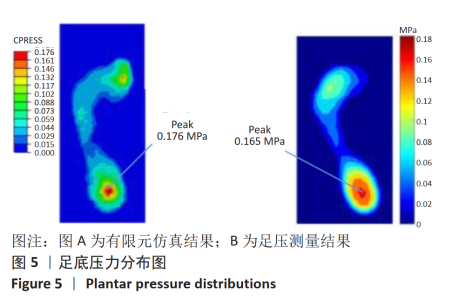
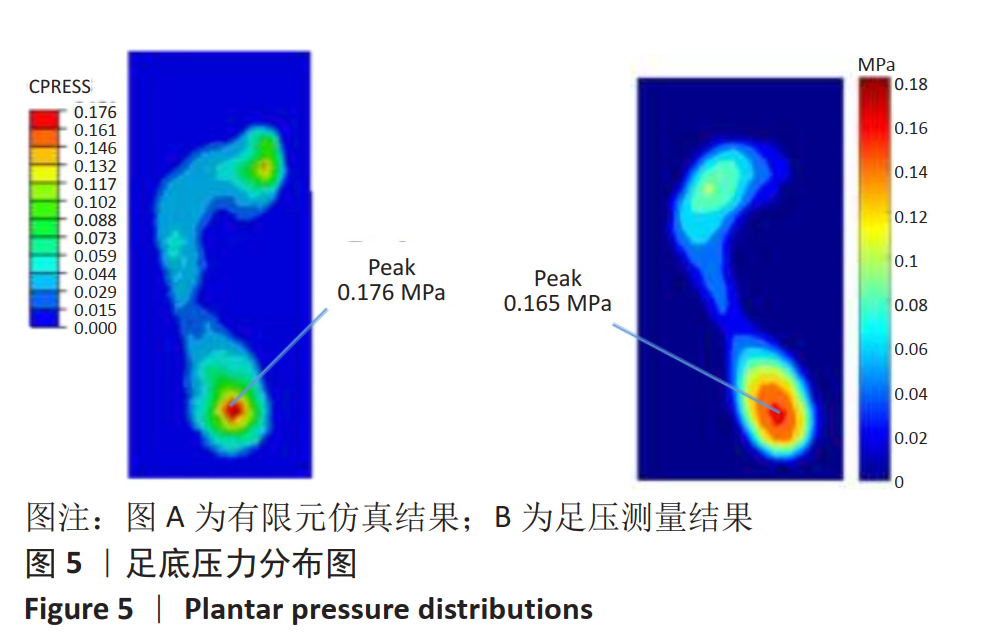
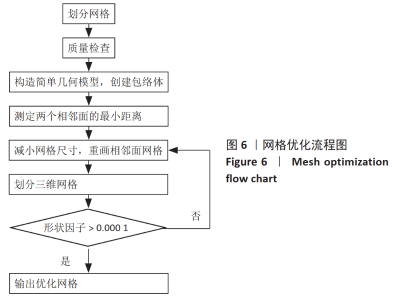
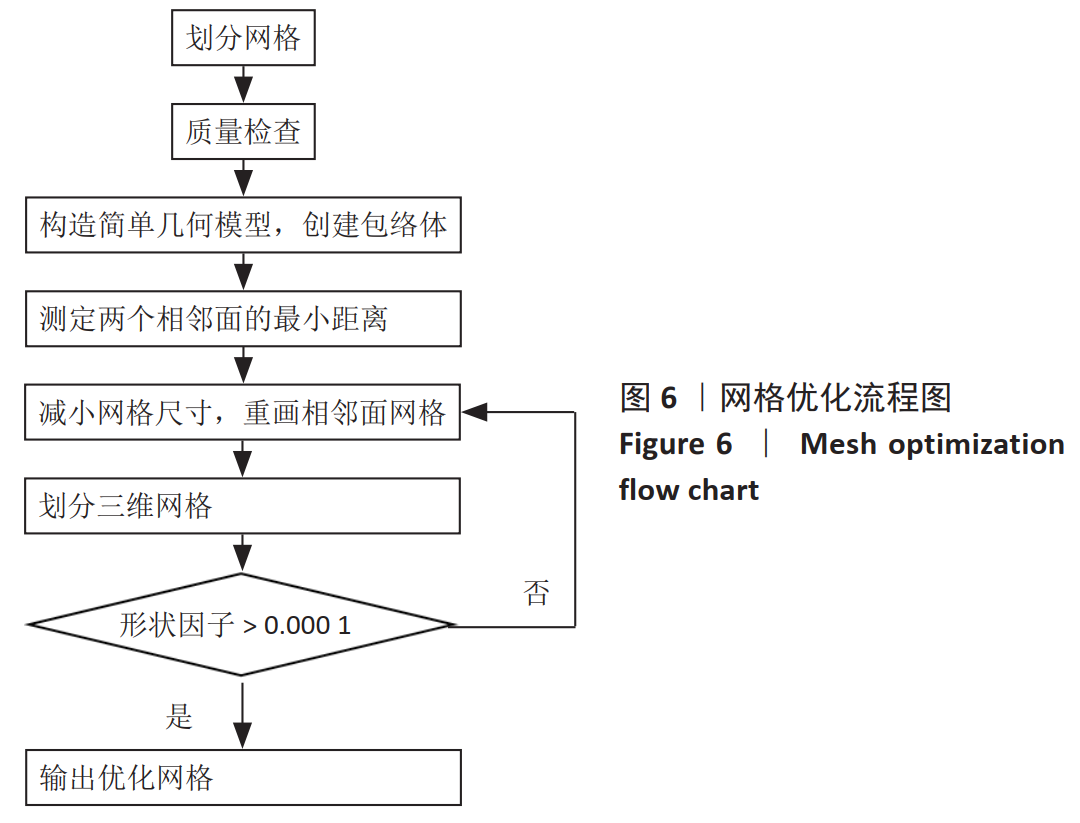
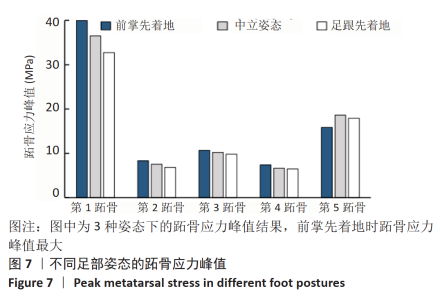
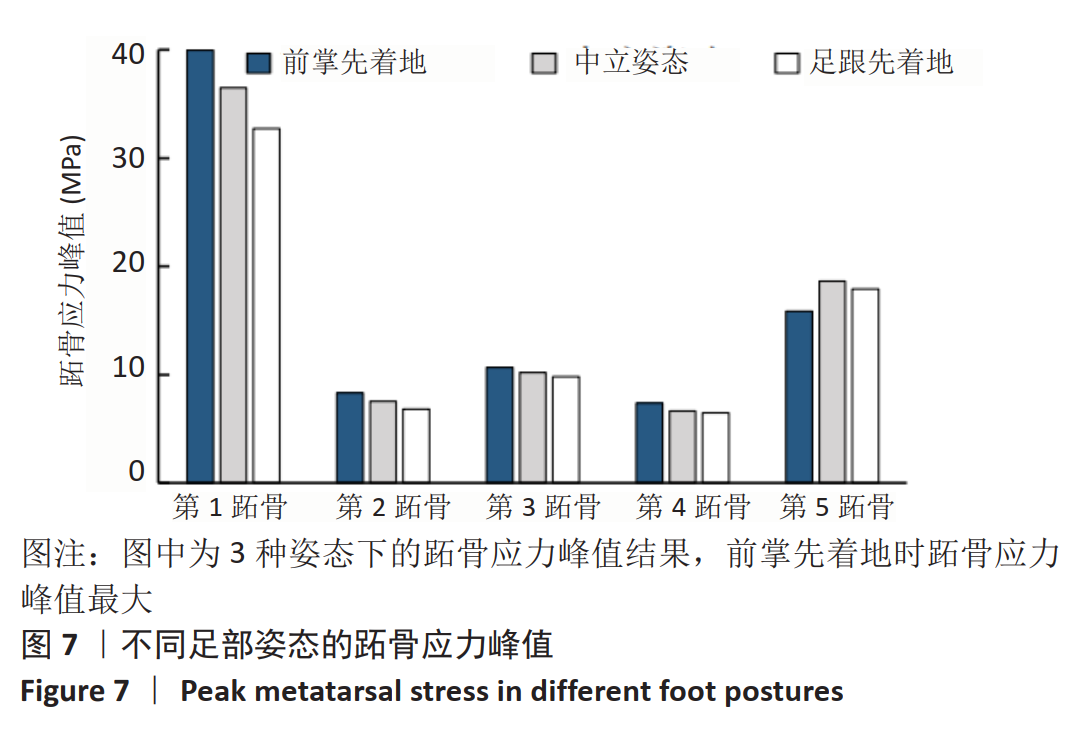
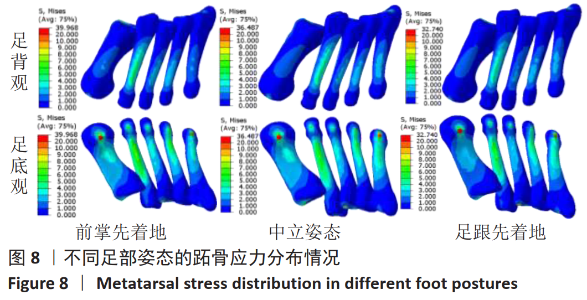
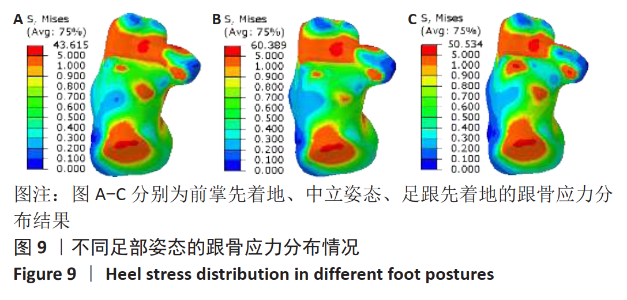
[1] LIEBERMAN DE, VENKADESAN M, WERBEL WA, et al. Foot strike patterns and collision forces in habitually barefoot versus shod runners. Nature. 2010;463(7280): 531-535.
[2] ADAM ID, GARY JG, FRANK W, et al. Foot Strike and Injury Rates in Endurance Runners: A Retrospective Study. Med Sci Sports Exer. 2012;44(7):1325-1334.
[3] 刘海霞. 脚着落点的变化对低心肺耐力大学生跑步经济性影响的实验性研究[D]. 石家庄:河北师范大学,2019.
[4] ENRIQUE MO, JAVIER B, ESTEVAM BLC. Computational Foot Modeling: Scope and Applications. Arch Computat Methods Eng. 2016;23:389-416.
[5] ELLISON MA, KENNY M, FULFOD J, et al. Incorporating subject-specific geometry to compare metatarsal stress during running with different foot strike patterns. J Biomech. 2020;105:1-7.
[6] GU YD, REN XJ, RUAN GQ, et al. Foot contact surface effect to the metatarsals loading character during inversion landing. Int J Numer Methods Biomed Eng. 2011;27(4):476-484.
[7] WANG Y , LI Z , WONG WC , et al. Finite element analysis of biomechanical effects of total ankle arthroplasty on the foot. J Orthop Translat. 2018;12:55-65.
[8] TAO K, JI W, WANG D, et al. Relative contributions of plantar fascia and ligaments on the arch static stability: a finite element study. Biomed Tech. 2010;55(5):265-271.
[9] CHEUNG JT, ZHANG M, AN KN. Effects of plantar fascia stiffness on the biomechanical responses of the ankle-foot complex. Clin Biomech. 2004;19:839-846.
[10] CHEUNG JT, ZHANG M, AN KN. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the foot during standing-a material sensitivity study. J Biomech. 2005;38:1045-1054.
[11] CHEN WM, LEE T, LEE PV, et al. Effects of internal stress concentrations in plantar soft-tissue—a preliminary three-dimensional finite element analysis. Med Eng Phys. 2010;32:324-331.
[12] CHEN TL, WONG DW, WANG Y, et al. Foot Arch Deformation and Plantar Fascia Loading during Running with Rearfoot Strike and Forefoot Strike: A Dynamic Finite Element Analysis. J Biomech. 2019;83:260-272.
[13] HSU CY, GUNG WY, SHIH LS, et al. Using an optimization approach to design an insole for lowering plantar fascia stress-A finite element study. Ann Biomech Eng. 2008;36:1345-1352.
[14] 陶凯. 人体足踝系统建模与相关力学问题研究[D]. 上海:上海交通大学,2010.
[15] AKRAMI M, QIAN Z, ZOU Z, et al. Subject-specific finite element modelling of the human foot complex during walking: sensitivity analysis of material properties, boundary and loading conditions. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2018;(17):569-576.
[16] LEMMON D, SHIANG TY, HASHMI A, et al. The effect of insoles in therapeutic footwear-a finite element approach. J Biomech. 1997;30(6):615-620.
[17] 孙晓昊. 软材料的大变形、接触和粘附等非线性问题的数值模拟研究[D]. 合肥:中国科学技术大学,2019.
[18] LIEBERMAN DE. What we can learn about running from barefoot running: an evolutionary medical perspective. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2012;40(2):63-72.
[19] ZHEN W, JING XL, FU WJ, et al. Plantar load characteristics among runners with different strike patterns during preferred speed. J Exerc Sci Fit. 2020;18(2):2152-2158.
[20] BRANDON DR, TIMOTHY RD. Joint contact loading in forefoot and rearfoot strike patterns during running. J Biomech. 2013;46(13):2201-2206.
[21] 李蜀东, 顾耀东. 足前掌在不同着地角度下跖骨应力状态的有限元研究[J]. 体育科学,2018,38(3):67-72+97.
[22] LI SD, ZHANG Y, GU YD, et al. Stress distribution of metatarsals during forefoot strike versus rearfoot strike: A finite element study. Comput Biol Med. 2017;91: 38-46.
[23] JENNIFER RY, CHRISTOPHER LD, AMY S, et al. Foot strike pattern during running alters muscle-tendon dynamics of the gastrocnemius and the soleus. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):5872.
[24] CHEN TLW, AGRESTA CE, LIPPS DB, et al. Ultrasound elastographic assessment of plantar fascia in runners using rearfoot strike and forefoot strike. J Biomech. 2019;89:65-71.
[25] 张燊. 足部功能训练对足弓形态及跑步生物力学影响的研究[D]. 上海:上海体育学院,2020.
[26] ANDERSON LM, BONANNO DR, HART HF, et al. What are the Benefits and Risks Associated with Changing Foot Strike Pattern During Running? A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Injury, Running Economy, and Biomechanics. Sports Med. 2020;50(3):885-917.
[27] 朱瑶佳. 不同类型运动对大学生足型及步态特征的影响研究[D]. 石家庄:河北师范大学,2020.
[28] MO SW, LAM WK, CHING ECK, et al. Effects of heel-toe drop on running biomechanics and perceived comfort of rearfoot strikers in standard cushioned running shoes. Footwear Sci. 2020;12(2):91-99.
[29] VERNILLO G, AGUIAR M, SAVOLDELLI A, et al. Regular changes in foot strike pattern during prolonged downhill running do not influence neuromuscular, energetics, or biomechanical parameters. Eur J Sport Sci. 2020;20(4):495-504. |