Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (27): 4300-4306.doi: 10.12307/2021.186
Previous Articles Next Articles
Prediction algorithm of hospitalization duration after total knee arthroplasty based on machine learning
Chen Chaofeng, Shi Yuxiong, Liang Jincheng, He Zhijun, He Dadong
- Department of Osteoarthritis, Panyu Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2020-10-19Revised:2020-10-22Accepted:2020-11-19Online:2021-09-28Published:2021-04-10 -
Contact:Chen Chaofeng, Department of Osteoarthritis, Panyu Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Chen Chaofeng, Associate chief physician, Department of Osteoarthritis, Panyu Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Research Project of Guangdong Bureau of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 20171202 (to CCF)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Chaofeng, Shi Yuxiong, Liang Jincheng, He Zhijun, He Dadong. Prediction algorithm of hospitalization duration after total knee arthroplasty based on machine learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(27): 4300-4306.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
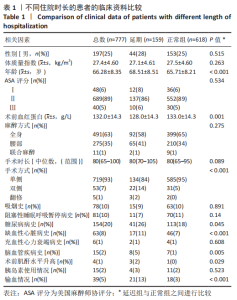
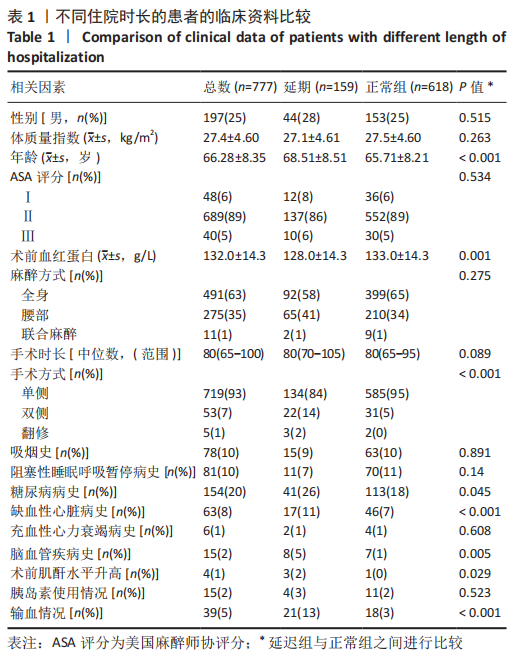
2.2 患者住院时长变化 所有全膝关节置换患者的平均住院时长为(5.8±4.6) d,中位住院时长为4 d,75%分位数为6 d。这个结果与既往研究报道的数据接近[6, 16],因此文章选取住院时长为6 d作为分界线。住院时长≤6 d的患者作为正常 组,> 6 d的患者作为延期组。 2.3 不同住院时长的患者的临床资料比较 共纳入777个样本数,其中包括618例住院时长≤6 d的患者和159例住院时 长 > 6 d的患者。正常组与延期组患者间的住院时长差异,见表1。延期组的平均年龄为(68.51±8.51)岁,正常组的平均年龄为(65.71±8.21)岁;两组的性别、体质量指数、ASA评分、麻醉方式、手术时长、吸烟史、阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停病史、充血性心力衰竭病史和胰岛素使用情况比较均无显著差异;而在年龄、术前血红蛋白、手术方式、糖尿病病史、缺血性心脏病病史、脑血管疾病史和输血情况方面差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。"
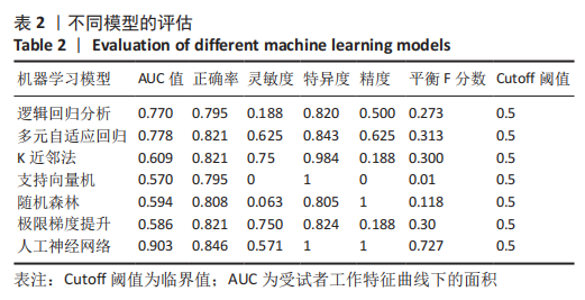
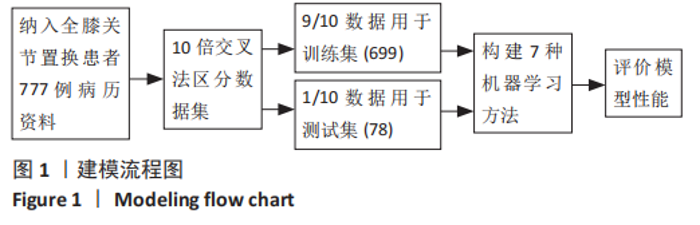
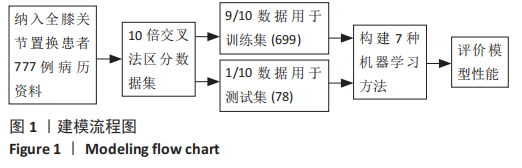
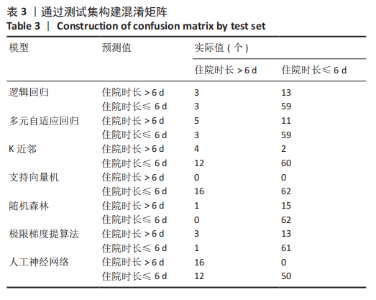
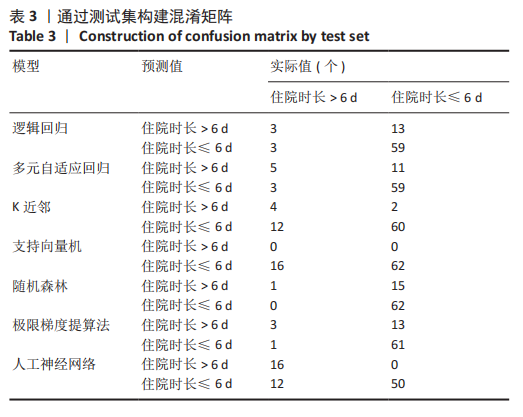
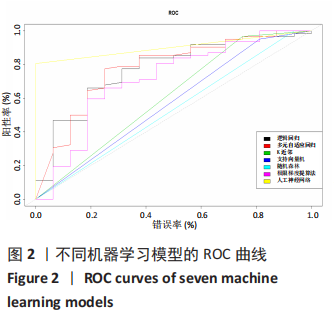
2.4 机器学习模型的评估与比较 为了选择用于预测结局指标的高性能模型,作者通过表1的临床资料分别构建模型并计算了7个模型的AUC值、正确率、灵敏度、特异度、精度和平衡F分数,获得每个训练集模型的最佳参数,通过验证集对预测模型进行验证(验证集数据通过10倍交叉验证法获得)。 逻辑回归分析、多元自适应回归、K近邻法、支持向量机、随机森林、极限梯度提升、人工神经网络的AUC值分别为0.770,0.778,0.609,0.570,0.594,0.586和0.903。总体而言,人工神经网络的AUC值在所有模型中最高,第2,3位分别为逻辑回归分析和多元自适应回归,这可能与数据集符合线性逻辑关系有关。而K近邻法、支持向量机、随机森林、极限梯度提升表现较差,AUC值在0.6附近,见表2。 此外,作者使用正确率、灵敏度、特异度、精度和F1比较了这7个机器学习模型的性能,见表2,3。"
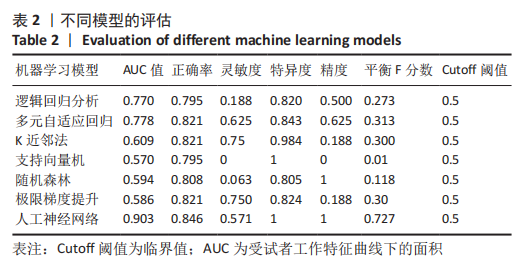
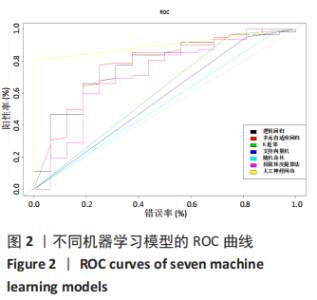
人工神经网络的AUC值高于其他组,同时具有最高的正确率(0.846)、特异度(1)、精度(1)和平衡F分数(0.727);多元自适应回归主要用于处理高维度(待回归因素较多的数据集)回归问题,而文章的纳入因素较多,符合多元自适应回归的适用性范围,因此多元自适应回归的所有检验指标相较于逻辑回归分析提高;虽然逻辑回归分析具有较高的AUC值和正确率,但是其灵敏度和平衡F分数较低,对住院时长延长患者的识别能力较差;而支持向量机和随机森林的灵敏度和AUC值较低,其识别能力和诊断准确性低。K近邻法和极限梯度提升的精度和AUC值较低,其精确性和诊断准确性不足。通过绘制ROC曲线,见图2,可见人工神经网络的线下面积最大。因此,就该结果来看,人工神经网络算法的表现优于其他算法。 "
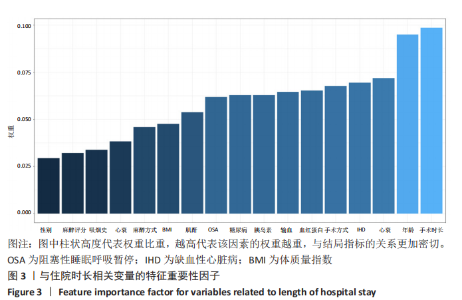
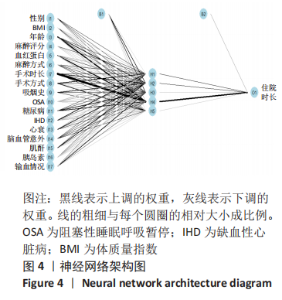
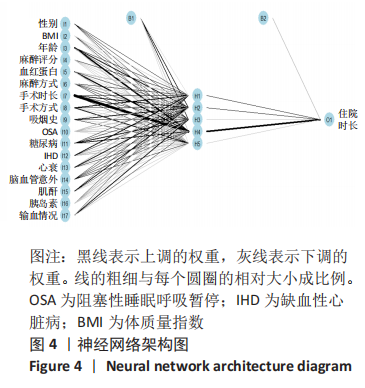
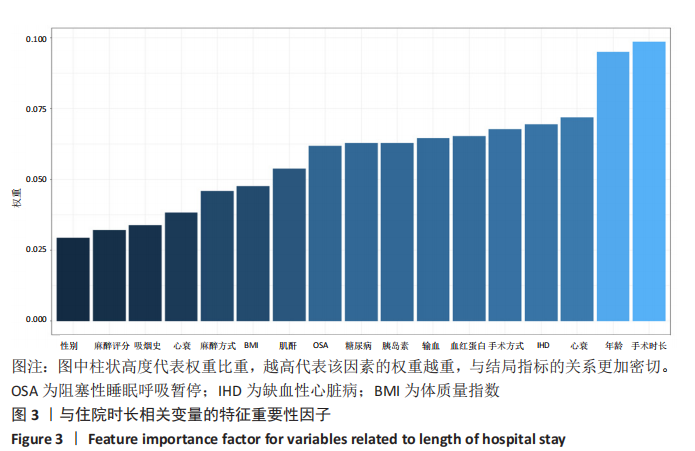
2.5 神经网络中与住院时长相关的特征重要性因子 人工神经网络可以对每1个输入变量进行特异性修正以达到预测的目的,通过Garson的算法建立人工神经网络模型,作者得到文章各个预测变量的重要性权重,并且将该重要性与最大指标值比对,获得标准化的重要性权重数据。从图3中可以看到手术时长和年龄在预测变量中的重要性最高,领先其他预测变量,而心力衰竭病史、心血管疾病、缺血性心脏病、手术方式、血红蛋白、输血情况、胰岛素使用情况、糖尿病病史和阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停等因素重要性较前两者低,仍为高相关性的预测变量。在表1的临床资料分析中,手术时长和心衰未见明显统计学差异,但在神经网络中,手术时长和心衰的特征重要性较高,是区分结局指标的重要变量。可见,人工神经网络的建模属性与权重方式之间不是简单的线性关系。而通过Garson的算法,发掘模型相关因素的权重与结局指标相关性的相对大小,这有利于临床工作者更好地理解人工神经网络。 "

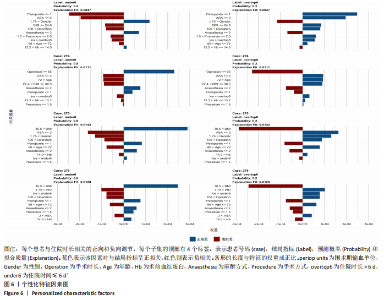
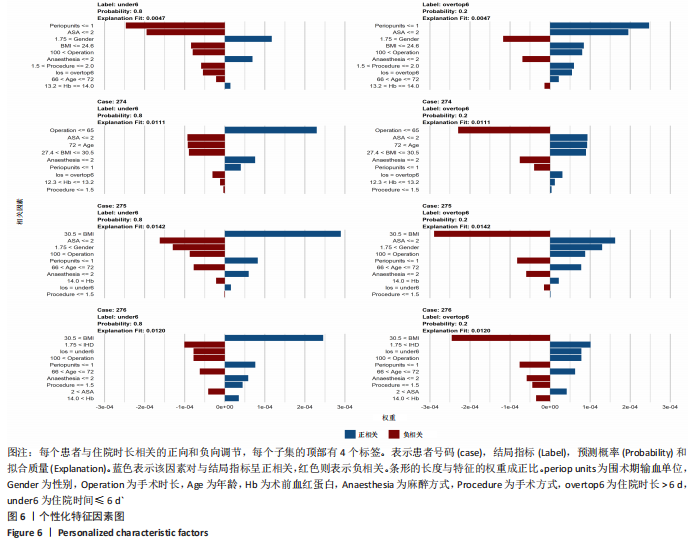
2.7 具体病例相关因素的热图分析 图5展示了具体患者的相关因素分层,图中上方横纵为两类结局事件(延长出院和常规事件出院),下方横轴为具体病例(第273-276例患者)。其中273例和274例患者为延长出院患者,275和276例为常规时间出院患者。在该例中,在左侧方框中,年龄大于66岁以蓝色表示,证明高龄与延长出院呈正相关关系。而在第3列中,非联合麻醉与住院时长呈现负相关,因此为了缩短住院时长,在考虑患者基本情况前提下,尽量选择单独的麻醉方式。体质量指数越高,患者延长出院的风险越低,这可能与患者的营养情况和血容量相关。而当手术时间少于 65 min时,患者的住院时长延长的风险下降。出现需要输血的情况,患者的延长住院时间的风险也相应增加。而复杂的手术方式也会增加患者住院时间的风险,这张图可以帮助临床医生理解神经网络如何进行预测。 同时图5可以帮助作者通过神经网络预测患者的重点结局(例如,因为患者高龄、麻醉评分高、体质量指数低,因此术中应该在保证手术质量的基础上尽快完成手术,减少术中失血;同时麻醉也应该以简单的单一麻醉为主,尽量减少使用联合麻醉),这些都是在整个临床决策过程中至关重要的变量。"

| [1] MARADIT KH, LARSON DR, CROWSON CS, et al. Prevalence of Total Hip and Knee Replacement in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(17):1386-1397. [2] WEISER TG, REGENBOGEN SE, THOMPSON KD, et al. An estimation of the global volume of surgery: a modelling strategy based on available data. Lancet. 2008;372(9633):139-144. [3] den HERTOG A, GLIESCHE K, TIMM J, et al. Pathway-controlled fast-track rehabilitation after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized prospective clinical study evaluating the recovery pattern, drug consumption, and length of stay. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018;132(8):1153-1163. [4] HUSTED H, JENSEN C M, SOLGAARD S, et al. Reduced length of stay following hip and knee arthroplasty in Denmark 2000-2009: from research to implementation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(1):101-104. [5] AYALON O, LIU S, FLICS S, et al. A multimodal clinical pathway can reduce length of stay after total knee arthroplasty. HSS J. 2017;7(1):9-15. [6] ABDULLAH HR, SIM YE, HAO Y, et al. Association between preoperative anaemia with length of hospital stay among patients undergoing primary total knee arthroplasty in Singapore: a single-centre retrospective study. BMJ Open. 2017; 7(6):e16403. [7] LIODAKIS E, BERGERON SG, ZUKOR DJ, et al. Perioperative complications and length of stay after revision total hip and knee arthroplasties: an analysis of the NSQIP Database. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(11):1868-1871. [8] VIOLA J, GOMEZ MM, RESTREPO C, et al. Preoperative anemia increases postoperative complications and mortality following total joint arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(5):846-848. [9] 段芳芳,吕艳伟,王立芳,等.北京市某三甲医院原发性膝关节炎住院费用分析[J].中国卫生统计,2018,35(6):863-866. [10] KENDALE S, KULKARNI P, ROSENBERG AD, et al. Supervised machine-learning predictive analytics for prediction of postinduction hypotension. Anesthesiology. 2018;129(4):675-688. [11] LEE CK, HOFER I, GABEL E, et al. Development and validation of a deep neural network model for prediction of postoperative in-hospital mortality. Anesthesiology. 2018;129(4):649-662. [12] 赵诣.大数据下的机器学习算法综述-以AlphaGO为例[J].信息记录材料, 2019,20(1):10-12. [13] 张中文,姚婷婷,张海泉,等.基于交叉验证的组合诊断方法在乳腺肿瘤诊断研究中的应用[J].中国卫生统计,2020,37(2):166-169. [14] ALICE Z. Evaluating Machine Learning Models. O’Reilly Media, Inc. 2015;9:125-130. [15] ZHANG Z, BECK MW, WINKLER DA, et al. Opening the black box of neural networks: methods for interpreting neural network models in clinical applications. Ann Transl Med. 2018;6(11):216. [16] CHEN JY, LEE WC, CHAN HY, et al. Drain use in total knee arthroplasty is neither associated with a greater transfusion rate nor a longer hospital stay. Int Orthop. 2016;40(12):2505-2509. [17] SESSLER DI, SIGL JC, MANBERG PJ, et al. Broadly applicable risk stratification system for predicting duration of hospitalization and mortality. Anesthesiology. 2010;113(5):1026-1037. [18] LUO W, PHUNG D, TRAN T, et al. Guidelines for developing and reporting machine learning predictive models in biomedical research: a multidisciplinary view. J Med Internet Res. 2016;18(12):e323. [19] NGUYEN P, TRAN T, WICKRAMASINGHE N, et al. $\mathtt {Deepr}$: A Convolutional Net for Medical Records. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2017;21(1):22-30. [20] XIAO J, DING R, XU X, et al. Comparison and development of machine learning tools in the prediction of chronic kidney disease progression. J Transl Med. 2019;17(1):119. [21] RAMKUMAR PN, KARNUTA JM, NAVARRO SM, et al. Deep learning preoperatively predicts value metrics for primary total knee arthroplasty: development and validation of an artificial neural network model. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(10): 2220-2227. [22] LO CK, LEE QJ, WONG YC. Predictive factors for length of hospital stay following primary total knee replacement in a total joint replacement centre in Hong Kong. Hong Kong Med J. 2017;23(5):435-440. [23] SONG X, XIA C, LI Q, et al. Perioperative predictors of prolonged length of hospital stay following total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective study from a single center in China. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):62. [24] 李杰,段光友,曾义,等.人工神经网络、极端梯度提升和Logistic回归用于预测再次剖宫产术中输血的比较分析[J].第三军医大学学报,2019,41(24): 2430-2437. [25] LE MANACH Y, COLLINS G, RODSETH R, et al. Preoperative score to predict postoperative mortality (POSPOM): derivation and validation. Anesthesiology. 2016;124(3):570-579. [26] ROOTH P, DAWIDSON I, DILLER K, et al. In vivo fluorescence microscopy reveals cyclosporine G to be less nephrotoxic than cyclosporine A. Transplant Proc. 1988;20(2 Suppl 2):707-709. [27] MISTRY PK, GAUNAY GS, HOENIG DM. Prediction of surgical complications in the elderly: can we improve outcomes? Asian J Urol. 2017;4(1):44-49. [28] Boehm O, Baumgarten G, Hoeft A. Preoperative patient assessment: identifying patients at high risk. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2016;30(2):131-143. [29] KAPPEN TH, PEELEN LM. Prediction models: the right tool for the right problem. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2016;29(6):717-726. |
| [1] | Zhong Yizheng, Huang Peizhen, Cai Qunbin, Zheng Liqin, He Xingpeng, Dong Hang. Microstructural indexes that determine the trabecular bone maximum stress of micro-finite element models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1313-1318. |
| [2] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [3] | Wu Tianliang, Tao Xiuxia, Xu Hongguang. Influence of different bone mineral densities on cage subsidence after stand-alone oblique lateral interbody fusion: three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1352-1358. |
| [4] | Wen Xinghua, Ding Huanwen, Cheng Kai, Yan Xiaonan, Peng Yuanhao, Wang Yuning, Liu Kang, Zhang Huiwu. Three-dimensional finite element model analysis of intramedullary nailing fixation design for large femoral defects in Beagle dogs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1371-1376. |
| [5] | Ke Yuqi, Chen Changjian, Wu Hao, Zheng Lianjie. Comparison of 12-month follow-up results of primary total hip arthroplasty between modified direct anterior approach and direct anterior approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1377-1382. |
| [6] | Zhang Lichuang, Gao Huali, Wang Jingchao, Lin Huijun, Wu Chonggui, Ma Yinghui, Huang Yunfei, Fang Xue, Zhai Weitao. Effect of tendon manipulation with equal emphasis on muscles and bones on accelerating the functional rehabilitation of quadriceps femoris after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1383-1389. |
| [7] | Zheng Hongrui, Zhang Wenjie, Wang Yunhua, He Bin, Shen Yajun, Fan Lei. Femoral neck system combined with platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of femoral neck fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1390-1395. |
| [8] | Du Xueting, Zhang Xiaodong, Chen Yanjun, Wang Mei, Chen Wubiao, Huang Wenhua. Application of compressed sensing technology in two-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging of the ankle joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1396-1402. |
| [9] | He Yinhao, Li Xiaosheng, Chen Hongwen, Chen Tiezhu. 3D printed porous tantalum metal in the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip: current status and application prospect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1455-1461. |
| [10] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [11] | Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [12] | Bai Yulong, Li Zhonghai, Zhao Yantao, Xia Cencan, Shi Lei. History, current situation and prospect of tissue banks in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1306-1312. |
| [13] | Sun Jiajia, Zhu Haidi, Lu Yun, Zhang Kai. Comparison of bone metabolism markers between type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with hip fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1156-1160. |
| [14] | Huang Linke, Wei Linhua, Jiang Jie, Liu Qian, Chen Weiwei. Effects of estrogen combined with treadmill exercise on bone mass and articular cartilage in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [15] | Bi Gengchao, Zhang Yanlong, Li Qiuyue, Hu Longwei, Zhang Yu. Knee joint mechanics and activation characteristics of surrounding muscles during deep jumps at different heights and distances [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1211-1218. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||