Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (20): 3250-3255.doi: 10.12307/2022.629
Previous Articles Next Articles
N6-methyladenosine methylation and its regulation in metabolic diseases
Chen Ziyang1, Pu Rui1, Deng Shuang2, Liu Min2
- 1College of Education and Sports Sciences, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China; 2Institute of Health, Tianhua College of Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai 201815, China
-
Received:2021-09-15Accepted:2021-10-10Online:2022-07-18Published:2022-01-20 -
Contact:Liu Min, Master, Lecturer, Institute of Health, Tianhua College of Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai 201815, China -
About author:Chen Ziyang, Master, Assistant, College of Education and Sports Sciences, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China Pu Rui, Master, Assistant, College of Education and Sports Sciences, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China Chen Ziyang and Pu Rui contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:Domestic Visiting Scholar Program for Young Key Teachers of Colleges and Universities in Shanghai, No. Z20005.20.006 (to LM); 2021 Shanghai Higher Education Teachers Research Project-Shanghai Tongji Hospital (to DS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Liu Min. N6-methyladenosine methylation and its regulation in metabolic diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(20): 3250-3255.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
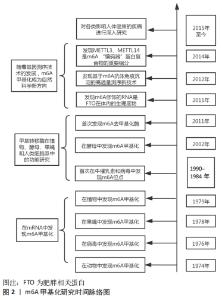
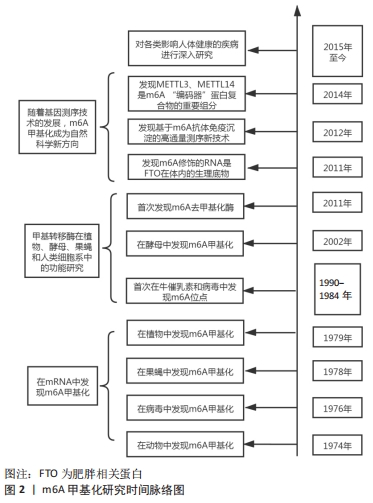
m6A甲基化修饰位点主要聚集在终止密码子和3’非翻译区,在转录后水平上调节RNA代谢,包括mRNA加工,mRNA从细胞核输送到细胞质,mRNA翻译,mRNA衰变以及长非编码RNA和microRNA的生物发生[7]。m6A修饰的生物学效应主要涉及m6A甲基化酶、m6A去甲基化酶和甲基化阅读蛋白这三类蛋白[8]。 2.1.1 m6A甲基化转移酶 m6A修饰通过m6A甲基转移酶复合物催化,由甲基转移酶样3(methyltransferase-like 3,METTL3)、甲基转移酶样14(methyltransferase-like 14,METTL14)和Wilms肿瘤1结合蛋白等蛋白共同组成m6A甲基转移酶复合物[8]。METTL3与METTL14共定位于核斑点并形成稳定的异二聚体,从而协同增加甲基化能力。此外,m6A甲基转移酶复合物还包括甲基转移酶样16、如病毒样m6A甲基转移酶相关蛋白、CCCH型锌指蛋白13以及RNA结合基序蛋白15/15B,对复合物的稳定性和m6A甲基化起关键的调节作用[9-10]。 2.1.2 m6A去甲基化酶 m6A去甲基化酶主要由肥胖相关蛋白(fat mass and obesity-associated protein,FTO)和Alk B同源蛋白5组成,FTO和Alk B同源蛋白5具有不同的细胞内定位和组织分布,并选择性的分布在核斑点中,赋予去甲基化酶活性[11]。FTO与Alk B同源蛋白5介导去甲基化过程中均涉及不同细胞环境中的m6A修饰,Alk B同源蛋白5过表达也能抑制mRNA和miRNA中的m6A修饰[12]。 2.1.3 m6A甲基化阅读蛋白 甲基化阅读蛋白主要由YT521-B同源结构域蛋白(细胞质中的YTHDF1-3,YTHDC2、细胞核中的YTHDC1)、异质核糖核蛋白家族成员以及胰岛素样生长因子2 mRNA结合蛋白组成[8,13]。m6A甲基化酶、m6A去甲基化酶和甲基化阅读蛋白的调节是m6A介导基因调控的基础,三者共同调节m6A甲基化的动态及可逆过程以发挥其生物效应。 2.2 m6A甲基化在代谢性疾病中的调控作用"
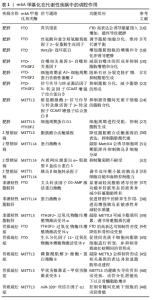
2.2.1 m6A甲基化与肥胖症 肥胖是由环境、遗传和内分泌等因素引起的慢性代谢疾病,肥胖增加了糖尿病、心血管疾病、骨骼肌疾病和癌症等并发症的风险,同时当前全球肥胖大流行也是导致代谢性疾病急剧上升的主要原因[14]。先前研究已阐明转录和表观遗传在脂肪发生过程中的重要作用,但对转录后调控脂肪生成与脂质代谢的机制尚未阐明[15]。 m6A去甲基化酶FTO的生物多样性与肥胖关系密切,可通过调节胃饥饿素、促脂肪生成因子、过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体等蛋白的表达,调控脂肪细胞分化和脂肪生成,从而影响肥胖的发生发展。KARRA等[16]发现FTO通过调节胃饥饿素及相关等位基因上调生长素表达,从而诱导能量摄入增加,最终导致肥胖。此外,FTO通过调节丝氨酸和富含精氨酸剪接因子2剪接位点周围m6A水平来控制促脂肪生成因子的表达,从而调节脂肪细胞分化[17]。这一研究提示,依赖FTO的m6A脱甲基化作用是RNA加工的新型调节机制,并且在脂肪形成的调节中发挥关键作用。另有研究发现,m6A去甲基化酶FTO可增加脂肪细胞的增殖和分化并诱导肥胖,其机制可能是FTO通过增强过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ和CAAT区/增强子结合蛋白的表达,并抑制Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号通路促进脂肪生成有关[18]。另有研究发现,AMP激活蛋白激酶可正向调节m6A甲基化水平,负向调节C2C12细胞的脂质积累。在分子水平上,AMP激活蛋白激酶通过调节FTO的表达和依赖FTO的m6A去甲基化来调节骨骼肌细胞的脂质积累[19],提示AMP激活蛋白激酶调节骨骼肌细胞脂质代谢提供了一种新的机制。而烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸可增强FTO活性,调控m6A甲基化,进而影响脂肪前体细胞的脂肪生产[20]。上述研究提示,FTO可通过多种途径促进脂肪生成,从而导致肥胖的发生。 m6A修饰相关的酶在调节脂质代谢和脂肪稳态中发挥不同生物效应,上述研究已说明FTO促进脂肪生成,而FTO基因的缺失可抑制脂肪细胞分化和脂肪生成。m6A脱甲基化酶FTO的抑制会降低自噬相关基因5和自噬相关基因7的表达,同时YTHDF2促进mRNA降解和减少蛋白质表达,导致自噬体形成的减弱,从而抑制自噬和脂肪形成[21]。m6A-YTHDF2信号通路可能对肥胖的发生至关重要。WU等[22]发现在脂肪细胞分化早期阶段,表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯可抑制FTO,同时上调YTHDF2,并促进YTHDF2识别和降解甲基化mRNA,进一步抑制细胞周期素A2和细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶2蛋白表达,阻断有丝分裂克隆扩增以抑制脂肪生成,从而预防肥胖的发生。此外,脂肪细胞中m6A去甲基化酶FTO的缺失抑制细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶2的表达和信号传导与转录激活因子3的磷酸化,并抑制转录因子CCAAT增强子结合蛋白β,从而减少脂肪的形成。而m6A阅读蛋白YTHDF2可直接靶向抑制酪氨酸激酶2,致信号传导与转录激活因子3/转录因子CCAAT增强子结合蛋白β信号通路失活,从而抑制脂肪的生成[23]。上述研究表明,FTO基因的缺失可通过不同信号通路抑制脂肪细胞分化和脂肪生成,从而延缓肥胖的发生。 与FTO相反,m6A甲基化酶METTL3、METTL14和WATP的高表达可通过促进脂肪形成中有丝分裂克隆扩增中的细胞周期转变,从而积极调解脂肪形成,减缓肥胖的发生,但其机制尚未阐明[24]。METTL3通过以m6A-YTHDF2依赖性方式靶向调节酪氨酸激酶1/信号传导与转录激活因子5/转录因子CCAAT增强子结合蛋白β信号通路来抑制猪骨髓间充质干细胞的脂肪分化[25]。转录因子锌指蛋白217是一个具有保守锌指结构的转录因子,在脂肪细胞的分化中发挥重要作用。SONG等[26]首次发现转录因子锌指蛋白217以依赖于m6A-YTHDF2的方式促进脂肪生成。而敲除转录因子锌指蛋白217可增加m6A甲基转移酶METTL3的表达,从而上调细胞周期蛋白D1(cyclinD1,CCND1)mRNA的m6A水平,促进YTHDF2识别并降解CCND1甲基化的mRNA,导致细胞周期进程受阻,脂肪生成受到抑制[27]。由此可见,上述研究也为m6A甲基化参与转录因子锌指蛋白217脂肪形成调控的潜在分子机制提供了新的见解。 综上所述,m6A去甲基化酶FTO通过多种信号通路调控脂肪生成和脂肪细胞的增殖分化。此外,m6A甲基化转移酶可通过抑制自噬体形成、阻断有丝分裂克隆扩增、制间充质干细胞的脂肪分化等进程,从而抑制脂肪生成,减缓肥胖的发生与进一步发展。但现阶段关于m6A甲基化阅读蛋白与肥胖的报道较少,还需以不同类型的酶为视角进行更深层次研究。 2.2.2 m6A甲基化与2型糖尿病 2型糖尿病是由环境和遗传等多种因素引起外周组织胰岛素抵抗和胰岛素分泌缺陷,使机体胰岛素相对不足和葡萄糖摄取利用减少,而导致的常见慢性疾病[28]。新进的研究表明,m6A甲基化与2型糖尿病关系密切,并在其调节中发挥关键作用。 FTO作为m6A去甲基化酶广泛参与2型糖尿病的发生发展。在2型糖尿病患者中,高脂饮食增强FTO表达而导致m6A甲基化表达减少,并促进与脂质代谢相关的叉头转录因子O1、葡萄糖催化酶6和二酰甘油酰基转移酶2的基因表达,从而使2型糖尿病患者血清葡萄糖水平显著升高,进一步加剧2型糖尿病病理进程[29]。 诸多研究已证实2型糖尿病的发病和进展与胰岛β细胞数量有关,而m6A甲基化酶METTL3和METTL14可通过调节胰岛β细胞数量和功能从而参与2型糖尿病的进程。最新研究发现,METTL3沉默降低了m6A甲基化和脂肪酸合成酶基因的水平,从而抑制脂肪酸代谢。此外,腺相关病毒介导的脂肪酸合成酶基因在METTL3基因敲除小鼠中高表达抑制了胰岛素敏感性的改善和脂肪酸合成的降低,说明METTL3通过脂肪酸合成酶基因的m6A甲基化抑制肝脏胰岛素敏感性,并促进脂肪酸代谢,最终导致2型糖尿病的发展[30]。这一研究强调了m6A甲基化酶METTL3可调节胰岛β功能和脂质代谢在2型糖尿病的重要性。m6A甲基化酶METTL14对胰岛β细胞存活、和胰岛素分泌也至关重要。DE JESUS等[31]发现2型糖尿病患者胰岛β细胞在Mettl14敲除小鼠中表达降低,诱导细胞周期阻滞,并通过降低蛋白激酶B磷酸化和胰腺十二指肠同源盒1水平抑制胰岛β细胞分泌,从而导致2型糖尿病的早期发生发展。此外,在成年小鼠β细胞中METTL14的缺失抑制内质网应激蛋白α-剪接型X盒结合蛋白1信号表达,从而抑制葡萄糖不耐受[32]。新近研究发现,METTL3/14对于β细胞分化至关重要,通过调节mRNA稳定性直接参与胰岛β细胞转录因子的表达,从而调节成年期小鼠的胰岛β细胞功能和血糖控制能力[33]。 上述研究揭示了m6A甲基化酶METTL3和METTL14通过调节血糖稳态、胰岛素敏感性以及胰岛β细胞存活和功能,从而抑制葡萄糖不耐受和2型糖尿病的发展,并为维持2型糖尿病患者β细胞存活和功能提供理论依据。 2.2.3 m6A甲基化与非酒精性脂肪肝 非酒精性脂肪肝是当前人类最常见的肝脏代谢综合征,是由脂肪生成、脂肪酸氧化摄取、三酰甘油分解的代谢失调以及线粒体功能障碍等多种因素引起,包括简单脂肪变性到非酒精性脂肪性肝炎,严重可发展为肝硬化并导致肝癌[34]。 先前的研究发现,m6A及相关酶的变化与非酒精性脂肪肝的发展高度相关。FTO下调m6A水平,降低线粒体含量,增加三酰甘油沉积,促进脂肪肝脏的积累,加剧非酒精性脂肪肝进程[35],表明FTO可调节肝细胞内m6A水平从而影响线粒体含量和脂肪代谢。ZHANG等[36]在非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠模型中发现,FTO mRNA和蛋白水平显著上升,且FTO水平与丙二醛和超氧化物歧化酶浓度呈正相关,肝脏中FTO水平升高与氧化应激和脂质沉积有关。FTO可增强非酒精性脂肪肝中的氧化应激和脂肪生成,而叉头转录因子O1是参与非酒精性脂肪肝的另一个重要基因。CHEN等[37]在非酒精性脂肪肝动物模型中发现,高脂饮食上调了FTO的表达和叉头转录因子O1磷酸化水平,导致AMP激活蛋白激酶磷酸化水平降低,从而显著减轻高脂肪诱导的肝功能和肝脏形态的损害并减少肝脏脂肪堆积,表明FTO和叉头转录因子O1的相互作用与非酒精性脂肪肝发病关系密切。高脂喂养小鼠中,METTL14可通过蛋白激酶B信号促进肝脏中的糖异生作用,进而增强胰岛素敏感性并减轻体质量[38]。此外,METTL3的敲除可增加YTHDF2与过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体α的结合,促进其稳定性并增加表达,从而减少脂质积累,调节肝脏脂质代谢[39]。由此可见,m6A甲基化修饰中的FTO、METTL3、METTL14和YTHDF2通过不同信号从而参与非酒精性脂肪肝发生发展。 甜菜碱作为一种重要的甲基供体,可调节脂肪代谢,减少肝脏脂肪的沉积,可有效抑制非酒精性脂肪肝。在青春期补充甜菜碱可以通过减少新生小鼠脂肪形成并增加脂解作用来保护小鼠免受高脂诱导的非酒精性脂肪肝损伤,其机制可能与甜菜碱通过抑制FTO表达,下调乙酰辅酶羧化酶基因和脂肪酸合成酶基因并上调激素敏感性脂肪酶和脂肪三酰甘油脂肪酶表达有关[40]。同时在非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠模型中,抑制受损的脂肪组织甲基化状态和脂肪分解过程有助于甜菜碱的肝保护作用[41]。另有研究发现,磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路的激活可能通过抑制FTO介导的肝脏细胞再生,从而延缓非酒精性脂肪肝的进程[42]。 上述研究提示,FTO可能是改善非酒精性脂肪肝病变的一个有利治疗靶点。但现阶段的研究表明,m6A甲基化与非酒精性脂肪肝间的联系仅局限于FTO,并未涉及到其它m6A甲基化酶。因此,未来的研究需要以m6A甲基化其它酶为新型靶点,从而为非酒精性脂肪肝的前期诊断和后期治疗提供理论基础。 2.2.4 m6A甲基化与骨质疏松症 骨质疏松症是一种以低骨量和骨组织微结构破坏为特征,导致骨质脆性增加和易于骨折的代谢性疾病[43]。先前的研究已证明,m6A甲基化在骨质疏松症的调控中发挥关键作用,但其具体机制仍不清楚。现阶段,m6A去甲基化酶FTO和甲基化转移酶METTL3已成为了防治骨质疏松症的突破口。 近日,有学者对骨质疏松症和骨坏死患者的差异基因信号进行了系统分析测序以鉴定成骨过程中潜在的调节基因,发现一个主要的m6A去甲基化酶FTO在骨质疏松症和骨坏死患者中显著下调。在人骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化过程中,FTO显著上调;此外,FTO的耗竭和FTO抑制剂FB23或FB23-2的应用都在一定程度上损害了人骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化;敲除小鼠体内的FTO导致骨密度降低和骨形成受损;进一步研究发现,FTO介导的m6A-过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体mRNA 3’UTR去甲基化以YTHDF1依赖的方式降低过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体mRNA的稳定性,过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体的过表达减轻了FTO介导的骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,而过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体的敲除促进了FTO诱导的成骨细胞生物标志物在成骨分化过程中的表达[44]。此外,FTO通过生长分化因子11-FTO-过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ轴调节骨质疏松症期间骨髓间充质干细胞的命运,促使间充质干细胞向脂肪细胞进行转变,并抑制骨质疏松症期间的骨形成[45]。上述2项研究表明,FTO-过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体信号轴在促进人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨中的功能中具有重要意义,FTO也可通过生长分化因子11-FTO-过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ轴调节骨形成。 除FTO外,m6A甲基化转移酶METTL3也在调控骨形成及其潜能中发挥重要作用。WU等[46]通过对小鼠进行条件性敲除METTL3基因发现,METTL3功能缺失导致骨形成受损,成骨分化潜能低下,骨髓脂肪增多。此外,骨髓间充质干细胞中Mettl3的过表达可保护小鼠免受雌激素缺乏引起的骨质疏松症并增强骨骼肌健康。进一步研究发现,甲状旁腺激素/甲状旁腺激素受体-1信号轴是间充质干细胞中受m6A调控的重要下游通路有关,其机制可能与通过敲除骨髓间充质干细胞中的METTL3,从而降低了间充质干细胞谱系分配器的翻译效率,并干扰了甲状旁腺激素诱导的体内成骨和脂肪反应。 核结合因子α1 是新发现的一类调控间充质干细胞向成骨方向分化的特异性转录因子,对骨形成、骨骼生长和发育起着重要作用[47]。另有研究表明,m6A 甲基化转移酶METTL3通过调节miR-320/核结合因子α1信号通路控制骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨潜能,并证明了METTL3的异常下调可能是患者和小鼠骨质疏松症的潜在机制之一[48]。此外,CHEN等[45]骨髓干细胞中METTL3的条件性敲除可抑制磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶-蛋白激酶B信号通路的传导,抑制骨形成相关基因和血管内皮生长因子的表达,并下调甲状旁腺激素受体1 mRNA的翻译效率。同时,敲除METTL3显著加速脂肪形成进程和酪氨酸激酶2蛋白表达。上述2项研究共同表明,METTL3与骨形成和成骨分化潜能关系密切,揭示了m6A表观遗传修饰调控与代谢相关的骨骼健康和疾病的新机制。 综上所述,FTO与METTL3在防治骨质疏松症中发挥着关键作用,并提示FTO可通过调节相关信号通路进而调控骨髓间充质干细胞的骨形成和成骨分化。此外,METTL3表达与骨髓间充质干细胞脂肪生成呈负相关,与成骨成正相关,并提示METTL3过表达可能是治疗人类骨质疏松症的一种新型替代疗法。也为进一步理解m6A 与骨质疏松症之间的联系提供了新的线索。 m6A甲基化在代谢性疾病中的调控作用总结,见表1。"


2.3 m6A甲基化可作为代谢性疾病的生物标记物 新型生物标记物的发掘可为代谢性疾病的预防和诊断提供更多的靶向治疗选择。m6A甲基化可通过各种信号通路参与癌症、心血管等疾病的发生发展,也可作为生物标记物为其诊断提供更多的选择。新进的研究表明,m6A广泛参与代谢性疾病的发生发展,并可作为生物标记物在各类代谢类疾病的诊断中发挥关键作用。 先前的研究已证明,FTO作为一种m6A去甲基化酶与成年人和儿童的早期肥胖密切相关,FTO的过表达增加小鼠脂肪积累并诱导肥胖的发生,而敲除FTO可减少小鼠体内脂肪量,从而降低肥胖发生率,提示FTO失活可预防肥胖的发生[49-50]。ZHAO等[17]在脂肪形成过程中发现,FTO表达与m6A水平成反比,且FTO耗尽会阻止脂肪细胞分化,只有具有催化活性的FTO才能恢复脂肪形成,提示FTO的高表达可促进脂肪细胞的分化。此外,FTO的抑制可降低2型糖尿病患者血清葡萄糖水平,从而延缓2型糖尿病的病理进程[29]。MASOUD等[51]研究发现,FTO基因表达和FTO蛋白水平在患有肥胖和2型糖尿病更严重人群中进一步显著增加,并提示FTO基因表达和FTO蛋白水平与肥胖、胰岛素抵抗和血糖指数以及糖尿病并发症的存在呈正相关。由此可见,m6A甲基化酶FTO与代谢性疾病的发生发展关系密切,可能成为诊断脂肪代谢、脂质分化等进程的有效指标。 除m6A甲基化酶FTO外,m6A甲基化酶METTL3、METTL14也可作为2型糖尿病新的潜在生物标记物。在糖尿病模型小鼠和2型糖尿病患者血清中均观察到β细胞中METTL3和METTL14表达的下降[25]。此外,敲除METTL3和METTL14可促进脂肪细胞的分化,并抑制β细胞分泌,进而导致代谢性疾病的进一步发展[30-31]。由此可见,代谢性疾病患病风险与m6A甲基化酶METTL3/14呈负相关,但METTL3和METTL14的变化在代谢性疾病中的时效性有待进一步研究。 综上所述,m6A甲基化酶FTO、及相关酶与代谢性疾病发生发展关系密切,可作为其诊断的生物标记物。同时,m6A甲基化水平的变化在也反映了代谢性疾病的发展进程,突出了m6A在代谢性疾病诊断中的潜力。但现阶段的研究仅局限于m6A甲基化酶中,尚未见m6A去甲基化酶和阅读蛋白的系统性描述。因此,需要进一步探讨m6A甲基化各种蛋白在代谢性疾病中的诊断作用。"

| [1] WATANABE J, KOTANI K. Metabolic Syndrome for Cardiovascular Disease Morbidity and Mortality Among General Japanese People: A Mini Review. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2020;17(16):149-155. [2] BEYER JN, RANISZEWSKI NR, BURSLEM GM. Advances and Opportunities in Epigenetic Chemical Biology. Chembiochem. 2021;22(1):17-42. [3] KADUMURI RV, JANGA SC. Epitranscriptomic Code and Its Alterations in Human Disease. Trends Mol Med. 2018;24(10):886-903. [4] ALARCÓN CR, LEE H, GOODARZI H, et al. N6-methyladenosine marks primary microRNAs for processing. Nature. 2015;519(7544):482-495. [5] ERSON-BENSAN AE, BEGIK O. m6A Modification and Implications for microRNAs. Microrna. 2017;6(2):97-101. [6] DESROSIERS R, FRIDERICI K, ROTTMAN F. Identification of methylated nucleosides in messenger RNA from Novikoff hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974; 71(10):3971-3985. [7] BERULAVA T, BUCHHOLZ E, ELERDASHVILI V, et al. Changes in m6A RNA methylation contribute to heart failure progression by modulating translation. Eur J Heart Fail. 2020;22(1):54-66. [8] ZACCARA S, RIES RJ, JAFFREY SR. Reading, writing and erasing mRNA methylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(10):608-624. [9] AOYAMA T, YAMASHITA S, TOMITA K. Mechanistic insights into m6A modification of U6 snRNA by human METTL16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48(9):5157-5168. [10] KNUCKLES P, LENCE T, HAUSSMANN IU, et al. Zc3h13/Flacc is required for adenosine methylation by bridging the mRNA-binding factor Rbm15/Spenito to the m6A machinery component Wtap/Fl(2)d. Genes Dev. 2018;32(5-6):415-429. [11] MELSTROM L, CHEN J. RNA N6-methyladenosine modification in solid tumors: new therapeutic frontiers. Cancer Gene Ther. 2020;27(9):625-633. [12] TANG C, KLUKOVICH R, PENG H, et al. ALKBH5-dependent m6A demethylation controls splicing and stability of long 3’-UTR mRNAs in male germ cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018;115(2):E325-E333. [13] REICHEL M, KÖSTER T, STAIGER D. Marking RNA: m6A writers, readers, and functions in Arabidopsis. J Mol Cell Biol. 2019;11(10):899-910. [14] SALTIEL AR, OLEFSKY JM. Inflammatory mechanisms linking obesity and metabolic disease. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(1):1-4. [15] PHANG M, ROSS J, RAYTHATHA JH, et al. Epigenetic aging in newborns: role of maternal diet. Am J Clin Nutr. 2020;111(3):555-561. [16] KARRA E, O’DALY OG, CHOUDHURY AI, et al. A link between FTO, ghrelin, and impaired brain food-cue responsivity. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(8):3539-3551. [17] ZHAO X, YANG Y, SUN BF, et al. FTO-dependent demethylation of N6-methyladenosine regulates mRNA splicing and is required for adipogenesis. Cell Res. 2014;24(12):1403-1419. [18] CHEN X, LUO Y, JIA G, et al. FTO Promotes Adipogenesis through Inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Pathway in Porcine Intramuscular Preadipocytes. Anim Biotechnol. 2017;28(4):268-274. [19] WU W, FENG J, JIANG D, et al. AMPK regulates lipid accumulation in skeletal muscle cells through FTO-dependent demethylation of N6-methyladenosine. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):406-416. [20] WANG L, SONG C, WANG N, et al. NADP modulates RNA m6A methylation and adipogenesis via enhancing FTO activity. Nat Chem Biol. 2020;16(12):1394-1402. [21] WANG X, WU R, LIU Y, et al. m6A mRNA methylation controls autophagy and adipogenesis by targeting Atg5 and Atg7. Autophagy. 2020;16(7):1221-1235. [22] WU R, YAO Y, JIANG Q, et al. Epigallocatechin gallate targets FTO and inhibits adipogenesis in an mRNA m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. Int J Obes (Lond). 2018;42(7):1378-1388. [23] WU R, GUO G, BI Z, et al. m6A methylation modulates adipogenesis through JAK2-STAT3-C/EBPβ signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2019; 1862(8):796-806. [24] WANG X, ZHU L, CHEN J, et al. mRNA m⁶A methylation downregulates adipogenesis in porcine adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;459(2): 201-207. [25] YAO Y, BI Z, WU R, et al. METTL3 inhibits BMSC adipogenic differentiation by targeting the JAK1/STAT5/C/EBPβ pathway via an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. FASEB J. 2019;33(6):7529-7544. [26] SONG T, YANG Y, WEI H, et al. Zfp217 mediates m6A mRNA methylation to orchestrate transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation to promote adipogenic differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(12):6130-6144. [27] LIU Q, ZHAO Y, WU R, et al. ZFP217 regulates adipogenesis by controlling mitotic clonal expansion in a METTL3-m6A dependent manner. RNA Biol. 2019;16(12): 1785-1793. [28] GENG T, HUANG T. Gene-environment interactions and type 2 diabetes. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2020;29(2):220-226. [29] YANG Y, SHEN F, HUANG W, et al. Glucose Is Involved in the Dynamic Regulation of m6A in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104(3):665-673. [30] XIE W, MA LL, XU YQ, et al. METTL3 inhibits hepatic insulin sensitivity via N6-methyladenosine modification of Fasn mRNA and promoting fatty acid metabolism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;518(1):120-126. [31] DE JESUS DF, ZHANG Z, KAHRAMAN S, et al. m6A mRNA Methylation Regulates Human β-Cell Biology in Physiological States and in Type 2 Diabetes. Nat Metab. 2019;1(8):765-774. [32] MEN L, SUN J, LUO G, et al. Acute Deletion of METTL14 in β-Cells of Adult Mice Results in Glucose Intolerance. Endocrinology. 2019;160(10):2388-2394. [33] WANG Y, SUN J, LIN Z, et al. m6A mRNA Methylation Controls Functional Maturation in Neonatal Murine β-Cells. Diabetes. 2020;69(8):1708-1722. [34] SHIHA G, KORENJAK M, ESKRIDGE W, et al. Redefining fatty liver disease: an international patient perspective. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;6(1):73-79. [35] GUO J, REN W, LI A, et al. Fat mass and obesity-associated gene enhances oxidative stress and lipogenesis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Dis Sci. 2013;58(4):1004-1009. [36] ZHANG J, LI S, LI J, et al. Expression and significance of fat mass and obesity associated gene and forkhead transcription factor O1 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(21):3771-3776. [37] CHEN J, ZHOU X, WU W, et al. FTO-dependent function of N6-methyladenosine is involved in the hepatoprotective effects of betaine on adolescent mice. J Physiol Biochem. 2015;71(3):405-413. [38] LIU J, LUO G, SUN J, et al. METTL14 is essential for β-cell survival and insulin secretion. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019;1865(9):2138-2148. [39] DOU X, XIA Y, CHEN J, et al. Rectification of impaired adipose tissue methylation status and lipolytic response contributes to hepatoprotective effect of betaine in a mouse model of alcoholic liver disease. Br J Pharmacol. 2014;171(17):4073-4086. [40] LI S, WANG X, ZHANG J, et al. Exenatide ameliorates hepatic steatosis and attenuates fat mass and FTO gene expression through PI3K signaling pathway in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2018;51(8):e7299. [41] VESKOVIC M, MLADENOVIC D, MILENKOVIC M, et al. Betaine modulates oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, autophagy, and Akt/mTOR signaling in methionine-choline deficiency-induced fatty liver disease. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;848(1):39-48. [42] PAPATHEODORIDI M, CHOLONGITAS E. Diagnosis of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Current Concepts. Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(38):4574-4586. [43] LANGDAHL BL. Overview of treatment approaches to osteoporosis. Br J Pharmacol. 2021;178(9):1891-1906. [44] CHEN LS, ZHANG M, CHEN P, et al. The m6A demethylase FTO promotes the osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells by downregulating PPARG. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021 Aug 30. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00756-8. [45] CHEN X, HUA W, HUANG X, et al. Regulatory Role of RNA N6-Methyladenosine Modification in Bone Biology and Osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;10:911. [46] WU Y, XIE L, WANG M, et al. Mettl3-mediated m6A RNA methylation regulates the fate of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and osteoporosis. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):4772. [47] YAN G, YUAN Y, HE M, et al. m6A Methylation of Precursor-miR-320/RUNX2 Controls Osteogenic Potential of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;19:421-436. [48] KOMORI T. Molecular Mechanism of Runx2-Dependent Bone Development. Mol Cells. 2020;43(2):168-175. [49] DINA C, MEYRE D, GALLINA S, et al. Variation in FTO contributes to childhood obesity and severe adult obesity. Nat Genet. 2007;39(6):724-726. [50] FISCHER J, KOCH L, EMMERLING C, et al. Inactivation of the Fto gene protects from obesity. Nature. 2019;458(7240):894-898. [51] MASOUD E, KAMAL S, RAGHEB A, et al. Fat mass and obesity-associated gene expression and disease severity in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Steroids. 2021;174: 108897. |
| [1] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [2] | Jiang Huanchang, Zhang Zhaofei, Liang De, Jiang Xiaobing, Yang Xiaodong, Liu Zhixiang. Comparison of advantages between unilateral multidirectional curved and straight vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1407-1411. |
| [3] | Li Wei, Zhu Hanmin, Wang Xin, Gao Xue, Cui Jing, Liu Yuxin, Huang Shuming. Effect of Zuogui Wan on bone morphogenetic protein 2 signaling pathway in ovariectomized osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1173-1179. |
| [4] | Chen Xianghe, Liu Bo, Yang Kang, Lu Pengcheng, Yu Huilin. Treadmill exercise improves the myocardial fibrosis of spontaneous type 2 diabetic mice: an exploration on the functional pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1210-1215. |
| [5] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [6] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [7] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [8] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [9] | Li Guijun, Fang Xiaohui, Kong Weifeng, Yuan Xiaoqing, Jin Rongzhong, Yang Jun. Finite element analysis of the treatment of hallux valgus deformity by microplate combined with super strong suture elastic fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 938-942. |
| [10] | Peng Kun. Improvement of the treatment effect of osteoporotic fractures: research status and strategy analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 980-984. |
| [11] | Fan Jianchao, Xu Paidi, Han Yongli, Wen Caiyuzhu, Zhang Hongxing, Pan Xiaoli. Effects of electroacupuncture at Zusanli acupoint on visceral hypersensitivity in rats with functional dyspepsia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 663-668. |
| [12] | Dong Miaomiao, Lai Han, Li Manling, Xu Xiuhong, Luo Meng, Wang Wenhao, Zhou Guoping. Effect of electroacupuncture on expression of nucleotide binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3/cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 1 in rats with cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 749-755. |
| [13] | Zhao Yuwei, Gao Yuting, Li Zhen, Hao Huiqin . Mechanism of Ermiao San in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 742-748. |
| [14] | Huang Shibo, Xie Hui, Wang Zongpu, Wang Weidan, Qin Kairong, Zhao Dewei. Application of degradable high-purity magnesium screw in the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 493-498. |
| [15] | Shen Song, Xu Bin. Diffuse distribution of bone cement in percutaneous vertebroplasty reduces the incidence of refracture of adjacent vertebral bodies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 499-503. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||