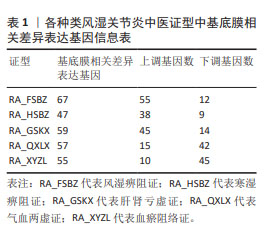
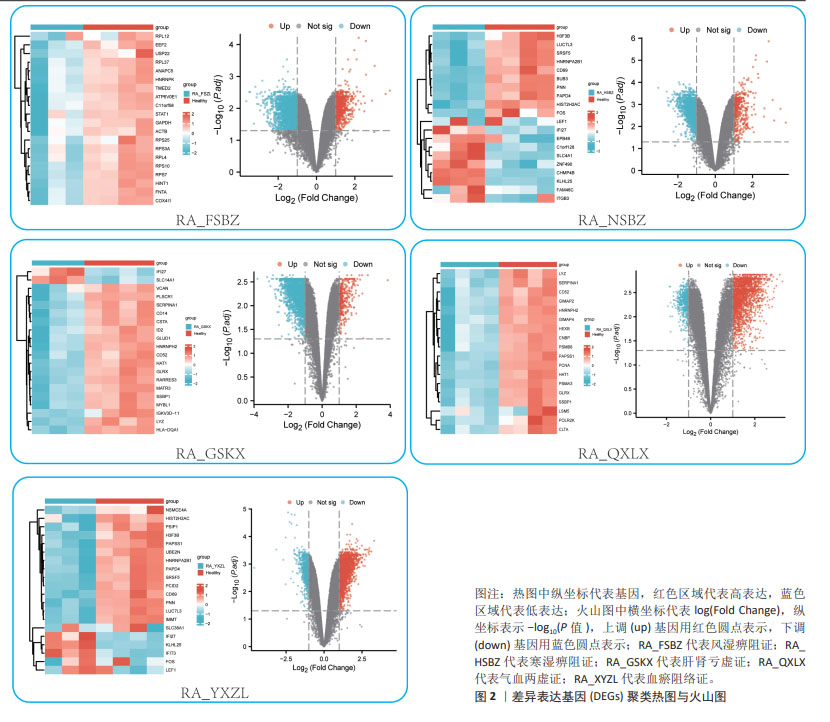
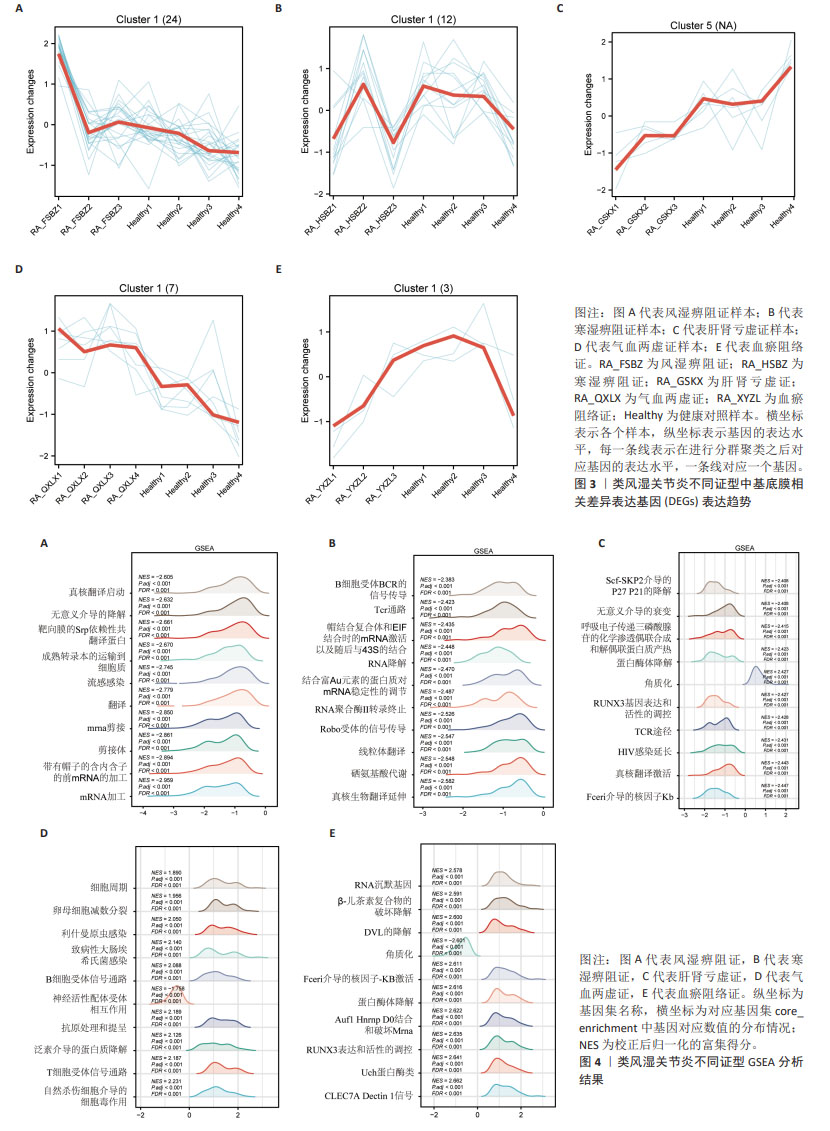
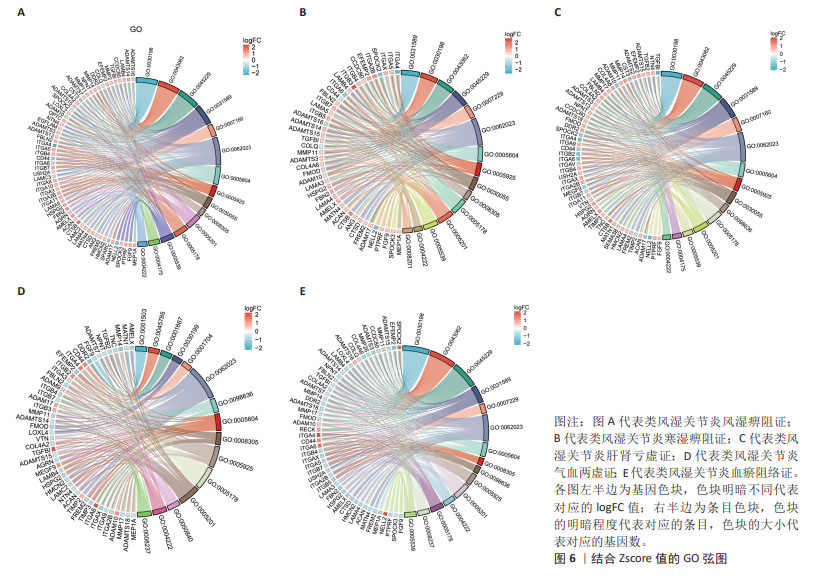
[1] RADU AF, BUNGAU SG. Management of rheumatoid arthritis: an overview. Cells. 2021;10(11):2857.
[2] HUANG J, FU X, CHEN X, et al. Promising therapeutic targets for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2021; 12:686155.
[3] FOSTER MH. Basement membranes and autoimmune diseases. Matrix Biol. 2017; 57-58:149-168.
[4] TöPFERU. Basement membrane dynamics and mechanics in tissue morphogenesis. Biol Open. 2023;12(8): bio059980.
[5] UESAKA K, OKA H, KATO R, et al. Bioinformatics in bioscience and bioengineering: recent advances, applications, and perspectives. J Biosci Bioeng. 2022;134(5):363-373.
[6] DING Z, CHEN W, WU H et al. Integrative network fusion-based multi-omics study for biomarker identification and patient classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Chin Med. 2023;18(1):48.
[7] ALBARADEI S, THAFAR M, ALSAEDI A, et al. Machine learning and deep learning methods that use omics data for metastasis prediction. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021;19:5008-5018.
[8] JAYADEV R, MORAIS MRPT, ELLINGFORD JM, et al. A basement membrane discovery pipeline uncovers network complexity, regulators, and human disease associations. Sci Adv. 2022;8(20): eabn2265.
[9] YU G, WANG LG, HAN Y, et al. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS. 2012; 16(5):284-287.
[10] GUSTAVSSON EK, ZHANG D, REYNOLDS RH, et al. ggtranscript: an R package for the visualization and interpretation of transcript isoforms using ggplot2. Bioinformatics. 2022;38(15):3844-3846.
[11] ROBIN X, TURCK N, HAINARD A, et al. pROC: an open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011;12:77.
[12] WU Y, ZHANG F, YANG K, et al. SymMap: an integrative database of traditional Chinese medicine enhanced by symptom mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1): D1110-D1117.
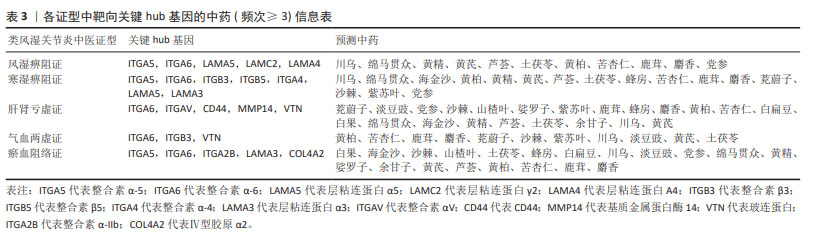
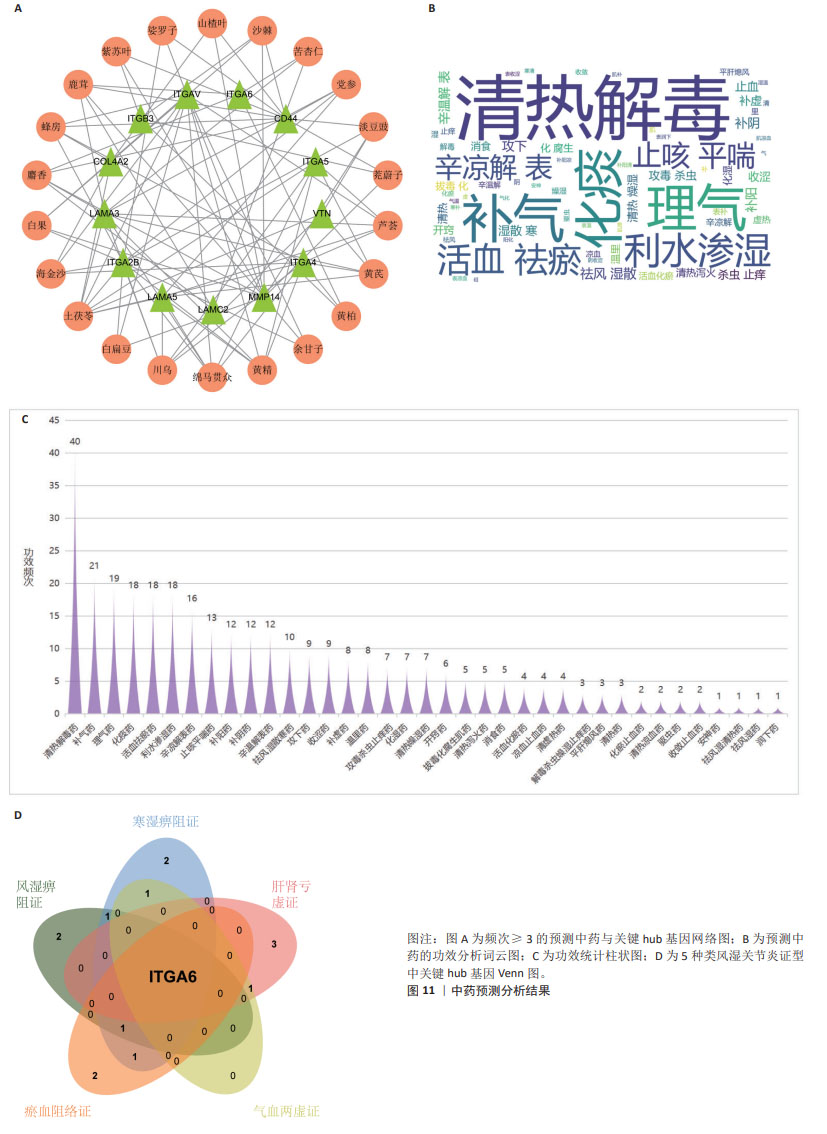
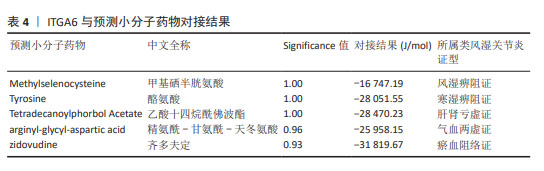
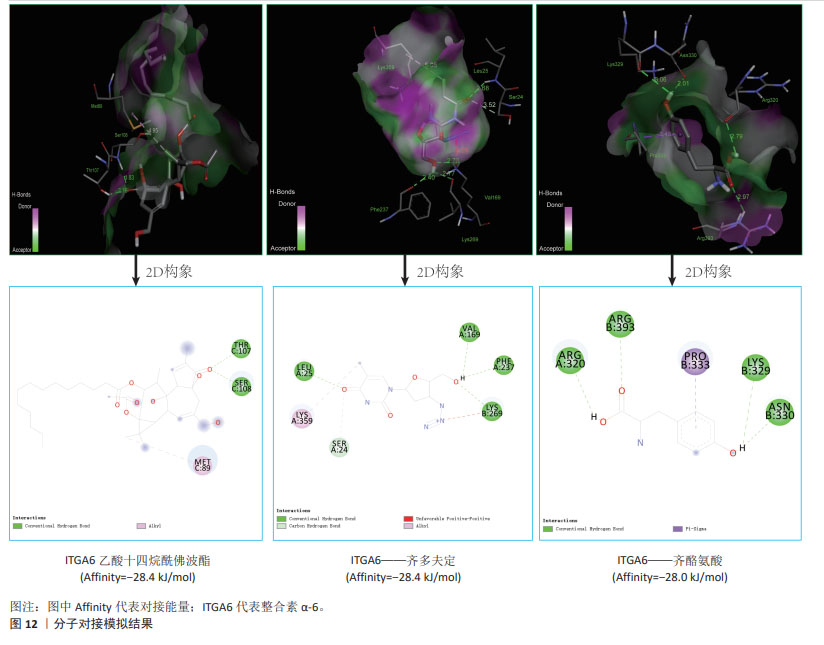
[13] 宋哲,劳慧敏,王晓,等.铁死亡基因在儿童川崎病中的生物信息学分析及中药预测研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2023, 38(5):2286-2291.
[14] HALFTER W, OERTLE P, MONNIER CA, et al. New concepts in basement membrane biology. FEBS J. 2015;282(23): 4466-4479.
[15] GUDMANN NS, JUNKER P, JUHL P, et al. Type IV collagen metabolism is associated with disease activity, radiographic progression and response to tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018;36(5):829-835.
[16] GUDMANN NS, HIRATA S, KARSDAL MA, et al. Increased remodelling of interstitial collagens and basement membrane is suppressed by treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: serological evaluation of a one-year prospective study of 149 Japanese patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018;36(3):462-470.
[17] KHALILGHARIBI N, MAO Y. To form and function: on the role of basement membrane mechanics in tissue development, homeostasis and disease. Open Biol. 2021;11(2):200360.
[18] DINESH P, RASOOL M. uPA/uPAR signaling in rheumatoid arthritis: shedding light on its mechanism of action. Pharmacol Res. 2018;134:31-39.
[19] BOUDKO SP, ASPIRNAUTS PEDCHENKO VK, POKIDYSHEVA EN, et al. Collagen IV of basement membranes: III. Chloride pressure is a primordial innovation that drives and maintains the assembly of scaffolds. J Biol Chem. 2023;299(11):105318.
[20] ONG S, ZHANG J, SU Q, et al. Downregulation of ITGA6 confers to the invasion of multiple myeloma and promotes progression to plasma cell leukaemia. Br J Cancer. 2021;124(11):1843-1853.
[21] TANSATHITAYA V, SARASIN W, PHAKHAM T, et al. Regulation of mi-RNAs target cancer genes between exercise and non-exercise in rat rheumatoid arthritis induction: pilot study. Epigenet Insights. 2022;15:25168657221110485.
[22] TU Y, MA T, WEN T, et al. MicroRNA-377-3p alleviates IL-1β-caused chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis in part by downregulating ITGA6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;523(1):46-53.
[23] HUANG JM, PANG ZY, QI GB, et al. Association of ITGAV polymorphisms and risk of rheumatoid arthritis: evidence from a meta-analysis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2020;16(6):631-640.
[24] HOLLIS-MOFFATT JE, ROWLEY KA, PHIPPS-GREEN AJ, et al. The ITGAV rs3738919 variant and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in four Caucasian sample sets. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009; 11(5):R152.
[25] SHAKIBA E, TAVILANI H, GOODARZI MT, et al. The ITGAV-rs3911238 polymorphism is associated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014;13(5):356-363.
[26] KOCA SS, KARA M, OZGEN M, et al. The rs3768777-G allele of ITGAV gene is associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2014;34(5):693-698.
[27] KANE BA, AN H, RAJASEKARIAH P, et al. Differential expression and regulation of the non-integrin 37/67-kDa laminin receptor on peripheral blood leukocytes of healthy individuals and patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1149.
[28] WANG J, LIU C, WANG T, et al. Single-cell communication patterns and their intracellular information flow in synovial fibroblastic osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Lett. 2023;263:1-13.
[29] WANG G, CHEN S, XIE Z, et al. TGFβ attenuates cartilage extracellular matrix degradation via enhancing FBXO6-mediated MMP14 ubiquitination. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(8):1111-1120.
[30] CHEN Z, WANG H, XIA Y, et al. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal cell-derived miRNA-150-5p-expressing exosomes in rheumatoid arthritis mediated by the modulation of MMP14 and VEGF. J Immunol. 2018;201(8):2472-2482.
[31] XIA XD, GILL G, LIN H, et al. Global, but not chondrocyte-specific, MT1-MMP deficiency in adult mice causes inflammatory arthritis. Matrix Biol. 2023;122:10-17.
[32] QADRI MM. Targeting CD44 receptor pathways in degenerative joint diseases: involvement of proteoglycan-4 (PRG4). Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023;16(10): 1425.
[33] SÁNCHEZ-ZUNO GA, BUCALA R, HERNÁNDEZ-BELLO J, et al. Canonical (CD74/CD44) and non-canonical (CXCR2, 4 and 7) MIF receptors are differentially expressed in rheumatoid arthritis patients evaluated by DAS28-ESR. J Clin Med. 2021; 11(1):120.
[34] HERNÁNDEZ DAZ, CHAGOLLÁN MG, ZUNO GAS, et al. Expression of transcriptional factors of T helper differentiation (T-bet, GATA-3, RORγt, and FOXP3), MIF receptors (CD44, CD74, CXCR2, 4, 7), and Th1, Th2, and Th17 cytokines in PBMC from control subjects and rheumatoid arthritis patients. Curr Mol Med. 2023. doi: 10.2174/0115665240260976230925095330.
[35] PARADOWSKA-GORYCKA A, WAJDA A, ROMANOWSKA-PRÓCHNICKA K, et al. Th17/Treg-related transcriptional factor expression and cytokine profile in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2020;11:572858.
[36] WEHR P, PURVIS H, LAW SC, et al. Dendritic cells, T cells and their interaction in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2019;196(1):12-27.
[37] KUCUKSEZER UC, AKTAS CETIN E, ESEN F, et al. The role of natural killer cells in autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. 2021;12:622306.
[38] 李慧,张林.土茯苓治疗类风湿关节炎的网络药理学研究[J].时珍国医国药, 2020,31(12):2854-2857.
[39] CHEN Q, WU C, WANG S, et al. Glycyrrhizic acid modified Poria cocos polyscaccharide carbon dots dissolving microneedles for methotrexate delivery to treat rheumatoid arthritis. Front Chem. 2023;11:1181159.
[40] LIU X, TAO H, TIAN R, et al. Hezi inhibits Tiebangchui-induced cardiotoxicity and preserves its anti-rheumatoid arthritis effects by regulating the pharmacokinetics of aconitine and deoxyaconitine. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;302(Pt A):115915.
[41] HE YN, OU SP, XIONG X, et al. Stems and leaves of Aconitum carmichaelii Debx. as potential herbal resources for treating rheumatoid arthritis: chemical analysis, toxicity and activity evaluation. Chin J Nat Med. 2018;16(9):644-652.
[42] QI Y, GAO F, HOU L,et al. Anti-inflammatory and immunostimulatory activities of astragalosides. Am J Chin Med. 2017;45(6): 1157-1167.
[43] WANG Y, LIU Y, XI Z, et al. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of Huangqi Guizhi Wuwutang granule in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019; 98(11):e14888.
[44] 曹培晨,付新利.张鸣鹤教授清热解毒法论治类风湿关节炎[J].吉林中医药, 2022,42(11):1269-1272. |