[1] 朱铭金,钟吉富,何光荣.江西蝮蛇咬伤流行病学及预防对策研究[J].中国民族民间医药,2010,19(3):94-96.
[2] 吴佳丽,潘俊卿,胡香君,等.南昌地区蝮蛇咬伤致急性肝损伤的临床特点及危险因素分析[J].蛇志,2021,33(3):257-260.
[3] RALPH R, FAIZ MA, SHARMA SK, et al. Managing snakebite. BMJ. 2022; 376:e057926.
[4] 颜时姣,胡燕兰,王选岩,等.中国蛇伤诊疗现状与展望[J].中华急诊医学杂志,2024,33(3):281-285.
[5] GOPAL G, SELVARAJ H, VENKATARAMANAN SK, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis on the efficacy of Indian polyvalent antivenom against the Indian snakes of clinical significance. Arch Toxicol. 2024; 98(2):375-393.
[6] 董德刚,宋梅,邓中平,等.植物药抗蛇毒局部毒性效应作用与机制研究进展[J].中国药理学通报,2020,36(7):907-911.
[7] 邓孝露,陈小雄,罗丽,等.蛇咬伤致急性肾损伤危险因素分析[J].临床急诊杂志,2024,25(8):428-432.
[8] 李玉梅,杨悦,易军,等.毒蛇咬伤后相关并发症的研究进展[J].中国比较医学杂志,2024,34(5):144-151.
[9] 黄宜谋,罗焕荣,王杰伟.竹叶青蛇咬伤51例临床分析[J].岭南急诊医学杂志,2021,26(1):77-79.
[10] RATHORE AS, KUMAR R, TIWARI OS. Recent advancements in snake antivenom production. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;240:124478.
[11] 李玉梅,杨悦,易军,等.细胞外基质:毒蛇咬伤致局部组织损伤的治疗新靶点[J].中国病理生理杂志,2024,40(7):1324-1330.
[12] STRAESSER M, KESHAVARZ B, BORISH L, et al. α-Gal on Crotalidae-polyvalent Fab antivenom (CroFab): Investigating the relevance to immediate hypersensitivity reactions. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9(2):1015-1017.e1.
[13] 姚学强,董朕,李江,等.动物毒液的抗菌活性研究进展[J].中兽医医药杂志,2024,43(3):43-47.
[14] 田雯,周发伟,杨美玲,等.纤维蛋白降解产物和D-二聚体与毒蛇咬伤患者病情严重程度的相关性[J].中国急救复苏与灾害医学杂志,2024,19(7):947-951.
[15] SAMPAT GH, HIREMATH K, DODAKALLANAVAR J, et al. Unraveling snake venom phospholipase A2: an overview of its structure, pharmacology, and inhibitors. Pharmacol Rep. 2023;75(6):1454-1473.
[16] YUSUF AJ, BUGAJE AI, SADIQ M, et al. Exploring the inhibitory potential of phytochemicals from Vernonia glaberrima leaves against snake venom toxins through computational simulation and experimental validation. Toxicon. 2024;247:107838.
[17] 黄国亮,覃晓波,吴雪,等.一次性覆盖式负压封闭引流技术在福建竹叶青属毒蛇咬伤救治中的应用[J].蛇志,2022,34(2):145-149.
[18] 陈俊,董德刚,严张仁,等.莲花解毒汤治疗五步蛇咬伤40例临床观察[J].北京中医药大学学报,2020,43(12):1053-1057.
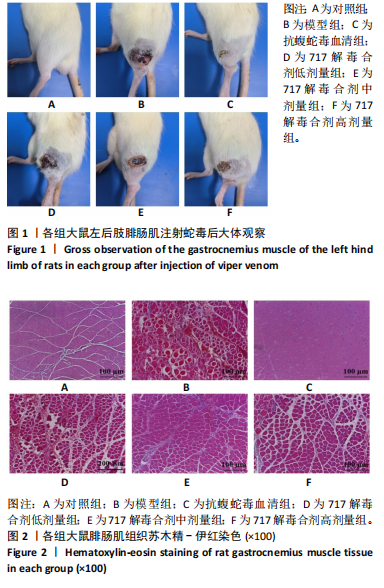
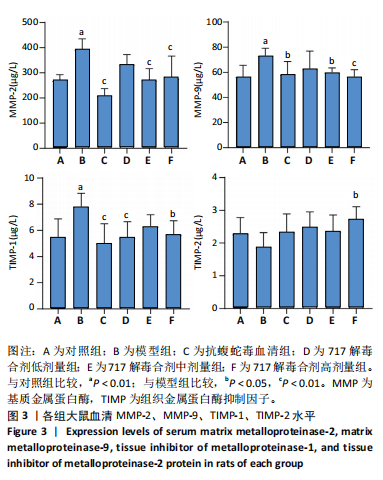
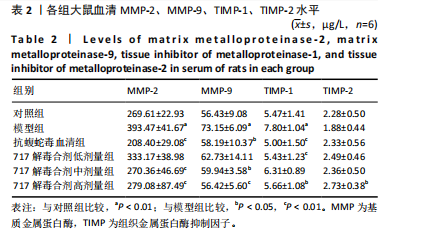
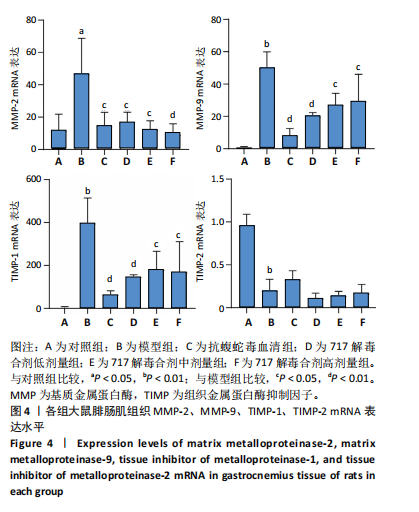
[19] 董德刚,杨悦,郑向龙,等.717解毒合剂通过NETs-CYR61/CCN1信号通路对蝮蛇咬伤大鼠局部组织损伤修复作用[J].中国药学杂志, 2024,59(2):151-160.
[20] 董德刚,宋梅,陈俊,等.717解毒合剂对蝮蛇毒所致局部组织损伤的保护作用与机制研究[J].中国中西医结合急救杂志,2021,28(2): 203-208.
[21] 张允申,方勇,陈海东,等.蝮蛇咬伤中医治疗优化方案的疗效评价[J].云南中医药大学学报,2024,47(1):33-39.
[22] THEOCHARIS AD, MANOU D, KARAMANOS NK. The extracellular matrix as a multitasking player in disease. FEBS J. 2019;286(15):2830-2869.
[23] ABIOLA J, BERG AM, AIYELAAGBE O, et al. Dabsylated Bradykinin Is Cleaved by Snake Venom Proteases from Echis ocellatus. Biomedicines. 2024;12(5):1027.
[24] 曾晓艳,林雅丽,刘应蛟,等.五步蛇蛇毒对脂多糖诱导的RAW264.7巨噬细胞炎症反应的影响研究[J].中南药学,2022,20(8): 1820-1824.
[25] 黄小梅,支慧,陈浩,等.皖南蝮蛇毒抑瘤组分-Ⅰ对胃癌MKN-28细胞增殖、迁移及凋亡的影响[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2024,29(3):270-276.
[26] 胡延星,李亚梅,杜义博,等.蛇毒抗肿瘤活性成分的研究进展[J].河北师范大学学报(自然科学版),2021,45(5):522-529.
[27] 刘明明,李爱玲,修瑞娟.基质金属蛋白酶的研究进展[J].中国病理生理杂志,2018,34(10):1914-1920.
[28] 肖曼琪,关哲哲,胡少聪,等.中华眼镜蛇毒致广西巴马小型猪坏死组织渗出液中的蛇毒成分分析[J].广西医科大学学报,2024, 41(8):1101-1110.
[29] ESCALANTE T, RUCAVADO A, FOX JW, et al. Key events in microvascular damage induced by snake venom hemorrhagic metalloproteinases. J Proteomics. 2011;74(9):1781-1794.
[30] SONAVANE M, ALMEIDA JR, RAJAN E, et al. Intramuscular Bleeding and Formation of Microthrombi during Skeletal Muscle Damage Caused by a Snake Venom Metalloprotease and a Cardiotoxin. Toxins (Basel). 2023;15(9):530.
[31] CAVALCANTE JDS, DE ALMEIDA CAS, CLASEN MA, et al. A fingerprint of plasma proteome alteration after local tissue damage induced by Bothrops leucurus snake venom in mice. J Proteomics. 2022;253:104464.
[32] WEBER GC, BUHREN BA, SCHRUMPF H, et al. Clinical Applications of Hyaluronidase. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1148:255-277.
[33] RUCAVADO A, NÚÑEZ J, GUTIÉRREZ JM. Blister formation and skin damage induced by BaP1, a haemorrhagic metalloproteinase from the venom of the snake Bothrops asper. Int J Exp Pathol. 1998;79(4):245-254.
[34] GOMES A, DAS R, SARKHEL S, et al. Herbs and herbal constituents active against snake bite. Indian J Exp Biol. 2010;48(9):865-878.
[35] HINZ B. Myofibroblasts. Exp Eye Res. 2016;142:56-70.
[36] FRANGOGIANNIS N. Transforming growth factor-β in tissue fibrosis. J Exp Med. 2020;217(3):e20190103.
[37] TAI Y, WOODS EL, DALLY J, et al. Myofibroblasts: Function, Formation, and Scope of Molecular Therapies for Skin Fibrosis. Biomolecules. 2021;11(8):1095.
[38] NEVE A, CANTATORE FP, MARUOTTI N, et al. Extracellular matrix modulates angiogenesis in physiological and pathological conditions. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:756078.
[39] GUTIÉRREZ JM, ESCALANTE T, RUCAVADO A, et al. A Comprehensive View of the Structural and Functional Alterations of Extracellular Matrix by Snake Venom Metalloproteinases (SVMPs): Novel Perspectives on the Pathophysiology of Envenoming. Toxins (Basel). 2016;8(10):304.
[40] GUTIÉRREZ JM, RUCAVADO A, ESCALANTE T, et al. Unresolved issues in the understanding of the pathogenesis of local tissue damage induced by snake venoms. Toxicon. 2018;148:123-131.
[41] RIVAS MERCADO E, NERI CASTRO E, BÉNARD VALLE M, et al. Disintegrins extracted from totonacan rattlesnake (Crotalus totonacus) venom and their anti-adhesive and anti-migration effects on MDA-MB-231 and HMEC-1 cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 2020;65:104809.
[42] SCHÖNTHAL AH, SWENSON SD, CHEN TC, et al. Preclinical studies of a novel snake venom-derived recombinant disintegrin with antitumor activity: A review. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;181:114149.
[43] CASTANHEIRA LE, LOPES DS, GIMENES SNC, et al. Angiogenenic effects of BpLec, a C-type lectin isolated from Bothrops pauloensis snake venom. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;102:153-161. |