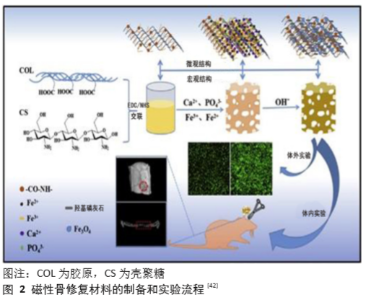
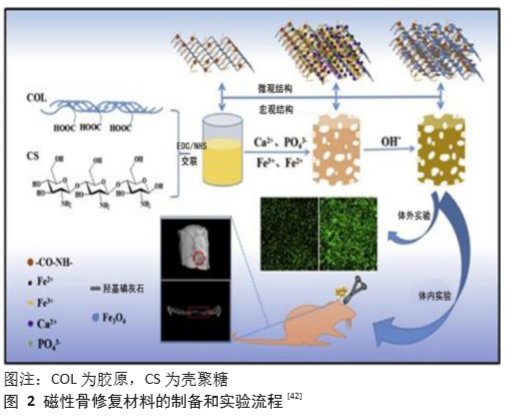
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (28): 4510-4515.doi: 10.12307/2021.066
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biological effect of magnetic fields to promote bone responses to biomaterials
Li Ruozhen1, Tian Yaping2, Wen Ning1
- 1Department of Stomatology, First Medical Center, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China; 2Core Laboratory of Translational Medicine, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China
-
Received:2020-06-22Revised:2020-06-30Accepted:2020-07-29Online:2021-10-08Published:2021-05-20 -
Contact:Wen Ning, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Stomatology, First Medical Center, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China Tian Yaping, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Core Laboratory of Translational Medicine, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China -
About author:Li Ruozhen, Doctoral candidate, Attending physician, Department of Stomatology, First Medical Center, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 51972339 (to WN)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Ruozhen, Tian Yaping, Wen Ning. Biological effect of magnetic fields to promote bone responses to biomaterials[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(28): 4510-4515.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] MOHAJERANI H, TABEIE F, VOSSOUGHI F, et al. Effect of pulsed electromagnetic field on mandibular fracture healing: A randomized control trial(RCT). J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019;120(5): 390-396. [2] BAMBINI F, SANTARELLI A, PUTIGNANO A, et al. Use of supercharged cover screw as static magnetic field generator for bone healing, 1st part: in vitro enhancement of osteoblast-like cell differentiation. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2017;31(1):215-220. [3] ZHENG L, ZHANG L, CHEN L, et al. Static magnetic field regulates proliferation, migration, differentiation, and YAP/TAZ activation of human dental pulp stem cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(10):2029-2040. [4] PAUN IA, CALIN BS, MUSTACIOSU CC, et al. 3D Superparamagnetic Scaffolds for Bone Mineralization under Static Magnetic Field Stimulation. Materials (Basel). 2019;12(17):2834. [5] DU L, FAN H, MIAO H, et al. Extremely low frequency magnetic fields inhibit adipogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells. Bioelectromagnetics. 2014;35(7):519-530. [6] KIM EC, PARK J, KWON IK, et al. Static magnetic fields promote osteoblastic/cementoblastic differentiation in osteoblasts, cementoblasts, and periodontal ligament cells. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2017;47(5):273-291. [7] EHNERT S, VAN GRIENSVEN M, UNGER M, et al. Co-Culture with Human Osteoblasts and Exposure to Extremely Low Frequency Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields Improve Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(4):994. [8] YANG J, ZHANG J, DING C, et al. Regulation of Osteoblast Differentiation and Iron Content in MC3T3-E1 Cells by Static Magnetic Field with Different Intensities. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2018;184(1):214-225. [9] YAN JL, ZHOU J, MA HP, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields promote osteoblast mineralization and maturation needing the existence of primary cilia. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015;404:132-140. [10] VERONESI F, FINI M, SARTORI M, PARRILLI A, MARTINI L, TSCHON M. Pulsed electromagnetic fields and platelet rich plasma alone and combined for the treatment of wear-mediated periprosthetic osteolysis: An in vivo study. Acta Biomater. 2018;77:106-115. [11] KIM EC, PARK J, NOH G, et al. Effects of moderate intensity static magnetic fields on osteoclastic differentiation in mouse bone marrow cells. Bioelectromagnetics. 2018;39(5):394-404. [12] WU S, YU Q, LAI A, TIAN J. Pulsed electromagnetic field induces Ca2+-dependent osteoblastogenesis in C3H10T1/2 mesenchymal cells through the Wnt-Ca2+/Wnt-β-catenin signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;503(2):715-721. [13] JING D, ZHAI M, TONG S, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields promote osteogenesis and osseointegration of porous titanium implants in bone defect repair through a Wnt/β-catenin signaling-associated mechanism. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32045. [14] ZHANG Y, LI W, LIU C, et al. Electromagnetic field treatment increases purinergic receptor P2X7 expression and activates its downstream Akt/GSK3β/β-catenin axis in mesenchymal stem cells under osteogenic induction. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):407.[15] ROTHERHAM M, HENSTOCK JR, QUTACHI O, et al. Remote regulation of magnetic particle targeted Wnt signaling for bone tissue engineering. Nanomedicine. 2018;14(1):173-184. [16] PI Y, LIANG H, YU Q, et al. Low frequency pulsed electromagnetic field inhibits RANKL induced osteoclastic differentiation in RAW264.7 cells by scavenging reactive oxygen species. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(5): 4129-4136. [17] FATHI E, FARAHZADI R. Enhancement of osteogenic differentiation of rat adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells by zinc sulphate under electromagnetic field via the PKA, ERK1/2 and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways. PLoS One. 2017;12(3):e0173877. [18] YANG X, HE H, GAO Q, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic field improves subchondral bone microstructure in knee osteoarthritis rats through a Wnt/β-catenin signaling-associated mechanism. Bioelectromagnetics. 2018;39(2):89-97. [19] YUN HM, AHN SJ, PARK KR, et al. Magnetic nanocomposite scaffolds combined with static magnetic field in the stimulation of osteoblastic differentiation and bone formation. Biomaterials. 2016;85:88-98. [20] REN Q, ZHOU J, WANG MG, et al. Pulsed Electromagnetic fields stimulating osteogenic differentiation and maturation involves primary cilia-PI3K/AKT pathway.Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019;51(2): 245-251. [21] MIYAMOTO H, SAWAJI Y, IWAKI T, et al. Intermittent pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation activates the mTOR pathway and stimulates the proliferation of osteoblast-like cells. Bioelectromagnetics. 2019;40(6):412-421. [22] KIM EC, LEESUNGBOK R, LEE SW, et al. Effects of static magnetic fields on bone regeneration of implants in the rabbit: micro-CT, histologic, microarray, and real-time PCR analyses. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2017; 28(4):396-405. [23] BAMBINI F, SANTARELLI A, PUTIGNANO A, et al. Use of supercharged cover screw as static magnetic field generator for bone healing, 2nd part: in vivo enhancement of bone regeneration in rabbits. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2017;31(2):481-485. [24] GUJJALAPUDI M, ANAM C, MAMIDI P, et al. Effect of magnetic field on bone healing around endosseous implants - An in-vivo study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016;10(10):ZF01-ZF04. [25] KATARIVAS LEVY G, BIRCH MA, BROOKS RA, et al. Stimulation of human osteoblast differentiation in magneto-mechanically actuated ferromagnetic fiber networks. J Clin Med. 2019;8(10):1522. [26] BLOISE N, PETECCHIA L, CECCARELLI G, et al. The effect of pulsed electromagnetic field exposure on osteoinduction of human mesenchymal stem cells cultured on nano-TiO2 surfaces. PLoS One. 2018;13(6):e0199046. [27] BAO Z, FAN M, MA L, et al. The effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields combined with a static magnetic intramedullary implant on the repair of bone defects: A preliminary study. Electromagn Biol Med. 2019;38(3):210-217. [28] BARAK S, NEUMAN M, IEZZI G, et al. A new device for improving dental implants anchorage: a histological and micro-computed tomography study in the rabbit. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016;27(8):935-942. [29] BARAK S, MATALON S, DOLKART O, et al. Miniaturized electromagnetic device abutment improves stability of the dental implants. J Craniofac Surg. 2019;30(4):1055-1057. [30] OTTANI V, RASPANTI M, MARTINI D, et al. Electromagnetic stimulation on the bone growth using backscattered electron imaging. Micron. 2002;33(2):121-125. [31] FINI M, GIAVARESI G, GIARDINO R, et al. Histomorphometric and mechanical analysis of the hydroxyapatite-bone interface after electromagnetic stimulation: an experimental study in rabbits. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88(1):123-128. [32] ZHUO X, LI C, LI B, et al. Effects of combined magnetic fields treatment and nano-hydroxyapatite coating on porous biphasic calcium phosphate bone graft in rabbit spinal fusion model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018;43(11):E625-E633. [33] XIA Y, CHEN H, ZHAO Y, et al. Novel magnetic calcium phosphate-stem cell construct with magnetic field enhances osteogenic differentiation and bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;98:30-41. [34] SINGH RK, PATEL KD, LEE JH, et al. Potential of magnetic nanofiber scaffolds with mechanical and biological properties applicable for bone regeneration. PLoS One. 2014;9(4):e91584. [35] SHANKHWAR N, SRINIVASAN A. Evaluation of sol-gel based magnetic 45S5 bioglass and bioglass-ceramics containing iron oxide. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;62:190-196. [36] ADAMS CF, PICKARD MR, CHARI DM. Magnetic nanoparticle mediated transfection of neural stem cell suspension cultures is enhanced by applied oscillating magnetic fields. Nanomedicine. 2013;9(6):737-741. [37] HUANG Z, WU Z, MA B, et al. Enhanced in vitrobiocompatibility and osteogenesis of titanium substrates immobilized with dopamine-assisted superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles for hBMSCs. R Soc Open Sci. 2018;5(8):172033. [38] USKOKOVIĆ V, GRAZIANI V, WU VM, et al. Gold is for the mistress, silver for the maid: Enhanced mechanical properties, osteoinduction and antibacterial activity due to iron doping of tricalcium phosphate bone cements. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;94:798-810. [39] ZHU Y, LI Z, ZHANG Y, et al. The essential role of osteoclast-derived exosomes in magnetic nanoparticle-infiltrated hydroxyapatite scaffold modulated osteoblast proliferation in an osteoporosis model. Nanoscale. 2020;12(16):8720-8726. [40] LI X, ZOU Q, MAN Y, et al. Synergistic effects of novel superparamagnetic/upconversion HA material and Ti/magnet implant on biological performance and long-term in vivo tracking. Small. 2019; 15(31):e1901617. [41] ZHAO Y, FAN T, CHEN J, et al. Magnetic bioinspired micro/nanostructured composite scaffold for bone regeneration. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019;174:70-79. [42] PAUN IA, POPESCU RC, CALIN BS, et al. 3D Biomimetic Magnetic Structures for Static Magnetic Field Stimulation of Osteogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(2):495. [43] YANG Y, REN S, ZHANG X, et al. Safety and efficacy of PLGA(Ag-Fe3O4)-coated dental implants in inhibiting bacteria adherence and osteogenic inducement under a magnetic field. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13: 3751-3762. [44] WANG H, TANG X, LI W, et al. Enhanced osteogenesis of bone marrow stem cells cultured on hydroxyapatite/collagen I scaffold in the presence of low-frequency magnetic field. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;30(8):89. [45] OLTEAN-DAN D, DOGARU GB, TOMOAIA-COTISEL M, et al. Enhancement of bone consolidation using high-frequency pulsed electromagnetic short-waves and titanium implants coated with biomimetic composite embedded into PLA matrix: in vivo evaluation. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:5799-5816. [46] D’AMORA U, RUSSO T, GLORIA A, et al. 3D additive-manufactured nanocomposite magnetic scaffolds: Effect of the application mode of a time-dependent magnetic field on hMSCs behavior. Bioact Mater. 2017;2(3):138-145. [47] RUSSO T, PELUSO V, GLORIA A, et al. Combination Design of Time-Dependent Magnetic Field and Magnetic Nanocomposites to Guide Cell Behavior. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020;10(3):577. [48] CHEN J, TU C, TANG X, et al. The combinatory effect of sinusoidal electromagnetic field and VEGF promotes osteogenesis and angiogenesis of mesenchymal stem cell-laden PCL/HA implants in a rat subcritical cranial defect. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):379. [49] HUANG WS, CHU IM. Injectable polypeptide hydrogel/inorganic nanoparticle composites for bone tissue engineering. PLoS One. 2019; 14(1):e0210285. [50] ZHUANG J, LIN S, DONG L, et al. Magnetically actuated mechanical stimuli on Fe3O4/mineralized collagen coatings to enhance osteogenic differentiation of the MC3T3-E1 cells. Acta Biomater. 2018;71:49-60. [51] ZE Q, KUANG X, WU S, et al. Magnetic Shape Memory Polymers with Integrated Multifunctional Shape Manipulation. Adv Mater. 2020;32(4): e1906657. [52] BOCK N, RIMINUCCI A, DIONIGI C, et al. A novel route in bone tissue engineering: magnetic biomimetic scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(3): 786-796. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [3] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| [4] | Liang Yan, Zhao Yongfei, Xu Shuai, Zhu Zhenqi, Wang Kaifeng, Liu Haiying, Mao Keya. Imaging evaluation of short-segment fixation and fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis assisted by highly selective nerve root block [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1423-1427. |
| [5] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [6] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [7] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [8] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [9] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [10] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [11] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [12] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [13] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [14] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [15] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||