中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (30): 6434-6440.doi: 10.12307/2025.800
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
抑制TRAF6调节mTORC1/ULK1信号通路促进自噬改善脓毒症小鼠的心肌损伤
周 颖1,2,田 勇2,钟芝梅1,古雍翔2,方 昊3
- 1贵州省黔西南州人民医院呼吸科,贵州省兴义市 562400;2贵州医科大学临床医学院,贵州省贵阳市 550004;3贵州医科大学附属医院内科ICU,贵州省贵阳市 550004
Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6 regulates mTORC1/ULK1 signaling and promotes autophagy to improve myocardial injury in sepsis mice
Zhou Ying1, 2, Tian Yong2, Zhong Zhimei1, Gu Yongxiang2, Fang Hao3
- 1Department of Respiratory Medicine, People’s Hospital of Qianxinan Prefecture, Xingyi 562400, Guizhou Province, China; 2School of Clinical Medicine, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 3Department of MICU, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6(tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6,TRAF6):是一种存在于细胞质的衔接蛋白,目前认为是肿瘤坏死因子受体家族和Toll 样受体/白细胞介素1受体家族中唯一的信号转导连接分子。TRAF6具有独特的特异性结合受体参与调节先天性和适应性免疫、自噬等病理生理过程。
哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR):是一种丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶,分为mTOR复合体1和复合体2(mTORC1,mTORC2),具有调节细胞生长和代谢等作用。mTORC1作为自噬的主要调节因子发挥负调节作用。
背景:研究发现抑制肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6能改善脓毒症心肌功能并促进心肌自噬水平,但具体机制尚不明确。
目的:探索抑制肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6调节mTORC1/ULK1自噬信号通路对脓毒症小鼠心肌损伤的作用。
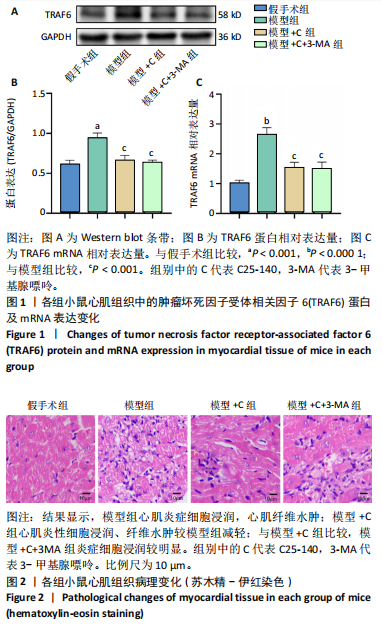
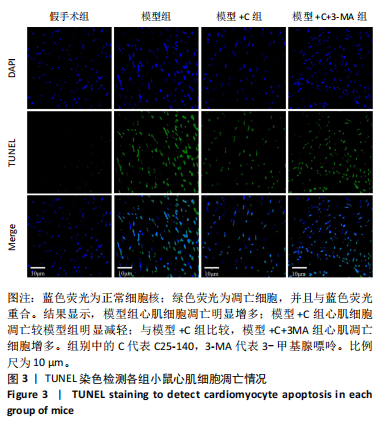
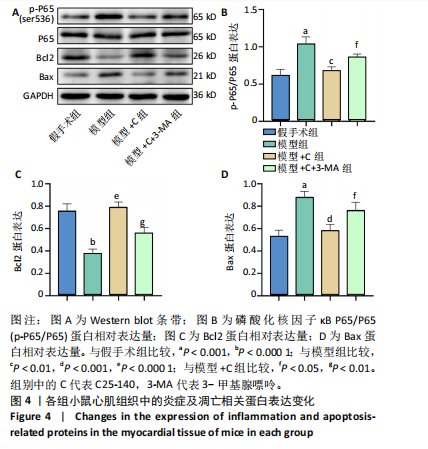
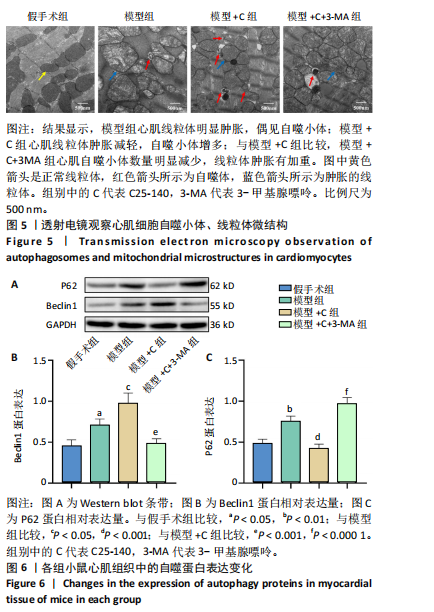
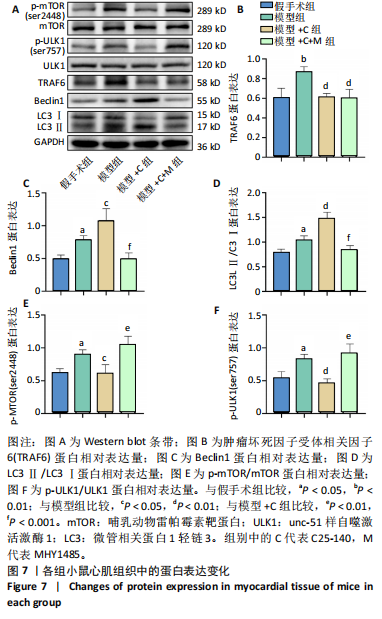
方法:雄性昆明小鼠30只,随机分为5组,分别为假手术组、盲肠结扎穿刺术组(模型组) 、模型+肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6特异性抑制剂C25-140(模型+C)组、模型+C25-140+自噬抑制剂3-甲基腺嘌呤(模型+C+3-MA)组、模型+C25-140+mTORC1特异性激动剂MHY1485(模型+C+M)组。假手术组小鼠盲肠不结扎穿刺;其余各组小鼠行盲肠结扎穿刺术建立小鼠脓毒症模型,按分组术后0.5 h分别腹腔注射C25-140、3-甲基腺嘌呤、MHY1485。术后24 h取心肌组织,苏木精-伊红染色评估心肌炎症病变;透射电镜观察心肌细胞自噬小体、线粒体微结构变化;TUNEL检测心肌细胞凋亡,PCR检测肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6 mRNA的相对表达量,Western blot检测相关蛋白的表达。
结果与结论:①与假手术组比较,模型组小鼠心肌炎症细胞浸润、纤维水肿;细胞线粒体明显肿胀,偶见自噬小体;心肌细胞凋亡显著增加;肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6、磷酸化核因子κB P65/P65、p-mTOR/mTOR、p-ULK1/ULK1、P62、Bax蛋白表达升高,Bcl2蛋白表达下降(P < 0.05)。②与模型组比较,模型+C组小鼠心肌炎症缓解、纤维水肿减轻;心肌线粒体肿胀减轻,自噬小体增多;心肌细胞凋亡减少;磷酸化核因子κB P65 /核因子κB P65、p-mTOR/mTOR、p-ULK1/ULK1、P62、Bax蛋白表达下降,Beclin-1、Bcl2蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05)。③与模型+C比,模型+C+3-MA组心肌自噬小体减少、心肌线粒体肿胀较明显;心肌炎症有加重;心肌细胞凋亡增多;磷酸化核因子κB65/核因子κB65、P62、Bax蛋白表达升高,Beclin-1、Bcl2蛋白表达下降(P < 0.05)。④与模型+C比,模型+C+M组p-mTOR/mTOR、p-ULK1/ULK1表达升高,Beclin-1、微管相关蛋白1轻链3Ⅱ/Ⅰ蛋白表达下降(P < 0.05)。结论:抑制肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6可以调节mTORC1/ULK1自噬信号促进心肌自噬参与改善脓毒症心肌损伤。
https://orcid.org/0009-0007-2333-4985(周颖)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: