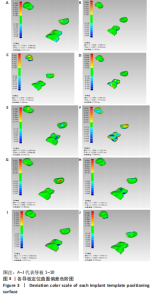
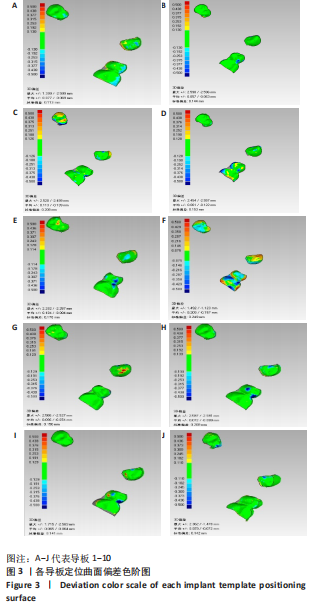
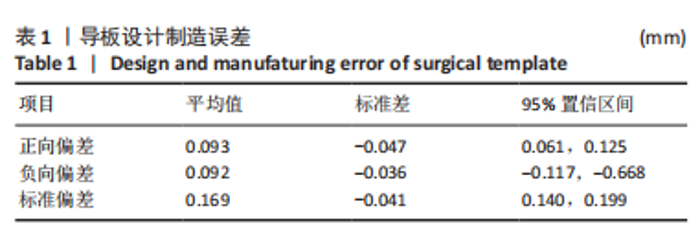
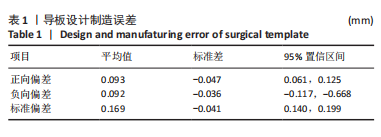
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (21): 3356-3360.doi: 10.12307/2023.466
Previous Articles Next Articles
Design and manufacturing error and implant accuracy of tooth-supported surgical template
Xu Liangwei, Zhang Kunling
- Ningbo Polytechnic, Ningbo 315800, Zhejiang Province, China
-
Received:2022-05-18Accepted:2022-07-27Online:2023-07-28Published:2022-11-24 -
Contact:Xu Liangwei, phD, Lecturer, Ningbo Polytechnic, Ningbo 315800, Zhejiang Province, China -
About author:Xu Liangwei, phD, Lecturer, Ningbo Polytechnic, Ningbo 315800, Zhejiang Province, China -
Supported by:Scientific Research Project of Introduction and Training of High-Level Talents of Ningbo Polytechnic, No. NZ22RC02 (to XLW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Liangwei, Zhang Kunling. Design and manufacturing error and implant accuracy of tooth-supported surgical template[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(21): 3356-3360.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] SCHNUTENHAUS S, EDELMANN C, RUDOLPH H. Does the macro design of an implant affect the accuracy of template-guided implantation? A prospective clinical study. Int J Implant Dent. 2021;7(1):42. [2] CASSETTA M, STEFANELLI LV, GIANSANTI M, et al. Accuracy of implant placement with a stereolithographic surgical template. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2012;27(3):655-663. [3] MISTRY A, UCER C, THOMPSON JD, et al. 3D guided dental implant placement: impact on surgical accuracy and collateral damage to the inferior alveolar nerve. Dent J. 2021;9(9):99-110. [4] ZHOU M, ZHOU H, LI S, et al. Accuracy of Implant Placement Guided with Surgical Template: An In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2021;41(2):e55-e62. [5] WU YT, PAPASPYRIDAKOS P, KANG K, et al. Accuracy of Different Surgical Guide Designs for Static Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery: An in vitro Study. J Oral Implantol. 2021. doi: 10.1563/aaid-joi-D-21-00055. [6] LOU F, RAO P, ZHANG M, et al. Accuracy evaluation of partially guided and fully guided templates applied to implant surgery of anterior teeth: A randomized controlled trial. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2021; 23(1):117-130. [7] CUNHA RM, SOUZA FA, HADAD H, et al. Accuracy evaluation of computer-guided implant surgery associated with prototyped surgical guides. J Prosthet Dent. 2021;125(2):266-272. [8] XINGZHOU Q, WANG Z, ONG HS, et al. Accuracy of Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing Surgical Template for Guidance of Dental Implant Distraction in Mandibular Reconstruction With Free Fibula Flaps. J Craniofac Surg. 2020;31(2):355-359. [9] EFTEKHAR ASHTIANI R, GHASEMI Z, NAMI M, et al. Accuracy of static digital surgical guides for dental implants based on the guide system: A systematic review. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2021;122(6):600-607. [10] TAHMASEB A, WU V, WISMEIJER D, et al. The accuracy of static computer‐aided implant surgery: A systematic review and meta‐analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018;29 Suppl 16:416-435. [11] VINCI R, MANACORDA M, ABUNDO R, et al. Accuracy of Edentulous Computer-Aided Implant Surgery as Compared to Virtual Planning: A Retrospective Multicenter Study. J Clin Med. 2020;9(3):774. [12] CHEN Z, LI J, SINJAB K, et al. Accuracy of flapless immediate implant placement in anterior maxilla using computer-assisted versus freehand surgery: A cadaver study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018;29(12):1186-1194. [13] CHEN C, YUH D, HUANG R, et al. Accuracy of Implant Placement with a Navigation System, a Laboratory Guide, and Freehand Drilling. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;33(6):1213-1218. [14] XU LW, YOU J, ZHANG JX, et al. Impact of Surgical Template on the Accuracy of Implant Placement. J Prosthodont. 2016;25(8):641-646. [15] SCHNEIDER D, MARQUARDT P, ZWAHLEN M, et al. A systematic review on the accuracy and the clinical outcome of computer-guided template-based implant dentistry. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009;20:73-86. [16] MEDIAVILLA GUZMÁN A, RIAD DEGLOW E, ZUBIZARRETA-MACHO Á, et al. Accuracy of Computer-Aided Dynamic Navigation Compared to Computer-Aided Static Navigation for Dental Implant Placement: An In Vitro Study. J Clin Med. 2019;8(12):2123. [17] PETTERSSON A, KERO T, GILLOT L, et al. Accuracy of CAD/CAM-guided surgical template implant surgery on human cadavers: Part I. J Prosthet Dent. 2010;103(6):334-342. [18] 徐良伟,程康杰,彭伟,等.一种通用型种植导板的精度分析[J].口腔医学研究,2017,33(4):382-385. [19] SUN T, LEE H, LAN T. Comparing Accuracy of Implant Installation with a Navigation System (NS), a Laboratory Guide (LG), NS with LG, and Freehand Drilling. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(6):2107. [20] SCHNUTENHAUS S, WAGNER M, EDELMANN C, et al. Factors Influencing the Accuracy of Freehand Implant Placement: A Prospective Clinical Study. Dent J. 2021;9(5):54. [21] KESSLER A, DOSCH M, REYMUS M, et al. Influence of 3D- printing method, resin material, and sterilization on the accuracy of virtually designed surgical implant guides. J Prosthet Dent. 2021;S0022-3913(20)30621-1. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2020.08.038 [22] KOMURO A, YAMADA Y, UESUGI S, et al. Accuracy and dimensional reproducibility by model scanning, intraoral scanning, and CBCT imaging for digital implant dentistry. Int J Implant Dent. 2021;7(1):63. [23] LEE D, AN S, HONG M, et al. Accuracy of a direct drill-guiding system with minimal tolerance of surgical instruments used for implant surgery: a prospective clinical study. J Adv Prosthodont. 2016;8(3):207-213. [24] FLÜGGE T, ATT W, METZGER M, et al. Precision of Dental Implant Digitization Using Intraoral Scanners. Int J Prosthodont. 2016;29(3):277-283. [25] LEE J, PARK J, KIM S, et al. An assessment of template-guided implant surgery in terms of accuracy and related factors. J Adv Prosthodont. 2013;5(4):440. [26] SCHNEIDER D, SCHOBER F, GROHMANN P, et al. In-vitro evaluation of the tolerance of surgical instruments in templates for computer-assisted guided implantology produced by 3-D printing. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015;26(3):320-325. [27] BEHNEKE A, BURWINKEL M, BEHNEKE N. Factors influencing transfer accuracy of cone beam CT-derived template-based implant placement. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012;23(4):416-423. [28] MULLER P, ENDER A, JODA T, et al. Impact of digital intraoral scan strategies on the impression accuracy using the TRIOS Pod scanner. Quintessence Int. 2016;47(4):343-349. [29] EL KHOLY K, JANNER S FM, SCHIMMEL M, et al. The influence of guided sleeve height, drilling distance, and drilling key length on the accuracy of static Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2019;21(1):101-107. [30] RUNGCHARASSAENG K, CARUSO JM, KAN JYK, et al. Accuracy of computer-guided surgery: A comparison of operator experience. J Prosthet Dent. 2015;114(3):407-413. [31] 王庆福,何正娣,于海洋,等.套筒高度和种植体长度对静态导板精度影响的研究[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2020,55(11):902-907. [32] RAICO GALLARDO YN, DA SILVA-OLIVIO IRT, MUKAI E, et al. Accuracy comparison of guided surgery for dental implants according to the tissue of support: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2017;28(5):602-612. [33] GENG W, LIU C, SU Y, et al. Accuracy of different types of computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing surgical guides for dental implant placement. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(6):8442-8449. [34] POZZI A, POLIZZI G, MOY PK. Guided surgery with tooth-supported templates for single missing teeth: A critical review. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2016;9 Suppl 1:S135-S153. [35] TANG W, LIU Q, ZENG X, et al. Accuracy of half-way mucosa-supported implant guides for edentulous jaws: a retrospective study with a median follow-up of 2 years. J Int Med Res. 2021;49(3):1221799291. [36] EL KHOLY K, LAZARIN R, JANNER SFM, et al. Influence of surgical guide support and implant site location on accuracy of static Computer‐Assisted Implant Surgery. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2019;30(11):1067-1075. |
| [1] | Sun Lianlian, Liu Yongchao, Wang Zhixing. Repair effects of two kinds of bone repair materials on rabbit femoral defects compared using synchrotron-radiation-based micro-computed tomography [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(21): 3343-3348. |
| [2] | Liang Hanying, Ma Yunhao, Li Han, Li Dongyang, Zhong Weijian, Ma Guowu. Osteogenic effects of partially demineralized autogenous dentin particles in implant site preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(16): 2488-2492. |
| [3] | Zhang Shengmin, Cao Changhong, Wang Ningning, Wang Jing, Li Zhangyi. Desferrioxamine-loaded polylactic-co-glycolic acid/hydroxyapatite composite scaffold: vascularization and osteogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(34): 5413-5418. |
| [4] | Wang Jinsi, Wang Shengfa, Wu Zhuguo, He Xiaoling, Wang Xinyu, Luo Xiaoyu, Zhao Yi, Zhang Jingying. Design and biological activity of beta-tricalcium phosphate biomimetic bone scaffold based on triply periodic minimal surfaces [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(21): 3291-3297. |
| [5] | Qu Yan, Li Jieyin, Zhuang Xiumei, Ye Jiantao, Ye Xiuhua. Heating palladium-silver alloys under various reduced air pressures and ceramic bond strength [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2526-2531. |
| [6] | Li Yuan, Song Liang, Zhang Jianguo, Hu Fengling. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of stress distributions in osteoporosis and normal mandibular dental implant-supported overdentures with flat-type and cushion-type magnetic attachments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2540-2544. |
| [7] | Gu Yueguang, Shen Jianhuan, Ni Jieli, Guo Shuyu, Yan Zhongyi, Zhang Yang. Effect of osteogenesis in patients with alveolar cleft after bone grafting investigated by volume analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1501-1504. |
| [8] | Liu Keke, Duan Xin, Ma Xiangrui, Zhang Yuntao. Effect of cinnamaldehyde on osteoblasts in high glucose environment with the electrospinning membrane as a carrier [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3500-3504. |
| [9] | Bi Qingwei, Liu Chengpu, Li Yan, Zhao Wenwen, Han Mei. Structure analysis of platelet-rich fibrin derived from two centrifugation procedures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3534-3539. |
| [10] | Zhang Shengmin, Cao Changhong, Liu Chao. Adipose-derived stem cells integrated with concentrated growth factors prevent bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws in SD rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2982-2987. |
| [11] | Wang Hongyuan, Wang Wei, Yang Shuqing, Dou Lixin, Liu Lijun. Preparation and properties of porous nitrogen oxygen bioglass scaffold for bone repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2521-2527. |
| [12] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [13] | Dong Wenjie, Zhang Shiyang, Zhao Lei, Wang Yukun. Icariin deproteinized inorganic bovine bone composite and deproteinized inorganic bovine bone material in repairing mandibular defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5467-5472. |
| [14] | Zhao Delu, Tie Chaorong, Yang Sisi, Sun Zhen, Wang Xin, Zhu Huaian, Yin Miao. Preparation and characterization of sodium methacrylate modified photocrosslinked alginate hydrogel scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(22): 3445-3451. |
| [15] | Cheng Yang, Liu Min, Zhu Zhongyan, Gao Shasha. Comparative analysis of hydroxyapatite, β-tricalcium phosphate, and carbonated hydroxyapatite alginate dental pulp replacement materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(30): 4804-4810. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||