Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (28): 4571-4576.doi: 10.12307/2023.585
Previous Articles Next Articles
Novel programmed cell death of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis
Lu Xiaojun1, Xiong Bohan1, Yang Tengyun1, Wang Xu2, Zhang Yaozhang1, Zhong Ruiying1, Li Yanlin1
- 1Department of Sports Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China
-
Received:2022-09-19Accepted:2022-11-08Online:2023-10-08Published:2023-01-29 -
Contact:Li Yanlin, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Sports Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Lu Xiaojun, Master candidate, Department of Sports Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, Nos. 81760403 and 81960409 (both to LYL); Chen Shiyi Expert Workstation Project of Yunnan Province, No. 2018IC102 (to LYL); Project of Clinical Medical Center for Bone and Joint Diseases of Yunnan Province, No. ZX2019-03-04 (to LYL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lu Xiaojun, Xiong Bohan, Yang Tengyun, Wang Xu, Zhang Yaozhang, Zhong Ruiying, Li Yanlin. Novel programmed cell death of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(28): 4571-4576.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
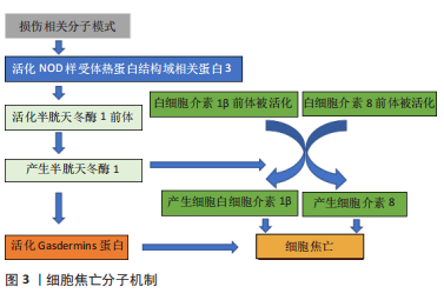
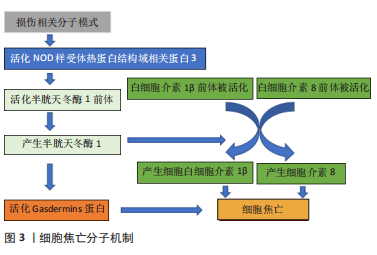
2.1 细胞焦亡与骨关节炎 当细胞受到细胞外或细胞内的先天免疫相关的扰动时,会产生损伤相关分子模式,继而活化NOD样受体热蛋白结构域相关蛋白3(NOD-like receptor family,pyrin domain containing 3,NLRP3),NLRP3可激活一个或多个炎性半胱天冬酶(caspase),包括caspase-1、3,小鼠caspase-11,人类caspase-4、5[11]。这些活性caspase可以活化炎性递质白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18的前体以及GSDMD,GSDMD最终导致细胞穿孔、肿胀、死亡[12],白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18被释放到细胞外,引起炎症反应。这种细胞死亡方式最初被认为是凋亡[13],但这种细胞死亡方式由炎性递质白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18介导[14],而凋亡是一种非炎症的程序性细胞死亡,因此COOKSON和BRENNAN首次使用焦亡来描述这一促炎性程序性细胞死亡方式,这是引起焦亡的经典途径。而非经典途径由脂多糖和多种天冬半胱氨酸酶共同介导,其结果依然是细胞穿孔破裂,最终死亡,如图3所示。"
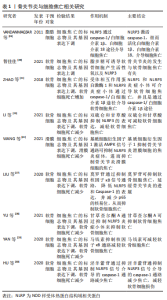
细胞焦亡已被证明与心血管疾病[15]、慢性肠道炎症及结直肠癌等多种疾病有关[16-17],这些疾病在一定程度上都存在着炎症反应。骨关节炎的危险因素包括多种因素[18],而肥胖为其常见危险因素。在一项肥胖人群的骨关节炎研究中,VANDANMAGSAr等[19]发现肥胖的人血液中的脂多糖水平较高。脂多糖激活caspase-4/5/11,可通过非典型的炎性小体途径在全身和组织水平启动焦亡,导致炎性软骨细胞死亡和软骨损失增加。同时,他们发现在消融小鼠NLRP3小体后,可防止肥胖诱导的脂肪沉积炎性小体的激活[19],换句话说,肥胖通过激活NLRP3炎症小体的释放来促进焦亡,他们认为这可能与骨关节炎的进展有关。此外,智佳佳[20]在脂多糖诱导的软骨细胞中发现活性氧和NLRP3升高,证明了细胞焦亡是骨关节炎的致病因素之一。ZHAO等[21]已明确发现,NLRP1和NLRP3炎症小体是通过caspase-1/白细胞介素1β炎症通路介导膝关节炎的。关节间隙中脂多糖和ATP的增加可能通过NLRP3炎性小体促进膝关节炎,再次说明细胞焦亡在关节炎的发病中发挥着重要作用,细胞焦亡与骨关节炎中的软骨降解、炎症反应和滑膜的破坏等都有一定的关系[22]。而对于防治细胞焦亡来缓解骨关节炎,研究者发现标准浓度的双硫仑和甘草酸的联合作用可以保护软骨细胞,抑制炎症反应并减少软骨细胞焦亡[23]。WANG等[24]研究发现,外源性基质细胞衍生因子1激活AMPK信号通路可抑制NLRP3炎症体,进而抑制骨关节炎滑膜细胞的焦亡过程。P2X7R是一种嘌呤受体,由三磷酸腺苷门控的非选择性阳离子通道组成,可介导钠和钙内流和钾外流,并参与多种炎症反应和细胞死亡的不同机制。研究发现P2X7R可参与NLRP3和caspase-11独特途径介导的细胞焦亡,并产生软骨降解酶,以激活滑膜组织中的炎症因子[25],P2X7R是可能的焦亡通路靶点之一。此外,LI等[26]的研究发现,USP7(泛素特异性蛋白酶的成员之一)抑制剂可以通过抑制NOX4/NLRP3信号通路,减轻双氧水诱导的软骨细胞损伤和焦亡。相关研究还发现,部分中药在防治软骨细胞焦亡中有着一定作用,如:莫罗苷通过抑制核因子κB信号通路,可降低NLRP3和Caspase-1的表达,并减少p65的核易位,从而抑制软骨细胞焦亡的发作并延缓骨关节炎的进展[27]。甘草查尔酮A通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体来抑制软骨细胞焦亡[28]。YAN等[29]的研究报道,马钱素通过抑制核因子κB活性和软骨细胞焦亡改善小鼠模型软骨退变和骨性关节炎的发生。在淫羊藿苷应用于动物模型中的研究发现,其可通过抑制NLRP3信号介导的caspase-1通路减少焦亡,减轻软骨细胞损伤和骨关节炎[30]。 目前焦亡的研究主要集中在NLRP3以及脂多糖上,对于焦亡的基因、miRNA的研究较少,是接下来研究者的工作重点和中心。 总的来说,炎症小体如NLRP3及其调节因子在焦亡中的作用表明,NLRP3可能是骨关节炎诊断和监测的一个有希望的生物标志物。NLRP3的靶向治疗可能是治疗骨关节炎的一种潜在策略。骨关节炎与细胞细胞焦亡的相关研究描述,见表1。"

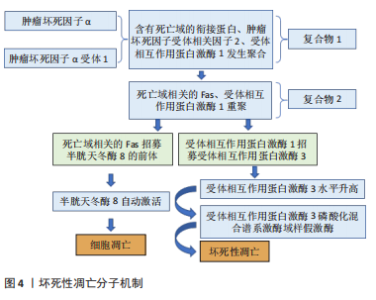
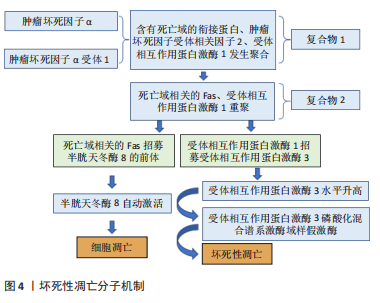
2.2 坏死性凋亡与骨关节炎 坏死性凋亡是由受体相互作用蛋白激酶1,3和MLKL在各种病理条件下引起的程序性坏死细胞死亡。凋亡和坏死性凋亡密切相关,肿瘤坏死因子α可以决定细胞的最终命运[31]。一旦肿瘤坏死因子α与肿瘤坏死因子α受体1结合,肿瘤坏死因子就会诱导受体三聚化,并招募含有死亡域(DD)的衔接蛋白(TRADD)、肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子2和受体相互作用蛋白激酶1,形成所谓的复合物Ⅰ[32]。复合物Ⅰ的几个组分(DD、RIP1)重组形成胞质复合物(复合物Ⅱ),包括通过死亡域介导的相互作用招募FADD(与死亡域相关的Fas)和受体相互作用蛋白激酶1。在复合体Ⅱ中,FADD招募pro caspase-8(caspase-8的前体),使caspase-8水平降低。而受体相互作用蛋白激酶1招募受体相互作用蛋白激酶3,使受体相互作用蛋白激酶3水平升高。随着caspase-8水平的降低,caspase-8会自动激活,细胞发生凋亡[33]。RIP3可以自动磷酸化以响应同源相互作用。自动磷酸化的受体相互作用蛋白激酶3可以招募并磷酸化MLKL[34],导致MLKL寡聚并易位到质膜。MLKL寡聚体通过产生阳离子通道导致质膜破裂来执行坏死性凋亡,高浓度受体相互作用蛋白激酶3存在的情况下复合体Ⅱ倾向于介导坏死性凋亡。总之,受体相互作用蛋白激酶1磷酸化对坏死小体组装和激活至关重要[35],而受体相互作用蛋白激酶3决定细胞走向坏死性凋亡的易感性[36],最终由磷酸化的MLKL执行,见图4所示。"

先前的研究确定了坏死性凋亡在心肌梗死和脑卒中[37]、动脉粥样硬化[38]、缺血再灌注损伤[39]、胰腺炎[40]、炎症性肠病和其他几种常见临床疾病中的重要性[41]。在关节炎中,坏死性凋亡的作用和机制的研究也正成为人们日益关注的领域。LIANG等[42]的研究发现,坏死抑素1通过高迁移率族蛋白B1/Toll样受体4/基质细胞衍生因子1通路减轻创伤诱导的小鼠骨关节炎。CHENG等[43]的研究证实,受体相互作用蛋白激酶1的上调通过骨形态发生蛋白7也可以介导软骨细胞坏死和细胞外基质破坏,参与关节炎发病。磷脂酶Cγ1可抑制凋亡和坏死性凋亡,增加白细胞介素1β处理后大鼠软骨细胞的软骨基质合成[44],说明关节炎中软骨细胞死亡与坏死性凋亡有关。最近的证据表明,氧化和机械应力可促进骨性关节炎坏死性凋亡的发生[45]。机械应力可通过受体相互作用蛋白激酶1介导下颌骨软骨的凋亡和坏死性凋亡[46]。此外,TRIM24-受体相互作用蛋白激酶3轴的扰动通过激活受体相互作用蛋白激酶3和调节分解代谢因子的表达,调节小鼠骨关节发病[47],这些研究证明关节炎中存在坏死性凋亡。在防治坏死性凋亡来缓解关节炎,GONG等[48]的研究发现,泛Raf激酶抑制剂AZ-628可通过抑制肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的软骨细胞坏死性凋亡以及调节破骨细胞形成来延缓骨关节炎的进展。但是关于坏死性凋亡的靶基因以及MLKL是否参与介导软骨细胞坏死性凋亡还未明确,仍需要进一步研究。 总之,骨性关节炎的发展和进展与受体相互作用蛋白激酶1、受体相互作用蛋白激酶3密切相关。最近的研究表明,坏死性凋亡在炎症相关疾病中具有重要地位。坏死性凋亡和细胞凋亡密切相关,突出了疾病机制的复杂性和多样性。骨关节炎与坏死性凋亡相关研究的描述,见表2。"

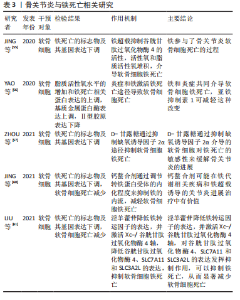
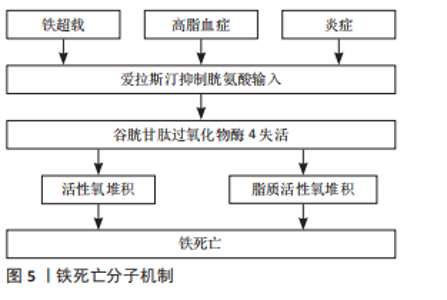
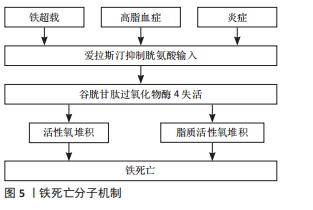
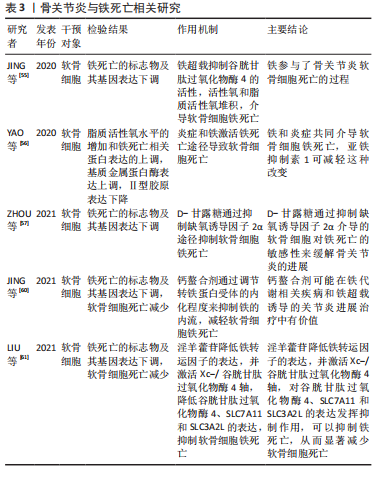
实验证据表明,过量的铁会导致组织损伤和器官功能障碍,从而导致肝硬化[50]、心肌病[51]、糖尿病和其他疾病[52-53]。大量研究表明,当细胞内铁过量时,在芬顿反应条件下可产生羟基自由基并促进脂质过氧化,诱导铁死亡[54]。过量的铁促进软骨细胞凋亡,促进基质降解酶的表达上调。JING等[55]使用柠檬酸铁铵建立了过量铁条件,他们报道过量铁的存在会加速软骨细胞凋亡,导致基质降解酶如基质金属蛋白酶3和基质金属蛋白酶13的表达。YAO等[56]报道,软骨细胞在炎症和铁过量的环境中容易发生铁死亡,该研究分别使用白细胞介素1β和FAC建立软骨细胞的炎症环境和产生铁超载的条件,在这些条件下也观察到脂质活性氧水平的增加和铁死亡相关蛋白表达的上调,进一步导致Ⅱ型胶原表达的增加和基质金属蛋白酶13表达的降低。而在诱导关节炎的小鼠关节内注射亚铁抑制素1(一种亚铁减少特异性抑制剂)可拯救谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白的表达,并改善了软骨被侵蚀的程度。这些研究证明关节炎中存在铁死亡,铁死亡在关节炎的发生发展中起一定作用。关节炎中软骨细胞发生铁超载以及谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4被抑制后,导致的致死性脂质过氧化与软骨细胞的死亡密切相关。然而,软骨细胞中铁死亡的分子机制尚不明确。近年来,缺氧诱导因子2α被报道具有促进脂质储存和脂质过氧化积累的作用。据报道,缺氧诱导因子2α促进肉碱棕榈酰转移酶1A介导的β-氧化,因此被确定为软骨细胞铁死亡的中心中介。此外,软骨细胞中过表达缺氧诱导因子2α可减弱谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4的表达,加重软骨退变。这些研究表明铁死亡可能与关节炎的进展有潜在关联[57]。近年来,氧化应激和线粒体功能障碍在关节炎发展中的作用逐渐引起研究者的关注[58]。然而,在过量铁的条件下,线粒体功能障碍对软骨细胞代谢的影响仍有待探索。JING等[59]的另一项研究表明,软骨细胞中过量的铁介导的线粒体功能障碍与氧化应激密切相关,该关联通过活性氧生成过程建立,进而促进关节炎相关分解代谢标志物的表达。钙螯合法进一步证实了铁在软骨细胞功能障碍中的重要作用。钙螯合剂可通过调节转铁蛋白受体的内化程度来抑制铁的内流,是治疗铁超载相关疾病的有效药物。JING等[60]基于铁超载通过诱导活性氧生成和线粒体功能障碍促进关节炎的理论,进一步揭示钙螯合剂BAPTA-AM抑制铁流入软骨细胞,有效抑制铁超载介导的活性氧积累和线粒体功能障碍,这表明钙螯合剂在治疗铁代谢相关的关节炎过程中发挥了重要作用。部分中药在抑制骨关节炎软骨细胞铁死亡这方面也有着一定作用,如:淫羊藿苷降低铁转运因子的表达,并激活Xc-/谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4轴,对谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4、SLC7A11和SLC3A2L的表达发挥抑制作用,可以抑制铁死亡,从而显著减少软骨细胞死亡[61],这些研究证明了关节炎中存在铁死亡,并且抑制铁超载可以缓解关节炎的病程。但是铁死亡相关基因和miRNA仍有待发现,可作为进一步研究铁死亡的方向。骨关节炎与铁死亡的相关研究描述,见表3。"
| [1] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393(10182):1745-1759. [2] MUSUMECI G, AIELLO FC, SZYCHLINSKA MA, et al. Osteoarthritis in the XXIst century: risk factors and behaviours that influence disease onset and progression. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(3):6093-6112. [3] MOBASHERI A, BATT M. An update on the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2016;59(5-6):333-339. [4] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: pathology, diagnosis, and treatment options. Med Clin. 2020;104(2):293-311. [5] GOZZELINO R, AROSIO P. Iron homeostasis in health and disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(1):130. [6] LI C, OUYANG N, WANG X, et al. Association between the ABO blood group and primary knee osteoarthritis: a case-control study. J Orthop Translat. 2020;21:129-135. [7] LOESER RF, COLLINS JA, DIEKMAN BO. Ageing and the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(7):412-420. [8] HOSSEINZADEH A, KAMRAVA SK, JOGHATAEI MT, et al. Apoptosis signaling pathways in osteoarthritis and possible protective role of melatonin. J Pineal Res. 2016;61(4):411-425. [9] YAO X, SUN K, YU S, et al. Chondrocyte ferroptosis contribute to the progression of osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 2021;27:33-43. [10] ZHAO LR, XING RL, WANG PM, et al. NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasomes mediate LPS/ATP‑induced pyroptosis in knee osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(4):5463-5469. [11] COOKSON BT, BRENNAN MA. Pro-inflammatory programmed cell death. Trends Microbiol. 2001;9(3):113-114. [12] GAO YL, ZHAI JH, CHAI YF. Recent Advances in the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Pyroptosis in Sepsis. Mediators Inflamm. 2018;2018:5823823. [13] HERSH D, MONACK DM, SMITH MR, et al. The Salmonella invasin SipB induces macrophage apoptosis by binding to caspase-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96(5):2396-2401. [14] FERNANDES-ALNEMRI T, WU J, YU JW, et al. The pyroptosome: a supramolecular assembly of ASC dimers mediating inflammatory cell death via caspase-1 activation. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14(9):1590-1604. [15] ZHAOLIN Z, GUOHUA L, SHIYUAN W, et al. Role of pyroptosis in cardiovascular disease. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(2):e12563. [16] SCHEIBE K, KERSTEN C, SCHMIED A, et al. Inhibiting Interleukin 36 Receptor Signaling Reduces Fibrosis in Mice With Chronic Intestinal Inflammation. Gastroenterology. 2019;156(4):1082-1097.e1011. [17] HANSON B. Necroptosis: A new way of dying? Cancer Biol Ther. 2016;17(9): 899-910. [18] CORR EM, CUNNINGHAM CC, HELBERT L, et al. Osteoarthritis-associated basic calcium phosphate crystals activate membrane proximal kinases in human innate immune cells. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):23. [19] VANDANMAGSAR B, YOUM YH, RAVUSSIN A, et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat Med. 2011;17(2):179-188. [20] 智佳佳.软骨细胞焦亡中ROS/NLRP3通路促进炎症因子分泌的实验研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2021. [21] ZHAO Y, SHI J, SHAO F. Inflammatory Caspases: Activation and Cleavage of Gasdermin-D In Vitro and During Pyroptosis. Methods Mol Biol. 2018; 1714:131-148. [22] 智佳佳,杜朝政,王宇泽.骨关节炎形成过程中细胞焦亡的作用与机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(32):5204-5209 [23] LI C, LI L, LAN T. Co-treatment with disulfiram and glycyrrhizic acid suppresses the inflammatory response of chondrocytes. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):132. [24] WANG S, MOBASHERI A, ZHANG Y, et al. Exogenous stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) suppresses the NLRP3 inflammasome and inhibits pyroptosis in synoviocytes from osteoarthritic joints via activation of the AMPK signaling pathway. Inflammopharmacology. 2021;29(3):695-704. [25] HASEEB A, HAQQI TM. Immunopathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Clin Immunol. M2013;146(3):185-196. [26] LI Z, HUANG Z, BAI L. The P2X7 Receptor in Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:628330. [27] LIU G, LIU Q, YAN B, et al. USP7 Inhibition Alleviates H(2)O(2)-Induced Injury in Chondrocytes via Inhibiting NOX4/NLRP3 Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:617270. [28] YU H, YAO S, ZHOU C, et al. Morroniside attenuates apoptosis and pyroptosis of chondrocytes and ameliorates osteoarthritic development by inhibiting NF-κB signaling. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;266:113447. [29] YAN Z, QI W, ZHAN J, et al. Activating Nrf2 signalling alleviates osteoarthritis development by inhibiting inflammasome activation. J Cell Mol Med. 2020; 24(22):13046-13057. [30] HU J, ZHOU J, WU J, et al. Loganin ameliorates cartilage degeneration and osteoarthritis development in an osteoarthritis mouse model through inhibition of NF-κB activity and pyroptosis in chondrocytes. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;247:112261. [31] ZU Y, MU Y, LI Q, et al. Icariin alleviates osteoarthritis by inhibiting NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):307. [32] VAN HERREWEGHE F, FESTJENS N, DECLERCQ W, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-mediated cell death: to break or to burst, that’s the question. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010;67(10):1567-1579. [33] ZHANG Y, CHEN X, GUEYDAN C, et al. Plasma membrane changes during programmed cell deaths. Cell Res. 2018;28(1):9-21. [34] SUN L, WANG H, WANG Z, et al. Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein mediates necrosis signaling downstream of RIP3 kinase. Cell. 2012;148(1-2): 213-227. [35] HITOMI J, CHRISTOFFERSON DE, NG A, et al. Identification of a molecular signaling network that regulates a cellular necrotic cell death pathway. Cell. 2008;135(7):1311-1323. [36] LINKERMANN A, GREEN DR. Necroptosis. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(5):455-465. [37] SMITH CC, DAVIDSON SM, LIM SY, et al. Necrostatin: a potentially novel cardioprotective agent? Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2007;21(4):227-233. [38] LIN J, LI H, YANG M, et al. A role of RIP3-mediated macrophage necrosis in atherosclerosis development. Cell Rep. 2013;3(1):200-210. [39] LINKERMANN A, BRÄSEN JH, HIMMERKUS N, et al. Rip1 (receptor-interacting protein kinase 1) mediates necroptosis and contributes to renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Kidney Int. 2012;81(8):751-761. [40] WU J, HUANG Z, REN J, et al. Mlkl knockout mice demonstrate the indispensable role of Mlkl in necroptosis. Cell Res. 2013;23(8):994-1006. [41] WELZ PS, WULLAERT A, VLANTIS K, et al. FADD prevents RIP3-mediated epithelial cell necrosis and chronic intestinal inflammation. Nature. 2011; 477(7364):330-334. [42] LIANG S, LV ZT, ZHANG JM, et al. Necrostatin-1 Attenuates Trauma-Induced Mouse Osteoarthritis and IL-1β Induced Apoptosis via HMGB1/TLR4/SDF-1 in Primary Mouse Chondrocytes. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1378. [43] CHENG J, DUAN X, FU X, et al. RIP1 Perturbation Induces Chondrocyte Necroptosis and Promotes Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis via Targeting BMP7. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:638382. [44] CHEN X, CHEN R, XU Y, et al. PLCγ1 inhibition combined with inhibition of apoptosis and necroptosis increases cartilage matrix synthesis in IL-1β-treated rat chondrocytes. FEBS Open Bio. 2021;11(2):435-445. [45] RIEGGER J, BRENNER RE. Evidence of necroptosis in osteoarthritic disease: investigation of blunt mechanical impact as possible trigger in regulated necrosis. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(10):683. [46] ZHANG C, LIN S, LI T, et al. Mechanical force-mediated pathological cartilage thinning is regulated by necroptosis and apoptosis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(8):1324-1334. [47] JEON J, NOH HJ, LEE H, et al. TRIM24-RIP3 axis perturbation accelerates osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(12):1635-1643. [48] GONG Y, QIU J, YE J, et al. AZ-628 delays osteoarthritis progression via inhibiting the TNF-α-induced chondrocyte necroptosis and regulating osteoclast formation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;111:109085. [49] STOCKWELL BR, FRIEDMANN ANGELI JP, BAYIR H, et al. Ferroptosis: A Regulated Cell Death Nexus Linking Metabolism, Redox Biology, and Disease. Cell. 2017; 171(2):273-285. [50] YU Y, JIANG L, WANG H, et al. Hepatic transferrin plays a role in systemic iron homeostasis and liver ferroptosis. Blood. 2020;136(6):726-739. [51] FANG X, CAI Z, WANG H, et al. Loss of Cardiac Ferritin H Facilitates Cardiomyopathy via Slc7a11-Mediated Ferroptosis. Circ Res. 2020;127(4):486-501. [52] STOCKWELL BR, JIANG X, GU W. Emerging Mechanisms and Disease Relevance of Ferroptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 2020;30(6):478-490. [53] SHA W, HU F, XI Y, et al. Mechanism of Ferroptosis and Its Role in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J Diabetes Res. 2021;2021:9999612. [54] SUN Y, CHEN P, ZHAI B, et al. The emerging role of ferroptosis in inflammation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;127:110108. [55] JING X, LIN J, DU T, et al. Iron Overload Is Associated With Accelerated Progression of Osteoarthritis: The Role of DMT1 Mediated Iron Homeostasis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:594509. [56] YAO X, SUN K, YU S, et al. Chondrocyte ferroptosis contribute to the progression of osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 2020;27:33-43. [57] ZHOU X, ZHENG Y, SUN W, et al. D-mannose alleviates osteoarthritis progression by inhibiting chondrocyte ferroptosis in a HIF-2α-dependent manner. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(11):e13134. [58] WANG FS, KUO CW, KO JY, et al. Irisin Mitigates Oxidative Stress, Chondrocyte Dysfunction and Osteoarthritis Development through Regulating Mitochondrial Integrity and Autophagy. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(9):810. [59] JING X, DU T, LI T, et al. The detrimental effect of iron on OA chondrocytes: Importance of pro-inflammatory cytokines induced iron influx and oxidative stress. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(12):5671-5680. [60] JING X, WANG Q, DU T, et al. Calcium chelator BAPTA‑AM protects against iron overload‑induced chondrocyte mitochondrial dysfunction and cartilage degeneration. Int J Mol Med. 2021;48(4):196. [61] LIU XJ, LV YF, CUI WZ, et al. Icariin inhibits hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced ferroptosis of cardiomyocytes via regulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. FEBS Open Bio. 2021;11(11):2966-2976. |
| [1] | He Xi, Wan Yu, Tang Yuting, Yang Anning, Wu Kai, Jiao Yun, Bai Zhigang, Jiang Yideng, Shen Jiangyong. Erastin inhibits proliferation of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Nong Fuxiang, Jiang Zhixiong, Li Yinghao, Xu Wencong, Shi Zhilan, Luo Hui, Zhang Qinglang, Zhong Shuang, Tang Meiwen. Bone cement augmented proximal femoral nail antirotation for type A3.3 intertrochanteric femoral fracturalysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [3] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [4] | Huang Linke, Wei Linhua, Jiang Jie, Liu Qian, Chen Weiwei. Effects of estrogen combined with treadmill exercise on bone mass and articular cartilage in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [5] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| [6] | Yuan Changshen, Guan Yanbing, Li Zhe, Rong Weiming, Liao Shuning, Chen Lewei, Mei Qijie, Duan Kan. Screening and verification of key genes of necroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 695-700. |
| [7] | Wan Guoli, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan, Li Ang, Shi Xunda, Cai Yi. Retrospective analysis of the influencing factors of chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 558-564. |
| [8] | Gu Mingxi, Wang Bo, Tian Fengde, An Ning, Hao Ruihu, Wang Changcheng, Guo Lin. Comparison of early efficacy and safety of simultaneous and staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 565-571. |
| [9] | Yu He, Zheng Jiafa, Song Xiufeng, Guan Shengyi. Tibiotalocalcaneal arthrodesis with blood supplied fibular flap combined with hollow screw in the treatment of end-stage ankle osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 588-593. |
| [10] | Guo Yingqi, Gong Xianxu, Zhang Yan, Xiao Han, Wang Ye, Gu Wenguang. Meniscus extrusion and patellofemoral joint cartilage injury and bone marrow lesions: MRI semi-quantitative score [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 600-605. |
| [11] | Yu Jiaan, Liu Xinwei, Lian Hongyu, Liu Kexin, Li Zitao. Medial open-wedge tibial osteotomy versus lateral closed-wedge tibial osteotomy for unicompartmental knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 632-639. |
| [12] | Huang Yuying, Guo Yi, Han Xinzuo, Min Hongwei, Li Xuemei, Liu Kemin. Functional correlation between the elasticity of the quadriceps and its tendons and osteoarthritis of the knee based on shear wave elastography measurements [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 4971-4976. |
| [13] | Chen Jingtao, Chen You, Li Yujing, Liu Zhigang. Astragalus polysaccharide inhibits Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor kappaB p65 pathway in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 5002-5008. |
| [14] | Chen Jianchao, Song Huiping. Distribution characteristics of bone mass in different parts of postmenopausal women with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 5035-5039. |
| [15] | Yang Chaoqiang, Zhang Hulin, Wang Xiaomin, Wang Liang, Wang Yican. Prevention and treatment of bone-related diseases by regulating macrophages with Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 5064-5070. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||