PAUDEL B, JANG JS, et al. Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy for All Types of Lumbar Disc Herniations (LDH) Including Severely Difficult and Extremely Difficult LDH Cases. Pain Physician. 2018;21(4):E401–E408.
[3] JING Z, LI L, SONG J. Percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy versus microendoscopic discectomy for upper lumbar disc herniation: a retrospective comparative study. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(4):3111-3119.
[4] 徐文强,张啸宇,王楠,等. 腰椎内镜下髓核摘除术对不同退变程度邻近节段椎间盘生物力学影响的有限元分析[J].中国骨伤,2021, 34(1):40-44.
[5] PAN M, LI Q, LI S, et al. Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy: Indications and Complications. Pain Physician. 2020;23(1):49-56.
[6] ZHOU C, ZHANG G, PANCHAL RR, et al.Unique Complications of Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy and Percutaneous Endoscopic Interlaminar Discectomy. Pain Physician. 2018;21(2): E105-E112.
[7] LEE JK, AMOROSA L, CHO SK, et al. Recurrent lumbar disk herniation. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18(6):327-337.
[8] KIM HS, YOU JD, JU CI. Predictive Scoring and Risk Factors of Early Recurrence after Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:6492675.
[9] YIN S, DU H, YANG W, et al. Prevalence of Recurrent Herniation Following Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy: A Meta-Analysis. Pain Physician. 2018;21(4):337-350.
[10] KONG M, XU D, GAO C, et al. Risk Factors for Recurrent L4-5 Disc Herniation After Percutaneous Endoscopic Transforaminal Discectomy: A Retrospective Analysis of 654 Cases. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2020;13:3051-3065.
[11] 王志鹏,张晓刚,李元贞,等. 经皮内窥镜下腰椎间盘切除术治疗复发性腰椎间盘突出症并发症的Meta分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2020,30(1):53-61.
[12] LI Y, WANG B, LI H, et al. Adjuvant surgical decision-making system for lumbar intervertebral disc herniation after percutaneous endoscopic lumber discectomy: a retrospective nonlinear multiple logistic regression prediction model based on a large sample. Spine J. 2021;21(12):2035-2048.
[13] KIM KT, LEE DH, CHO DC, et al. Preoperative Risk Factors for Recurrent Lumbar Disk Herniation in L5-S1. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015;28(10): E571-577.
[14] 钱宇章,王楠,董煜祺,等. 经皮椎间孔镜治疗腰椎间盘突出症术后复发相关因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(36): 5886-5896.
[15] WEI FL, ZHOU CP, ZHU KL, et al. Comparison of Different Operative Approaches for Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Network Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Pain Physician. 2021;24(4):E381-E392.
[16] YU P, ZAN P, ZHANG X, et al. Comparison of Percutaneous Transforaminal Endoscopic Discectomy and Microendoscopic Discectomy for the Surgical Management of Symptomatic Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study with a Minimum of 2 Years’ Follow-Up. Pain Physician. 2021;24(1):E117-E125.
[17] CHEN Q, ZHANG Z, LIU B, et al. Evaluation of Percutaneous Transforaminal Endoscopic Discectomy in the Treatment of Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Retrospective Study. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(2):599-607.
[18] 李宏达,冯波,王秀双,等. 内镜与通道下腰椎间盘切除术的并发症与疗效比较[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(9):785-790.
[19] SICCOLI A, SCHRÖDER ML, STAARTJES VE. Association of age with incidence and timing of recurrence after microdiscectomy for lumbar disc herniation. Eur Spine J. 2021;30(4):893-898.
[20] KIM J, LEE S, AHN Y, et al. Recurrence after Successful Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2007; 50(2):82-85.
[21] GRUBER HE, HANLEY EN. Observations on morphologic changes in the aging and degenerating human disc: Secondary collagen alterations. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2002;3:9.
[22] YAO Y, LIU H, ZHANG H, et al. Risk Factors for the Recurrent Herniation After Microendoscopic Discectomy. World Neurosurgery. 2016;95:451-455.
[23] YAMAN ME, KAZANCI A, YAMAN ND, et al. Factors that influence recurrent lumbar disc herniation. Hong Kong Med J. 2017;23(3):258-263.
[24] WILKE HJ, RESSEL L, HEUER F, et al. Can prevention of a reherniation be investigated? Establishment of a herniation model and experiments with an anular closure device. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(10): E587-593.
[25] HASEGAWA K, KITAHARA K, HARA T, et al. Evaluation of lumbar segmental instability in degenerative diseases by using a new intraoperative measurement system. J Neurosurg Spine. 2008;8(3):255-262.
[26] LO WC, CHIOU CS, TSAI FC, et al. Platelet-Derived Biomaterials Inhibit Nicotine-Induced Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Through Regulating IGF-1/AKT/IRS-1 Signaling Axis.Cell Transplant. 2021;30: 9636897211045319.
[27] ELMASRY S, ASFOUR S, DE RIVERO VACCARI JP, et al.Effects of Tobacco Smoking on the Degeneration of the Intervertebral Disc: A Finite Element Study. PloS One. 2015;10(8):e0136137.
[28] AMIN DB, MOAWAD CM, COSTI JJ. New Findings Confirm Regional Internal Disc Strain Changes During Simulation of Repetitive Lifting Motions. Ann Biomed Eng. 2019;47(6):1378-1390.
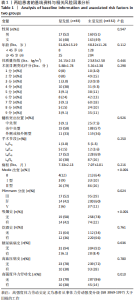
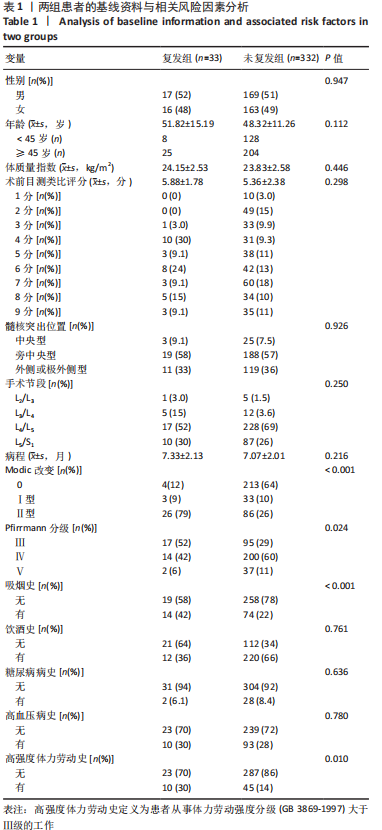
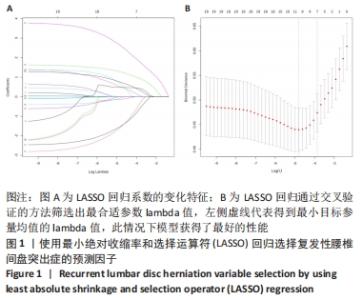
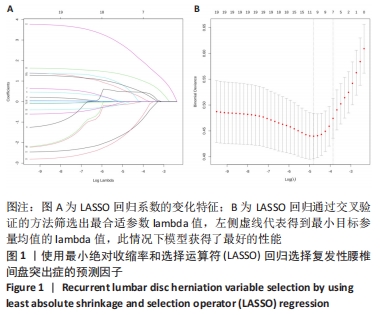
|