Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (26): 4243-4248.doi: 10.12307/2021.128
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hypertrophic fibrosis of the ligamentum flavum: signaling pathways and molecular level characteristics
Fan Xiaoqian1, Chen Feng2, Liang Xiongqin1, Gao Sen1, Yang Xinqiang1
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2020-07-20Revised:2020-07-22Accepted:2020-09-05Online:2021-09-18Published:2021-05-13 -
Contact:Chen Feng, MD, Professor, Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China E-mail:hfxuanxuan0123@163.com -
About author:Fan Xiaoqian, Master candidate, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81560778 and 81960879 (both to CF)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fan Xiaoqian, Chen Feng, Liang Xiongqin, Gao Sen, Yang Xinqiang. Hypertrophic fibrosis of the ligamentum flavum: signaling pathways and molecular level characteristics[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(26): 4243-4248.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

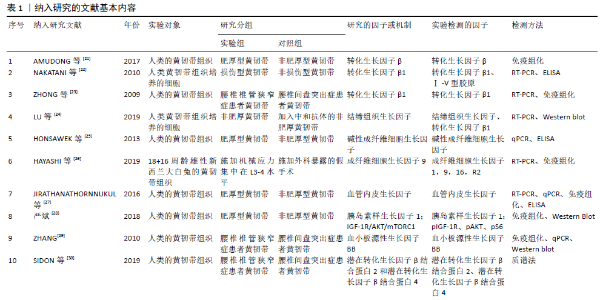
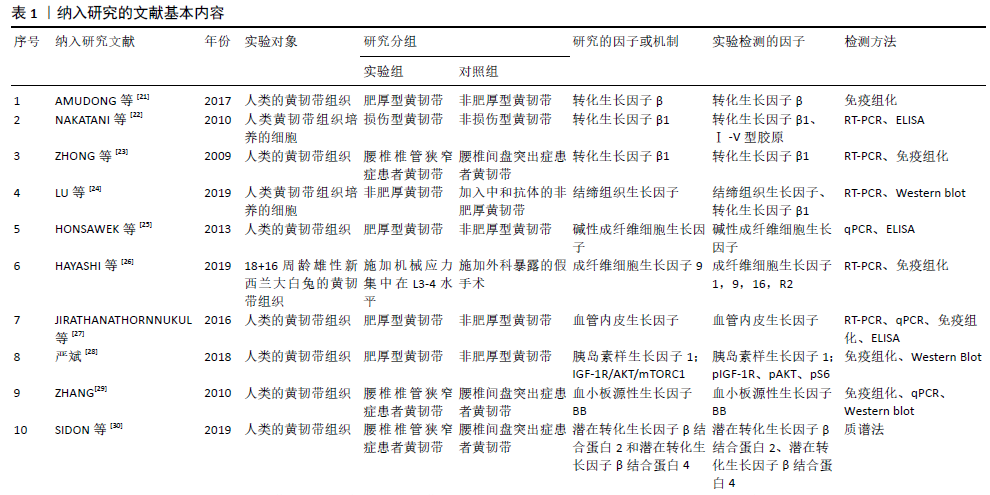
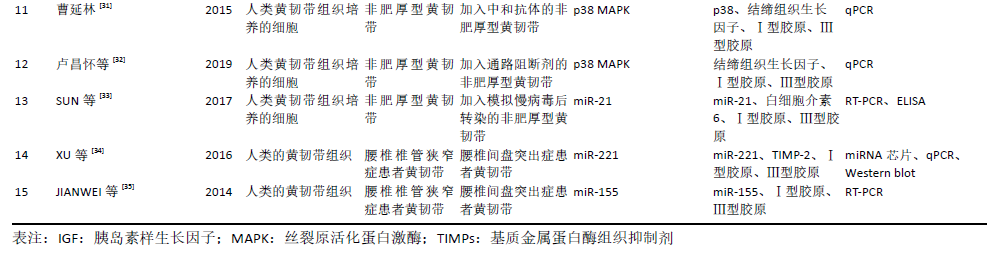
2.2 黄韧带生理病理机制 黄韧带主要由弹力纤维、胶原纤维构成[5],其能够将2个相邻椎弓板之间的节段连接起来,协助维持脊柱的稳定性,限制脊柱的过度前屈,是脊柱后部的重要韧带组织结构之一。黄韧带肥厚是指黄韧带组织细胞中胞外基质胶原纤维含量明显增加、弹力纤维显著减少、纤维排列紊乱的病理改变结果[6-7],其病因或发病机制尚未完全清楚,猜测可能与慢性退变、炎症、外伤、代谢障碍等因素有关,目前普遍认为黄韧带肥厚的机制是韧带在机械应力作用下导致炎症反应,随后机体产生瘢痕修复,黄韧带从而逐渐发生纤维化。在1937年,APRKRE首次提出黄韧带肥厚会造成的继发性椎管狭窄的观点,随着医学科学的日益发展,人们逐渐发现黄韧带肥厚的最终结果确会造成椎管狭窄,特别是侧隐窝引起始部的狭窄[8],从而导致马尾神经受压及神经根压迫,引起间歇性跛行及下腰痛等症状。 2.3 与黄韧带纤维化相关的生长因子及其结合蛋白 已有实验研究证实,在黄韧带组织增生肥厚过程中,有多种分子参与表达并表现出活性增加,包括基质金属蛋白酶[9-11]、基质金属蛋白酶组织抑制剂(tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases,TIMPs)[12-13]、白细胞介素[14-16]、肿瘤坏死因子[17-18]、骨形态发生蛋白[19]、血管生成素样蛋白2等[20],其中生长因子这一类细胞因子参与黄韧带组织纤维化的相关度最高。 生长因子是一类通过与特异的、高亲和力的细胞膜受体结合,调节细胞生长与其他细胞功能等多效应的多肽类物质,对人体的炎症与感染、创伤愈合、血管形成、细胞分化、形态发生等方面有着重要的调控作用,多个实验证实,在黄韧带组织纤维化的过程中可有多种生长因子一同参与、协同工作。 2.3.1 转化生长因子β 转化生长因子(transforming growth factor,TGF)最初在1978年由DELARCO在小鼠肉瘤病毒转化的细胞株条件培养基中鉴定而发现,是一种具有多种生物学活性的多肽类细胞因子,也是一类具有调节细胞生长和分化功能的蛋白质物质,其中转化生长因子β是最重要的促纤维化细胞因子之一,对细胞生长、分化和免疫反应都有广泛潜在的影响力。AMUDONG等[21]对黄韧带肥厚和非肥厚两组进行免疫组化检测,以比较两组间转化生长因子β表达的差异。结果显示,肥厚组转化生长因子β表达阳性,而非肥厚组转化生长因子β表达阴性,结论提示转化生长因子β的表达与黄韧带肥厚密切相关。NAKATANI 等[22]从腰椎手术患者的黄韧带组织中分离并提取黄韧带细胞,使用拉伸装置对黄韧带细胞施加机械拉伸力,使细胞发生物理变形,人为因素制造黄韧带细胞损伤化,使其产生瘢痕修复,之后的检测发现损伤黄韧带细胞中转化生长因子β1显著增加,该实验数据表明,机械拉伸力可以促进黄韧带细胞产生转化生长因子β1。亦有ZHONG等[23]使用反转录聚合酶链反应(reverse transcription PCR,RT-PCR)分别检测腰椎椎管狭窄症患者和急性腰椎间盘突出症患者其黄韧带组织中转化生长因子β1的mRNA表达,结果显示,腰椎椎管狭窄症组转化生长因子β1的mRNA和蛋白表达明显高于急性腰椎间盘突出症组,同时免疫组化显示转化生长因子蛋白定位于黄韧带内的成纤维细胞。综上推断可根据转化生长因子β表达水平预测黄韧带组织的成纤维化进展。 2.3.2 结缔组织生长因子(connective tissue growth factor,CTGF) 结缔组织生长因子是由血管内皮细胞分泌的促进软骨细胞增殖和分化的因子,可介导多种细胞类型的肝素和二价阳离子依赖性细胞黏附,包括成纤维细胞和内皮细胞,同时促进成纤维细胞生长因子诱导的DNA合成。LU等[24]取腰椎椎管狭窄症髓核摘除术中的黄韧带组织分离培养黄韧带细胞,而后取第3代黄韧带细胞分为5组:A组中加入转化生长因子β1,B组加入结缔组织生长因子,C组及D组分别加入不同剂量的转化生长因子β1和结缔组织生长因子的中和抗体,E组加入无血清DMEM作为对照,随后采用Western blot检测黄韧带细胞中结缔组织生长因子的表达,结果显示A,B组结缔组织生长因子蛋白相对表达量明显高于E组,而C,D组结缔组织生长因子蛋白相对表达量显著降低,但仍高于E组。结果证明结缔组织生长因子mRNA的表达可由转化生长因子β1调控,但是其加入中和抗体后,上述的关联可以被阻断。由此认为在黄韧带微损伤早期,黄韧带细胞通过释放转化生长因子β1调控结缔组织生长因子以修复损伤的黄韧带,而随着修复持续发展,结缔组织生长因子引起的瘢痕炎性反应出现,从而促使黄韧带细胞纤维化,最终导致黄韧带组织增生肥厚。 2.3.3 成纤维细胞生长因子 成纤维细胞生长因子在胚胎发育、细胞增殖、细胞分化和细胞迁移中起着重要的调节作用,能在组织损伤后增生胶质以参与修复和再生过程。HONSAWEK等[25]对腰椎椎管狭窄症患者黄韧带中碱性成纤维细胞生长因子的表达进行检测,实时荧光定量多聚核苷酸链式反应(Quantitative Real-time PCR,qPCR)显示,肥厚型黄韧带组碱性成纤维细胞生长因子表达明显高于对照组;随后的ELISA分析显示,肥厚黄韧带组碱性成纤维细胞生长因子浓度明显高于对照组,这些结果提示,碱性成纤维细胞生长因子浓度与黄韧带厚度呈正相关。HAYASHI等[26]研究设计动物模型,探讨机械应力集中时黄韧带因子改变的潜在相关因素,采用免疫组织法检测成纤维细胞生长因子9蛋白的表达,结果发现成纤维细胞生长因子9蛋白在机械应力作用下增加,特别是在退行性改变的区域,推测成纤维细胞生长因子9有助于机械应力后黄韧带的退行性改变。 2.3.4 血管内皮生长因子 血管内皮生长因子是多种细胞功能的有效调节因子,功能包括增殖、分化、伤口愈合和血管生成,能诱导内皮细胞增殖,促进细胞迁移,抑制细胞凋亡,诱导血管通透性。JIRATHANATHORNNUKUL等[27]对在手术中获取的黄韧带组织进行血管内皮生长因子表达的定量及定位检测,qPCR检测肥厚型黄韧带组血管内皮生长因子表达明显高于非病理型黄韧带组;进一步ELISA分析显示,与对照组相比,增生性黄韧带中血管内皮生长因子的平均浓度明显升高;此外,免疫组化研究显示,与对照组的非病理性黄韧带相比,血管内皮生长因子在增生性黄韧带的成纤维细胞、炎性细胞和代表新生血管的内皮细胞上呈阳性染色。实验证明血管内皮生长因子的表达增加与肥厚型黄韧带的退行性改变有关,提示血管内皮生长因子可能参与了腰椎椎管狭窄症的发病机制之一。 2.3.5 胰岛素样生长因子 胰岛素样生长因子是一组具有促生长作用的多肽类物质。严斌[28]收集术中肥厚和正常的黄韧带组织,通过Western Blot检测两组黄韧带组织中胰岛素样生长因子1的表达情况,结果显示肥厚黄韧带组织中存在胰岛素样生长因子1显著表达,因此,推测胰岛素样生长因子的表达水平与黄韧带肥厚纤维化有密切关系。 2.3.6 血小板源性生长因子 血小板源性生长因子是一种可刺激结缔组织增生的常见肽类调节因子,能刺激血管平滑肌细胞、成纤维细胞、胶质细胞等多种细胞的分裂和增殖,在创伤愈合中作用突出。ZHANG等[29]以腰椎椎管狭窄症患者为研究实验组,以腰椎间盘突出症患者作为对照组,用免疫组化染色、qPCR和Western blot分析血小板源性生长因子BB的定位和表达。结果显示血小板源性生长因子BB在肥大的黄韧带中有表达,尤其在背侧层,腰椎椎管狭窄症组血小板源性生长因子BB表达高于腰椎间盘突出症组。该实验证明在腰椎椎管狭窄症患者黄韧带中存在较高的血小板源性生长因子BB表达,提示高表达的血小板源性生长因子BB可能是纤维化的危险因素。 2.3.7 潜在转化生长因子β结合蛋白 潜在转化生长因子β结合蛋白能在弹性纤维的结构组织或组装中起重要作用。Sidon等[30]将腰椎椎管狭窄症患者与腰椎间盘突出症患者的黄韧带组织进行比较,使用质谱法分析组织中蛋白质的变化,发现腰椎椎管狭窄症患者黄韧带组织内的潜在转化生长因子β结合蛋白2和4水平显著升高。由此,可以推测潜在转化生长因子β结合蛋白2和潜在转化生长因子β结合蛋白4的表达水平与黄韧带纤维化有着一定程度的相关性。 2.4 与黄韧带肥厚相关的通路 2.4.1 p38 MAPK 通路 p38MAPK通路可以介导TGF-β1/CTGF表达,在人腰椎黄韧带细胞增生肥厚过程中具有重要作用。曹延林[31]从手术所取的非肥厚的黄韧带标本进行原代培养,添加外源性转化生长因子β1及结缔组织生长因子,结果均显示黄韧带细胞明显增殖;而加入结缔组织生长因子中和抗体后可减少转化生长因子β1和结缔组织生长因子对黄韧带细胞增殖的效应;其后在细胞中加入p38MAPK通路抑制剂SB203580,发现抑制剂可以抑制转化生长因子β1诱导结缔组织生长因子,控制Ⅰ型胶原及Ⅲ型胶原蛋白mRNA的表达。另外,该研究发现转化生长因子β1可以提高p38表达和磷酸化的水平,并且实验证明在沉默p38 MAP后,p38、结缔组织生长因子、Ⅰ型胶原及Ⅲ型胶原蛋白mRNA的表达均下降。其进一步证实了p38通路是转化生长因子β1活化主要通路,p38具有成纤维活性。该研究认为转化生长因子β1通过p38 MAPK信号途径增加结缔组织生长因子表达,从而提高黄韧带细胞中胶原纤维数量,造成黄韧带纤维化。另有卢昌怀等[32]取腰椎椎管狭窄症术中的黄韧带组织分离培养黄韧带细胞,使用细胞外调节蛋白激酶通路阻断剂PD98059、c-Jun氨基末端激酶通路阻断剂SP600125、p38通路阻断剂SB203580处理黄韧带细胞,利用qPCR检测结缔组织生长因子、Ⅰ型胶原和Ⅲ型胶原mRNA的相对表达量。结果显示p38通路阻断剂SB203580可明显降低黄韧带细胞结缔组织生长因子、Ⅰ型胶原和Ⅲ型胶原mRNA相对表达量,上述实验表明TGF-β1/CTGF可以通过p38 MAPK通路协同参与黄韧带细胞增生肥厚的过程。 2.4.2 IGF-1R/AKT/mTORC1信号通路 严斌[28]收集术中肥厚和正常黄韧带组织,通过免疫组化和Western Blot检测两组黄韧带组织IGF-1R/AKT/mTORC1信号通路相关蛋白的表达情况。结果显示,肥厚的黄韧带组织中IGF-1R/AKT/mTORC1信号通路的活性相比于正常黄韧带组织明显增强,IGF-1R/AKT/mTORC1信号通路中的相关蛋白pIGF-1R、pAKT、pS6的表达也明显高于正常组。该实验表明IGF-1R/AKT/mTORC1信号通路与黄韧带细胞增生肥厚存在一定关联性。 2.5 与黄韧带肥厚相关的RNA 微小RNA(microRNA;miRNA)是生物界中普遍存在的可调控靶基因表达的一类非编码小RNA,其成熟体含22个核苷酸,miRNAs通过诱导翻译抑制和转录降解以达到负调控基因的表达[36]。miRNA作为内源性调控性RNA[37],影响靶向mRNA翻译水平的变化,进而参与细胞增殖、分化、凋亡、器官发育、免疫调节、代谢、炎症反应、死亡等生理病理过程[38]。越来越多的证据表明,miRNAs参与了许多生理过程,包括细胞增殖、分化和纤维化,但特异性miRNAs在黄韧带肥大中的作用尚不清楚。 2.5.1 miR-21 SUN等[33]在手术过程中采集黄韧带样本并采用RT-PCR检测miR-21在黄韧带组织中的表达,此外,构建miR-21模拟慢病毒载体并将其转染黄韧带细胞,以检测miR-21在黄韧带纤维化中的作用,以Ⅰ型和Ⅲ型胶原作纤维化指标,用RT-PCR和ELISA检测转染后黄韧带细胞白细胞介素6的表达。结果显示,腰椎椎管狭窄症组miR-21的表达明显高于腰椎间盘突出症组,同时值得注意的是,miR-21的过度表达增加了Ⅰ、Ⅲ型胶原的表达水平。转染miR-21模拟物后,黄韧带细胞白细胞介素6表达和分泌增加,证明miR-21是一种纤维化相关miRNA,可以通过激活白细胞介素6的表达促进黄韧带组织炎症,导致黄韧带纤维化和肥大。 2.5.2 miR-221 XU等[34]用miRNA芯片对收集的黄韧带组织进行miRNA表达的初步筛选。随后,经qPCR证实,腰椎椎管狭窄症患者黄韧带组织中miR-221明显低于对照组。此外,采用生物信息学靶点预测将TIMP-2作为miR-221的假定靶点,qPCR报告分析显示miR-221直接靶向TIMP-2并影响从黄韧带分离的成纤维细胞中TIMP-2的蛋白表达。值得注意的是,miR-221模拟了从黄韧带分离的成纤维细胞中胶原Ⅰ和胶原Ⅲ的mRNA和蛋白表达降低。由此可以推断miR-221的下调可能通过TIMP-2的诱导促进胶原Ⅰ和Ⅲ的表达而导致黄韧带肥大。 2.5.3 miR-155 JIANWEI 等[35]将术中收集的黄韧带组织分别进行检测,结果发现,腰椎椎管狭窄症患者黄韧带组织中Ⅰ、Ⅲ型胶原的表达明显高于腰椎间盘突出症患者。腰椎椎管狭窄症组黄韧带中miR-155的表达明显高于腰椎间盘突出症组,同时miR-155水平与Ⅰ型及Ⅲ型胶原水平呈正相关。另外添加的miR-155可提高黄韧带成纤维细胞Ⅰ型胶原和Ⅲ型胶原的mRNA和蛋白表达。该实验证明miR-155是一种纤维化相关的miRNA,可能在黄韧带肥大的发病机制中起重要作用。"

| [1] HENK VERBIEST. A Radicular Syndrome From Developmental Narrowing of the Lumbar Vertebral Canal. SAS Journal. 2009;3(2):77-84. [2] 何齐芳.老年性腰椎管狭窄的椎间孔镜治疗分析[J].中华全科医学, 2015,13(6):902-905. [3] MACHADO GC, MAHER CG, FERREIRA PH, et al. Trends, complications, and costs for hospital admission and surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine. 2017;42(22):1737-1743. [4] BENDITZ A, SPRENGER S, RAUCH L, et al. Increased pain and sensory hyperinnervation of the ligamentum flavum in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(3):737-743. [5] VIEJO-FUERTES D, LIGUORO D, RIVEL J, et al.Morphologic and histologic study of the ligamentum flavum in the thoraco-lumbar region. Surg Radiol Anat. 1998;20(3):171-176. [6] KOSAKA H, SAIRYO K, BIYANI A, et al. Pathomechanism of loss of elasticity and hypertrophy of lumbar ligamentum flavum in elderly patients with lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(25):2805-2811. [7] SCHRÄDER PK, GROB D, RAHN BA, et al. Histology of the ligamentum flavum in patients with degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J. 1999;8(4):323-328. [8] CHEN HB, CHEN M, PENG HH, et al. Relationship between the benefits of paraspinal mapping and diffusion tensor imaging and the increase of decompression levels determined by conventional magnetic resonance imaging in degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):23. [9] KIM BJ, HUR JW, PARK JS, et al. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in human ligamentum flavum cells treated with tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;24(3):428-435. [10] OH IS, HA KY.Matrix metalloproteinase-3 on ligamentum flavum in degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34(16):E552-E557. [11] PARK JB, KONG CG, SUHL KH, et al.The increased expression of matrix metalloproteinases associated with elastin degradation and fibrosis of the ligamentum flavum in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis.Clin Orthop Surg. 2009;1(2):81-89. [12] YABE Y, HAGIWARA Y, ANDO A, et al. Chondrogenic and fibrotic process in the ligamentum flavum of patients with lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Spine.2015;40(7):429-435. [13] LAKEMEIER S, SCHOFER MD, FOLTZ L, et al. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 [alpha], vascular endothelial growth factor, and matrix metalloproteinases 1, 3 and 9 in hypertrophied ligamentum flavum. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(7):400-406. [14] SAIRYO K, BIYANI A, GOEL VK , et al. Lumbar Ligamentum Flavum Hypertrophy Is Due to Accumulation of Inflammation-Related Scar Tissue. Spine. 2007;32(11):E340-E347. [15] NAKAMURA T, OKADA T, ENDO M, et al. Angiopoietin-like protein 2 promotes inflammatory conditions in the ligamentum flavum in the pathogenesis of lumbar spinal canal stenosis by activating interleukin-6 expression. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(9):2001-2009. [16] CHAO YH, TSUANG YH, SUN JS, et al. Centrifugal force in duces human ligamentum flavum fibroblasts inflammation through activation of JNK and p38 pathways. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014;27(7):382-389. [17] PARK JO, LEE BH, KANG YM, et al. Inflammatory cytokines induce fibrosis and ossification of human ligamentum flavum cells. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(1):E6-12. [18] KANG YM, SUK KS, LEE BH, et al. Herniated intervertebral disk induces hypertrophy and ossification of ligamentum flavum. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014;27(7):382-389. [19] SHAFAQ N, SUZUKI A, TERAI H, et al. Cellularity and cartilage matrix increased in hypertrophied ligamentum flavum: histopathological analysis focusing on the mechanical stress and bone morphogenetic protein signaling. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012;25(2):107-115. [20] TABATA M, KADOMATSU T, FUKUHARA S, et al. Angiopoietinlike protein 2 promotes chronic adipose tissue inflammation andobesity-related systemic insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2009;10(3):178-188. [21] AMUDONG A, MUHEREMU A, ABUDOUREXITI T. Hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum and expression of transforming growth factor beta.J Int Med Res. 2017;45(6):2036-2041. [22] NAKATANI T, MARUI T T, DOITA M, et al. Mechanical stretching force promotes collagen synthesis by cultured cells from human ligamentum flavum via transforming growth factor-beta1.J Orthop Res. 2002;20(6):1380-1386. [23] ZHONG ZM, CHEN JT. Overexpression of transforming growth factor-beta1 in degenerative ligamentum flavum. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2009;29(2):316-318. [24] LU C, LIU Z, ZHANG H, et al. Proliferation effect of ligamentum flavum cells induced by transforming growth factor β1 and its effect on connective tissue growth factor.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019;33(7):883-888. [25] HONSAWEK S, POONPUKDEE J, CHALERMPANPIPAT C, et al.Hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum in lumbar spinal canal stenosis is associated with increased bFGF expression. Int Orthop. 2013;37(7):1387-1392. [26] HAYASHI K, SUZUKI A, TERAI H, et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor 9 Is Upregulated Upon Intervertebral Mechanical Stress-Induced Ligamentum Flavum Hypertrophy in a Rabbit Model.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019;44(20):E1172-E1180. [27] JIRATHANATHORNNUKUL N, LIMTHONGKUL W, YINGSAKMONGKOL W, et al. Increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with hypertrophic ligamentum flavum in lumbar spinal canal stenosis.J Investig Med. 2016;64(4):882-887. [28] 严斌. IGF-1通过激活IGF-1R/AKT/mTORC1信号通路促进黄韧带增生肥厚[D].广州:南方医科大学,2018. [29] ZHANG Y, CHEN J, ZHONG ZM, et al. Is Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB Expression Proportional to Fibrosis in the Hypertrophied Lumber Ligamentum Flavum?. Spine.2010;35(25):E1479-E1486. [30] SIDON E, SHEMESH SS, MOR-YOSSEF MOLDOVAN L, et al. Molecular profile of ultrastructure changes of the ligamentum flavum related to lumbar spinal canal stenosis. J Cell Biochem. 2019 Mar 1.doi: 10.1002/jcb.28451. [31] 曹延林. p38 MAPK通路介导TGF-β1/CTGF调控人黄韧带肥厚增生的实验研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2015. [32] 卢昌怀,刘志军,张宏波,等.p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路介导TGF-β1/结缔组织生长因子调控人腰椎黄韧带增生肥厚的机制研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2019,33(6):730-735. [33] SUN C, TIAN J, LIU X, et al. MiR-21 promotes fibrosis and hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum in lumbar spinal canal stenosis by activating IL-6 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;490(3):1106-1111. [34] XU YQ, ZHANG ZH, ZHENG YF, et al. MicroRNA-221 Regulates Hypertrophy of Ligamentum Flavum in Lumbar Spinal Stenosis by Targeting TIMP-2.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41(4):275-282. [35] JIANWEI C, ZUDE L, GUIBIN Z, et al. Hypertrophy of Ligamentum Flavum in Lumbar Spine Stenosis Is Associated with Increased miR-155 Level. Dis Markers. 2014;2014:786543. [36] HAN JJ, TAN HF, FENG C, et al. Data on cell spread area and directional contraction in human umbilicalvein endothelial cells on fibronectin and on collagen type I-coated micro-posts. Data Brief. 2016;6:803-810. [37] POORMASJEDI‐MEIBOD MS, SALIMI ELIZEI S, LEUNG V, et al.Kynurenine Modulates MMP‐1 and Type‐I Collagen Expression Via Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation in Dermal Fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 2016;231(12):2749-2760. [38] FABIAN M R, SONENBERG N, FILIPOWICZ W. Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 2010;79: 351-379. |
| [1] | Wu Xun, Meng Juanhong, Zhang Jianyun, Wang Liang. Concentrated growth factors in the repair of a full-thickness condylar cartilage defect in a rabbit [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1166-1171. |
| [2] | Yuan Mei, Zhang Xinxin, Guo Yisha, Bi Xia. Diagnostic potential of circulating microRNA in vascular cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [3] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [4] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [5] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [6] | Li Cai, Zhao Ting, Tan Ge, Zheng Yulin, Zhang Ruonan, Wu Yan, Tang Junming. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of skeletal muscle myoblast [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1050-1055. |
| [7] | Luo Xuanxiang, Jing Li, Pan Bin, Feng Hu. Effect of mecobalamine combined with mouse nerve growth factor on nerve function recovery after cervical spondylotic myelopathy surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 719-722. |
| [8] | Nie Huijuan, Huang Zhichun. The role of Hedgehog signaling pathway in transforming growth factor beta1-induced myofibroblast transdifferentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 754-760. |
| [9] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [10] | Shi Qin, Sun Baolan, Yang Xiaoqing, Zhang Yuquan . Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes carrying miRNAs in tissue repair and treatment of related diseases: application and advantages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 5040-5045. |
| [11] | Wei Xiaoling, Hu Weiping, Liu Mingyue, Shi Xin, Liu Jie, Gao Li, Wang Siran, Duan Yajun. Dental pulp fibroblasts inducing and regulating dentin-pulp regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 5079-5084. |
| [12] | Li Jie, Ma Yuewen, Kang Nan, Zhang Jing, Zhang Yu. Radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy promotes the proliferation of neural stem cells in hippocampus of cerebral infarction rats and inhibits miR-124 expression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 4981-4987. |
| [13] | Liu Lei, Di Haiping, Guo Haina, Cao Dayong, Niu Xihua, Xia Chengde. Changes in biological characteristics of platelet-rich fibrin by freeze-drying technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 4995-4999. |
| [14] | Zheng Feng, Zhang Fucai, Xu Zhe. MicroRNA-98-5p promotes osteoblast proliferation and differentiation: possibilities and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(26): 4112-4117. |
| [15] | Qin Jianfang, Wang Huan, Wu Bingbing, Ma Xiaojing. Effect of GOLM1 gene knockout on renal fibrosis in mice with unilateral ureteral obstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(26): 4162-4167. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||