中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (35): 7519-7528.doi: 10.12307/2025.961
• 血管组织构建 vascular tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
蒙药蓝刺头对血管内皮细胞增殖和血管生成能力的潜在作用机制
方 源1,2,钱智勇3,何源哈达3,王海燕3,沙丽蓉1,李筱贺3,刘 婧4,贺雅超4,张 凯5,特木日巴根6
- 内蒙古医科大学,1研究生院,3基础医学院人体解剖教研室,4巴彦淖尔临床医学院,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010000;2内蒙古巴彦淖尔市医院,内蒙古自治区巴彦淖尔市 015000;5乌兰察布市第二医院骨科,内蒙古自治区乌兰察布市 012000;6呼和浩特市中医蒙医医院蒙医骨伤科,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010000
Mechanism of Mongolian medicine Echinops sphaerocephalus L. in proliferation and angiogenesis of vascular endothelial cells
Fang Yuan1, 2, Qian Zhiyong3, He Yuanhada3, Wang Haiyan3, Sha Lirong1, Li Xiaohe3, Liu Jing4, He Yachao4, Zhang Kai5, Temribagen6
- 1Graduate School, 3Department of Human Anatomy, School of Basic Medicine, 4Bayannur Clinical College of Medicine, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 2Bayannur Hospital, Bayannur 015000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 5Department of Orthopedics, The Second Hospital of Ulanqab, Ulanqab 012000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 6Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Hohhot TCM Mongolian Hospital, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
蒙药蓝刺头:蒙名乌日格苏图-呼和,在蒙医学中具有固骨、接骨、愈伤、止痛等疗效,临床上用于治疗筋伤骨折、骨不愈合、骨热、刺痛症、疮疡等疾病。
网络药理学:基于系统生物学理论,通过对生物网络进行系统性分析,筛选出特定信号节点,进而开展多靶点药物分子设计,形成了一个
新兴的交叉学科领域。网络药理学结合了系统生物学与多靶向药理学的理论,致力于将生物学网络与药物作用网络进行融合性研究,深入探讨药物与网络中的节点或模块之间的相互作用,从而实现了从传统单一靶点研究向全面网络分析的转变。
背景:蒙药蓝刺头对于筋伤骨折、骨不愈合、骨热、刺痛症、疮疡等疾病的疗效显著,是蒙医常用骨伤用药。课题组前期研究证实蒙药蓝刺头可促进骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖及成骨分化,但它对骨缺损修复过程中血管生成的影响尚未可知。
目的:利用人脐静脉血管内皮细胞进行体外细胞实验,探讨蓝刺头对血管生成的影响,利用网络药理学技术挖掘蓝刺头中可能存在的促进
血管形成的活性成分及其潜在作用机制。
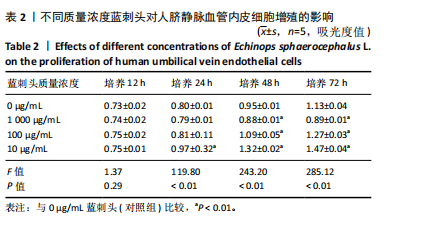
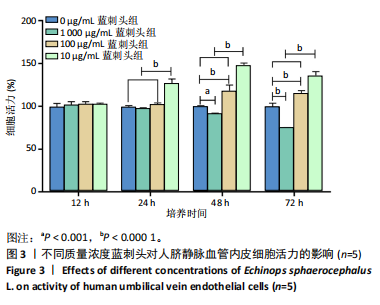
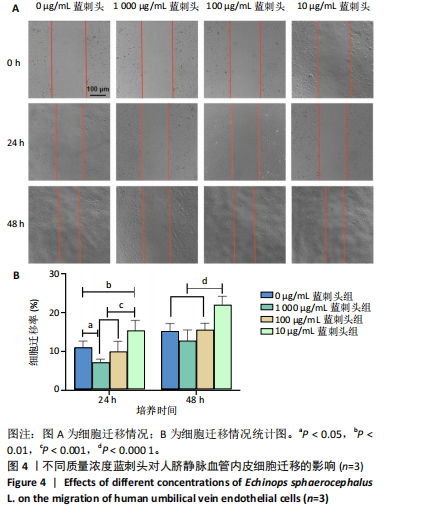
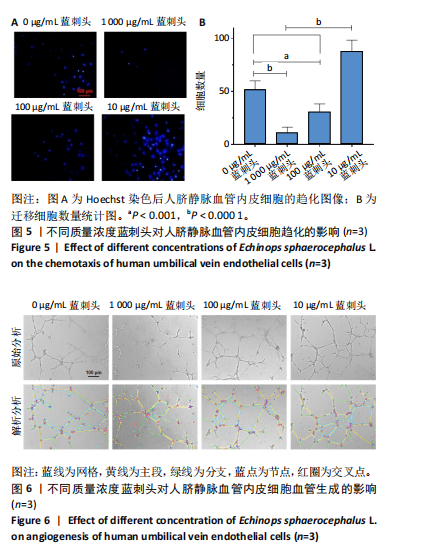
方法:制备蓝刺头乙醇提取物并冻干保存。观察不同质量浓度(1 000,100,10 μg/mL)蓝刺头干预对人脐静脉内皮细胞增殖、迁移、趋化及血管生成能力的影响。利用网络药理学对蒙药蓝刺头中具有促血管生成作用的有效成分及可能信号通路进行富集和分析。
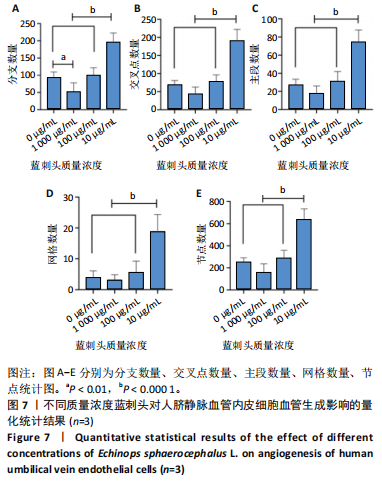
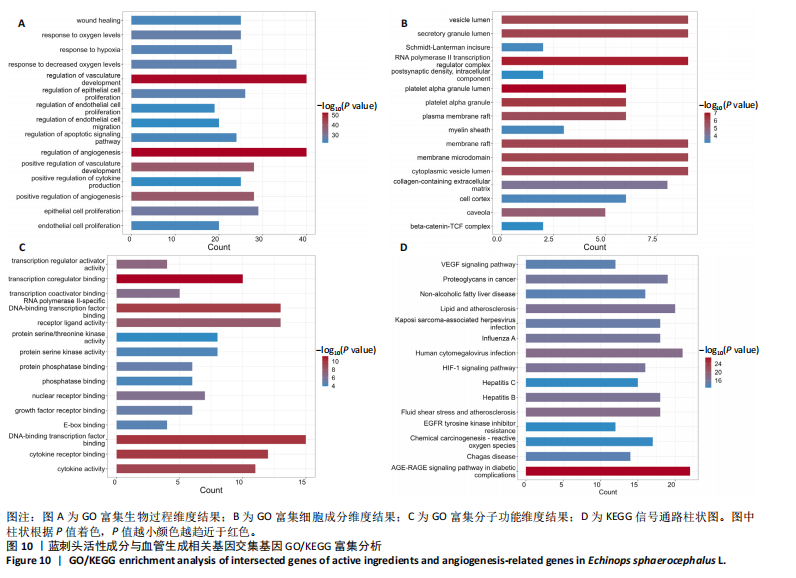
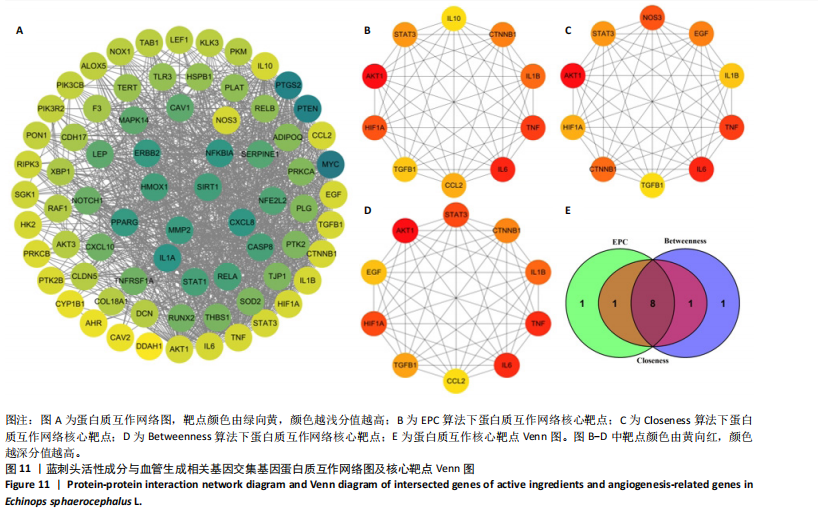
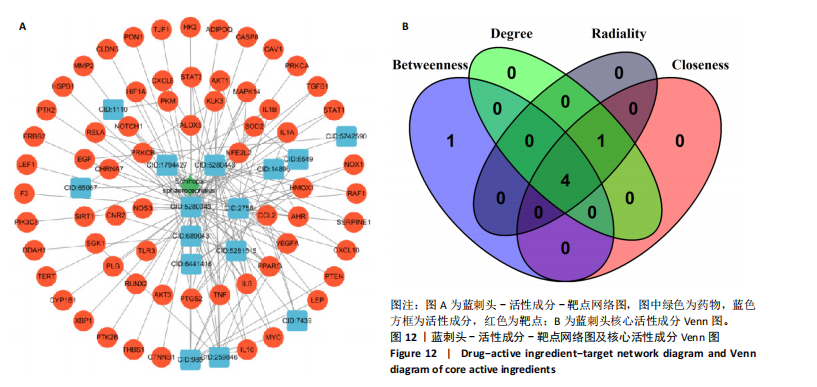
结果与结论:①蓝刺头对血管生成的影响受其质量浓度的调节:在低质量浓度(10 μg/mL)条件下,蓝刺头能够促进人脐静脉血管内皮细胞的增殖、迁移、趋化及血管生成;相反,在高质量浓度(1 000 μg/mL)下,蓝刺头抑制人脐静脉内皮细胞的增殖、迁移和趋化,由于实验时间的限制,高质量浓度蓝刺头对血管生成的抑制作用并不显著。10 μg/mL蓝刺头能够上调与血管生成相关因子(激酶插入域蛋白受体、血管内皮生长因A和缺氧诱导因子α)mRNA的表达,从而影响骨修复过程中的血管生成。②网络药理学分析表明,蓝刺头可能通过4种核心活性成分(芹菜素、咖啡酸、槲皮素和绿原酸)与8个核心靶点(TGFB1、TNF、IL-6、STAT3、CTNNB1、IL-1B、AKT1、HIF-1A)的结合,对血管生成、动脉粥样硬化、多种病毒感染以及肿瘤血管生成相关的信号通路产生影响。
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-4943-5917(方源)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: