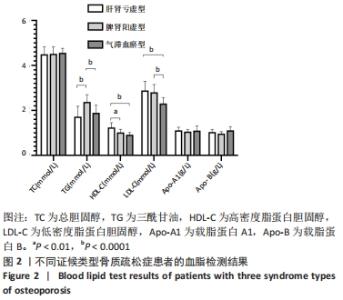
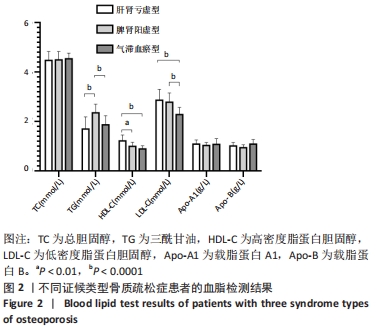
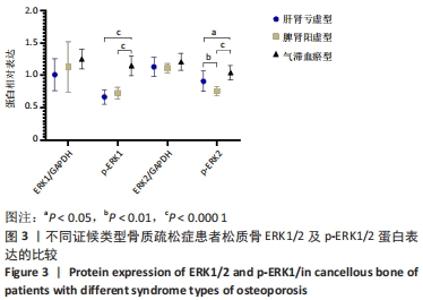
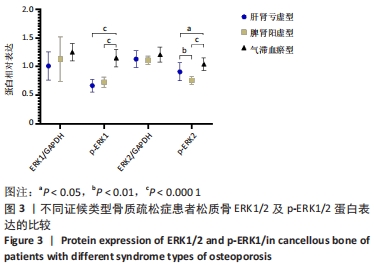
[1] LANE JM, RUSSELL L, KHAN SN. Osteoporosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000; (372):139-150.
[2] 彭方亮,于洪涛,邵辉,等.骨质疏松骨折史和合并症对健康相关生活质量的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(11):1585-1588.
[3] 朱佩佩,曹玉霖,刘勇,等.骨质疏松性骨折与再骨折风险评估的研究进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2019,21(11):1005-1008.
[4] 夏维波,章振林,林华,等.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2017)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(3):281-309.
[5] ZHANG M, BAI L, KANG J, et al. Links between arterial stiffness and bone mineral density in middle-aged and elderly Chinese individuals: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2019;9(8):e029946.
[6] PIERCE JL, BEGUN DL, WESTENDORF JJ, et al. Defining osteoblast and adipocyte lineages in the bone marrow. Bone. 2019;118:2-7.
[7] ZHANG Y, GU X, LI D, et al. METTL3 Regulates Osteoblast Differentiation and Inflammatory Response via Smad Signaling and MAPK Signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;21(1):199.
[8] ANAGNOSTIS P, GKEKAS NK, POTOUPNIS M, et al. New therapeutic targets for osteoporosis. Maturitas. 2019;120:1-6.
[9] ZHOU Y, DENG T, ZHANG H, et al. Hypercholesterolaemia increases the risk of high‑turnover osteoporosis in men. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(6): 4603-4612.
[10] TIAN L, YU X. Lipid metabolism disorders and bone dysfunction-interrelated and mutually regulated (review). Mol Med Rep. 2015; 12(1):783-794.
[11] 尹恒,苏秋菊,王建伟,等.骨质疏松症中医证型现代化研究思路探索[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(3):454-457.
[12] 刘庆思.实用骨质疏松症防治指南[M].广州:广州出版社,2001.
[13] 李建国,谢兴文,黄晋,等.基于中医体质学说探讨中医药防治骨质疏松症的作用及现状[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(11):1623-1626.
[14] 申浩,蒋红岩,章轶立,等.骨质疏松症患者中医证候与骨代谢标志物相关性研究[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2021,27(6):970-972,1046.
[15] 孙继高,傅繁誉,王荣田,等.基于德尔菲法的骨质疏松高风险人群中医症状辨识研究[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2021,27(5):792-795.
[16] 李月.骨质疏松症中医证型分布规律、脾肾阳虚型骨质疏松症与相关代谢指标关系探讨[D].天津:天津中医药大学, 2020.
[17] 曾昭洋,胡文斌,魏学玲,等.中老年人群原发性骨质疏松中医体质及辨证分型分布[J].中国老年学杂志,2018,38(2):435-438.
[18] 温经渊,曾晗冰,吴连国.骨质疏松症中医辨证分型研究进展[J].安徽中医药大学学报,2021,40(5):101-104.
[19] 徐东江,王克迪,吴俊.补体及脂代谢水平与老年人群骨密度的相关性分析[J].中华检验医学杂志,2019,42(12):1020-1024.
[20] 张雪竹,彭应梅,于建春,等.老年性骨质疏松症:一种年龄相关的脂代谢障碍疾病[J].国际内分泌代谢杂志,2007,27(5):348-351.
[21] 李平,林煜,朱曦,等.补肾健脾方影响高脂肪饮食骨质疏松模型大鼠代谢及瘦素的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(3):470-475.
[22] 黄磊涛,吴霞,赖琦,等.脂联素通过调控骨代谢在骨质疏松症中的研究与进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(12):1944-1949.
[23] 王磊,李兴.脂联素影响骨代谢致骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].现代药物与临床,2011,26(6):426-429.
[24] ZHONG L, YAO L, TOWER RJ, et al. Single cell transcriptomics identifies a unique adipose lineage cell population that regulates bone marrow environment. Elife. 2020;9:e54695.
[25] 胡松华,王乾兴,路建,等.骨质疏松病理微环境对骨髓间充质干细胞生物学特性的影响[J].遵义医科大学学报,2020,43(1):13-20.
[26] Park-Min KH. Metabolic reprogramming in osteoclasts. Semin Immunopathol. 2019;41(5):565-572.
[27] 沈云玲,魏静,徐小宇.阿仑膦酸钠通过调控NF-κB和MAPK信号通路改善大鼠骨质疏松的发展[J].实用药物与临床,2020,23(5): 391-395.
[28] LU N, MALEMUD CJ. Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase: A Regulator of Cell Growth, Inflammation, Chondrocyte and Bone Cell Receptor-Mediated Gene Expression. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(15):3792.
[29] BERTI DA, SEGER R. The Nuclear Translocation of ERK. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1487:175-194.
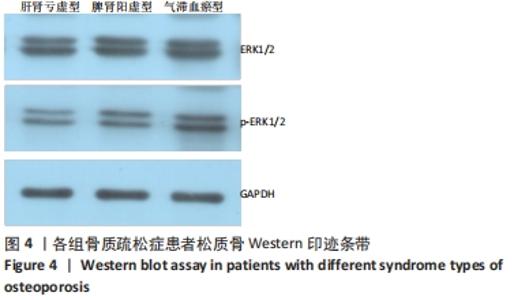
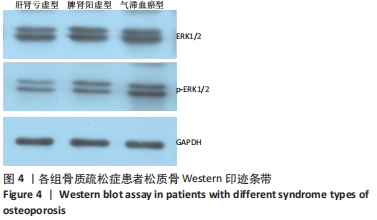
[30] 章建华,邢婧,范连霞,等.骨质疏松肾阳虚、肾阴虚证型下右归丸含药血清对大鼠成骨细胞ERK1/2、Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2018,33(7):3018-3022.
[31] 章建华,邢婧,范连霞,等.骨质疏松肾阳虚和肾阴虚证型下左归丸含药血清干预成骨细胞ERK1/2,Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路的研究[J].中国中药杂志,2017,42(20):3983-3989.
[32] YANG X, YANG Y, ZHOU S, et al. Puerarin Stimulates Osteogenic Differentiation and Bone Formation Through the ERK1/2 and p38-MAPK Signaling Pathways. Curr Mol Med. 2018;17(7):488-496.
[33] 赵继荣,杨涛,赵宁,等.杜仲诱导骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化防治骨质疏松症相关信号通路研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020, 26(12):1868-1872.
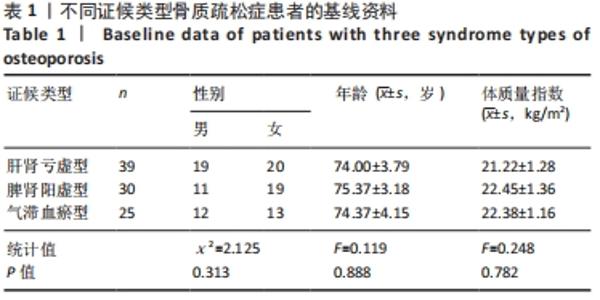
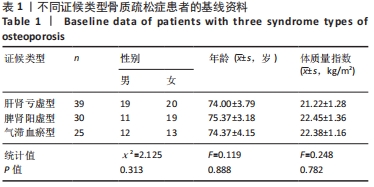
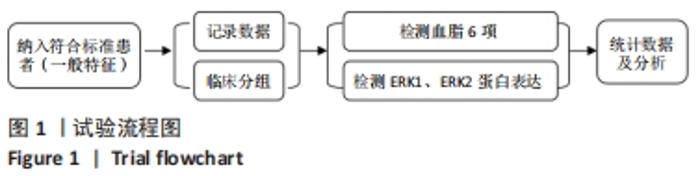
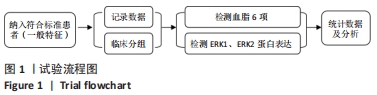
|