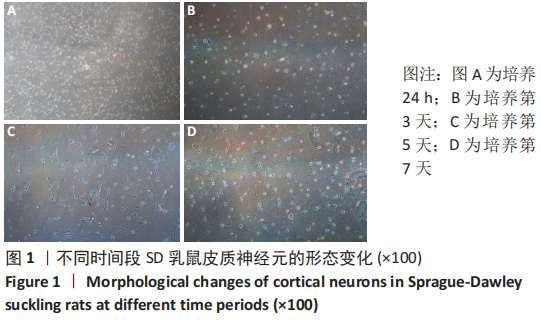
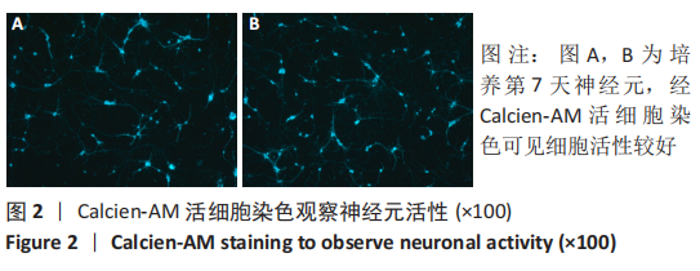
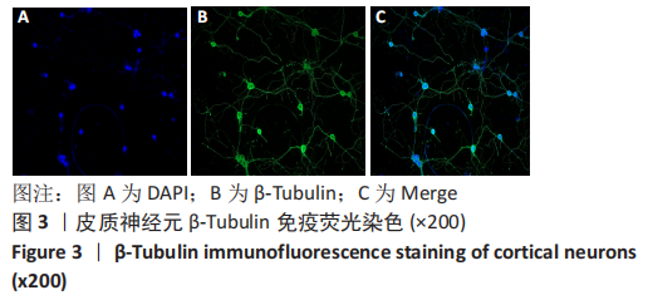
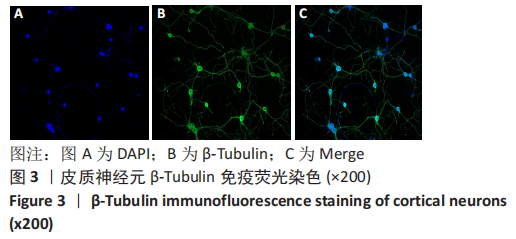
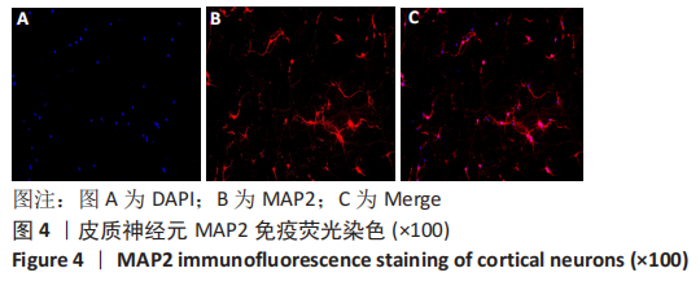
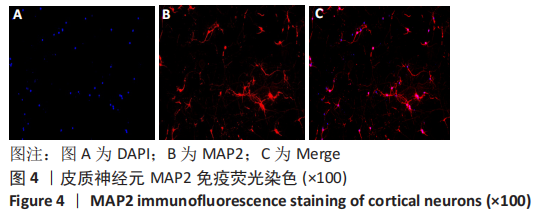
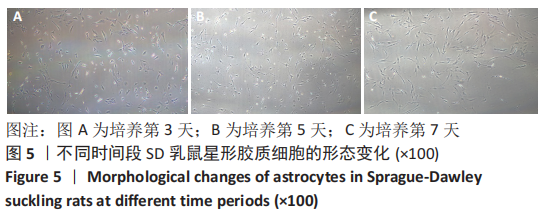
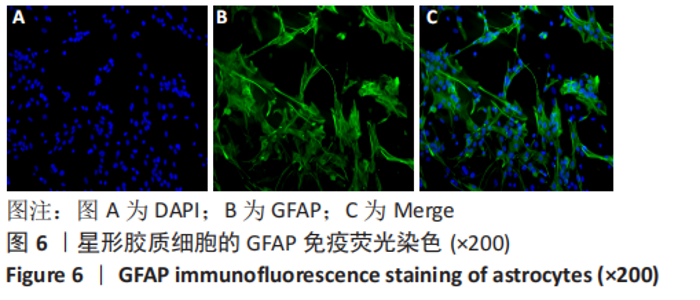
[1] 李兴统,汤红艳,马微,等.一种高纯度原代神经元培养和高效率转染的方法[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(32):5186-5190.
[2] 唐仕军,赵冬,朱立仓,等.一种简便的皮层神经元原代培养方法的建立及其培养结果分析[J].山东医药,2015,55(48):19-22,126.
[3] 丁娟,丁敬宾,马小虎,等.一种改进的大鼠大脑皮质星形胶质细胞的培养方法[J].神经解剖学杂志,2017,33(3):349-353.
[4] 薛建锋,魏娜,杨淳.一种同时培养原代神经元和原代星形胶质细胞的实验方法[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2021,37(12):1479-1482.
[5] 邓莉,代荣阳,廖彦生,等.新生大鼠皮层神经元的培养与鉴定[J].西南军医, 2011,13(4):617-619.
[6] GALLAND F, SEADY M, TADAY J, et al. Astrocyte culture models: Molecular and function characterization of primary culture, immortalized astrocytes and C6 glioma cells. Neurochem Int. 2019;131:104538.
[7] 李烨,张家骅,吴建云.大脑皮质星形胶质细胞的培养和鉴定[J].动物医学进展,2010,31(4):42-46.
[8] ROBERT F, CLOIX JF, HEVOR T. Ultrastructural characterization of rat neurons in primary culture. Neuroscience. 2012;200:248-260.
[9] 杨传豪,赵冬,刘祺,等.新生大鼠皮层神经元体外无血清原代培养[J].重庆医学,2014,43(29):3901-3903,3906.
[10] 周国凤,汤京龙,周亮,等.一种改进的大脑皮层神经元原代培养方法的研究[J].药物分析杂志,2011,31(2):299-301.
[11] WANG CP, LI GC, SHI YW, et al . Neuroprotective effect of schizandrin A on oxygen and glucose deprivation/reperfusion-induced cell injury in primary culture of rat cortical neurons. J Physiol Biochem. 2014;70(3):735-747.
[12] BREWER GJ, TORRICELLI JR, EVEGE EK, et al. Optimized survival of hippocampal neurons in B27-supplemented Neurobasal, a new serum-free medium combination. J Neurosci Res. 1993;35(5):567-576.
[13] 赵艳萌,马秀娟,张怡,等.新生大鼠皮层神经元分离和培养方法的优化[J].神经解剖学杂志,2021,37(4):405-410.
[14] 郭慧,毛萌,俞丹,等.大鼠大脑皮层星形胶质细胞体外培养改良方法的研究[J].中国当代儿科杂志,2014,16(12):1271-1274.
[15] 于海艳,黄巨恩,吴世芬,等.体外SD大鼠皮层星形胶质细胞培养及酒精的损伤作用研究[J].广西医科大学学报,2013,30(2):184-186.
[16] 田青,叶文华,陶玉倩.体外培养的乳鼠皮层神经元氧糖剥夺后轴突损伤的实验观察[J].新医学,2016,47(11):730-734.
[17] 吕媛媛,伍小安,陈瑶,等.葡萄糖剥夺对原代培养大鼠皮层神经元BKCa通道的影响[J].北京体育大学学报,2013,36(12):68-72.
[18] 栗建新.大鼠原代神经元的培养及操作技巧[J].北方药学,2017,14(8):137,170.
[19] 张忠胜,余炳坚,梅元武.新生大鼠大脑皮层神经元原代培养与鉴定[J].热带医学杂志,2017,17(1):8-10,138.
[20] 杨云凤,吴碧华,辜建伟.大鼠胚鼠皮层神经元培养与鉴定[J].医学理论与实践,2016,29(24):3301-3303,3311.
[21] 孙凤军,杨建东,蔡俊,等.四种大鼠星形胶质细胞原代纯化培养方法的比较[J].科学技术创新,2019(6):20-22.
[22] 刘检,王宇红,徐雅岚,等.大鼠脑皮质星形胶质细胞的原代培养、纯化及采用HCA技术进行GFAP鉴定[J].沈阳药科大学学报,2016,33(7):581-587.
[23] 张学平,王高华,王惠玲,等.海马神经元原代培养与纯度鉴定方法的优化[J].武汉大学学报(医学版),2013,34(5):703-706,710.
[24] 任玥,苏秋香,张勇,等.大鼠脑海马神经元原代培养方法的建立及其纯度的鉴定[J].沈阳医学院学报,2010,12(4):203-205.
[25] 葛汝村,吕涌涛,魏巍,等.大鼠皮质神经元的体外培养及不同浓度尿激酶干预后的观察[J].神经损伤与功能重建,2019,14(6):271-274.
[26] 李晓晓,陈欣月,刘丽娜,等.SD大鼠乳鼠皮层神经元细胞原代培养模型的建立及鉴定[J].现代生物医学进展,2021,21(21):4001-4005.
[27] 张磊,韩延峰,戴朝,等.一种改良后的大脑皮质神经元细胞的原代培养模型建立及鉴定[J].石河子大学学报(自然科学版),2022,40(1):100-105.
[28] 马悦,李文,李振舒,等.新生大鼠大脑皮质星形胶质细胞纯化及培养方法的改进[J].卫生研究,2019,48(5):795-798.
[29] 刘阳生.小鼠大脑皮质星形胶质细胞的培养、鉴定及其TRPC1-7 mRNA的表达[J]. 湖北科技学院学报(医学版),2021,35(5):409-411,415
[30] 汤婷婷,官志忠,禹文峰. SD大鼠大脑皮层星形胶质细胞的体外原代培养[J].贵阳医学院学报,2014,39(2):158-161. |