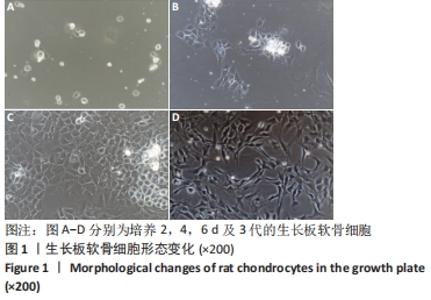
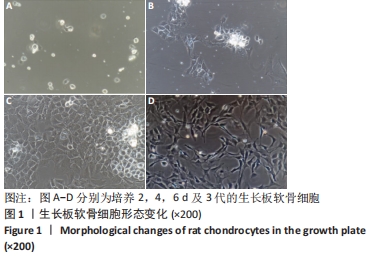
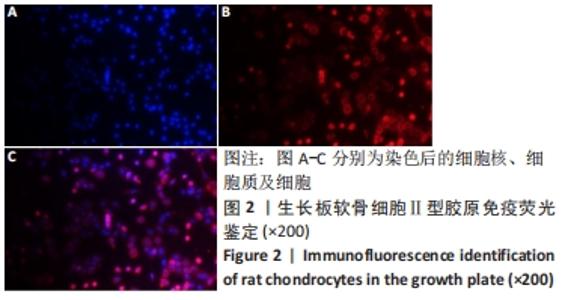
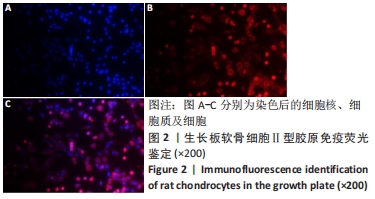
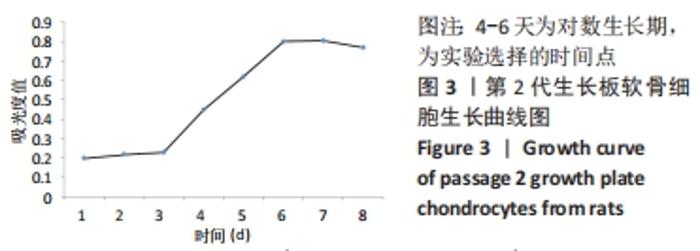
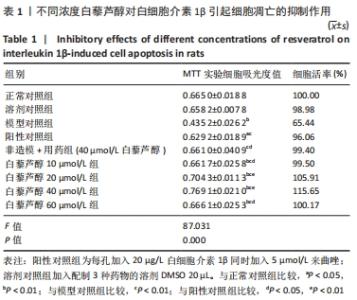
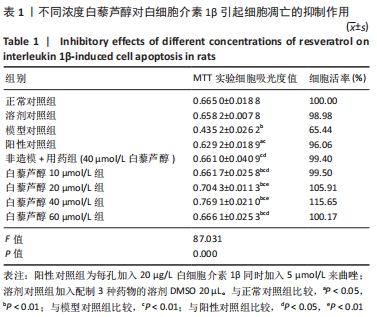
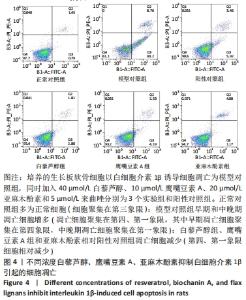
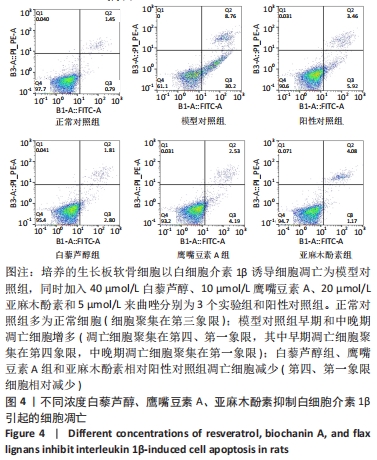
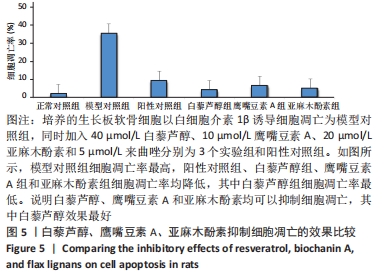
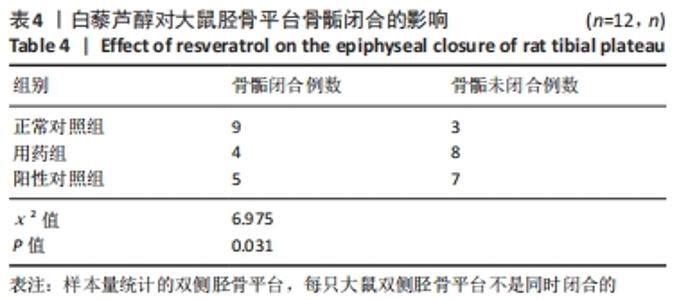
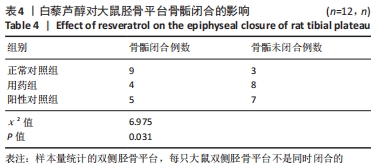
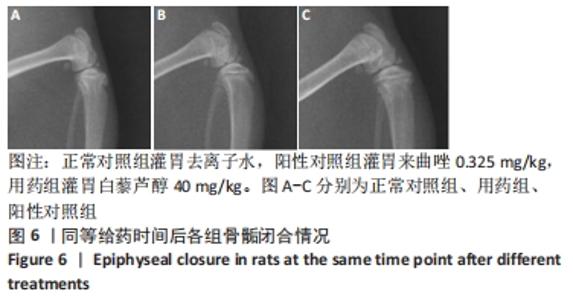
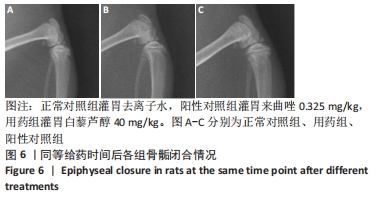
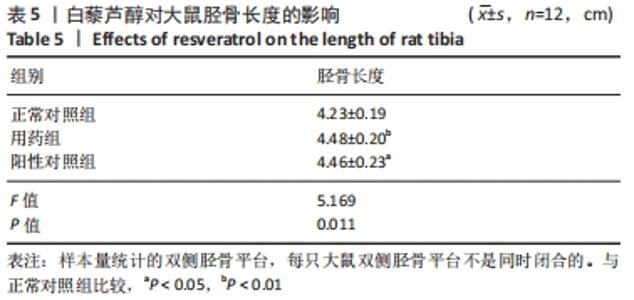
[1] 史升. 雌激素对椎体和长骨骺板生长代谢差异性作用的实验研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2017.
[2] TIAN XY, FENG Y, CHENG ZP, et al. Progress in the study of the aromatase in skeletal muscle. Chem Life. 2017;37(4):595-600.
[3] 尹雅倩. 针刺对卵巢储备功能减退模型大鼠HPO轴及FSH-cAMP信号通路的影响[D].北京:中国中医科学院,2020.
[4] 张姗姗. 二甲双胍对雌鼠性早熟伴胰岛素抵抗与脂肪芳香化酶作用的研究[D].天津:天津医科大学,2016.
[5] 王春林,梁黎.第三代非甾体类芳香化酶抑制剂在儿科内分泌临床应用的再认识[J].浙江大学学报 (医学版),2020,49(3):275-282.
[6] 欧阳力雪,杨凡.芳香化酶抑制剂在矮身材青少年男童中的应用研究进展[J].中华实用儿科临床杂志,2020,35(9):712-715.
[7] QIAO XH. Research progress of aromatase inhibitors in children. World Clinic Drugs. 2020;41(3):160-165.
[8] 李坤,杨义芳.天然产物及其衍生物中的芳香化酶抑制剂[J].中草药,2008, 39(9):1417-1424.
[9] 徐文珊, 黄鸣清, 陈修平, 等. 天然产物来源的芳香化酶抑制剂研究进展[J]. 时珍国医国药,2012,23(4):1008-1011.
[10] WANG Y, MAN GHO W, CHAN FL, et al. The red clover (Trifoliumprat-ense) isoflavonebiocha- nin A inhibits aromatase activity and expression. Br J Nutr. 2008;99(2):303-310.
[11] 胡晓军. 亚麻木酚素的营养保健作用[J]. 中国食物与营养,2005,11(8):36-37.
[12] 张文斌. 亚麻木酚素的提取纯化与生物活性研究[D].无锡:江南大学,2007.
[13] 周强, 杨柳, 戴刚, 等.骺板组织工程的研究进展[J].第三军医大学学报, 2003,25(2):170-173.
[14] 岳永彬. 黄芪苷Ⅱ促成骨机制及对股骨头坏死兔脂联素、促黑素的影响[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2019.
[15] 姚运峰.骨骺骺板的生长发育及其影响因素[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010, 18(17):1430-1433.
[16] 王波, 谢秀琴, 黄荷凤. 芳香化酶抑制剂在妇科内分泌治疗中的应用[J]. 中华医学杂志,2007,87(3):209-212.
[17] 彭子俊. 来曲唑应用于青春早中期男童对其特性和线性生长的影响[J]. 国际医药卫生导报,2019,25(23):3855-3856+3877.
[18] CARANI C, QIN K, SIMONI M, et al. Effect of testosterone and estradiol in a man with aromatase deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1997;337(2):91-95.
[19] LI XL, YE J. Effectiveness and safety of the third generation aromatase inhibitors for growth promotion. Central South Pharm. 2020;171(4):112-116.
[20] 林娟, 马华梅, 李燕虹, 等. 来曲唑对青春早中期男童生殖功能与线性生长的近期影响[J]. 中山大学学报(医学科学版),2018,39(3):386-392.
[21] 孔元梅, 陈虹, 梁黎, 等. 芳香化酶抑制剂联合生长激素治疗青春期矮身材男性患儿的临床研究[J]. 浙江大学学报(医学版),2020,49(3):307-314.
[22] 牟田, 王建六. 芳香化酶抑制剂治疗子宫内膜癌及癌前病变的进展[J]. 实用妇产科杂志,2011,27(10):738-740.
[23] 苏慧萍. 骨成熟影响因素的研究进展[J].国际儿科学杂志,2020,47(4):279-282.
[24] FILES JA, KO MG, PRUTHI S. Managing aromatase inhibitors in breast cancer survivors: not just for oncologists. Mayo Clin Proc. 2010;85(6):560-566.
[25] 刘建平, 黄路圣, 叶林华. 胰岛素样生长因子-1水平监测在重组人生长激素治疗特发性矮小症中的临床意义[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志,2017,26(32): 3568-3571.
[26] ZHENG YB, XU JL. Efficacy of recombinant human growth hormone in the treatment of dwarfism in children at different ages and its effect on bone metabolism, insulin-like growth factor-1 and vitamin D3.Chin J Prim Med Pharm. 2021;28(4):500-503.
[27] 王盼盼,邵倩,班博.软骨生长板相关因素调控生长的研究进展[J].中国儿童保健杂志,2017,25(11):1131-1133.
[28] 孙长英, 张宏其, 鲁世金,等. 雌激素受体α和雌激素受体β在调控青少年椎体生长板软骨细胞分化和增殖中的相互作用[J]. 山西医药杂志,2015, 46(9):977-981.
[29] 李明珠.特发性中枢性性早熟女童雌激素受体α基因Pvu Ⅱ和Xba Ⅰ多态性分析及血清骨形成标志物的研究[D]. 广州:南方医科大学,2015.
[30] 王春林, 傅君芬, 梁黎. 改善矮小儿童成年身高的药物研究进展[J]. 中国实用儿科杂志,2020,35(6):460-464.
[31] SONGJR, DONG Y. Effect of AI Combined with rhGH on Growth Rate, Bone Mineral Density and Bone Metabolism of Children with Idiopathic Dwarfism. Med Recapit. 2020;26(24):4952-4956.
|