Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (28): 4447-4453.doi: 10.12307/2021.056
Previous Articles Next Articles
Three-dimensional printed artificial bone loaded with anti-tuberculosis drugs and bone morphogenetic protein 2 sustained-release microspheres can promote osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Liu Changhao1, Zheng Jianping2, Shi Jiandang3, Zhu Xi3, Zhou Zhanwen1, Zhang Xu1
- 1School of Clinical Medicine, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Orthopedic Trauma, 3Department of Spinal Orthopedics, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2020-09-08Revised:2020-09-09Accepted:2020-10-09Online:2021-10-08Published:2021-05-15 -
Contact:Shi Jiandang, Doctoral supervisor, Chief physician, Department of Spinal Orthopedics, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Liu Changhao, Master candidate, School of Clinical Medicine, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China Zheng Jianping, Doctoral candidate, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedic Trauma, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750000, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 8176090169 (to SJD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Changhao, Zheng Jianping, Shi Jiandang, Zhu Xi, Zhou Zhanwen, Zhang Xu. Three-dimensional printed artificial bone loaded with anti-tuberculosis drugs and bone morphogenetic protein 2 sustained-release microspheres can promote osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(28): 4447-4453.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
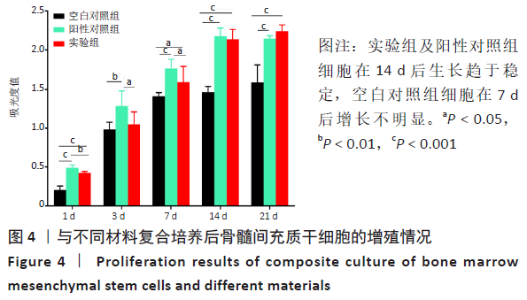
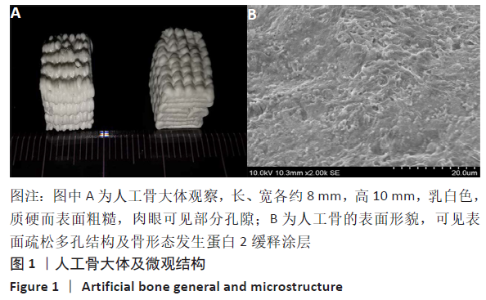
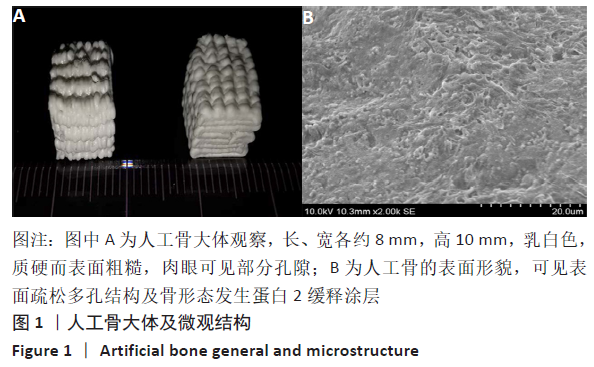
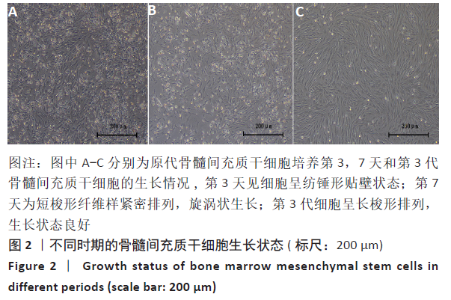
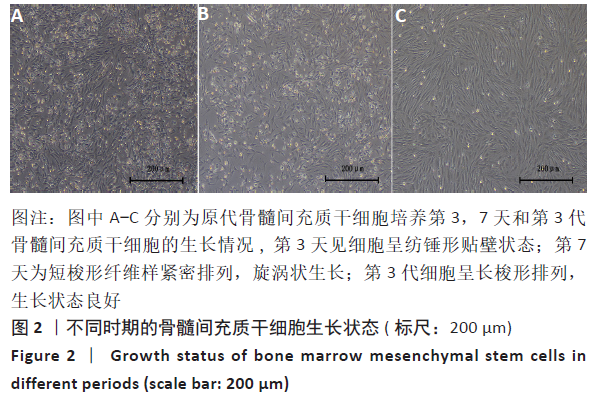
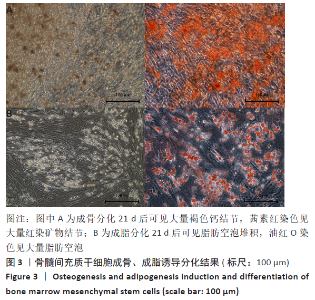
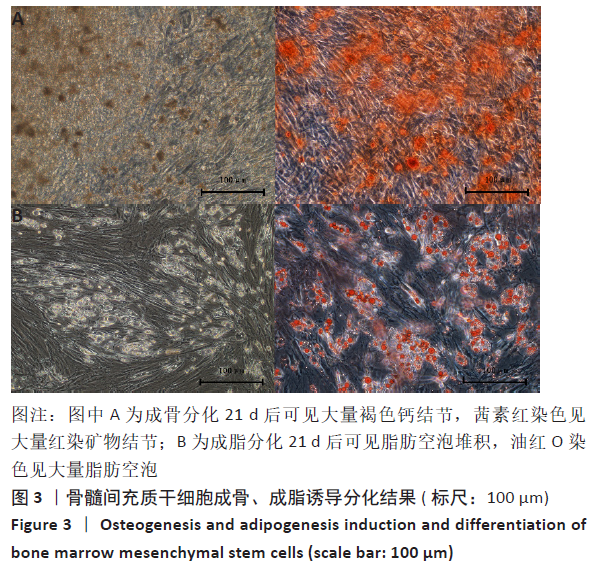
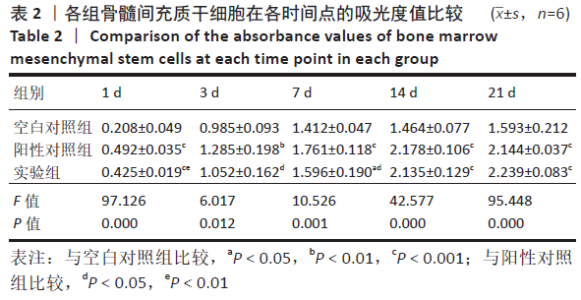
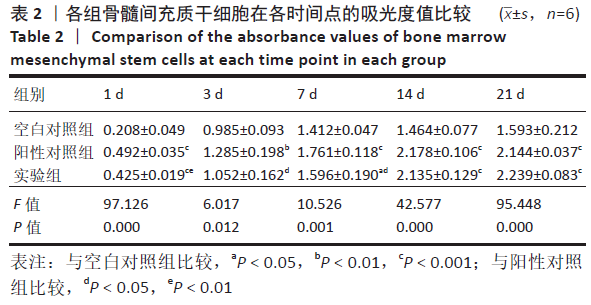
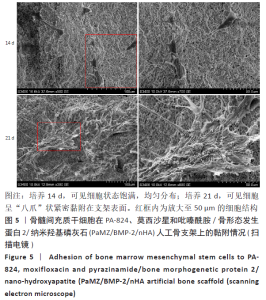
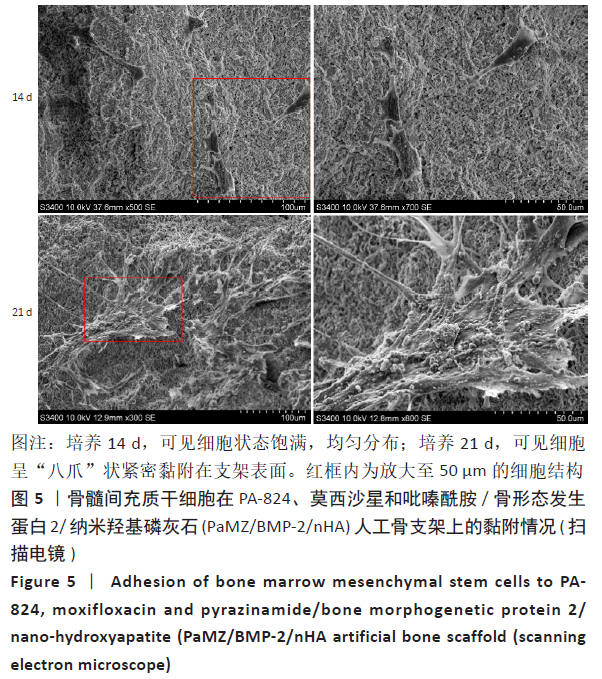
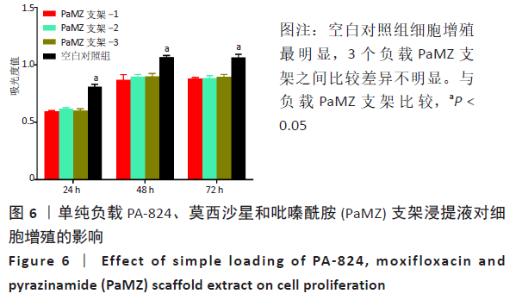
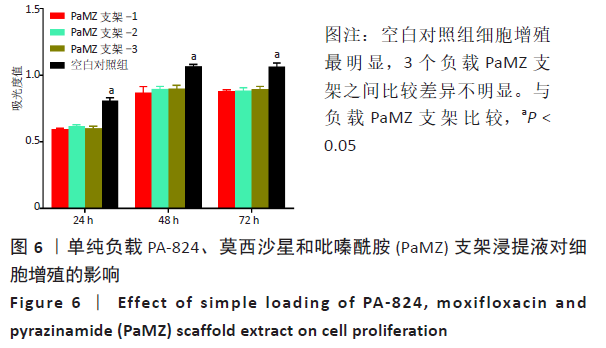
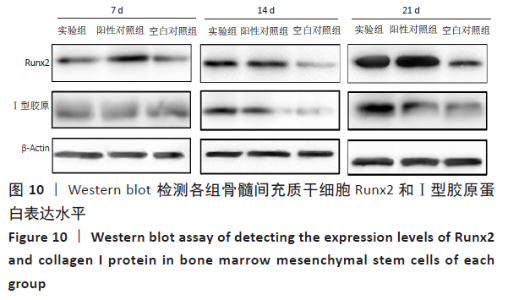
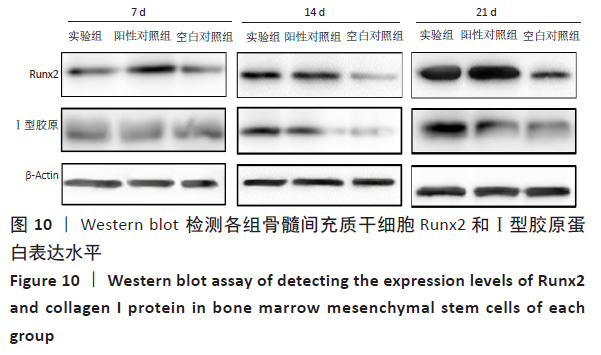
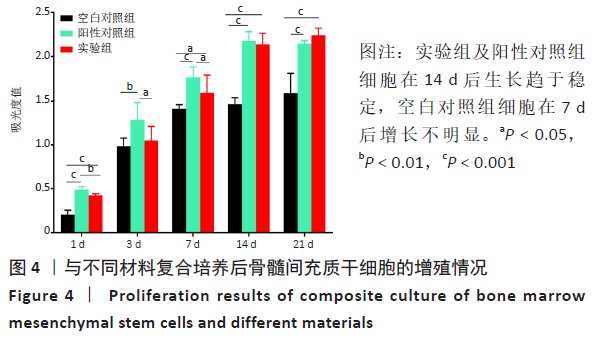
2.3 PaMZ/BMP-2/nHA人工骨生物相容性 2.3.1 人工骨对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖的影响 根据PaMZ/BMP-2/nHA人工骨的释药特性和力学强度,取药物配比为Pa∶M∶Z∶PLGA=3∶12∶45∶140复合人工骨与第3代骨髓间充质干细胞共培养。培养1,3,7,14,21 d后,检测各时间点骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖情况,见图4和表2。CCK-8法检测结果显示实验组及阳性对照组细胞增殖良好,在培养第3天后迅速增殖,阳性对照组至14 d后生长达到平台期,且阳性对照组细胞增殖活性比实验组更明显,但实验组持续增殖达到21 d,与阳性对照组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);空白对照组至第7天即达到增殖平台期,几乎无增殖,与实验组及阳性对照组比较各时间点差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),说明PaMZ/BMP-2/nHA人工骨无细胞毒性,具有良好的细胞相容性。"
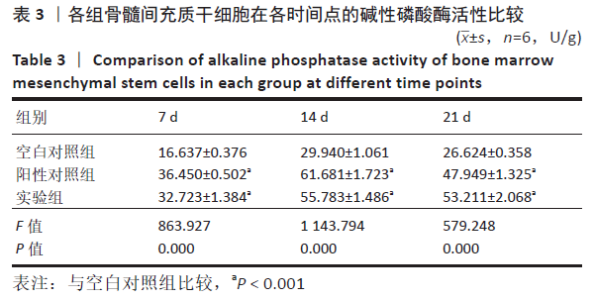
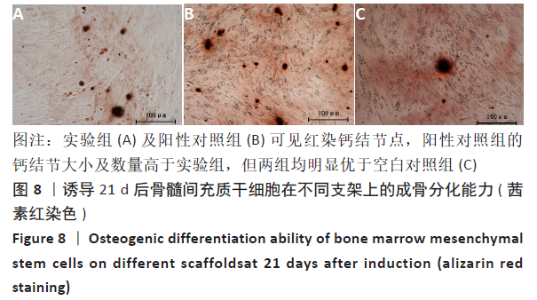
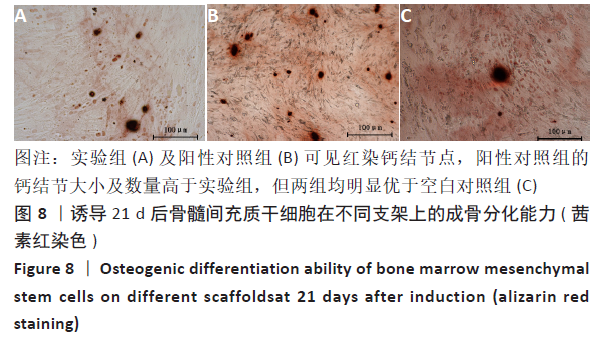
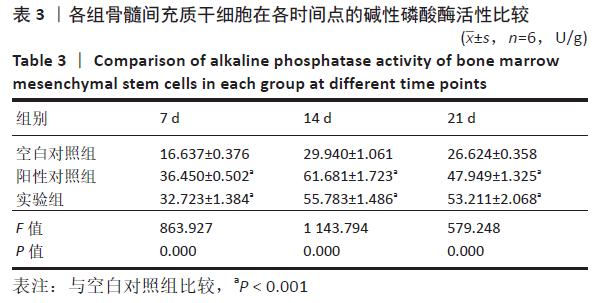
2.5 PaMZ/BMP-2/nHA人工骨对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨能力的影响 2.5.1 碱性磷酸酶活性和茜素红染色 随着时间推移,实验组及阳性对照组碱性磷酸酶活性呈先上升后下降的变化趋势,见表3和图7。碱性磷酸酶活性在第14天达到峰值,随后下降,阳性对照组和实验组在各检测时间点的碱性磷酸酶活性差异不明显(P > 0.05),却均显著高于空白对照组(P < 0.01)。为更进一步确定该支架的成骨分化能力,在第1,3,7,14,21天分别对3组骨髓间充质干细胞进行茜素红染色,结果显示,第21天时实验组及阳性对照组骨髓间充质干细胞大体观察到红染区域,镜下观察可见红染钙结节点,阳性对照组的钙结节大小及数量高于实验组,但两组均明显优于空白对照组。由于培养至第3天时,空白对照组其中2孔由成骨诱导培养基诱导成骨分化,该组染色则明显优于其他组,见图8。"
| [1] WANG B, GAO W, HAO D. Current Study of the Detection and Treatment Targets of Spinal Tuberculosis.Curr Drug Targets. 2020;21(4):320-327. [2] 中华医学会结核病学分会.中国耐多药和利福平耐药结核病治疗专家共识(2019年版)[J].中华结核和呼吸杂志,2019,42(10):733-749. [3] YADAV G, KANDWAL P, ARORA SS. Short-term outcome of lamina-sparing decompression in thoracolumbar spinal tuberculosis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2020:1-8. [4] DUNN RN, BEN HUSIEN M. Spinal tuberculosis: review of current management. Bone Joint J. 2018;100-B(4):425-431. [5] 巩栋,马永海,杨新乐,等.3D打印β-磷酸三钙负载聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物抗结核药物缓释微球细胞毒性及对BMSCs成骨分化影响的研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(9):1131-1136. [6] 孙伟,薛骋,唐先业,等.不同方法构建抗结核β-磷酸三钙药物缓释系统的载药和缓释性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(30): 4824-4828. [7] KHANNA K, SABHARWAL S. Spinal tuberculosis: a comprehensive review for the modern spine surgeon. Spine J. 2019;19(11):1858-1870. [8] DING P, LI X, JIA Z, et al. Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) disease burden in China: a systematic review and spatio-temporal analysis. BMC Infect Dis. 2017;17(1):57. [9] YANG S, YU Y, JI Y, et al. Multi-drug resistant spinal tuberculosis-epidemiological characteristics of in-patients: a multicentre retrospective study. Epidemiol Infect. 2020;148:e11. [10] 韦媛媛,杨帆,汤杰,等.抗结核药物的研究进展[J].中国药科大学学报,2020,51(2): 231-239. [11] 陈浩,武楠楠,胡文辉,等.抗结核药物作用新靶点及其研究进展[J].中国防痨杂志,2020,42(3):286-292. [12] AHMAD N, AHUJA SD, AKKERMAN OW, et al. Treatment correlates of successful outcomes in pulmonary multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: an individual patient data meta-analysis. Lancet. 2018;392(10150):821-834. [13] KIM TW, AHN WB, KIM JM, et al. Combined Delivery of Two Different Bioactive Factors Incorporated in Hydroxyapatite Microcarrier for Bone Regeneration. Tissue EngRegen Med. 2020;17(5):607-624. [14] KOVERMANN NJ, BASOLI V, DELLA BELLA E, et al. BMP2 and TGF-β Cooperate Differently during Synovial-Derived Stem-Cell Chondrogenesis in a Dexamethasone-Dependent Manner. Cells. 2019;8(6):636. [15] 唐学峰,刘昌昊,于树印,等.载PaMZ/nHA抗结核人工骨的最优配方筛选[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2020,42(6):565-572. [16] BASYUNI S, FERRO A, SANTHANAM V, et al. Systematic scoping review of mandibular bone tissue engineering. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020; 58(6):632-642. [17] MAJI K, DASGUPTA S, BHASKAR R, et al. Photo-crosslinked alginate nano-hydroxyapatite paste for bone tissue engineering. Biomed Mater. 2020;15(5):055019. [18] 张贺龙,王慧燕,李卓,等.壳聚糖-明胶/聚乳酸-羟基乙酸联合载药水凝胶的体外抗结核作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(22): 3480-3485. [19] 孟磊,甄平,梁晓燕,等.3D打印多孔β-磷酸三钙负载聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物抗结核药物缓释微球复合材料:构建及细胞毒性评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(25):3750-3756. [20] 李广杰,陈永刚,张学良,等.硫酸钙/纳米羟基磷灰石免疫人工骨对兔结核性骨缺损治疗的研究[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2020,40(8):1130-1134. [21] 岳学锋,唐学峰,施建党,等.抗结核药缓释涂层在兔脊柱结核模型体内的抗结核性能及组织相容性观察[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2020,30(6):558-565. [22] HE J, HAN X, WANG S, et al. Cell sheets of co-cultured BMP-2-modified bone marrow stromal cells and endothelial progenitor cells accelerate bone regeneration in vitro. ExpTher Med. 2019;18(5):3333-3340. [23] LIU H, JIAO Y, ZHOU W, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells improve the therapeutic effect of mesenchymal stem cell sheets on irradiated bone defect repair in a rat model. J Transl Med. 2018;16(1):137. [24] CARREIRA AC, ZAMBUZZI WF, ROSSI MC, et al. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins: Promising Molecules for Bone Healing, Bioengineering, and Regenerative Medicine. VitamHorm. 2015;99:293-322. [25] LUU HH, SONG WX, LUO X, et al. Distinct roles of bone morphogenetic proteins in osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res. 2007;25(5):665-677. [26] The Role of Tantalum Nanoparticles in Bone Regeneration Involves the BMP2/Smad4/Runx2 Signaling Pathway [Retraction]. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:3391. [27] KÄMMERER PW, PABST AM, DAU M, et al. Immobilization of BMP-2, BMP-7 and alendronic acid on titanium surfaces: Adhesion, proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow-derived stem cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020;108(2):212-220. [28] 洪亮,焦根龙.骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化过程中碱性磷酸酶基因表达含量的变化[J].中国医学物理学杂志,2017,34(8):825-828. [29] 白燕,王士斌,陈爱政,等.BMP-2及FGF-2对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[J].重庆医科大学学报,2017,42(12):1575-1581. [30] WANG J, WANG M, CHEN F, et al. Nano-Hydroxyapatite Coating Promotes Porous Calcium Phosphate Ceramic-Induced Osteogenesis Via BMP/Smad Signaling Pathway. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:7987-8000. [31] TANG Z, WANG Z, QING F, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein Smads signaling in mesenchymal stem cells affected by osteoinductive calcium phosphate ceramics. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(3):1001-1010. [32] HUMBERT P, BRENNAN MÁ, DAVISON N, et al. Immune Modulation by Transplanted Calcium Phosphate Biomaterials and Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Bone Regeneration. Front Immunol. 2019;10:663. [33] ZHAO C, WANG X, GAO L, et al. The role of the micro-pattern and nano-topography of hydroxyapatite bioceramics on stimulating osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.ActaBiomater. 2018;73:509-521. [34] HARDY E, FERNANDEZ-PATRON C. Destroy to Rebuild: The Connection Between Bone Tissue Remodeling and Matrix Metalloproteinases. Front Physiol. 2020;11:47. [35] YAMAGUCHI A, KOMORI T, SUDA T. Regulation of osteoblast differentiation mediated by bone morphogenetic proteins, hedgehogs, and Cbfa1. Endocr Rev. 2000;21(4):393-411. [36] ZHU B, LIU W, LIU Y, et al. Jawbone microenvironment promotes periodontium regeneration by regulating the function of periodontal ligament stem cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7:40088. [37] WANG YQ, WANG NX, LUO Y, et al. Ganoderal A effectively induces osteogenic differentiation of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells via cross-talk between Wnt/β-catenin and BMP/SMAD signaling pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;123:109807. [38] RAPHAEL-MIZRAHI B, GABET Y. The Cannabinoids Effect on Bone Formation and Bone Healing.CurrOsteoporos Rep. 2020;18(5):433-438. [39] COLUZZI F, SCERPA MS, CENTANNI M. The Effect of Opiates on Bone Formation and Bone Healing.CurrOsteoporos Rep. 2020;18(3):325-335. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [4] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [5] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [6] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [7] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [8] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [9] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [10] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [11] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [12] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [13] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [14] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [15] | Liu Bo, Chen Xianghe, Yang Kang, Yu Huilin, Lu Pengcheng. Mechanism of DNA methylation in exercise intervention for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 791-797. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||