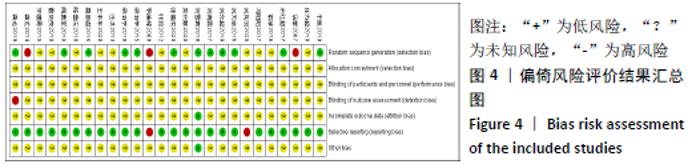
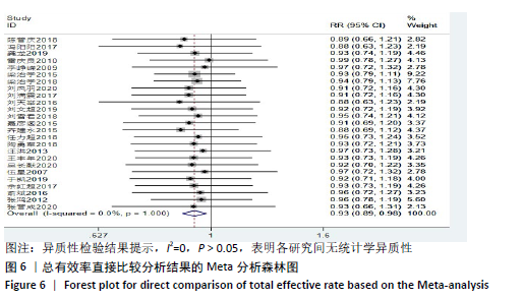
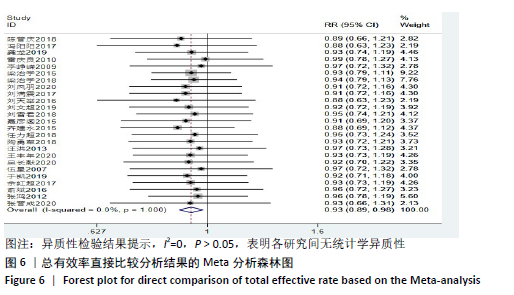
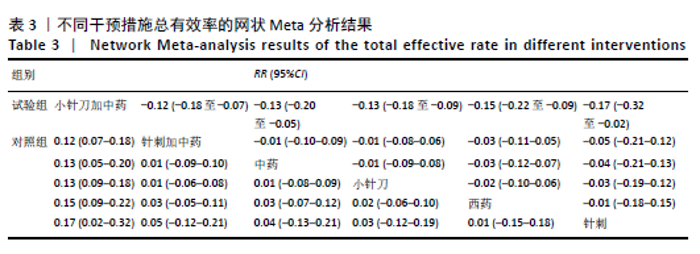
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (32): 5240-5248.doi: 10.12307/2021.231
Clinical efficacy of small needle knife combined with traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a network Meta-analysis
Huang Cihui1, Liu Jiayue1, Huang Yingjie1, Zhuang Zeqin1, Lin Yunxin2, Li Dan1, Zheng Liang3
- 1The First Clinical Medicine School, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2The Fourth Clinical Medicine School, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen 518033, Guangdong Province, China; 3The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2020-09-23Revised:2020-09-23Accepted:2020-10-30Online:2021-11-18Published:2021-07-26 -
Contact:Zheng Liang, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Huang Cihui, Master candidate, The First Clinical Medicine School, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Guangdong Provincial Famous Chinese Medicine Inheritance Studio Construction Project, No. [2019]5 (to ZL); the Innovative Research Project of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2019IIT31 (to ZL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Cihui, Liu Jiayue, Huang Yingjie, Zhuang Zeqin, Lin Yunxin, Li Dan, Zheng Liang. Clinical efficacy of small needle knife combined with traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a network Meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5240-5248.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
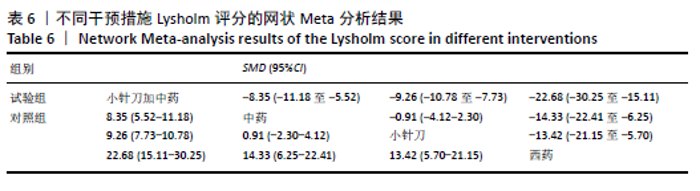
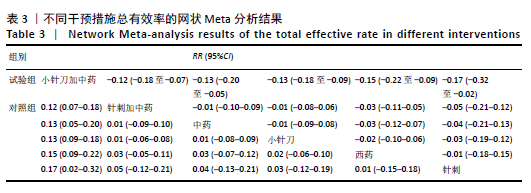
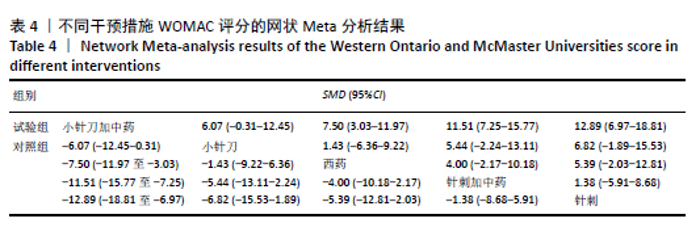
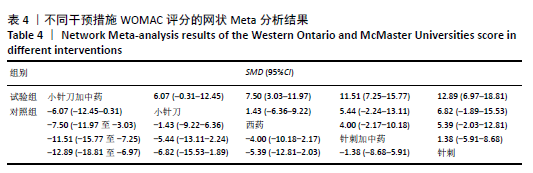
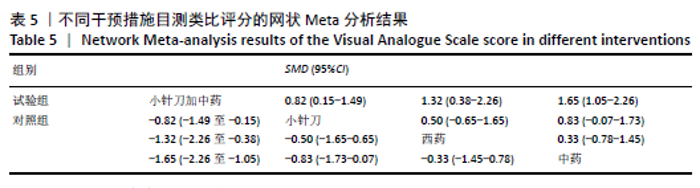
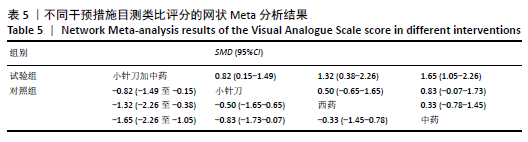
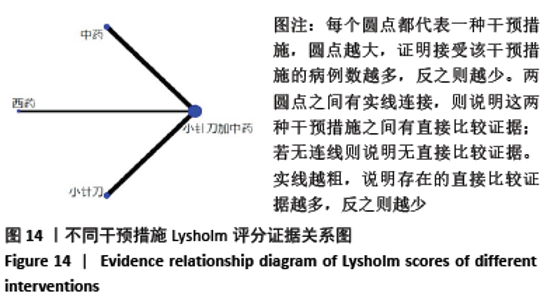
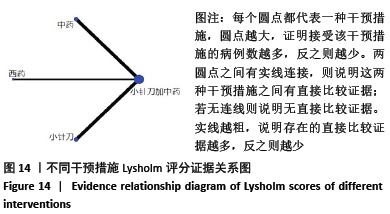
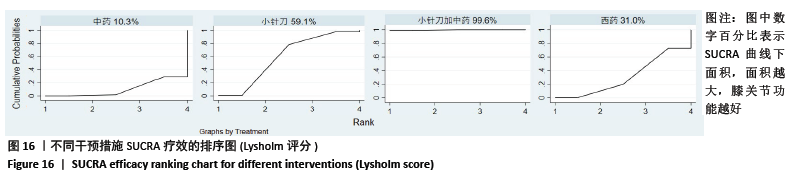
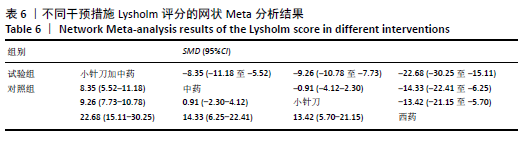
2.6.3 Lysholm评分的网状Meta分析结果 小针刀加中药与西药(SMD= 22.68,95%CI:15.11-30.25)、中药(SMD=8.35,95%CI:5.52-11.18)、小针刀(SMD=9.26,95%CI:7.73-10.78)相比,能显著提高Lysholm膝关节功能评分(P < 0.05)。与西药相比,中药(SMD=14.33,95%CI:6.25-22.41)、小针刀(SMD=13.42,95%CI:5.70-21.15)均能显著改善Lysholm膝关节功能评分(P < 0.05)。其他各干预措施之间的Lysholm评分差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表6。 "
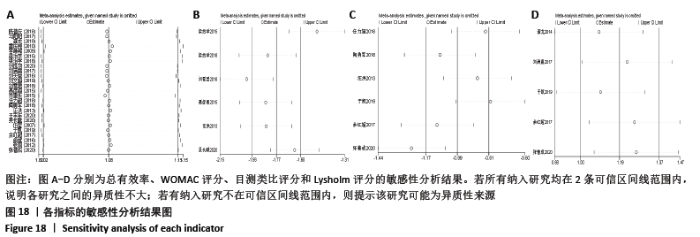
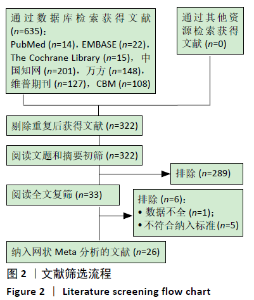
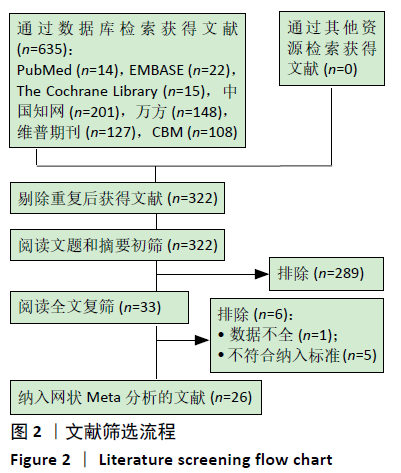
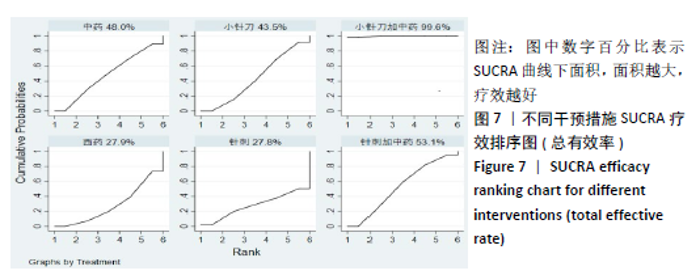
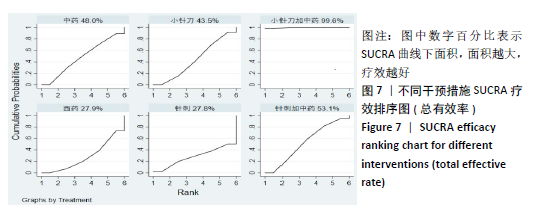
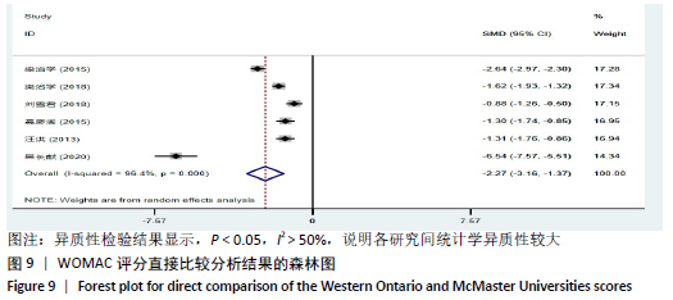
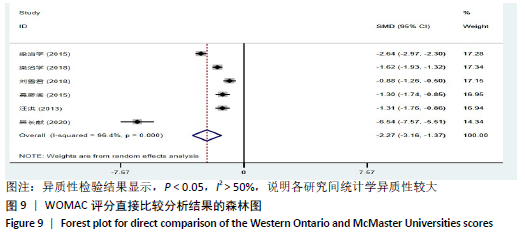
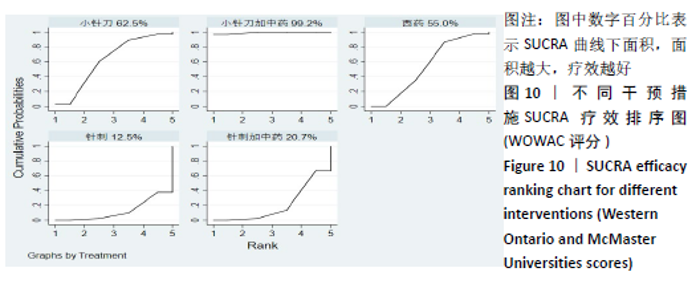
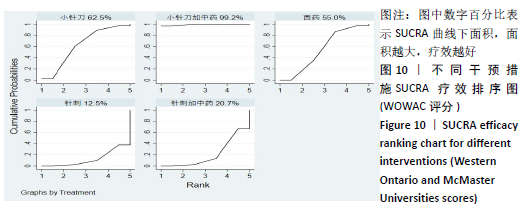
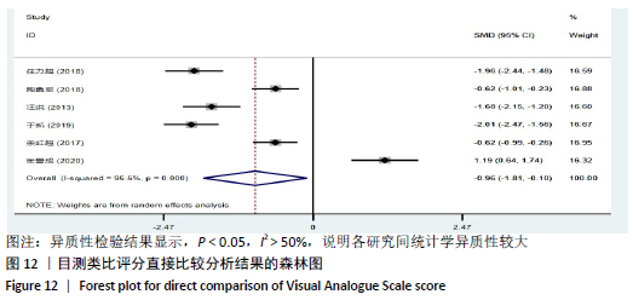
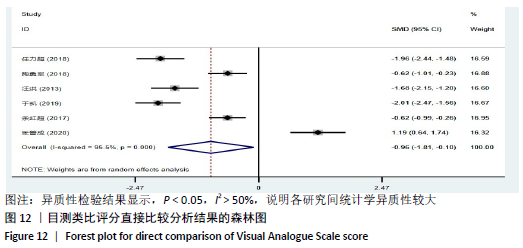
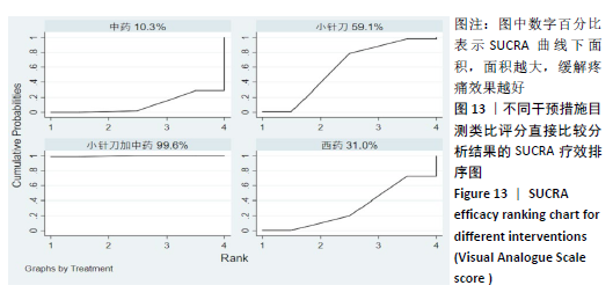
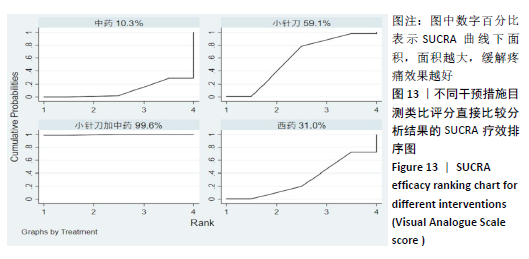
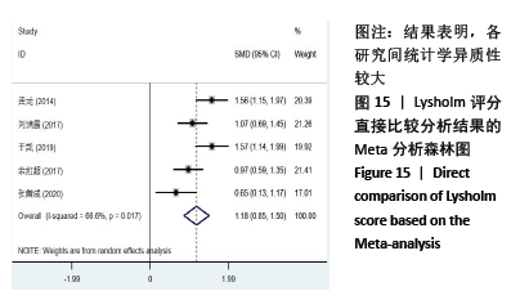
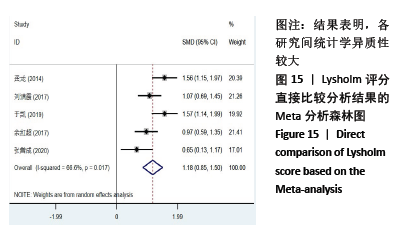
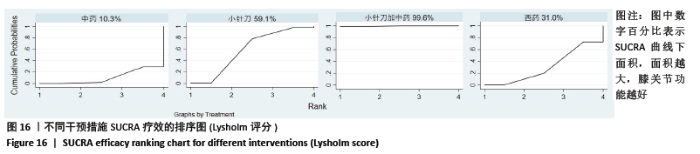
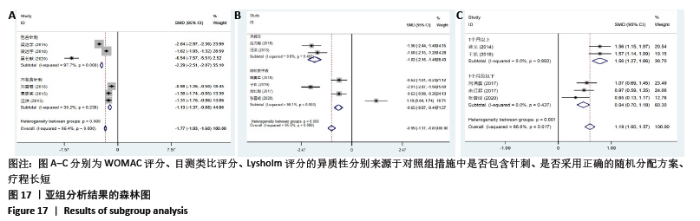
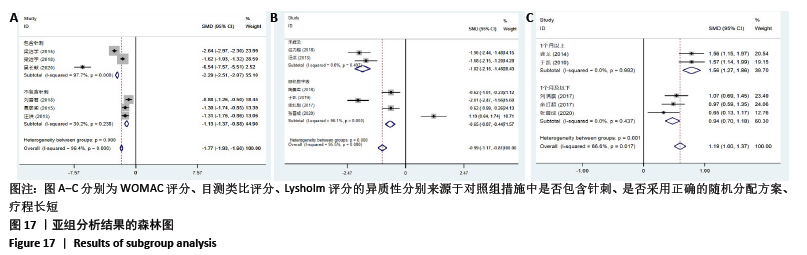
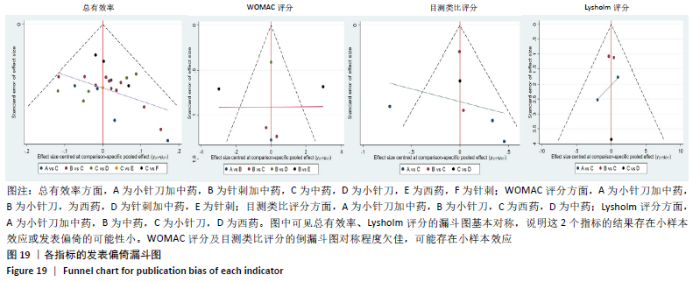
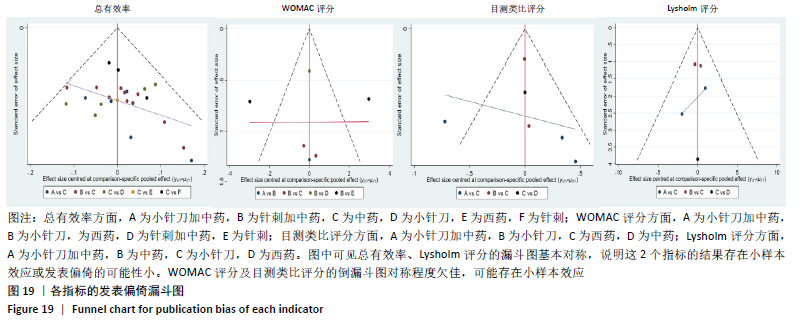
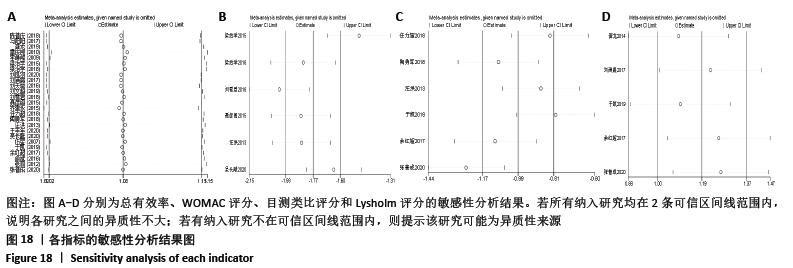
2.8 敏感性分析结果 见图18,以总有效率为疗效指标,各个研究无明显异质性,对其进行敏感性分析,结果显示临床疗效的Meta分析稳定性较高。 以WOMAC评分变化为疗效指标,各个研究有显著的异质性,对其进行敏感性分析,显示WOMAC评分的Meta分析结果不稳定,推测异质性可能来源于2个研究[15, 21]。将该研究剔除后,再次分析异质性,发现异质性仍然较大(I2=96.2%,P < 0.001),分析原因,可能与涉及该指标的文献数量过少有关,因此应谨慎对待WOMAC评分这一指标的分析结果。 以目测类比评分变化为疗效指标,各个研究有显著的异质性,对其进行敏感性分析,显示目测类比评分的Meta分析结果不稳定,异质性可能来源于2个研究[25,31]。将这2个研究剔除后,重新进行分析,发现异质性仍然较大(I2=96.9%,P < 0.001),其原因可能是报道该指标的文献数量过少,提示目测类比评分的结果不稳定,需谨慎解读。 以Lysholm评分为疗效指标,各个研究有中等异质性,对其进行敏感性分析,显示Lysholm评分的Meta分析结果欠稳定,异质性可能来源于2个研究[11,30],造成异质性的原因可能是这2个研究与其他研究疗程的差异。剔除此2个研究后,发现其他研究无明显的异质性(I2=0,P=0.437),用固定效应模型对剔除此2个研究后的其他研究进行分析,结果显示,与单用中药(SMD=0.85,95%CI:1.16-0.54)、单用西药(SMD=1.06,95%CI:1.45-0.68)相比,小针刀加中药能显著提升Lysholm膝关节功能评分(P < 0.05),与单用中药相比,单用西药改善Lysholm膝关节功能评分的疗效无显著差异(P < 0.05);概率排序结果显示,改善Lysholm膝关节功能评分的疗效由优到劣的排序为小针刀加中药>中药>西药。 "
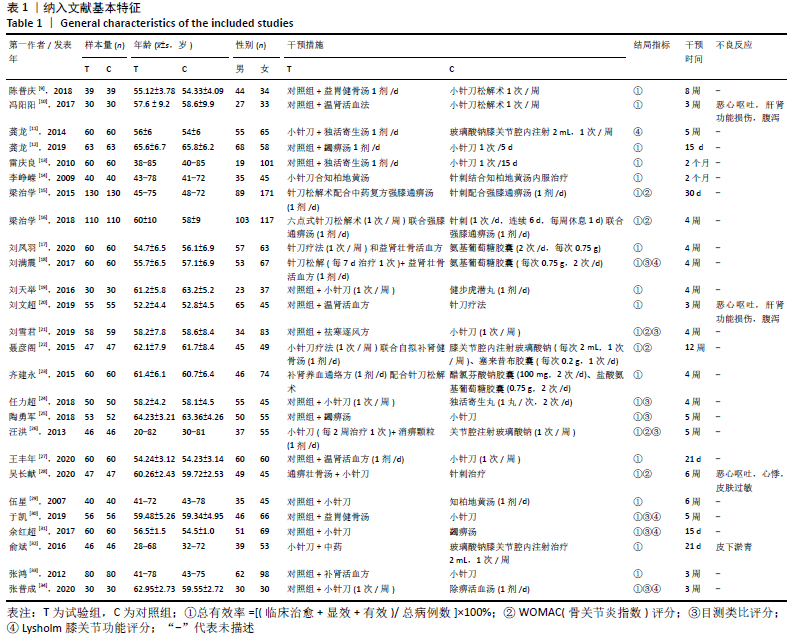
| [1] YUAN XL, MENG HY, WANG YC, et al. Bone-cartilage interface crosstalk in osteoarthritis: potential pathways and future therapeutic strategies. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(8):1077-1089. [2] 根呷她姆.膝骨关节炎的日常护理[J].世界最新医学信息文摘(连续型电子期刊), 2020,20(62):39,41. [3] TANG X, WANG S, ZHAN S, et al. The prevalence of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis in China: results from the china health and retirement longitudinal study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(3):648-653. [4] 王尚全,朱立国,展嘉文,等.中医康复临床实践指南▪膝骨关节炎[J].康复学报,2020, 30(3):177-182. [5] 陈李专,陈斌,林安阳,等.膝骨关节炎中西医疗法的临床研究进展[J].辽宁中医杂志, 2020,47(2):203-206. [6] 李晓乐,李无阴.针刀疗法治疗膝骨关节炎的研究进展[J].中国中医急症,2020,29(5):922-924. [7] 田金徽,李伦,赵晔,等.网状Meta分析的撰写与报告[J].中国药物评价,2013,30(6): 321-323,333. [8] 中华医学会风湿病学分会.骨关节炎诊断及治疗指南[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2010, 14(6):416-419. [9] 陈普庆,余通汉.小针刀联合益胃健骨汤内服治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的临床价值分析[J].临床医药文献电子杂志,2018,236(23):74. [10] 冯阳阳,路喻清,常宝生,等.温肾活血法联合针刀松解法治疗膝骨关节炎疗效及对血清IL-2、IL-10的影响[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2017,26(31):99-101. [11] 龚龙,郝明,张立新,等.小针刀结合中药治疗膝关节骨性关节炎120例临床观察[J].中医临床研究,2014,6(28):29-31. [12] 龚龙,石雷,王迪,等.小针刀配合蠲痹汤加减治疗肝肾亏虚型膝关节骨性关节炎的临床效果研究[J].世界中医药,2019,14(5): 1314-1317. [13] 雷庆良.小针刀配合中药治疗膝关节骨性关节炎肝肾不足阳虚寒凝证临床观察[J].新中医,2010,42(3):45-46. [14] 李峥嵘.小针刀结合中药治疗膝关节骨性关节炎40例临床观察[J].新中医,2009,41(9): 89-90. [15] 梁治学,胡燕,丁永红,等.针刀松解术配合强膝通痹汤治疗膝骨关节炎的临床观察[J].中国中医药科技,2015,22(1):77-78. [16] 梁治学,胡燕,孟志雄,等.六点式针刀松解术配合强膝通痹汤治疗大骨节病膝关节炎的临床研究[J].中医药学报,2018,46(5):100-103. [17] 刘凤羽.益肾壮骨活血方联合针刀疗法治疗膝骨关节炎的临床疗效[J].中国保健营养, 2020,30(13):170-173. [18] 刘满震,尹学永,马林升,等.益肾壮骨活血方联合针刀疗法治疗膝骨关节炎60例疗效观察[J].现代养生月刊,2017(7):58-60. [19] 刘天举,吴芳,申震,等.健步虎潜丸联合小针刀治疗膝关节骨性关节炎30例疗效观察[J].湖南中医杂志,2016,32(12):78-80. [20] 刘文超,王丰年,李炜,等.温肾活血方联合针刀疗法治疗膝骨关节炎安全性及有效性分析[J].医学食疗与健康,2019,(4):151. [21] 刘雪君,王晓萍,王海东.小针刀配合祛寒逐风方治疗寒湿阻痹型膝关节骨性关节炎的临床观察[J].甘肃医药,2019,38(7):618-620. [22] 聂彦阁.小针刀疗法联合补肾健骨汤治疗膝骨关节炎临床观察[J].新中医,2015,47(6):255-257. [23] 齐建永,张丽萍,王旭东.补肾养血通络方配合针刀治疗膝骨关节炎临床观察[J].四川中医,2015,33(9):115-117. [24] 任力超,汤肖,靳磊超,等.小针刀疗法联合独活寄生丸治疗膝关节骨性关节炎临床效果观察[J].饮食保健,2018,5(9):88-89. [25] 陶勇军.小针刀配合蠲痹汤加减治疗膝关节骨性关节炎临床研究[J].实用中医药杂志, 2018,34(12):1416-1417. [26] 汪洪,黄建,丁本湖,等.针刀骨减压合消痹颗粒治疗膝关节骨性关节炎46例[J].安徽中医学院学报,2013,32(5):58-61. [27] 王丰年.针刀配合温肾活血方治疗瘀血阻滞型膝骨关节炎的临床效果观察[J].饮食保健, 2020,7(11):103. [28] 吴长献.通痹壮骨汤结合小针刀治疗膝关节骨性关节炎疗效观察[J].实用中医药杂志, 2020,36(4):427-428. [29] 伍星,杨明,祁开泽.小针刀配合中药治疗膝关节骨性关节炎40例临床观察[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2007,27(6):62-63. [30] 于凯.益胃健骨汤配合针刀松解术治疗膝骨性关节炎疗效观察[J].实用中西医结合临床, 2019,19(6):25-27. [31] 余红超,孙菊,董博,等.针刀整体松解术配合蠲痹汤治疗肝肾亏虚型膝骨性关节炎临床观察[J].中国医药导报,2017,14(3):169-172. [32] 俞斌,姚新苗.针刀微创松解结合中药内服治疗膝骨性关节炎46例临床观察[J].甘肃中医药大学学报,2016,33(3):83-86. [33] 张鸿,寇久社,张保平,等.针刀配合补肾活血方治疗膝骨性关节炎160例[J].现代中医药,2012,32(5):51-53. [34] 张普成,王勇.针刀联合除痹活血汤治疗膝骨关节炎骨髓水肿综合征临床观察[J].山西中医,2020,36(1):29-31. [35] TANG X, WANG S, ZHAN S, et al. The prevalence of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis in China: results from the China health and retirement longitudinal study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68(3):648. [36] 王进辉.膝关节骨性关节炎的发病因素及治疗进展研究[J].医学信息,2019,32(4):57-59. [37] ESSEX MN, O′CONNELL MA, BEHAR R, et al. Efficacy and safety of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in Asian patients with knee osteoarthritis: summary of a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016;19(3):262-270. [38] 苏耀辉,周明旺,陈彦同,等.中医药治疗膝骨关节炎临床研究进展[J].甘肃中医药大学学报,2020,37(1):110-115. [39] 陈李专,陈斌,林安阳,等.膝骨关节炎中西医疗法的临床研究进展[J].辽宁中医杂志, 2020,47(2):203-206. [40] 朱凯辉,邰东旭.中医外治法治疗膝骨关节炎的临床进展[J].实用中医内科杂志,2020, 34(2):45-47. [41] 杨波,王青松,王大华,等.中医治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的研究进展[J].双足与保健, 2019,28(19):197-198. [42] 中国中西医结合学会骨伤科专业委员会.膝骨关节炎中西医结合诊疗指南[J].中华医学杂志,2018,98(45):3653. [43] 陈土均,涂明中,李海涛,等.小针刀治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的效果及对患者TNF-α、MMMs水平的影响[J].中医临床研究,2019, 11(31):60-62. [44] 武永彪,石晓兵.膝骨性关节炎中医治疗现状研究[J].陕西中医,2019,40(4):543-545. |
| [1] | Zhong Yizheng, Huang Peizhen, Cai Qunbin, Zheng Liqin, He Xingpeng, Dong Hang. Microstructural indexes that determine the trabecular bone maximum stress of micro-finite element models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1313-1318. |
| [2] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [3] | Wu Tianliang, Tao Xiuxia, Xu Hongguang. Influence of different bone mineral densities on cage subsidence after stand-alone oblique lateral interbody fusion: three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1352-1358. |
| [4] | Wen Xinghua, Ding Huanwen, Cheng Kai, Yan Xiaonan, Peng Yuanhao, Wang Yuning, Liu Kang, Zhang Huiwu. Three-dimensional finite element model analysis of intramedullary nailing fixation design for large femoral defects in Beagle dogs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1371-1376. |
| [5] | Zhang Lichuang, Gao Huali, Wang Jingchao, Lin Huijun, Wu Chonggui, Ma Yinghui, Huang Yunfei, Fang Xue, Zhai Weitao. Effect of tendon manipulation with equal emphasis on muscles and bones on accelerating the functional rehabilitation of quadriceps femoris after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1383-1389. |
| [6] | Li Chao, Zhang Peipei, Xu Mengting, Li Linlin, Ding Jiangtao, Liu Xihua, Bi Hongyan. Respiratory training improves morphological changes of the multifidus muscle in patients with chronic nonspecific lower back pain assessed by musculoskeletal ultrasound [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1417-1421. |
| [7] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [8] | Jiang Xiaocheng, Shi Lu, Wang Yinbin, Li Qiujiang, Xi Chuangzhen, Ma Zefeng, Cai Lijun. Systematical evaluation of bone fusion rate after interbody fusion in patients with osteoporosis and lumbar degenerative disease treated with teriparatide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1427-1433. |
| [9] | Bai Yulong, Li Zhonghai, Zhao Yantao, Xia Cencan, Shi Lei. History, current situation and prospect of tissue banks in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1306-1312. |
| [10] | Sun Jiajia, Zhu Haidi, Lu Yun, Zhang Kai. Comparison of bone metabolism markers between type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with hip fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1156-1160. |
| [11] | Huang Linke, Wei Linhua, Jiang Jie, Liu Qian, Chen Weiwei. Effects of estrogen combined with treadmill exercise on bone mass and articular cartilage in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [12] | Bi Gengchao, Zhang Yanlong, Li Qiuyue, Hu Longwei, Zhang Yu. Knee joint mechanics and activation characteristics of surrounding muscles during deep jumps at different heights and distances [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1211-1218. |
| [13] | Zhang Qiming, Bao Sairong, Shan Sharui, Zhong Zhiliang, Liu Chunlong. Effect of deep muscle stimulation on muscle tone and stiffness of erector spinaes in patients with chronic nonspecific low back pain: a digital muscle testing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1250-1256. |
| [14] | Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [15] | Zhang Tingting, Liu Juan, Zhang Xu. Bioactivity of phase-transition lysozyme for surface modification of zirconia all-ceramic implant material mediating hydroxyapatite coating [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1043-1049. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||