Oral lichen planus is a T lymphocyte-mediated inflammatory disease, and the strip-shaped infiltration in a large number of lymphocytes in the epithelial lamina propria is one of its typical pathological manifestations. Increasing evidences have proved that the variation of T cell-mediated immune function is closely related to the pathogenesis of oral lichen planus, which is presented with the Th1/Th2 imbalance in lesions, saliva and tissue exudates[10-12]. Infiltrated T lymphocytes can secrete a variety of cytokines. Studies have shown that Th1 and Th2 dominant reactions exist in patients with oral lichen planus. Th1 cells produce interferon-γ, interleukin-2, and tumor necrosis factor-α, while Th2 cells produce interleukin-4, interleukin-5, interleukin-6, and interleukin-10. When a class of cytokines occurs, the activities of another type of cytokines may be increased accordingly in order to effectively prevent immune imbalance. Therefore, the balance of Th1 and Th2 cytokines is very important for the maintenance of normal immune function. The reactions between the two types of cytokines can be cross-regulated to achieve a balance. For example, interleukin-4 and interleukin-10 can inhibit Th1 response to prevent the infinite value of Th1 cell and its cytokines. Interferon-γ can develop an inhibitor effect on Th2 activity[13]. Different cytokines have different biological roles in promoting or inhibiting the development of inflammation, and thus, they show different roles in the development of the disease. In the treatment of oral lichen planus, local application of corticosteroids is mainly preferred, and new factors and new technologies have been applied constantly[14-15], such as, the subcutaneous injection of epidermal specific transfer factor in patients with oral lichen planus[16].
Interferon-γ is a typical Th1-type cytokine that can upregulate the expression of major histocompatibility complex II molecules on cell surface, and it is indispensable in Th1 cell differentiation. Interferon-γ can activate macrophages, and enhance expression of endothelial cell adhesion molecules, exerting an important pro-inflammatory role. Interferon-γ contributes to the removal of lymphocytes from the blood vessels, and then the lymphocytes enter into the infiltration zone to play a role. Interleukin-10 is mainly produced by Th2 cells, which are derived from mononuclear macrophages, B lymphocytes, and mast cells, and interleukin-10 inhibits the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and delivery of antigens, which is a pleiotropic cytokine and has anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effects, thus playing an important role in regulating the immune response[17-22]. Deng et al [23] found that the interleukin-10 level in the peripheral blood was significantly higher in the patients with oral lichen planus than healthy controls.
Saliva is the most accessible human biological fluid containing a series of proteins, NDA, RNA that can be used for early diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring of diseases[24]. Saliva as a diagnostic specimen is easy and inexpensive to be obtained as a result of painless, and has greater advantages than serum. Saliva and serum detection results are highly comparable[25]. As a result of local production, saliva also has a greater value than serum in disease diagnosis. Influencing factors that exist in the saliva test are that overflow of carbon dioxide during the collection, changes in pH, easy to produce bacteria and precipitation.
If the saliva specimen cannot be saved in time, the experimental results will be impacted. As above, the collection and storage of saliva is crucial for ensuring the objective results. Therefore, after collecting the saliva specimens should be centrifuged to take the supernatant within 5 minutes that is then placed at a -70 ℃ refrigerator. Repeated freezing and thawing is the most taboo. In addition, the immune status of the patient is changing at the different stages of oral lichen planus, and the level of serum cytokines may also vary. Therefore, different proportions of enrolled patients at different stages of oral lichen planus can result in different testing results.
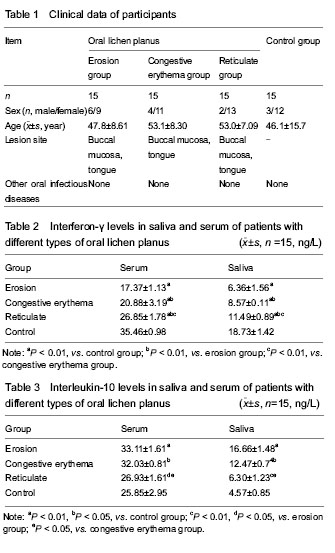
In this study, the levels of interferon-γ and interleukin-10 in saliva and serum of patients with three types of oral lichen planus were detected and compared with normal controls. The levels of interferon-γ in saliva and serum of patients with three types of oral lichen planus were significantly lower than those in the control group (
P < 0.05 or
P < 0.01), indicating that interferon-γ exerts an important role in the development of oral lichen planus. The interleukin-10 levels in serum and saliva were significantly higher in the erosion group and congestive erythema group than those in the control group and reticulate group (
P < 0.01 or
P < 0.05), suggesting that interleukin-10 is of great significance in the development of oral lichen planus. Experimental findings from the present study demonstrate that the levels of interferon-γ and interleukin-10 in serum and saliva are highly correlated in patients with different types of oral lichen planus.