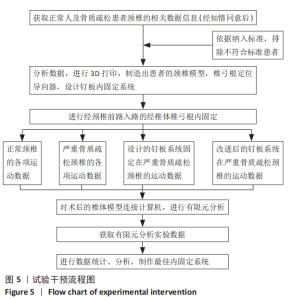
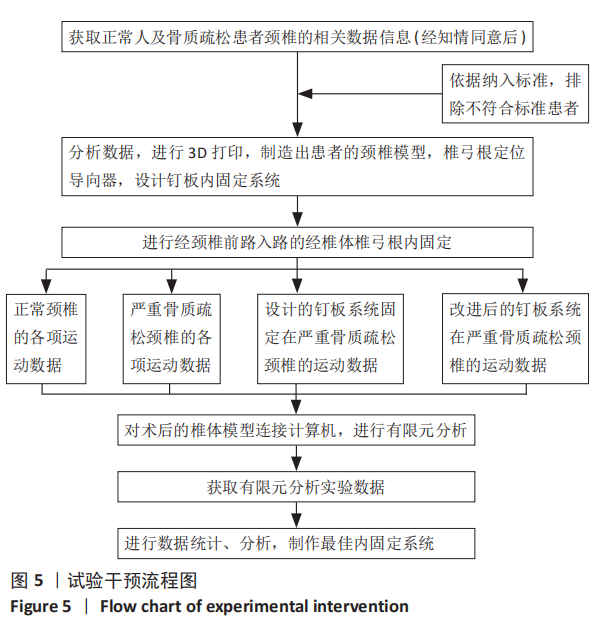
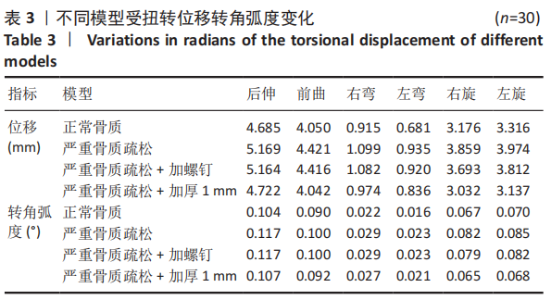
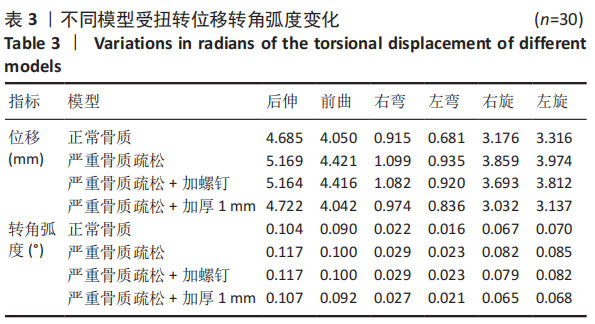
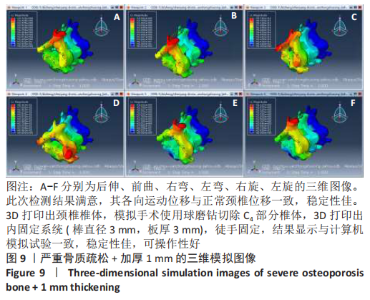
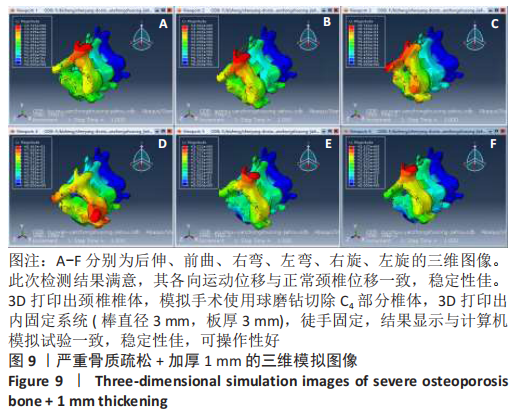
[1] 尹恒,苏秋菊,王建伟,等.骨质疏松症中医证型现代化研究思路探索[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(3):454-457.
[2] BARBOSA AP, MASCARENHAS MR, BICHO M, et al. The main autoimmune and nonautoimmune etiologies of endogenous hyperthyroidism do not seem to influence the increased prevalence of morphometric vertebral fractures and osteoporosis in Portuguese men. Osteoporos Sarcopenia. 2017;3(3):149-154.
[3] YANG X, TANG W, MAO D, et al. Prevalence and risk factors associated with osteoporosis among residents aged above 20 years old in Chongqing, China. Arch Osteoporos. 2021;16(1):57.
[4] TAO Y, TANG S, HUANG X, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of osteoporosis in chinese postmenopausal women awaiting total knee arthroplasty. Clin Interv Aging. 2021;16:379-387.
[5] CHOI MH, YANG JH, SEO JS, et al. Prevalence and diagnosis experience of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women over 50: focusing on socioeconomic factors. PLoS One. 2021;16(3):e0248020.
[6] 杨敬,何保华,王强,等.不同固定节段钛板固定单开门椎板成形术治疗老年多节段脊髓型颈椎病的效果[J].中国综合临床,2017,33(12):1122-1126.
[7] 冯大鹏,许卫兵,赵智,等.颈椎管成形微钛板固定与椎板切除内固定后C5神经根麻痹的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,30(53):8554-8559.
[8] 刘彦宾.脊柱骨盆参数在颈椎病术后轴性症状与退变性侧凸生活质量改善中的作用[D].济南:山东大学,2017.
[9] 高尧.不同前路融合固定手术治疗老年颈椎间盘突出症疗效的对比分析[D].长春:吉林大学,2013.
[10] 刘俭涛,徐明国,王润青,等.颈椎前路微型记忆加压合金板的体外生物力学研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2020,30(3):263-269.
[11] 齐德泰,赵晓峰,赵轶波,等.三叶加强型颈椎前路钉板系统的研制以及生物力学研究与初步临床应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2019,39(24):1496-1506.
[12] 王远政.下颈椎前路经椎弓根螺钉内固定技术的研究与应用[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2013:1-101.
[13] 吴长福.颈椎前路椎弓根螺钉内固定稳定性的生物力学研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2012:1-60.
[14] 崔西龙,于海洋,姜济世,等.齿状突骨折伴寰枢椎不稳的手术治疗[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2016,26(4):316-322.
[15] 夏天,孙宇,赵衍斌,等.3D打印定制钛合金融合器在先天性颈椎侧凸畸形治疗中的应用[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2020,30(9):791-796.
[16] 吴敏飞,王洋,矫健航,等.3D打印椎间融合器在脊髓型颈椎病椎间盘摘除减压融合内固定术的应用效果[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2019, 12(2):98-101.
[17] AMELOT A, COLMAN M, LORET JE. Vertebral body replacement using patient-specific three-dimensional-printed polymer implants in cervical spondylotic myelopathy: an encouraging preliminary report. Spine J. 2018; 18(5):892-899.
[18] 吴家昌,李修往,方国芳,等.3D打印人工椎体在脊柱肿瘤手术中的设计及初步应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2020,22(10):855-861.
[19] LU T, LIU C, YANG B, et al. Single-Level Anterior Cervical Corpectomy and Fusion Using a New 3D-Printed Anatomy-Adaptive Titanium Mesh Cage for Treatment of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy and Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament: A Retrospective Case Series Study. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:3105-3114.
[20] 张帆.新型纳米金刚石-PLGA可吸收复合材料3D打印制备颈椎间融合器的研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2015:1-114.
[21] 张智海,刘忠厚,李娜,等.中国人骨质疏松症诊断标准专家共识(第三稿.2014版)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,21(9):1007-1010.
[22] LIU G, LI Q, SHENG F, et al. Outcomes of occipitocervical fixation using a spinous process screw in C2 as a third anchor point for occipitocervical fixation: a case presentation. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):307.
[23] CHEN HY, LUO MQ, LI W, et al. Surgical treatment of atypical unstable Hangman fracture in elderly osteoporotic patients. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2019;32(7):641-646.
[24] REHOUSEK P, JENNER E, HOLTON J, et al. Biomechanical comparison of cemented versus non-cemented anterior screw fixation in type II odontoid fractures in the elderly: a cadaveric study. Spine J. 2018;18(10):1888-1895.
[25] 孙玛骥,王秋安,张星晨,等.新型颈椎前路经椎弓根固定钉板系统的研制及生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(24):3821-3825.
[26] 张海博,冷辉,沈永帅.前路颈椎椎间盘切除融合术后早期应用唑来膦酸改善骨质疏松患者临床疗效[J].脊柱外科杂志,2020,18(5):335-338.
[27] 徐双,李军,段毅,等.后路内固定融合手术治疗类风湿性寰枢椎不稳[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2017,27(4):289-295.
[28] 韦葛堇.颅颈交界区容积预判颅底凹陷症经口寰枢椎复位钢板手术疗效的研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2016:1-95.
(责任编辑:WJ,ZN,ZH)
|