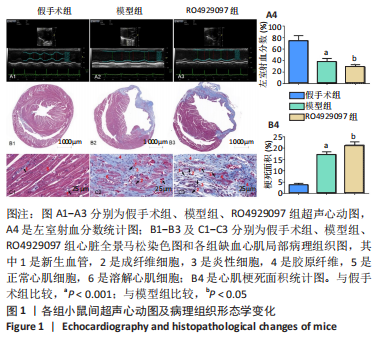
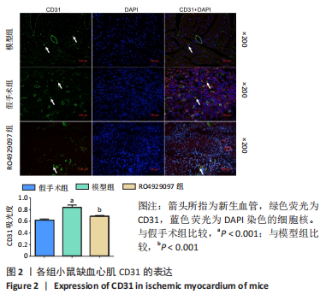
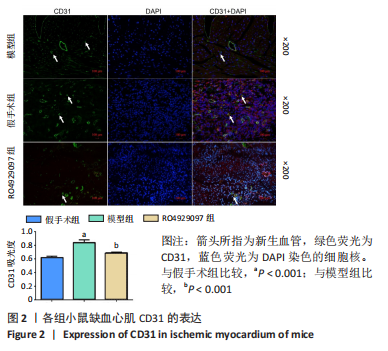
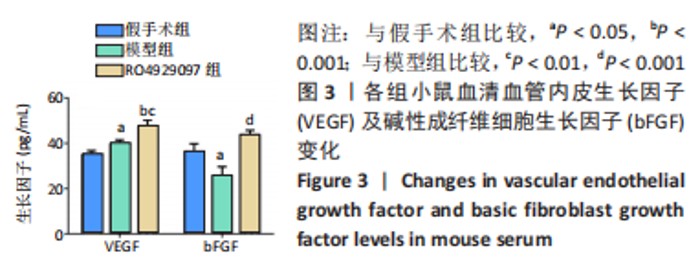
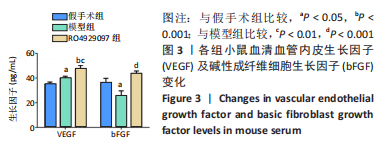
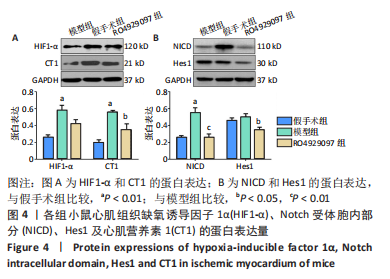
[1] DEINDL E, QUAX P. Arteriogenesis and therapeutic angiogenesis-an update. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(24):13244.
[2] VEITH AP, HENDERSON K, SPENCER A, et al. Therapeutic strategies for enhancing angiogenesis in wound healing. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;146: 97-125.
[3] CARMELIET P, JAIN RK. Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature. 2011;473(7347):298-307.
[4] SABRA M, KARBASIAFSHAR C, ABOULGHEIT A, et al. Clinical application of novel therapies for coronary angiogenesis: overview, challenges, and prospects. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(7):3722-3738.
[5] MAJUMDER S, CRABTREE JS, GOLDE TE, et al. Targeting Notch in oncology: the path forward. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021;20(2):125-144.
[6] SPRINZAK D, BLACKLOW SC. Biophysics of Notch signaling. Annu Rev Biophys. 2021;50:157-189.
[7] KATSUSHIMA K, NATSUME A, OHKA F, et al. Targeting the Notch-regulated non-coding RNA TUG1 for glioma treatment. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13616.
[8] YU L, LIANG H, LU Z, et al. Membrane receptor-dependent Notch1/Hes1 activation by melatonin protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: in vivo and in vitro studies. J Pineal Res. 2015;59(4):420-433.
[9] REN C, YAO Y, HAN R, et al. Cerebral ischemia induces angiogenesis in the peri-infarct regions via Notch1 signaling activation. Exp Neurol. 2018; 304:30-40.
[10] LU W, CHEN X, SI Y, et al. Transplantation of rat mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing hypoxia-inducible factor 2α improves blood perfusion and arteriogenesis in a rat hindlimb ischemia model. Stem Cells Int. 2017; 2017:3794817.
[11] ROCA C, ADAMS RH. Regulation of vascular morphogenesis by Notch signaling. Genes Dev. 2007;21(20):2511-2524.
[12] BLANCO R, GERHARDT H. VEGF and Notch in tip and stalk cell selection. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2013;3(1):a006569.
[13] BISWAS S, SHAFIQUZZAMAN M, YU G, et al. Notch1 signaling in keratocytes maintains corneal transparency by suppressing VEGF expression. Stem cell Reports. 2022;17(6):1442-1457.
[14] WONG B W, MARSCH E, TREPS L, et al. Endothelial cell metabolism in health and disease: impact of hypoxia. EMBO J. 2017;36(15):2187-2203.
[15] MANUELLI V, PECORARI C, FILOMENI G, et al. Regulation of redox signaling in HIF-1-dependent tumor angiogenesis. FEBS J. 2022;289(18):5413-5425.
[16] ZHANG YC, LIU TH, LIU L, et al. Efficacy of Shouzhangshen (Rhizoma Gymnadeniae Crassinervidis) extract against acute high altitude hypoxia-induced brain injury in mice. J Tradit Chin Med. 2021;41(4):546-555.
[17] RANGANATH SH, LEVY O, INAMDAR MS, et al. Harnessing the mesenchymal stem cell secretome for the treatment of cardiovascular disease. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10(3):244-258.
[18] KARANTALIS V, HARE JM. Use of mesenchymal stem cells for therapy of cardiac disease. Circ Res. 2015;116(8):1413-1430.
[19] TSANG KM, HYUN JS, CHENG KT, et al. Embryonic stem cell differentiation to functional arterial endothelial cells through sequential activation of Etv2 and Notch1 signaling by Hif1α. Stem Cell Reports. 2017;9(3):796-806.
[20] BORTOLOTTI F, RUOZI G, FALCIONE A, et al. In Vivo functional selection identifies cardiotrophin-1 as a cardiac engraftment factor for mesenchymal stromal cells. Circulation. 2017;136(16):1509-1524.
[21] MARTÍNEZ-MARTÍNEZ E, BRUGNOLARO C, IBARROLA J, et al. CT-1 (Cardiotrophin-1)-Gal-3 (Galectin-3) Axis in cardiac fibrosis and inflammation. Hypertension. 2019;73(3):602-611.
[22] ABDELHAFFEZ AS, ABD EE, TOHAMY MB, et al. N-acetyl cysteine can blunt metabolic and cardiovascular effects via down-regulation of cardiotrophin-1 in rat model of fructose-induced metabolic syndrome. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2021:1-16. doi: 10.1080/13813455.2021.1876735.
|