Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (28): 4473-4479.doi: 10.12307/2021.060
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation of alginate-gelatin-adipose-derived stem cells microspheres by electrospray and feasibility on repairing articular cartilage injury
Liao Sida1,2, Meng Haoye2, Li Junkang2, Xu Yichi2, Li Huo2, Tian Xiaoyu1, Feng Yong2, Wang Aiyuan2, Peng Jiang2
- 1Medical School of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100853, China; 2Institute Orthopedics, The First Medical Center of the PLA General Hospital, Beijing Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine in Orthopedics, Key Laboratory of Musculoskeletal Trauma & War Injuries, PLA, Beijing 100853, China
-
Received:2020-07-15Revised:2020-07-17Accepted:2020-08-22Online:2021-10-08Published:2021-05-19 -
Contact:Peng Jiang, Researcher, Institute Orthopedics, The First Medical Center of the PLA General Hospital, Beijing Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine in Orthopedics, Key Laboratory of Musculoskeletal Trauma & War Injuries, PLA, Beijing 100853, China -
About author:Liao Sida, Master candidate, Medical School of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100853, China; Institute Orthopedics, The First Medical Center of the PLA General Hospital, Beijing Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine in Orthopedics, Key Laboratory of Musculoskeletal Trauma & War Injuries, PLA, Beijing 100853, China -
Supported by:the National natural science foundation of china, no. 81972047 (to pj); the national key research and development program, no. 2016YFC1102104 (to PJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liao Sida, Meng Haoye, Li Junkang, Xu Yichi, Li Huo, Tian Xiaoyu, Feng Yong, Wang Aiyuan, Peng Jiang. Preparation of alginate-gelatin-adipose-derived stem cells microspheres by electrospray and feasibility on repairing articular cartilage injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(28): 4473-4479.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
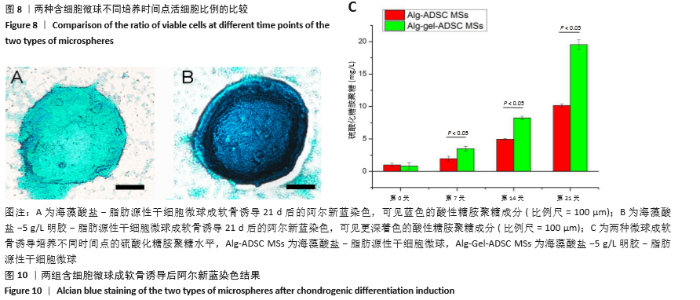
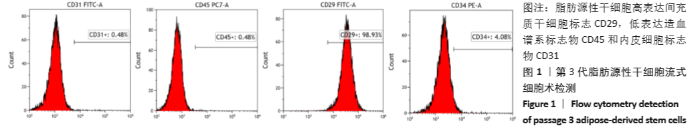
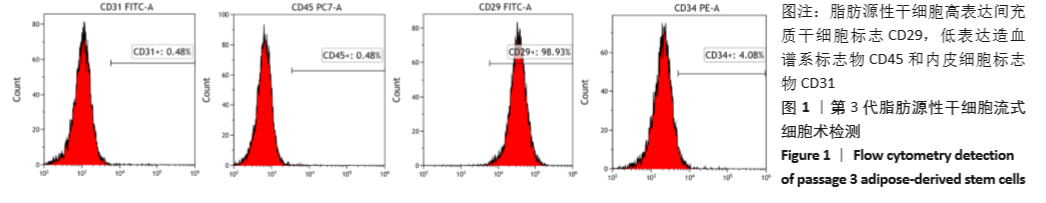
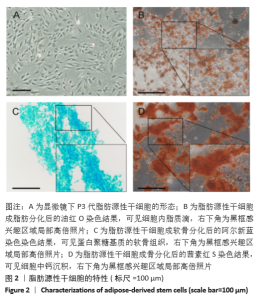
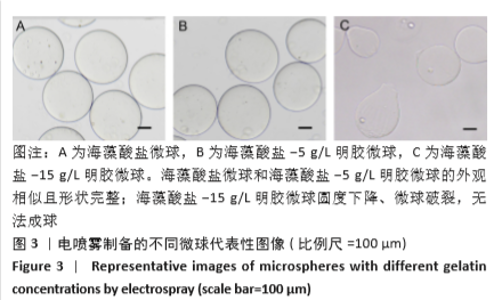
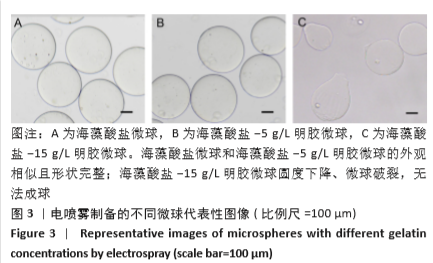
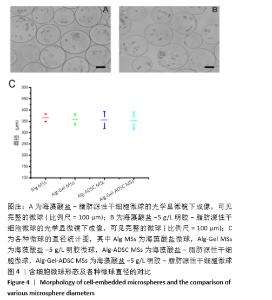
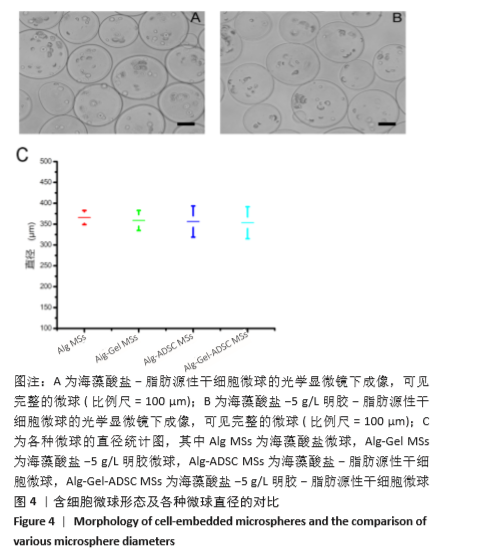
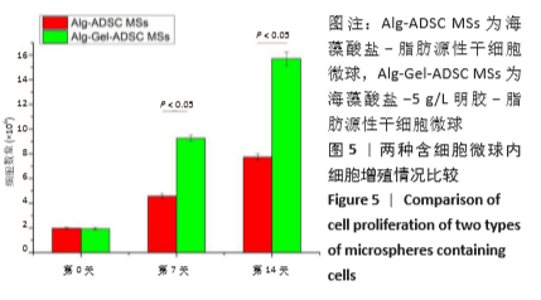
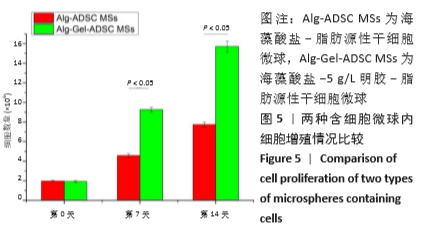
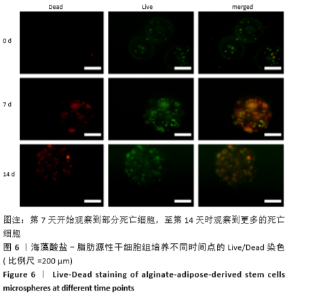
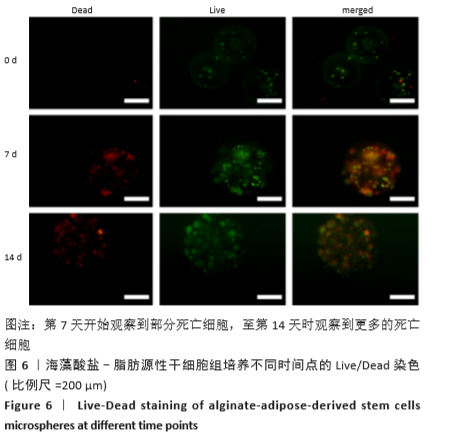
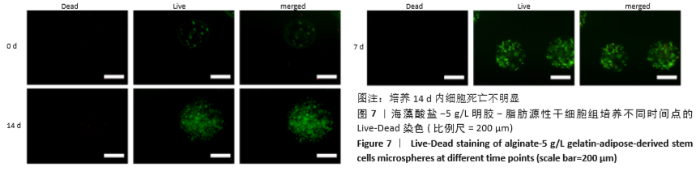
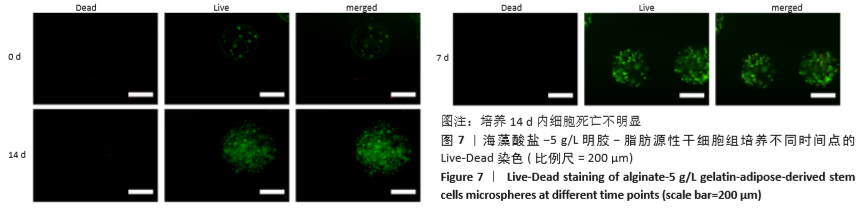
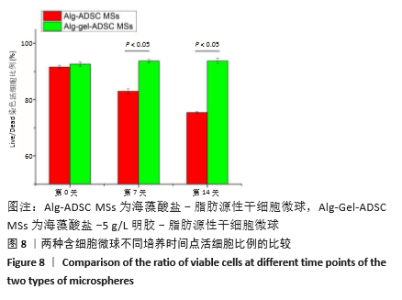
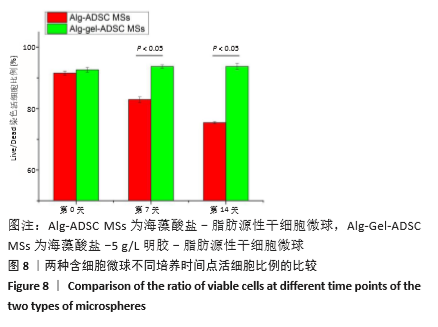
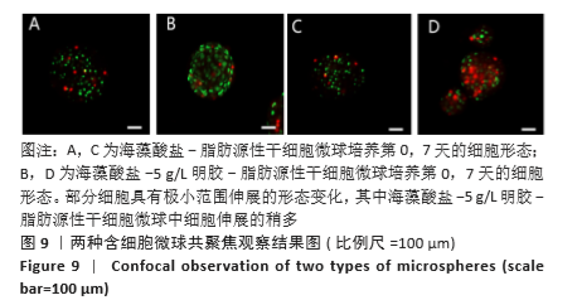
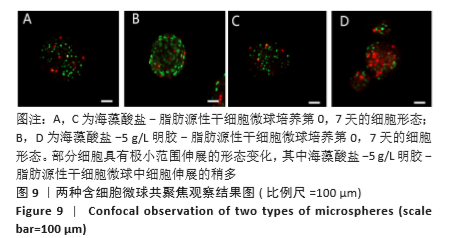
2.8 含细胞微球的成软骨能力 成软骨诱导培养基诱导21 d后分阿尔新蓝染色显示,海藻酸盐-ADSCs微球内含有可被阿尔新蓝染色为蓝色的酸性糖胺聚糖成分,见图10A;海藻酸盐-5 g/L明胶-ADSCs微球诱导后的染色着色更深,见图10B,且两组使用相同种类、浓度的阿尔新蓝染色液,进行相同的染色时间,保证了染色方法两组间均一,证实了海藻酸盐-5 g/L明胶-ADSCs微球有更多的细胞外基质沉积,使着色更深。硫酸化糖胺聚糖定量分析结果显示,随着诱导时间的增加,两种含细胞微球内的硫酸化糖胺聚糖水平增加,与染色定性实验相似,海藻酸盐-5 g/L明胶-ADSCs微球诱导培养第7,14,21天分泌的硫酸化糖胺聚糖水平高于海藻酸盐-ADSCs微球[第7天:(3.50±0.64),(1.96±0.64) mg/L, P < 0.05;第14天:(8.24±0.42),(4.93±0.24) mg/L,P < 0.05;第21天:(19.54±1.28),(10.15±0.43) mg/L,P < 0.05],见图10C。"

| [1] KRISHNAN Y, GRODZINSKY AJ. Cartilage diseases. Matrix Biol. 2018;71-72: 51-69. [2] VACANTI CA, LANGER R, SCHLOO B, et al. Synthetic polymers seeded with chondrocytes provide a template for new cartilage formation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1991;88(5):753-759. [3] HOLLAND TA, BODDE EW, CUIJPERS VM, et al. Degradable hydrogel scaffolds for in vivo delivery of single and dual growth factors in cartilage repair. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007;15(2):187-197. [4] BASIRI A, FAROKHI M, AZAMI M, et al. A silk fibroin/decellularized extract of Wharton’s jelly hydrogel intended for cartilage tissue engineering. Prog Biomater. 2019;8(1):31-42 [5] GAO J, DENNIS JE, SOLCHAGA LA, et al. Tissue-engineered fabrication of an osteochondral composite graft using rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(4):363-371. [6] CASTRO-VIÑUELAS R, SANJURJO-RODRÍGUEZ C, PIÑEIRO-RAMIL M, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cells for cartilage repair: current status and future perspectives. Eur Cell Mater. 2018;36:96-109. [7] HAN Y, LI X, ZHANG Y, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Regenerative Medicine. Cells. 2019;8(8):886 [8] PAK J, LEE JH, KARTOLO WA, et al. Cartilage Regeneration in Human with Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells: Current Status in Clinical Implications. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:4702674. [9] 严波,凌晓宇,童培建,等.脂肪干细胞对膝骨关节炎疼痛及软骨修复的影响[J].中国现代医学杂志,2020,30(3):1-6. [10] ZHU Y, LIU T, SONG K, et al. Adipose-derived stem cell: a better stem cell than BMSC. Cell Biochem Funct. 2008;26(6):664-675. [11] CHEN XY, CHEN JY, TONG XM, et al. Recent advances in the use of microcarriers for cell cultures and their ex vivo and in vivo applications.Biotechnol Lett. 2020;42(1):1-10. [12] HONG Y, GAO C, XIE Y, et al. Collagen-coated polylactide microspheres as chondrocyte microcarriers. Biomaterials. 2005;26(32):6305-6313. [13] CHOI YS, PARK SN, SUH H. Adipose tissue engineering using mesenchymal stem cells attached to injectable PLGA spheres. Biomaterials. 2005;26(29): 5855-5863. [14] VAN WEZEL AL. Growth of cell-strains and primary cells on micro-carriers in homogeneous culture. Nature. 1967;216(5110):64-65. [15] MARTIN Y, ELDARDIRI M, LAWRENCE-WATT DJ, et al. Microcarriers and their potential in tissue regeneration. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2011;17(1):71-80. [16] SOLORIO LD, VIEREGGE EL, DHAMI CD, et al. High-density cell systems incorporating polymer microspheres as microenvironmental regulators in engineered cartilage tissues. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2013;19(3):209-220. [17] SUN J, TAN H. Alginate-Based Biomaterials for Regenerative Medicine Applications. Materials (Basel). 2013;6(4):1285-1309. [18] AB-RAHIM S, SELVARATNAM L, RAGHAVENDRAN HR, et al. Chondrocyte-alginate constructs with or without TGF-β1 produces superior extracellular matrix expression than monolayer cultures. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013;376(1-2): 11-20. [19] LEE KY, MOONEY DJ. Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering. Chem Rev. 2001; 101(7):1869-1879. [20] XU M, WANG X, YAN Y, et al. An cell-assembly derived physiological 3D model of the metabolic syndrome, based on adipose-derived stromal cells and a gelatin/alginate/fibrinogen matrix. Biomaterials. 2010;31(14): 3868-3877. [21] SHIMIZU M, MATSUMINE H, OSAKI H, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells and the stromal vascular fraction in polyglycolic acid-collagen nerve conduits promote rat facial nerve regeneration. Wound Repair Regen. 2018;26(6): 446-455. [22] UYEN NTT, HAMID ZAA, TRAM NXT, et al. Fabrication of alginate microspheres for drug delivery: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;153: 1035-1046. [23] BAJEK A, GURTOWSKA N, OLKOWSKA J, et al. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells as a Tool in Cell-Based Therapies. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2016;64(6): 443-454. [24] ASTORI G, VIGNATI F, BARDELLI S, et al. “In vitro” and multicolor phenotypic characterization of cell subpopulations identified in fresh human adipose tissue stromal vascular fraction and in the derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Transl Med. 2007;5:55. [25] BARBA M, DI TARANTO G, LATTANZI W. Adipose-derived stem cell therapies for bone regeneration. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2017;17(6):677-689. [26] 谢盼盼,叶方,叶积飞.距骨软骨损伤的诊疗进展[J].中国骨伤,2018, 31(9):880-884. [27] ARMIENTO AR, STODDART MJ, ALINI M, et al. Biomaterials for articular cartilage tissue engineering: Learning from biology. Acta Biomater. 2018;65: 1-20. [28] CALDWELL KL, WANG J. Cell-based articular cartilage repair: the link between development and regeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015; 23(3):351-362. [29] ORTVED KF, NIXON AJ. Cell-based cartilage repair strategies in the horse. Vet J. 2016;208:1-12. [30] MA Q, LIAO J, CAI X. Different Sources of Stem Cells and their Application in Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;13(7):568-575 [31] VERONESI F, MAGLIO M, TSCHON M, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage tissue engineering: state-of-the-art in in vivo studies. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(7):2448-2466. [32] BURKE J, HUNTER M, KOLHE R, et al. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell based therapy for osteoarthritis. ClinTransl Med. 2016;5(1):27. [33] WANG Y, YUAN X, YU K, et al. Fabrication of nanofibrousmicrocarriers mimicking extracellular matrix for functional microtissue formation and cartilage regeneration. Biomaterials. 2018;171:118-132. [34] ZAMANI M, PRABHAKARAN MP, RAMAKRISHNA S. Advances in drug delivery via electrospun and electrosprayednanomaterials. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:2997-3017. [35] HAO S, WANG Y, WANG B, et al. Formulation of porous poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microparticles by electrospray deposition method for controlled drug release. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;39:113-119. [36] JAYARAMAN P, GANDHIMATHI C, VENUGOPAL JR, et al. Controlled release of drugs in electrosprayed nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;94:77-95. [37] MA Z, JI H, TENG Y, et al. Engineering and optimization of nano- and mesoporous silica fibers using sol-gel and electrospinning techniques for sorption of heavy metal ions. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2011;358(2):547-553. [38] VENKATESAN J, BHATNAGAR I, MANIVASAGAN P, et al. Alginate composites for bone tissue engineering: a review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;72:269-281. [39] JAYASURIYA CT, CHEN Y, LIU W, et al.The influence of tissue microenvironment on stem cell-based cartilage repair. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2016;1383(1):21-33. [40] AXPE E, OYEN ML. Applications of Alginate-Based Bioinks in 3D Bioprinting. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(12):1976. [41] RASTOGI P, KANDASUBRAMANIAN B. Review of alginate-based hydrogel bioprinting for application in tissue engineering. Biofabrication. 2019;11(4): 042001. [42] ECHAVE MC, HERNÁEZ-MOYA R, ITURRIAGA L, et al. Recent advances in gelatin-based therapeutics. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2019;19(8):773-779. [43] FU N, DONG T, MENG A, et al. Research progress of the types and preparation techniques of scaffold materials in cartilage tissue engineering. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;13(7):583-590. [44] OHTA S, NITTA N, WATANABE S, et al. Gelatin microspheres: correlation between embolic effect/degradability and cross-linkage/particle size. CardiovascInterventRadiol. 2013;36(4):1105-1111. [45] DHAMECHA D, MOVSAS R, SANO U, et al. Applications of alginate microspheres in therapeutics delivery and cell culture: Past, present and future. Int J Pharm. 2019;569:118627. |
| [1] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [2] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| [3] | Liang Yan, Zhao Yongfei, Xu Shuai, Zhu Zhenqi, Wang Kaifeng, Liu Haiying, Mao Keya. Imaging evaluation of short-segment fixation and fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis assisted by highly selective nerve root block [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1423-1427. |
| [4] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [5] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [6] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [7] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [8] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [9] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [10] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [11] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [12] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [13] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [14] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [15] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||