中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 2101-2112.doi: 10.12307/2026.072
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯介导活性氧双向调控及在纳米材料中的应用
刘大为1,2,崔颖颖1,2,王方辉2,王子轩1,2,陈宇涵1,李友瑞2,张荣和2
- 1滨州医学院,山东省烟台市 256603;2滨州医学院附属医院,山东省滨州市 256600
-
收稿日期:2024-12-25接受日期:2025-03-24出版日期:2026-03-18发布日期:2025-07-29 -
通讯作者:张荣和,硕士,主任医师,硕士生导师,滨州医学院附属医院口腔正畸科,山东省滨州市 256600 李友瑞,博士,副主任医师,硕士生导师,滨州医学院附属医院口腔修复科,山东省滨州市 256600 -
作者简介:刘大为,男,2000年生,山东省日照市人,汉族,滨州医学院在读硕士,医师,主要从事口腔正畸力学与正畸相关的骨组织工程方向研究。 崔颖颖,女,2000年生,河南省濮阳市人,汉族,滨州医学院在读硕士,医师,主要从事口腔修复学及骨再生相关纳米材料的研究。 -
基金资助:山东省自然科学基金面上项目(ZR2023MH039),课题名称:序贯释放镁离子与BMP-2的新型材料调控巨噬细胞行为修复骨缺损的机制研究,项目负责人:李友瑞
Epigallocatechin gallate-mediated bidirectional regulation of reactive oxygen species and its application in nanomaterials
Liu Dawei1, 2, Cui Yingying1, 2, Wang Fanghui2, Wang Zixuan1, 2, Chen Yuhan1, Li Yourui2, Zhang Ronghe2
- 1Binzhou Medical University, Yantai 256603, Shandong Province, China; 2Affiliated Hospital, Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2024-12-25Accepted:2025-03-24Online:2026-03-18Published:2025-07-29 -
Contact:Zhang Ronghe, MS, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Affiliated Hospital, Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China Li Yourui, PhD, Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Affiliated Hospital, Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Liu Dawei, Master candidate, Physician, Binzhou Medical University, Yantai 256603, Shandong Province, China; Affiliated Hospital, Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China Cui Yingying, Master candidate, Physician, Binzhou Medical University, Yantai 256603, Shandong Province, China; Affiliated Hospital, Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:Shandong Natural Science Foundation (General Project), No. ZR2023MH039 (to LYR)
摘要:
文题释义:
表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯:是一种来源于绿茶的天然多酚类化合物,具有广泛的生物活性和良好的生物相容性。表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯具有显著的抗氧化、抗炎特性,在神经保护、心血管健康和代谢调节等领域展现出重要应用潜力。表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯具有浓度依赖性的特性,在低浓度下发挥抗氧化作用,在高浓度或特殊微环境中展现促氧化能力,成为抗肿瘤、协同化疗等领域的重要研究对象。
活性氧:是细胞代谢过程中产生的一类具有高反应活性的氧化物,包括超氧阴离子、过氧化氢和羟基自由基等,在细胞信号传递、免疫防御和凋亡调控中具有重要作用。过量的活性氧会导致氧化应激,从而损伤细胞和组织,与多种疾病(如癌症、炎症性疾病和神经退行性疾病)的发生发展密切相关。因此,如何精准调控活性氧的生成与清除成为现代生物医学研究的热点。
背景:表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯具有广泛的抗氧化和抗炎特性,在神经保护、心血管健康及代谢调节等领域展现出重要的应用潜力。近年来,负载表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯的纳米材料在调控活性氧生成与清除的双向特性上受到关注,特别是在抗肿瘤、抗菌等领域的应用研究逐渐成为热点。
目的:系统综述表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯在活性氧生成与清除中的作用机制,探讨负载表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯纳米材料在抗氧化保护及抗肿瘤治疗中的潜在应用,分析未来发展方向与挑战。
方法:由第一作者检索PubMed、万方医学网及中国知网2009-2024年发表的相关文献,中文检索关键词为“表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯,活性氧,抗氧化,促氧化,抗癌症,心血管疾病,骨缺损、纳米材料”,英文检索关键词为“Epigallocatechin gallate,reactive oxygen species,antioxidation,oxidation,anticancer,Angio cardiopathy,bone defect,nanomaterials”,最终筛选79篇高质量文献进行综述分析。
结果与结论:表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯在低浓度或正常生理条件下表现出抗氧化特性,通过上调抗氧化酶(如超氧化物歧化酶和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶)表达、抑制促氧化酶活性来保护正常细胞;在高浓度或特定微环境(如肿瘤细胞)中则展现出促氧化特性,通过促进活性氧生成诱导癌细胞凋亡或自噬。近年来,采用纳米载体、水凝胶及金属复合材料等技术显著提升了表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯的稳定性、生物利用度及靶向释放效果,通过光动力治疗等手段进一步增强材料的促氧化能力。这种基于表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯双向调控活性氧的机制为抗肿瘤、抗菌及抗氧化保护提供了重要策略,展现出广阔的应用前景与研究价值。
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-5892-988X (刘大为)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
刘大为, 崔颖颖, 王方辉, 王子轩, 陈宇涵, 李友瑞, 张荣和. 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯介导活性氧双向调控及在纳米材料中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2101-2112.
Liu Dawei, Cui Yingying, Wang Fanghui, Wang Zixuan, Chen Yuhan, Li Yourui, Zhang Ronghe. Epigallocatechin gallate-mediated bidirectional regulation of reactive oxygen species and its application in nanomaterials[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2101-2112.
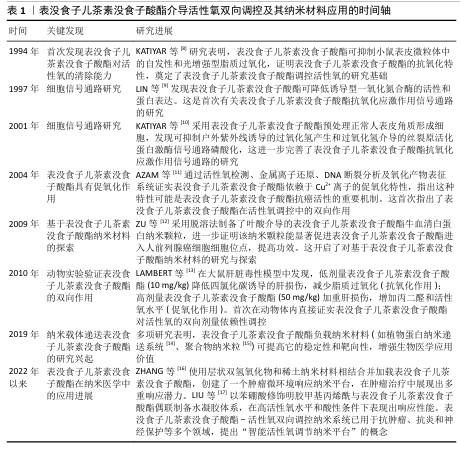
2.2 EGCG的抗氧化作用 EGCG作为一种天然的抗氧化剂,在多种生理和病理条件下展现出显著的抗氧化能力[18]。EGCG通过直接清除自由基、增强抗氧化酶的表达以及抑制氧化酶的活性显著降低细胞内的氧化应激水平(表2),从而在神经保护、心血管保护和抗癌等领域显示出广泛的应用前景[19]。接下来将详细探讨EGCG的抗氧化机制及其在不同领域的应用。

2.2.1 抗氧化机制
自由基清除:活性氧是指在生物体内与氧化代谢有关的、含氧自由基和易形成自由基的过氧化物总称,常见的活性氧包括超氧阴离子、羟自由基和过氧化氢等。活性氧的过量产生会对细胞膜、蛋白质和DNA等生物分子造成损害,从而诱发氧化应激导致细胞功能障碍甚至细胞死亡[20]。作为一种有效的抗氧化剂,EGCG能够通过直接清除自由基来减轻氧化损伤。EGCG比其他多酚具有更强的生物活性,这是因为它的芳香环上有大量的羟基及独特的排列方式,EGCG分子由3个芳香环和1个吡喃环构成,含有8个羟基(图3),其中酚羟基中的氢原子是易于提供的。酚类分子的苯环和相连的氢原子形成了一种特殊的化学结构,使它能够以相对较低的能量释放氢原子而作为氢原子供体。当自由基进入生物体并与酚类化合物接触时,酚基中的氢原子会被转移到自由基分子上,这个过程是通过氢原子转移机制完成的。在氢原子转移过程中,酚基的氢原子与自由基中的未配对电子形成键,生成一个新的、较为稳定的分子,这样原本活跃的自由基被“中和”了,因为自由基的未配对电子通过氢原子的供给得到了配对,从而降低了它的反应性。另外,酚自由基本身虽然也不稳定,但它通常比原始的自由基更为稳定,因为酚自由基的未配对电子可以通过苯环的共轭结构进行分布,从而稳定化该自由基。除了提供氢原子中和自由基,EGCG还能够在自由基引发的连锁反应早期阶段通过电子转移反应实现自由基的中和,有效降低活性氧浓度,阻止进一步扩展链式反应的能力[5]。这种清除自由基的特性使EGCG在预防和治疗由氧化应激引起的多种疾病(如慢性炎症和老年性疾病)中具有广泛应用潜力。
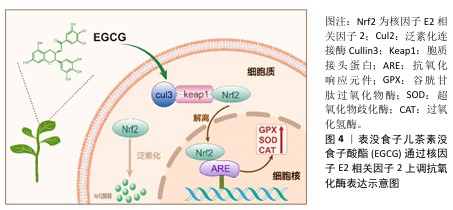
上调抗氧化酶:除了直接清除自由基,EGCG还通过多种机制上调抗氧化酶的表达和活性,帮助清除体内的活性氧,从而保护细胞免受氧化损伤。EGCG能够激活核因子E2相关因子2,这一转录因子是一种重要的抗氧化转录因子,在细胞应对氧化应激中发挥核心作用。在静息状态下,核因子E2相关因子2与胞质接头蛋白结合,被锚定在细胞质中,通过泛素化途径降解。EGCG的酚羟基可以直接与胞质接头蛋白中的半胱氨酸残基发生化学反应,改变其构向,导致核因子E2相关因子2释放并转移到细胞核中并与抗氧化基因的抗氧化反应元件结合,启动抗氧化酶如超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化氢酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶等的表达(图4)。这些抗氧化酶能够迅速清除细胞内的活性氧,并将活性氧代谢为无毒产物,从而减少活性氧对细胞的损伤。HUANG等[21]探讨了EGCG对冠心病小鼠的治疗作用及机制,发现EGCG以浓度依赖的方式显著减轻小鼠心肌损伤并改善血脂水平;EGCG可以显著降低心肌组织中活性氧的含量,上调核因子E2相关因子2的表达,提高抗氧化酶活性。EGCG通过激活核因子E2相关因子2通路有效提高了细胞内抗氧化酶的水平,进一步增强了细胞的抗氧化防御能力,这对于应对慢性氧化应激及预防与氧化相关的疾病具有重要意义。
抑制氧化酶活性:EGCG通过多种机制抑制氧化酶的活性,从而有效降低活性氧的生成并缓解氧化应激。EGCG能够直接作用于氧化酶的活性位点,阻碍其催化功能。例如,EGCG通过与还原型辅酶Ⅱ氧化酶结合抑制酶复合物的组装与激活[22],其多酚羟基结构能够直接与黄嘌呤氧化酶的钼辅因子螯合,阻止黄嘌呤转化为尿酸,从而减少超氧阴离子和过氧化氢的生成[23]。另外,EGCG还能够清除髓过氧化物酶生成的次氯酸、抑制髓过氧化物酶的氯化活性,进一步打断氧化损伤的链式反应。EGCG通过调节氧化酶的表达及其信号通路间接抑制其活性。例如,EGCG通过抑制核因子κB等促炎转录因子降低黄嘌呤氧化酶和髓过氧化物酶基因的表达;EGCG能够阻断丝裂原活化蛋白激酶和蛋白激酶C等信号通路,从而抑制黄嘌呤氧化酶的激活及膜转位,进而从上游减少活性氧的生成[24]。EGCG通过清除活性氧和调节氧化还原平衡协同抑制氧化酶效应,其多酚羟基可直接中和超氧阴离子和羟自由基,促进谷胱甘肽再生,提高还原型谷胱甘肽/氧化型谷胱甘肽比值,增强细胞的还原能力。这些机制共同作用,使EGCG在炎症、代谢性疾病及癌症模型中表现出显著的抗氧化酶抑制活性,为靶向氧化应激相关疾病的治疗提供了理论依据。
调节线粒体功能:线粒体是细胞内活性氧的主要来源之一,主要通过氧化磷酸化过程为细胞提供ATP。在电子传递链中,电子从底物传递到氧气生成水的过程中部分电子会泄漏,导致氧分子不完全还原,从而生成活性氧。EGCG通过多种机制调节线粒体功能,包括改善线粒体生物合成、抑制活性氧生成、保护线粒体膜完整性以及调控线粒体介导的细胞凋亡。EGCG中的酚羟基可直接中和线粒体产生的超氧阴离子和羟自由基,减少氧化应激对线粒体DNA和膜的损伤;EGCG通过稳定线粒体呼吸链复合物(如复合物Ⅰ和Ⅲ)减少电子传递过程中的泄漏,从而降低活性氧生成[25]。SARKAR等[26]评估了在破骨细胞分化过程中EGCG对线粒体的影响,通过线粒体超氧化物染色证实EGCG可显著降低破骨细胞分化时线粒体所产生的活性氧;通过线粒体膜电位荧光探针染色证实,在破骨细胞分化期间线粒体膜电位增加,而EGCG处理会显著降低线粒体膜电位。综上所述,EGCG通过多种机制对线粒体产生深远影响,以减少线粒体生成的活性氧,调控细胞内的氧化还原平衡。
2.2.2 抗氧化应用
神经保护:EGCG的抗氧化特性在神经保护方面尤为显著。神经元内的氧化应激及活性氧积累是导致神经退行性疾病(如阿尔茨海默症和帕金森症)发生的重要因素。高浓度的活性氧会损害神经元的线粒体、DNA和蛋白质,进而引起神经元的凋亡或功能障碍[27]。EGCG通过抗氧化机制能够降低神经元内的活性氧水平,从而帮助保护神经细胞免受氧化损伤;此外,EGCG还可激活核因子E2相关因子2信号通路,促进神经细胞抗氧化酶的表达,进一步增强神经元的抗氧化能力[28]。在阿尔茨海默症动物模型中,EGCG能够显著减少β-淀粉样蛋白的沉积、降低神经炎症,保护神经元,从而延缓疾病的进展[29]。因此,表EGCG在预防和治疗神经退行性疾病方面展现出潜在的应用前景。
心血管保护:EGCG在心血管保护方面的作用引起了广泛的关注。动脉硬化和心血管疾病的发生与氧化应激及炎症反应密切相关,而EGCG通过清除活性氧和上调抗氧化酶的表达能够有效减轻心血管系统中的氧化应激,从而延缓动脉硬化的进程[30]。研究表明,EGCG能够抑制内皮细胞中还原型辅酶Ⅱ氧化酶的活性,降低活性氧的生成,防止低密度脂蛋白的氧化,从而降低动脉粥样硬化的风
险[15]。YU等[31]研究表明,EGCG可依赖于微小RNA-450b-5p/长链酰基辅酶A合酶4轴,通过靶向铁下垂减轻心肌缺血损伤,提示EGCG可能作为一种新型的抗铁离子中毒药物在急性心肌梗死中发挥治疗作用。多项临床研究表明,定期摄入EGCG能够有效降低血压和血脂水平,对心血管健康具有显著保护作用。
骨保护:EGCG具有显著的抗氧化特性,展现出在与骨损伤相关疾病中应用的潜力。骨损伤发生时,受损骨组织及其周围细胞释放大量自由基,从而加剧骨组织的破坏程度;此外,活性氧在骨吸收过程中发挥关键作用,尤其是诱导破骨细胞的分化[32]。活性氧可以促进M1型巨噬细胞的极化,M1型巨噬细胞作为破骨细胞的前体能够进一步分化为成熟的破骨细胞,分泌促炎细胞因子,从而引发骨吸收的过程[33]。EGCG通过清除活性氧和上调抗氧化酶等机制减轻骨损伤后的氧化应激,进而减少骨吸收和破坏。多项实验表明,EGCG凭借强大的抗氧化能力能够有效清除受损骨组织中产生的活性氧,从而减缓骨损伤后骨细胞的损害,为骨愈合创造有利环境[26,34]。EGCG还可显著降低破骨细胞生成因子的表达水平,这一机制有助于抑制破骨细胞的形成及骨吸收的发生。
除了通过抗氧化作用抑制破骨细胞的分化和减少骨吸收外,EGCG还通过激活Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号通路促进成骨细胞的增殖与分化,从而有助于骨组织的修复与再生[35]。尤其在骨损伤伴随炎症反应的情况下,EGCG还抑制炎症因子如肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1的分泌,减轻损伤部位的炎症反应,进一步减少骨吸收[36]。综上所述,EGCG通过多种机制发挥作用,包括清除活性氧、上调抗氧化酶以减轻骨损伤时的氧化应激、抑制破骨细胞的分化,从而减少骨吸收。有相关研究表明,EGCG还通过其他途径促进骨组织的修复与再生(表3),显示出在骨损伤治疗中的广泛应用前景。
口腔疾病:在常见口腔疾病(如牙周炎、牙髓炎)的发生发展过程中,活性氧的过度累积是导致组织损伤和炎症持续的关键因素,近年来,大量研究聚焦于通过恢复氧化还原稳态来重塑有益微环境,进而实现对这类疾病的治疗。在牙周病中,活性氧主要由宿主免疫细胞(如中性粒细胞和巨噬细胞)通过还原型辅酶Ⅱ氧化酶和髓过氧化物酶途径产生,同时牙周致病菌(如牙龈卟啉单胞菌)及其代谢产物进一步刺激活性氧生成。过量的活性氧通过激活基质金属蛋白酶导致胶原降解和牙龈附着丧失,通过破骨细胞生成因子受体/核因子活化T细胞1信号通路促进破骨细胞分化和骨吸收;此外,活性氧激活核因子κB和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路,释放肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β等促炎因子,形成炎症恶性循环,最终导致牙周组织破坏和牙槽骨吸收。目前已有大量研究集中于EGCG基纳米材料在牙周炎治疗中的作用和应用,例如,FENG等[35]合成了一种加载EGCG的由苯基硼酸功能化氧化海藻酸钠和羧甲基壳聚糖组成的可注射水凝胶系统,该水凝胶具有优良的生物相容性、可注射性和活性氧/葡萄糖响应的药物释放性能;在糖尿病大鼠牙周炎模型中,该水凝胶显示了良好的抗氧化和抗炎特性,同时可抑制巨噬细胞M1向极化,为牙周组织再生提供了良好的免疫微环境,并为增殖后期的成骨细胞/破骨细胞分化调节提供了有利的机械支持。MING等[44]报道了一种硒-铜锶羟基磷灰石@EGCG纳米颗粒,通过体内外实验证明了该纳米颗粒能够有效清除活性氧、调节巨噬细胞极化、增加抗炎细胞因子的分泌,平衡免疫微环境;此外,硒-铜锶羟基磷灰石@EGCG还能刺激血管生成、抑制破骨细胞,加速牙周组织修复。在牙髓炎中,活性氧主要来源于免疫细胞的呼吸爆发和细菌毒素(如内毒素)诱导的线粒体功能障碍。过量活性氧通过线粒体途径诱导牙髓细胞凋亡,通过炎性小体激活促炎因子的释放,加剧炎症反应。同时,活性氧抑制成牙本质细胞分化和修复性牙本质形成,诱导牙髓干细胞衰老,降低干细胞增殖和分化潜能,最终导致牙髓组织损伤和修复障碍。NAKANISHI等[45]考察了EGCG对牙髓炎组织的治疗作用,发现EGCG显著降低了脂多糖作用下牙髓细胞中白细胞介素6和白细胞介素8的表达,并呈浓度依赖性,EGCG也降低了细胞间黏附分子1和血管细胞黏附分子1的表达,表明绿茶儿茶素可以阻止牙髓炎的恶化。
2.3 EGCG的促氧化作用 EGCG因显著的抗氧化活性而受到广泛关注,但在特定条件下它也可能展现出促氧化特性,即在特定环境或浓度下促进活性氧的生成,这种促氧化特性使EGCG成为一种具有双向调控能力的化合物,具有在抗肿瘤、抗菌、抗病毒以及协同化疗等领域的应用潜力。EGCG的促氧化作用主要通过与金属离子的相互作用及其自身的氧化过程实现,从而有效引发氧化应激和细胞死亡等生物过程。接下来,将从EGCG的促氧化机制出发,深入探讨它在生物医学领域的应用潜力。
2.3.1 促氧化机制
自氧化:在高浓度条件或特定环境(如光照和碱性环境)下,EGCG能够通过自身的氧化反应生成活性氧,从而引发促氧化作用。EGCG分子中的酚羟基在强碱性环境或光照激发下易于发生氧化反应,形成过氧化氢及其他活性氧种,这些活性氧分子在细胞内引发显著的氧化应激,能够攻击DNA、蛋白质和脂质,进而损害细胞的基本生物功能[46]。这一特性使EGCG在抗肿瘤和抗菌等领域中具有重要的应用价值。因此,EGCG通过自身氧化生成活性氧的能力,为它在调控特定细胞或病原体的氧化应激提供了理论基础。
催化芬顿反应:EGCG在细胞内促氧化的机制之一是与过渡金属离子(如Fe2+、Cu2+)的相互作用,这一过程催化了活性氧的生成。在许多病理环境中,例如肿瘤微环境,游离铁离子的浓度较高,这些金属离子能够与EGCG形成络合物并充当芬顿反应的催化剂[47]。在这一过程中,EGCG通过络合铁离子加速过氧化氢的分解,生成具有强氧化性的羟基自由基,这些自由基具有极强的细胞毒性,能够迅速破坏癌细胞或病原体的细胞膜和细胞器,从而实现靶向破坏的效果[48]。研究表明,在富含铁离子的环境中,EGCG通过促进芬顿反应生成活性氧,显著提高癌细胞内的氧化应激水平,最终导致癌细胞的凋亡或自噬[49]。这种通过金属离子诱导的活性氧生成机制,使得EGCG在富铁的肿瘤微环境中展现出选择性毒性,成为一种潜在的肿瘤治疗策略。
2.3.2 促氧化应用
抗肿瘤:EGCG的促氧化特性在抗肿瘤治疗中展现出显著的应用潜力。在肿瘤细胞中,适量的活性氧对于信号传导和细胞功能至关重要,而活性氧的过度生成则会引发细胞毒性,导致DNA损伤和细胞凋亡[50]。因此,通过进一步提升肿瘤细胞内的活性氧水平,可以有效破坏肿瘤细胞的氧化还原平衡,从而选择性地诱导癌细胞的凋亡[51]。
EGCG的促氧化作用不仅能够促进活性氧的生成,还可以通过诱导氧化应激来激发细胞凋亡或自噬,尤其是在癌细胞中。研究表明,癌细胞对氧化应激的敏感性高于正常细胞,因此EGCG能够通过提升癌细胞内的活性氧水平有效启动凋亡机制[52]。癌细胞内活性氧的积累进一步激活了p53蛋白、应激活化蛋白激酶和蛋白激酶B等与细胞凋亡相关的信号通路,最终导致细胞的凋亡或自噬[53];此外,肿瘤细胞的微环境中富含金属离子,EGCG在此环境中能够进一步激活芬顿反应,显著增强活性氧的生成,从而对癌细胞展现出选择性毒性作 用[49]。因此,EGCG在肿瘤治疗中,尤其是在耐药性肿瘤中,展现出良好的前景。
协同化疗:EGCG的促氧化特性可以与某些抗癌药物联合使用,以增强化疗的效果。化疗药物通过诱导肿瘤细胞内的氧化应激来杀死癌细胞,而EGCG的促氧化特性能够进一步提升肿瘤细胞内的活性氧水平,从而增强肿瘤细胞对化疗药物的敏感性[54]。这种促氧化作用有助于提高化疗药物的疗效,尤其是在肿瘤细胞对化疗药物产生耐药性的情况下[55]。LI等[56] 研究表明,EGCG与顺铂联合使用时可以提升多种卵巢癌细胞系中的过氧化氢水平、增强氧化应激,从而抑制卵巢癌细胞的增殖,提高卵巢癌细胞对顺铂的敏感性。因此,EGCG在协同化疗中的应用展现出广阔的前景,为提高化疗药物的疗效和减少不良反应提供了新的治疗策略。

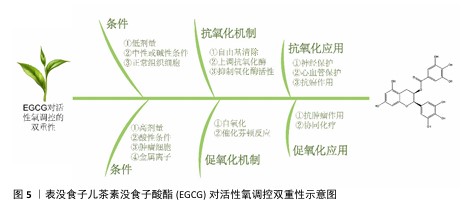
2.4 EGCG对活性氧的双重调节作用的影响因素 EGCG作为一种重要的天然抗氧化剂,在体内外不同条件下通过自氧化及催化芬顿反应等机制表达出促氧化的作用,这一双重特性使EGCG在多种生物医学领域中表现出较强的应用潜力,如神经保护、心血管保护及抗肿瘤治疗等领域(图5)。EGCG的双向活性氧调节效应受到多种因素的影响,如剂量依赖性、微环境、细胞类型及外部应用条件等(表4)。以下将详细探讨这些影响因素及其在EGCG对活性氧调控中的作用机制。
2.4.1 剂量依赖性 EGCG对活性氧的调节具有明显的剂量依赖性,在不同浓度下,EGCG可能表现出截然相反的作用。通常情况下,低剂量EGCG表现为抗氧化剂,主要通过清除活性氧和上调细胞内抗氧化酶系统来降低细胞的氧化应激水平[57]。在低浓度下,EGCG中的酚羟基可以提供氢原子并与自由基结合,从而中和活性氧并减轻氧化损伤;此外,EGCG在低剂量时能够激活核因子E2相关因子2通路,从而诱导超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶等抗氧化酶的表达,这一机制为EGCG的抗氧化特性提供了重要的分子基础[58-59]。
然而在高浓度条件下,EGCG易表现出促氧化作用,促进活性氧的生成,诱导细胞凋亡或自噬,这可能与EGCG在细胞内的自氧化和芬顿反应催化作用有关[60]。高浓度EGCG分子结构中的酚羟基易发生氧化反应,生成过氧化氢等活性氧;此外,EGCG与细胞内金属离子结合后可以加速芬顿反应,进一步生成高活性的羟基自由基,从而诱导细胞氧化应激并导致细胞损伤。因此,EGCG在低剂量时主要表现为抗氧化剂,而在高剂量时则倾向于促氧化,这一剂量依赖性在其临床应用中需谨慎考虑,以确保安全性和有效性。
2.4.2 微环境 EGCG在不同细胞微环境中对活性氧的调节效应差异显著。细胞内的金属离子浓度直接影响EGCG的促氧化能力,特别是在亚铁离子浓度较高的环境中,EGCG更容易表现出促氧化作用。亚铁离子在细胞内能够与EGCG络合,催化过氧化氢分解生成羟基自由基,加剧氧化应激。例如,在肿瘤微环境中,细胞内的过渡金属浓度较高,因此,EGCG在该环境下更易表现出促氧化作用,从而选择性地杀伤癌细胞[61]。
此外,pH值也是影响EGCG调控活性氧机制的关键因素。在酸性条件下EGCG的促氧化作用更为显著,因为酸性环境加速了EGCG的降解和氧化反应。相反,在中性或弱碱性条件下,EGCG表现为较强的抗氧化作用,其分子结构更加稳定,能够通过提供氢原子来清除活性氧,从而减少细胞氧化损伤。EGCG在不同pH值环境中的作用差异,为它在肿瘤、炎症等特定病理环境中的应用提供了理论依据。
2.4.3 细胞类型 EGCG对活性氧的调节效应还与细胞类型密切相关。在肿瘤细胞和正常细胞中,EGCG的抗氧化或促氧化效果存在显著差异,EGCG在肿瘤细胞中更易表现出促氧化作用,而在正常细胞中则倾向于抗氧化[61]。肿瘤细胞的代谢活性较高,通常伴有较高的活性氧水平,但抗氧化防御系统相对较弱,因此,EGCG在肿瘤细胞中进一步增加活性氧水平,会更容易触发氧化应激并诱导细胞凋亡;此外,由于肿瘤细胞中的过渡金属浓度较高,EGCG在肿瘤细胞中可以与这些金属离子结合,通过芬顿反应生成更多的活性氧,在肿瘤治疗中表现出较强的选择性毒性[62]。
相比之下,正常细胞具有较强的抗氧化防御系统,因此EGCG在正常细胞中主要表现为抗氧化效果,通过清除过量的活性氧来保护细胞免受氧化损伤。EGCG能够在正常细胞中上调抗氧化酶的表达,并通过抑制还原型辅酶Ⅱ氧化酶等促氧化酶的活性来减少活性氧的生成[58]。因此,EGCG对不同细胞类型中活性氧的双重调控作用,使它在肿瘤治疗中具有潜在的选择性毒性,即在杀伤癌细胞的同时保护正常细胞免受氧化应激,这为EGCG在癌症治疗中的应用提供了良好的前景。
2.4.4 应用条件 EGCG对活性氧的双重调节作用还受到温度、光照等外界应用条件的显著影响。EGCG在高温条件下会发生自氧化,从而产生过氧化氢等活性氧,表达促氧化作用[63]。光照也是影响EGCG对活性氧调控机制的重要因素。EGCG分子在紫外光或强光照射下会发生氧化反应,生成活性氧并表现促氧化特性[64]。因此在光动力治疗中,EGCG被用于作为一种光敏剂,通过光照触发活性氧生成从而诱导癌细胞凋亡或抗菌效果[49]。
在实际应用中,EGCG的稳定性问题需要通过合理的载体或环境控制来优化。例如,通过纳米载体、聚合物微胶囊等包裹EGCG,可以有效提高EGCG在特定条件下的稳定性,延长其半衰期,从而保持其抗氧化或促氧化活性[64]。此外,不同的EGCG递送系统可以根据环境和温度变化实现精确的活性氧调节功能,为EGCG在肿瘤治疗和抗菌治疗等领域的应用提供支持。

2.5 负载EGCG纳米材料的设计与应用 纳米载体是一种在纳米尺度上的材料,它们可以是天然或合成的高分子及无机纳米材料,以不同形式形成的纳米分散系统。纳米载体的主要作用是作为药物的输送系统,它们能够将药物包封或吸附在其结构中,以调节药物释放速度、增加生物膜透过性、改变药物在体内的分布、提高生物利用度等[65]。
EGCG是一种天然酚类物质,多存在于绿茶中,具有广泛的生物活性,在心血管和大脑健康方面的潜力已引起极大的关注,但它的应用受到在碱性和中性条件下稳定性差的限制。纳米载体技术可以通过将EGCG包裹在纳米颗粒中来提高其稳定性、有效性和药代动力学特征。基于EGCG的纳米材料的设计主要集中于增强稳定性、溶解性和功能性,以优化药物递送和活性调控[66]。下文将从EGCG纳米材料的负载机制、释放机制及其在活性氧平衡工程中的应用3个方面(图6)进行综合论述。
2.5.1 EGCG纳米材料的负载机制 负载是指通过各种方式将药物搭载在载体上,以实现药物的靶向递送和可控释放。EGCG是一种来自绿茶的多酚类化合物,分子中含有多个酚羟基,这些羟基不仅赋予EGCG强大的水溶性,使它在水溶液中具有很好的分散性,而且也是其化学活性的主要来源,能够与多种生物大分子相互作用。EGCG良好的分子特性为其负载纳米材料提供了理论基础[67]。当前EGCG的纳米载体主要采用3种负载策略(表5)。针对不同的应用条件选择适当的负载策略及纳米载体类型,可以显著提升EGCG的稳定性和生物利用度。
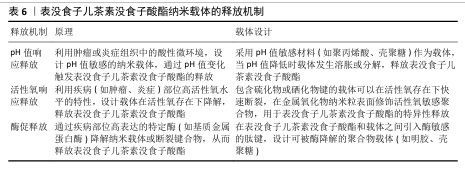
2.5.2 EGCG纳米材料的释放机制 EGCG纳米载体释放机制的意义在于它能够显著提升EGCG的生物利用度和治疗效果,通过控制药物释放的速度和位置减少了药物在体内的快速降解和非特异性分布,从而提高了靶向性、减少了不良反应。这种机制使得EGCG能够在特定的病变部位维持有效浓度,延长药物作用时间,并且能够响应特定的生理或病理条件,实现智能释放,为治疗癌症、炎症和其他疾病提供了一种有效的策略[68]。目前常见的释放机制包括pH值响应释放、活性氧响应释放和酶促释放(表6)。
药物的负载与释放机制是纳米载体研究中重要的组成部分,EGCG作为一种天然活性物质,其负载与释放是确保其药理功能的重要步骤。根据实际应用,合理设计纳米载体负载和释放方式对于实现EGCG的有效释放和活性氧双向调控具有关键作用。
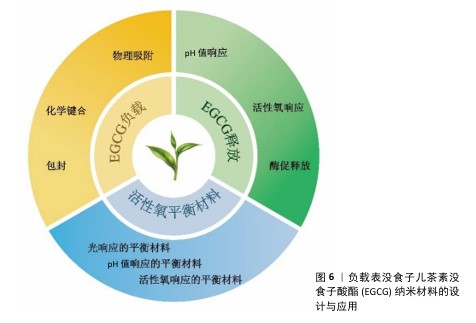
2.5.3 EGCG负载纳米材料在活性氧平衡工程中的应用
光响应的活性氧平衡材料:光响应纳米材料是指那些能够响应外部光信号(如紫外光、可见光或红外光)并产生特定物理或化学变化的纳米尺度材料[69]。在活性氧平衡领域中,光响应纳米材料通过特定波长的光刺激可以调控活性氧的产生或清除,以实现对氧化应激的调控。例如,GAO等[70]研究开发了以金纳米笼为载体的近红外响应系统,加载EGCG后通过近红外光激发产生热效应,从而促进癌细胞内活性氧水平的升高,引发细胞凋亡,这种系统在肝细胞癌治疗中表现出显著效果,同时具备光稳定性和优良的生物相容性。另外,将光敏剂与EGCG结合的纳米平台也被用于增强抗肿瘤活性,此类光响应系统不仅可以诱导活性氧的定点生成,还能通过光热效应释放EGCG,有效提高肿瘤治疗的精确性和抗氧化活性。
pH值响应的活性氧平衡材料:肿瘤细胞代谢活性较强,尤其是糖酵解过程,导致产生的乳酸增多,因此,相比于正常组织的pH值,肿瘤细胞内环境的pH值通常在6.5-7.2之间,甚至更低。pH值响应纳米材料是利用肿瘤微环境中的酸性特性而设计的智能释放机制。研究显示,EGCG负载的脂质体在肿瘤酸性环境中能够精准释放内容物,通过调节活性氧水平来促进抗癌作用。基于pH值响应的纳米载体结合EGCG和其他抗癌药物在酸性环境中解离,释放EGCG并通过活性氧调控协同增强抗癌效果[71],这种双重功能载体展示了提高治疗效果的潜力,同时降低了药物的非特异性毒性。
活性氧响应的活性氧平衡材料:是一类能够感知活性氧并对活性氧浓度变化产生特异性响应(如结构变化、药物释放、信号触发等)的智能材料[72]。这类材料的设计核心在于利用活性氧的高氧化性,通过化学键或功能基团的氧化反应实现可控的物理或化学响应,广泛应用于药物递送、疾病诊断、抗肿瘤治疗和炎症调控等领域。这些材料通常结合了抗氧化和促氧化特性,可以通过微环境中的活性氧水平的变化调控其结构和功能,从而实现动态平衡。例如,BI等[73]设计了一种含有甲氨蝶呤和EGCG的可拆卸活性氧响应性凝胶基微针贴片,用于改善银屑病的治疗效率,凝胶基微针可快速扩散释放甲氨蝶呤,并以活性氧响应方式持续释放EGCG;与传统的溶解型微针相比,凝胶基微针延长了EGCG在皮肤中的滞留时间,从而延长了抗氧化作用效果。这种活性氧响应性的微针贴片通过经皮递送抗氧化和抗炎药物,在银屑病样和预防性银屑病样动物模型中均改善了治疗效果。

2.6 EGCG双面性在医学应用中的挑战与前景 EGCG的多面性在临床应用中也带来了一系列挑战。EGCG的应用既需精准调控其抗氧化与促氧化作用以获得最佳效果,也需在实际制剂中克服其稳定性和安全性等问题,以实现它在疾病预防和治疗中的理想应用。以下将详细讨论EGCG在医学应用中的挑战与未来前景。
2.6.1 挑战 EGCG在不同浓度下表现出抗氧化和促氧化的双重作用,为其医学应用带来了安全性方面的挑战。当前研究主要集中在体外实验和动物模型中,尚缺乏系统的人体剂量反应研究,不同个体对EGCG的敏感性不同,给剂量设计带来了更多的不确定性;此外,EGCG的水溶性较强但脂溶性较弱的特性,使其在体内的生物利用度低,这限制了它在靶向组织中积累至合适的药物浓度[74]。因此,确定EGCG的安全剂量以及实现药物在靶向组织中的缓释,是它在投入临床应用前需要解决的关键问题。解决剂量安全性的问题,需要更多的临床试验和系统性研究,以确定不同疾病条件下的适用剂量范围。
EGCG还在不同细胞类型及环境条件中表现出对活性氧调控的双重性,这种细胞类型依赖性为它在癌症治疗中的选择性杀伤效果提供了基础,但也带来了调控挑战。如何在正常组织和肿瘤组织中实现EGCG作用的精准调控,确保它在发挥促氧化杀伤作用的同时避免对正常细胞造成损伤,是临床应用中的一大难题。未来的研究需聚焦于细胞特异性递送系统的开发,探索EGCG在不同组织、细胞和病理条件下的作用机制,从而实现更具针对性的调控。最后,EGCG的化学结构并不稳定,对光、温度和pH值敏感,极易降解,从而影响其生物活性。这种不稳定性给EGCG存储、运输和体内药物递送带来了挑战[64]。
为解决上述问题,近年来许多研究致力于开发各种纳米载体系统,如脂质体、聚合物纳米颗粒、金属有机框架等,以提升EGCG的稳定性和递送效率[75]。这些递送系统能够在体内实现EGCG的缓释和靶向递送,减少它在正常组织中的促氧化风险、增强它在靶组织中的药理活性。但如何进一步提升EGCG递送系统的生物相容性和有效性,仍是亟待解决的技术难题。
2.6.2 前景 为解决EGCG的双重调节特性及不稳定性,开发能够靶向控释EGCG的系统成为未来研究的一个重要方向。控释系统可以在体内实现EGCG的精确释放和剂量调控,从而在发挥抗氧化或促氧化作用时提供更多的控制力。近年来,各种新型制剂已被开发用于提升EGCG的稳定性和生物利用度,包括脂质体、纳米乳剂、聚合物微球等[75]。例如,脂质体包裹增强EGCG在体内的稳定性,同时实现靶向递送,避免在体内快速降解。另外,通过设计智能化的控释系统,如光响应、pH值响应、超声响应的EGCG载体,可以实现EGCG在特定环境下的释放,从而在肿瘤治疗、抗氧化防护等领域发挥更好的效果[76]。这些新型制剂的发展为EGCG在医学领域的应用开辟了新前景。
EGCG控释系统的研究还为个性化抗癌治疗提供了一种全新的策略。研究表明,EGCG在特定肿瘤微环境中,尤其是在富含金属离子和酸性条件下,能够通过增加活性氧水平选择性诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡或自噬[49]。EGCG的这种选择性毒性使它在个性化抗癌治疗中具有巨大的潜力和应用基础,结合EGCG的靶向递送系统有望实现对特定肿瘤细胞的精准杀伤,并结合患者的个体特征调整剂量和治疗策略。凭借基因测序和分子标记技术,未来可以设计基于EGCG的个性化抗癌方案,以提高治疗效果、减少不良反应。
EGCG抗氧化活性使它在神经保护和心血管保护等领域展现出广泛的应用潜力。EGCG通过上调抗氧化酶和清除自由基等多种机制有效减轻氧化应激反应,因而在预防和治疗与氧化应激相关的慢性疾病方面具有独特的优势[77]。在协同抗氧化疗法中,EGCG可以与其他抗氧化剂或药物联合使用,以进一步增强治疗效果。例如,LIU等[78]构建了一种抗菌肽-EGCG纳米药物,通过减轻氧化应激和促进上皮迁移有效地恢复结肠上皮屏障,为溃疡性结肠炎治疗提供了新策略;KUMAZOE等[79]证明黄烷醇增强了EGCG诱导的多发性骨髓瘤细胞中环磷酸鸟苷/内皮型一氧化氮合酶轴的激活,这种化学组合可在不影响正常细胞的情况下显著促进骨髓瘤细胞的死亡。这种协同抗氧化策略不仅有助于减缓疾病的进展,还能降低药物剂量,从而减少潜在的不良反应。
| [1] ZHAO Y, CAO G, WANG Z, et al. The recent progress of bone regeneration materials containing EGCG.Mater Chem B. 2024;12(39):9835-9844. [2] ALAM M, ALI S, ASHRAF GM, et al. Epigallocatechin 3-gallate: From green tea to cancer therapeutics. Food Chem. 2022;379:132-135. [3] MOKRA D, JOSKOVA M, MOKRY J. Therapeutic Effects of Green Tea Polyphenol (‒)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) in Relation to Molecular Pathways Controlling Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis . Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 24(1):340-366. [4] DE PACE RC, LIU X, SUN M, et al. Anticancer activities of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate encapsulated nanoliposomes in MCF7 breast cancer cells. J Liposome Res. 2013; 23(3):187-196. [5] SINGH BN, SHANKAR S, SRIVASTAVA RK. Green tea catechin, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG): mechanisms, perspectives and clinical applications. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011;82(12):1807-1821. [6] WU P, ZHANG H, YIN Y, et al. Engineered EGCG-Containing Biomimetic Nanoassemblies as Effective Delivery Platform for Enhanced Cancer Therapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(15):1-12. [7] 闫晓佳,梁秀萍,李思琪,等.表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯性质、稳定性及其递送体系的研究进展[J].食品科学, 2020,41(1):258-266. [8] KATIYAR SK, AGARWAL R, MUKHTAR H. Inhibition of spontaneous and photo-enhanced lipid peroxidation in mouse epidermal microsomes by epicatechin derivatives from green tea. Cancer Lett. 1994;79(1):61-66. [9] LIN YL, LIN JK. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate blocks the induction of nitric oxide synthase by down-regulating lipopolysaccharide-induced activity of transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB. Mol Pharmacol. 1997;52(3):465-472. [10] KATIYAR SK, AFAQ F, AZIZUDDIN K, et al. Inhibition of UVB-induced oxidative stress-mediated phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in cultured human epidermal keratinocytes by green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2001;176(2):110-117. [11] AZAM S, HADI N, KHAN NU, et al. Prooxidant property of green tea polyphenols epicatechin and epigallocatechin-3-gallate: implications for anticancer properties. Toxicol In Vitro. 2004;18(5):555-561. [12] ZU YG, YUAN S, ZHAO XH, et al. [Preparation, activity and targeting ability evaluation in vitro on folate mediated epigallocatechin-3-gallate albumin nanoparticles] . Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2009;44(5):525-531. [13] LAMBERT JD, KENNETT MJ, SANG S, et al. Hepatotoxicity of high oral dose (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate in mice . Food Chem Toxicol. 2010;48(1):409-416. [14] YAN X, ZHANG X, MCCLEMENTS DJ, et al. Co-encapsulation of Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) and Curcumin by Two Proteins-Based Nanoparticles: Role of EGCG. J Agric Food Chem. 2019;67(48): 13228-13236. [15] ZHANG J, NIE S, ZU Y, et al. Anti-atherogenic effects of CD36-targeted epigallocatechin gallate-loaded nanoparticles . J Control Release. 2019;303:263-273. [16] ZHANG S, HAN X, CHEN X, et al. Rational Design of a Triple Tumor Microenvironment-Responsive Nanoplatform for Enhanced Tumor Theranostics. Chemistry. 2023;29(7): e202202469. [17] LIU L, WANG W, HUANG L, et al. Injectable pathological microenvironment-responsive anti-inflammatory hydrogels for ameliorating intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomaterials. 2024;306: 122509. [18] FARHAN M. Green Tea Catechins: Nature’s Way of Preventing and Treating Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(18):10713. [19] NEHA, CHAUDHARY S, TIWARI P, et al. Amelioration of Phytanic Acid-Induced Neurotoxicity by Nutraceuticals: Mechanistic Insights. Mol Neurobiol. 2024; 61(10):7303-7318. [20] NISSANKA N, MORAES CT. Mitochondrial DNA damage and reactive oxygen species in neurodegenerative disease. FEBS Lett. 2018;592(5):728-742. [21] HUANG X, CHU Y, REN H, et al. Antioxidation Function of EGCG by Activating Nrf2/HO‐1 Pathway in Mice with Coronary Heart Disease. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022; 2022:8639139. [22] LU Y, WANG Y, XIONG L, et al. Physiological Dose of EGCG Attenuates the Health Defects of High Dose by Regulating MEMO‐1 inCaenorhabditis elegans. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:5546493. [23] 李昕卓,郑丽丽,艾斌凌,等.黄嘌呤氧化酶多酚抑制剂的筛选及其作用机制[J].食品研究与开发,2020,41(9):12-19. [24] 刘婷婷,孟馨.表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯抗氧化作用机制的研究进展[J].现代药物与临床,2016,31(6):919-923. [25] OLIVEIRA MR, NABAVI SF, DAGLIA M, et al. Epigallocatechin gallate and mitochondria-A story of life and death. Pharmacol Res. 2016;104:70-85. [26] SARKAR J, DAS M, HOWLADER M, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits osteoclastic differentiation by modulating mitophagy and mitochondrial functions. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(10):908. [27] ZHAO Y, ZHANG J, ZHENG Y, et al. NAD(+) improves cognitive function and reduces neuroinflammation by ameliorating mitochondrial damage and decreasing ROS production in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion models through Sirt1/PGC-1alpha pathway. J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18(1):207. [28] KIM TY, LEEM E, LEE JM, et al. Control of Reactive Oxygen Species for the Prevention of Parkinson’s Disease: The Possible Application of Flavonoids. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(7):583. [29] VALVERDE-SALAZAR V, RUIZ-GABARRE D, GARCIA-ESCUDERO V. Alzheimer’s Disease and Green Tea: Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate as a Modulator of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023;12(7):1460. [30] ZHANG Q, LIU J, DUAN H, et al. Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling: An important molecular mechanism of herbal medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis via the protection of vascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress. J Adv Res. 2021;34:43-63. [31] YU Q, ZHANG N, GAN X, et al. EGCG attenuated acute myocardial infarction by inhibiting ferroptosis via miR-450b-5p/ACSL4 axis. Phytomedicine. 2023;119:154999. [32] ZHANG B, YANG Y, YI J, et al. Hyperglycemia modulates M1/M2 macrophage polarization via reactive oxygen species overproduction in ligature-induced periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 2021;56(5):991-1005. [33] LAHA D, SARKAR J, MAITY J, et al. Polyphenolic Compounds Inhibit Osteoclast Differentiation While Reducing Autophagy through Limiting ROS and the Mitochondrial Membrane Potential. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(9):1220. [34] YANG Y, LIU Z, WU J, et al. Nrf2 Mitigates RANKL and M-CSF Induced Osteoclast Differentiation via ROS-Dependent Mechanisms. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023;12(12):2094. [35] FENG Q, ZHANG M, ZHANG G, et al. A whole-course-repair system based on ROS/glucose stimuli-responsive EGCG release and tunable mechanical property for efficient treatment of chronic periodontitis in diabetic rats. J Mater Chem B. 2024; 12(15):3719-3740. [36] HE Z, LUO H, WANG Z, et al. Injectable and tissue adhesive EGCG-laden hyaluronic acid hydrogel depot for treating oxidative stress and inflammation. Carbohydr Polym. 2023;299:120180. [37] FUJITA K, OTSUKA T, YAMAMOTO N, et al. (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate but not chlorogenic acid upregulates osteoprotegerin synthesis through regulation of bone morphogenetic protein-4 in osteoblasts. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(1):417-423. [38] XI J, LI Q, LUO X, et al. Epigallocatechin‑ 3‑gallate protects against secondary osteoporosis in a mouse model via the Wnt/beta‑catenin signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(5):4555-4562. [39] LIN SY, KANG L, WANG CZ, et al. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) Enhances Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Molecules. 2018;23(12):3221. [40] LIN SY, KANG L, CHEN JC, et al. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) enhances healing of femoral bone defect . Phytomedicine. 2019;55:165-171. [41] VERMA NK, KAR AK, SINGH A, et al. Control Release of Adenosine Potentiate Osteogenic Differentiation within a Bone Integrative EGCG-g-NOCC/Collagen Composite Scaffold toward Guided Bone Regeneration in a Critical-Sized Calvarial Defect. Biomacromolecules. 2021;22(7):3069-3083. [42] ZHANG X, HE J, QIAO L, et al. 3D printed PCLA scaffold with nano-hydroxyapatite coating doped green tea EGCG promotes bone growth and inhibits multidrug-resistant bacteria colonization. Cell Prolif. 2022;55(10):e13289. [43] YAO D, GUO J, QIN T, et al. Effect of Alleviating Fibrosis with EGCG-Modified Bone Graft in Murine Model Depended on Less Accumulation of Inflammatory Macrophage. Biomed Res Int. 2023;2023:9466110. [44] MING P, LI B, LI Q, et al. Multifunctional sericin-based biomineralized nanoplatforms with immunomodulatory and angio/osteo-genic activity for accelerated bone regeneration in periodontitis . Biomaterials. 2025;314:122885. [45] NAKANISHI T, MUKAI K, YUMOTO H, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of catechin on cultured human dental pulp cells affected by bacteria-derived factors. Eur J Oral Sci. 2010;118(2):145-150. [46] LUO P, AN Y, HE J, et al. Icaritin with autophagy/mitophagy inhibitors synergistically enhances anticancer efficacy and apoptotic effects through PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2024;587:216621. [47] QIAN X, ZHANG J, GU Z, et al. Nanocatalysts-augmented Fenton chemical reaction for nanocatalytic tumor therapy. Biomaterials. 2019;211:1-13. [48] GLORIEUX C, LIU S, TRACHOOTHAM D, et al. Targeting ROS in cancer: rationale and strategies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024;23(8): 583-606. [49] CHEN Y, LI H, LIU N, et al. Multi-mechanism antitumor/antibacterial effects of Cu-EGCG self-assembling nanocomposite in tumor nanotherapy and drug-resistant bacterial wound infections. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2024;671:751-769. [50] ANDRES C, LASTRA J, JUAN CA, et al. Chemical Insights into Oxidative and Nitrative Modifications of DNA. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(20):15240. [51] NARAYANAN S, PAVITHRAN M, VISWANATH A, et al. Sequentially releasing dual-drug-loaded PLGA-casein core/shell nanomedicine: design, synthesis, biocompatibility and pharmacokinetics . Acta Biomater. 2014;10(5):2112-2124. [52] STEARNS ME, WANG M. Synergistic Effects of the Green Tea Extract Epigallocatechin-3-gallate and Taxane in Eradication of Malignant Human Prostate Tumors. Transl Oncol. 2011;4(3):147-156. [53] MIN KJ, KWON TK. Anticancer effects and molecular mechanisms of epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Integr Med Res. 2014;3(1):16-24. [54] WANG L, LI P, FENG K. EGCG adjuvant chemotherapy: Current status and future perspectives . Eur J Med Chem. 2023;250: 115197. [55] LI H, KRSTIN S, WINK M. Modulation of multidrug resistant in cancer cells by EGCG, tannic acid and curcumin . Phytomedicine. 2018;50:213-222. [56] LI X, HOU Y, HAN G, et al. S100A4/NF-kappaB axis mediates the anticancer effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer. iScience. 2024;27(2):108885. [57] PISTOLLATO F, CALDERON IR, RUIZ R, et al. The use of natural compounds for the targeting and chemoprevention of ovarian cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017;411:191-200. [58] LAMBERT JD, ELIAS RJ. The antioxidant and pro-oxidant activities of green tea polyphenols: a role in cancer prevention. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2010;501(1):65-72. [59] LIU C, VAN MIL J, NOORLANDER A, et al. Use of Physiologically Based Kinetic Modeling-Based Reverse Dosimetry to Predict In Vivo Nrf2 Activation by EGCG and Its Colonic Metabolites in Humans . J Agric Food Chem. 2022;70(43):14015-14031. [60] KIM HS, QUON MJ, KIM JA. New insights into the mechanisms of polyphenols beyond antioxidant properties; lessons from the green tea polyphenol, epigallocatechin 3-gallate. Redox Biol. 2014;2:187-195. [61] TAO L, PARK JY, LAMBERT JD. Differential prooxidative effects of the green tea polyphenol, (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate, in normal and oral cancer cells are related to differences in sirtuin 3 signaling. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2015;59(2):203-211. [62] LI K, WU L, WANG H, et al. Apoptosis and cuproptosis Co-activated Copper-based metal-organic frameworks for cancer therapy. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024; 22(1):546. [63] LIU F, MAJEED H, ANTONIOU J, et al. pH and temperature stability of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate-beta-cyclodextrin inclusion complex-loaded chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym. 2016;149:340-347. [64] SAHADEVAN R, SINGH S, BINOY A, et al. Chemico-biological aspects of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) to improve its stability, bioavailability and membrane permeability: Current status and future prospects . Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(30):10382-10411. [65] BARZIN M, BAGHERI AM, OHADI M, et al. Application of plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles in drug delivery . Pharm Dev Technol. 2023;28(5):383-402. [66] RAKOTONDRABE TF, FAN MX, MUEMA FW, et al. Modulating Inflammation-Mediated Diseases via Natural Phenolic Compounds Loaded in Nanocarrier Systems. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(2):699. [67] YANG QQ, WEI XL, FANG YP, et al. Nanochemoprevention with therapeutic benefits: An updated review focused on epigallocatechin gallate delivery. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020;60(8):1243-1264. [68] GRANJA A, FRIAS I, NEVES AR, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Epigallocatechin Gallate Nanodelivery Systems. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:5813793. [69] ZHANG X, XIONG S, SATHIYASEELAN A, et al. Recent advances in photocatalytic nanomaterials for environmental remediation: Strategies, mechanisms, and future directions. Chemosphere. 2024; 364:143142. [70] GAO W, FAN X, BI Y, et al. Preparation of NIR-Responsive Gold Nanocages as Efficient Carrier for Controlling Release of EGCG in Anticancer Application. Front Chem. 2022;10:926002. [71] LI J, JIANG X, SHANG L, et al. L-EGCG-Mn nanoparticles as a pH-sensitive MRI contrast agent. Drug Deliv. 2021;28(1):134-143. [72] CHI T, SANG T, WANG Y, et al. Cleavage and Noncleavage Chemistry in Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-Responsive Materials for Smart Drug Delivery. Bioconjug Chem. 2024;35(1):1-21. [73] BI D, QU F, XIAO W, et al. Reactive Oxygen Species-Responsive Gel-Based Microneedle Patches for Prolonged and Intelligent Psoriasis Management. ACS Nano. 2023; 17(5):4346-4357. [74] ZHANG J, CUI H, QIU J, et al. Stability of glycosylated complexes loaded with Epigallocatechin 3-gallate (EGCG). Food Chem. 2023;410:135364. [75] PENG X, MCCLEMENTS DJ, LIU X, et al. EGCG-based nanoparticles: synthesis, properties, and applications. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025;65(12):2177-2198. [76] SONG H, WANG Q, HE A, et al. Antioxidant activity, storage stability and in vitro release of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) encapsulated in hordein nanoparticles . Food Chem. 2022;388:132903. [77] SHEN M, YOU Y, XU C, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate attenuates lipopolysacharide-induced pneumonia via modification of inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and autophagy . BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024;24(1):147. [78] LIU S, CAO Y, MA L, Et al. Oral antimicrobial peptide-EGCG nanomedicines for synergistic treatment of ulcerative colitis . J Control Release. 2022;347:544-560. [79] KUMAZOE M, FUJIMURA Y, YOSHITOMI R, et al. Fustin, a Flavanonol, Synergically Potentiates the Anticancer Effect of Green Tea Catechin Epigallocatechin-3-O-Gallate with Activation of the eNOS/cGMP Axis . J Agric Food Chem. 2022;70(11):3458-3466. |
| [1] | 杨学涛, 朱梦菡, 张宸熙, 孙一民, 叶 玲. 抗氧化纳米材料在口腔中的应用和不足[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2044-2053. |
| [2] | 郭宇超, 倪前伟, 尹 晨, 吉格尔·赛义力汗, 高 瞻. 季铵化壳聚糖紧急止血材料:合成、机制与应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2091-2100. |
| [3] | 刘宏杰, 牟秋菊, 申玉雪, 梁 飞, 祝丽丽. 金属有机框架/羧甲基壳聚糖-氧化海藻酸钠/富血小板血浆水凝胶促糖尿病感染创面愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1929-1939. |
| [4] | 王菘芃, 刘玉三, 于焕英, 高晓丽, 徐英江, 张晓明, 刘 敏. 沸石基咪唑盐框架8纳米材料的活性氧双向调控:从肿瘤治疗、抗菌到细胞保护[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2033-2013. |
| [5] | 王宇航, 张 涵, 张超晶, 寇绪容, 井桐桐, 林日梅, 刘鑫宇, 娄石磊, 阎 慧, 孙 聪. 姜黄素提取及姜黄素纳米粒的制备及优化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 362-374. |
| [6] | 冯淑琦, 张诗咏, 姚珂奕, 唐渝菲, 王 锴, 周雪梅, 向 琳 . 光响应纳米材料在骨组织再生中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(16): 3469-3475. |
| [7] | 冯 楠, 李运峰. 抗菌压电材料:对细菌无选择性杀伤和不产生细菌耐药性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(10): 2105-2112. |
EGCG对活性氧的调控机制受到多种内外因素的综合影响,包括浓度、细胞类型、微环境特性(如氧化还原状态和pH值)以及与其他分子的相互作用。研究表明,在低浓度或正常生理条件下,EGCG主要展现出抗氧化剂特性,它通过上调抗氧化酶(如超氧化物歧化酶和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶)的表达、抑制促氧化酶的活性有效降低细胞内的活性氧水平,保护正常细胞免受氧化损伤[5],这一特性使EGCG在神经退行性疾病、心血管疾病以及其他与氧化应激相关疾病的治疗中展现出广阔应用前景。相反,在高浓度或特定微环境(如肿瘤细胞)中,EGCG则表现出促氧化特性,通过促进活性氧生成诱导癌细胞凋亡或自噬。这种依赖浓度和环境的双向调控机制,使EGCG在抗肿瘤和抗菌治疗领域展现出独特优势,进一步彰显了它作为多功能治疗剂的潜力。
随着EGCG双向调控特性的深入研究,近年来研究者致力于开发基于药物递送系统和材料复合技术的策略,以实现EGCG的靶向释放与功能增强[6]。例如,利用纳米载体或水凝胶包裹EGCG,不仅显著提升它在体内的稳定性和生物利用度,还通过精确调控EGCG的释放速率,实现对活性氧的精准调控,从而进一步强化它在抗氧化保护和抗肿瘤治疗中的作用[7]。另外,将EGCG与光敏材料或金属纳米颗粒复合,可以借助光照条件显著增强促氧化特性,为光动力疗法提供了新的应用途径。该文系统性综述EGCG在活性氧调控中的双重作用,重点探讨它在抗氧化与促氧化机制、复合材料设计及药物递送系统等方面的最新研究进展,同时展望EGCG在多领域的潜在应用与技术挑战。
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在 2024 年11月进行检索。
1.1.2 文献检索时限 2009年1月至2024 年11月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 万方医学网、中国知网、PubMed 数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯,活性氧,抗氧化,促氧化,抗癌症,心血管疾病,骨缺损,纳米材料”,英文检索词为“Epigallocatechin gallate,reactive oxygen species、antioxidation,oxidation,anticancer,Angio cardiopathy,bone defect,nanomaterials”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述、述评、病例报告和荟萃分析。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 通过手工检索相关文献。
1.1.7 检索策略 以 PubMed 数据库检索策略为例,见图1。
1.1.8 检索文献量 经检索,共获取各类文献资料248篇,其中英文文献113篇、中文文献135篇。
1.2 纳入标准与排除标准
纳入标准:研究内容与EGCG的抗氧化、促氧化机制及其在活性氧调控中的双向调控特性相关,或涉及EGCG与纳米材料、药物递送系统的结合及其在抗肿瘤、抗炎等领域的应用;近15年内发表的原创研究、系统评价或综述,数据可靠、设计严谨,优先考虑权威期刊文献;涉及不同浓度、微环境条件下EGCG功能变化的实验或理论分析,覆盖多种疾病模型,如肿瘤、神经退行性疾病等。
排除标准:内容与EGCG或它在活性氧调控中的作用无关;数据不足、实验设计不严谨或未经过同行评审的研究;重复已有文献或无显著信息增量的综述;发表时间超过15年的文献(里程碑式研究除外);缺乏实验支持的假说或理论性文章。
1.3 数据提取和质量评估 共获取各类文献资料248篇,排除对主题研究意义不大、内容陈旧、重复或无法获取全文的文献,最终收录79篇符合标准的中英文文献进行供综述。文献筛选流程见图2。
3.2 该综述的学术价值与创新特色 该综述系统总结了EGCG在不同浓度及病理环境下的双向调控特性,阐述了其抗氧化保护与促氧化治疗的核心机制,重点分析了它在神经保护、抗肿瘤和心血管健康中的应用潜力。通过结合药物递送系统和材料复合技术,探讨了提升EGCG稳定性和靶向性的最新研究进展。综述明确提出了当前领域的研究瓶颈,并从剂量控制、功能增强及精准调控等角度提出了未来发展方向,为相关研究提供了理论支持和实践参考。
3.3 该综述的局限性 该综述聚焦于EGCG在活性氧调控中的双重作用,但对其他天然多酚类化合物的比较分析较少,可能影响视角的全面性;此外,对于EGCG在临床应用中的长期安全性、代谢途径及实际剂量分布等问题的探讨尚不充分,部分结论基于间接推断,需更多实验数据验证。未来研究应结合多学科方法,系统评估EGCG的药效特性和潜在不良反应。
3.4 该综述对未来研究的指导意 该综述在理论和实践层面均具有重要意义。在理论上,全面梳理了EGCG在活性氧调控中的双向作用机制,为进一步理解其多功能性奠定了坚实基础。在实践上,通过总结EGCG在抗氧化治疗、抗肿瘤和靶向递送中的研究进展,为开发高效稳定的EGCG制剂和个性化治疗方案提供了具体方向。与此同时,综述结合跨学科视角,为材料科学、生物医学及药物化学领域的研究者提供了新的研究思路,有助于推动EGCG在多学科领域的应用发展。这些成果不仅总结了现有研究,还为未来的深入探索和临床转化提供了明确指引。
该文系统综述了表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯在活性氧双向调控中的独特机制及其纳米材料应用的前沿进展。研究首次整合了表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯的浓度与环境依赖性双重功能:低浓度下通过激活Nrf2通路增强抗氧化酶表达,保护正常细胞;高浓度或肿瘤微环境中则通过自氧化及催化芬顿反应诱导促氧化效应,选择性杀伤癌细胞。文章创新性地总结了表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯与纳米材料的协同策略,如脂质体、金属有机框架及响应性水凝胶,显著提升其稳定性、靶向性和生物利用度,并实现活性氧的精准调控。在应用层面,重点探讨了表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯纳米系统在抗肿瘤、神经保护、骨再生及口腔疾病(如牙周炎、牙髓炎)中的突破性进展,尤其是光/活性氧/pH值响应型纳米载体的设计,为光动力疗法和免疫调节提供了新思路。此外,该文深入分析了表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯双向调控的剂量安全性与稳定性挑战,提出了基于智能递送系统的解决方案,并展望其在个性化医学中的转化潜力。该综述为天然多酚的氧化还原调控机制与纳米医学的交叉研究提供了重要理论依据和实践指导。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||