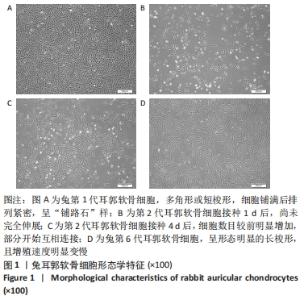
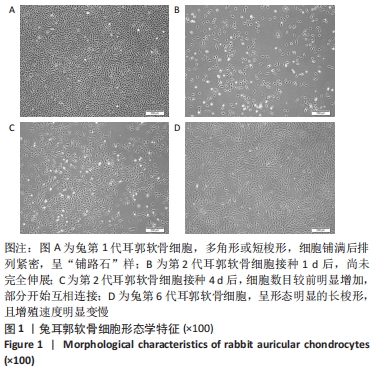
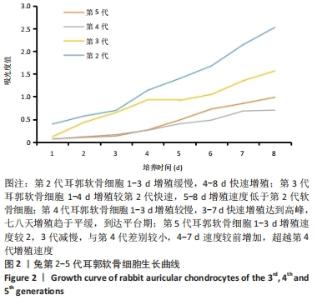
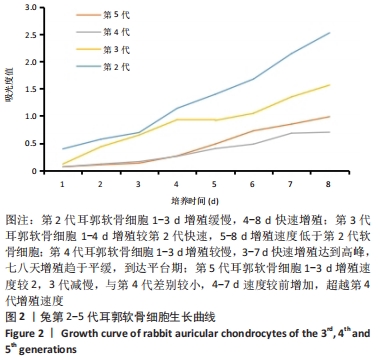
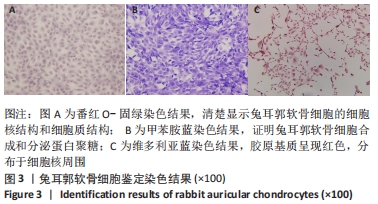
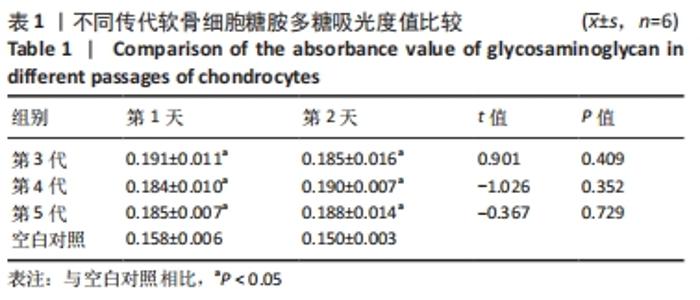
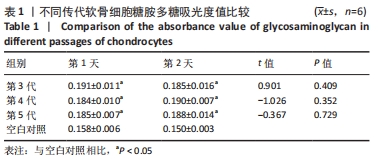
[1] JEON B, LEE C, KIM M, et al. Fabrication of three-dimensional scan-to-print ear model for microtia reconstruction. J Surg Res. 2016;206(2):490-497.
[2] SMITH W, TOYE J, REID A, et al. Nonsurgical correction of congenital ear abnormalities in the newborn: Case series. Paediatr Child Health. 2005; 10(6):327-331.
[3] JUNG BK, KIM JY, KIM YS, et al. Ideal scaffold design for total ear reconstruction using a three-dimensional printing technique. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2019;107(4):1295-1303.
[4] FLORES RL, LISS H, RAFFAELLI S, et al. The technique for 3D printing patient-specific models for auricular reconstruction. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2017;45(6):937-943.
[5] TJELLSTROM A. Osseointegrated implants for replacement of absent or defective ears. Clin Plast Surg. 1990;17(2):355-366.
[6] BALUCH N, NAGATA S, PARK C, et al. Auricular reconstruction for microtia: A review of available methods. Plast Surg (Oakv). 2014; 22(1): 39-43.
[7] YUE H, PATHAK JL, ZOU R, et al. Fabrication of chondrocytes/chondrocyte-microtissues laden fibrin gel auricular scaffold for microtia reconstruction. J Biomater Appl. 2021;35(7):838-848.
[8] DANISOVIC L, VARGA I, ZAMBORSKY R, et al. The tissue engineering of articular cartilage: cells, scaffolds and stimulating factors. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2012; 237(1): 10-17.
[9] RENNER G, LANE RV. Auricular reconstruction: an update. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004;12(4):277-280.
[10] JESSOP ZM, JAVED M, OTTO IA, et al. Combining regenerative medicine strategies to provide durable reconstructive options: auricular cartilage tissue engineering. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7:19.
[11] BERNSTEIN JL, COHEN BP, LIN A, et al. Tissue engineering auricular cartilage using late passage human auricular chondrocytes. Ann Plast Surg. 2018;80(4 Suppl 4):S168-s173.
[12] BERNSTEIN JL. Tissue engineering the human auricle for clinical application: Weill Medical College of Cornell University,2018.
[13] VANKOEVERING KK, HOLLISTER SJ, GREEN GE. Advances in 3-dimensional printing in otolaryngology: A review. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017;143(2):178-183.
[14] YUAN H, XING K, HSU HY. Trinity of Three-Dimensional (3D) Scaffold, Vibration, and 3D Printing on Cell Culture Application: A Systematic Review and Indicating Future Direction. Bioengineering (Basel, Switzerland). 2018;5(3):57.
[15] ZHOU G, JIANG H, YIN Z, et al. In vitro regeneration of patient-specific ear-shaped cartilage and its first clinical application for auricular reconstruction. EBio Medicine. 2018;28:287-302.
[16] LIAO J, CHEN Y, CHEN J, et al. Auricle shaping using 3D printing and autologous diced cartilage. Laryngoscope. 2019;129(11):2467-2474.
[17] RUIZ-CANTU L, GLEADALL A, FARIS C, et al. Multi-material 3D bioprinting of porous constructs for cartilage regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;109:110578.
[18] ISOGAI N, KUSUHARA H, IKADA Y, et al. Comparison of different chondrocytes for use in tissue engineering of cartilage model structures. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(4):691-703.
[19] MUSSI E, FURFERI R, VOLPE Y, et al. Ear reconstruction simulation: From handcrafting to 3D printing. Bioengineering (Basel). 2019;6(1):14.
[20] KIM HY, JUNG SY, LEE SJ, et al. Fabrication and characterization of 3D-printed elastic auricular scaffolds: A pilot study. Laryngoscope. 2019;129(2):351-357.
[21] MELLOR LF, BAKER TL, BROWN RJ, et al. Optimal 3D culture of primary articular chondrocytes for use in the rotating wall vessel bioreactor. Aviat Space Environ Med. 2014;85(8):798-804.
[22] 谢波,冯娟娟,马梦婷,等.兔耳廓软骨的体外培养及细胞特性研究[J].安徽农业科学,2014,42(8):2323-2325.
[23] 杨帆,刘保一,刘家河,等.体外培养SD大鼠关节软骨细胞原代至第3代的形态学特点[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(14):2161-2165.
[24] 邓林峡,余慕雪,潘思年,等.比较单独消化法及分步消化法培养新生大鼠原代软骨细胞的生物学特性[J].中国组织工程研究,2018, 22(25):4047-4052.
[25] KANG SW, YOO SP, KIM BS. Effect of chondrocyte passage number on histological aspects of tissue-engineered cartilage. Biomed Mater Eng. 2007;17(5):269-276.
[26] 于斐,曾晖,于红燕,等.软骨细胞特殊染色技术的比较与应用[J].中国比较医学杂志,2015,25(8):58-61+75+89.
|