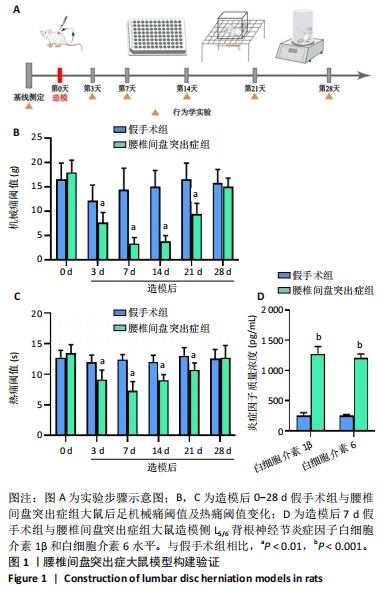
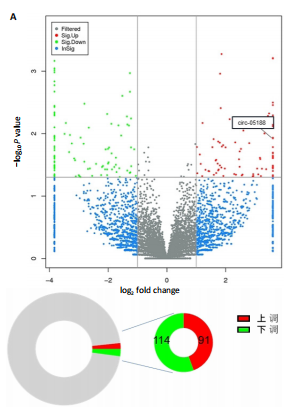
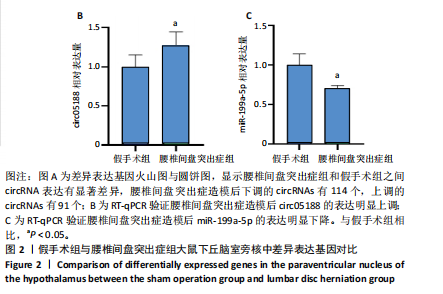
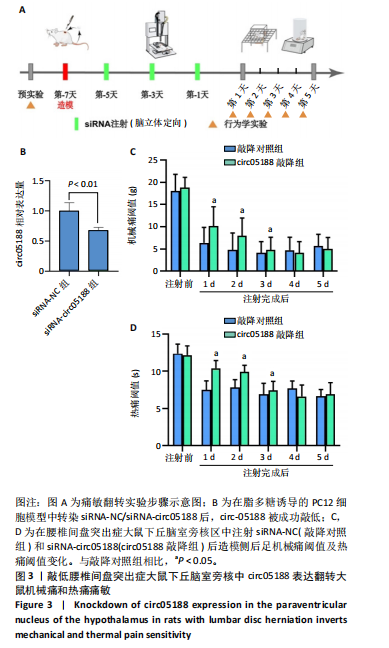
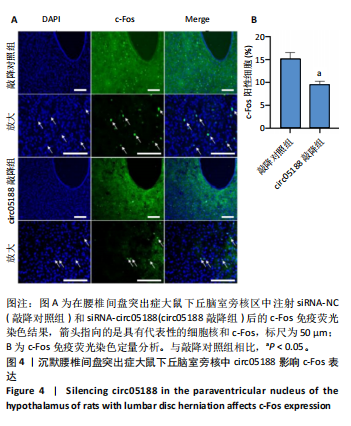
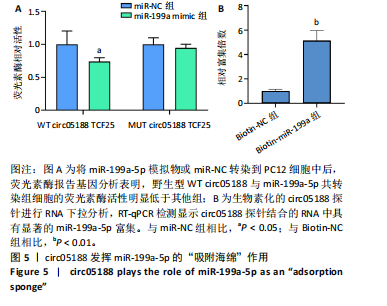
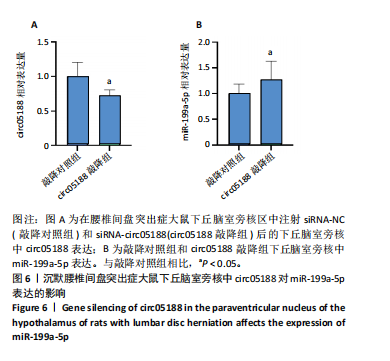
[1] CIEZA A, CAUSEY K, KAMENOV K, et al. Global estimates of the need for rehabilitation based on the Global Burden of Disease study 2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2021;396(10267):2006-2017.
[2] RICKERS KW, PEDERSEN PH, TVEDEBRINK T, et al. Comparison of interventions for lumbar disc herniation: a systematic review with network meta-analysis. Spine J. 2021;21(10):1750-1762.
[3] ZHANG AS, XU A, ANSARI K, et al. Lumbar Disc Herniation: Diagnosis and Management. Am J Med. 2023;136(7):645-651.
[4] KNEZEVIC NN, CANDIDO KD, VLAEYEN JWS, et al. Low back pain. Lancet. 2021;398(10294):78-92.
[5] CHOU R. Low Back Pain. Ann Intern Med. 2021;174(8):Itc113-itc128.
[6] URITS I, BURSHTEIN A, SHARMA M, et al. Low Back Pain, a Comprehensive Review: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2019;23(3):23.
[7] HORNUNG AL, BAKER JD, MALLOW GM, et al. Resorption of Lumbar Disk Herniation: Mechanisms, Clinical Predictors, and Future Directions. JBJS Rev. 2023;11(1).doi: 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.22.00148.
[8] YU P, MAO F, CHEN J, et al. Characteristics and mechanisms of resorption in lumbar disc herniation. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022;24(1):205.
[9] HAHNE AJ, FORD JJ, HINMAN RS, et al. Individualized functional restoration as an adjunct to advice for lumbar disc herniation with associated radiculopathy. A preplanned subgroup analysis of a randomized controlled trial. Spine J. 2017;17(3):346-359.
[10] XU J, DING X, WU J, et al. A randomized controlled study for the treatment of middle-aged and old-aged lumbar disc herniation by Shis spine balance manipulation combined with bone and muscle guidance. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(51):e23812.
[11] WANG Y, HU H, YIN J, et al. TLR4 participates in sympathetic hyperactivity Post-MI in the PVN by regulating NF-κB pathway and ROS production. Redox Biol. 2019;24:101186.
[12] JIANG Z, RAJAMANICKAM S, JUSTICE NJ. CRF signaling between neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN) coordinates stress responses. Neurobiol Stress. 2019;11: 100192.
[13] CHANG YT, CHEN WH, SHIH HC, et al. Anterior nucleus of paraventricular thalamus mediates chronic mechanical hyperalgesia. Pain. 2019;160(5):1208-1223.
[14] LIU Y, LI A, BAIR-MARSHALL C, et al. Oxytocin promotes prefrontal population activity via the PVN-PFC pathway to regulate pain. Neuron. 2023;111(11):1795-1811.e1797.
[15] ZHANG P, DAI M. CircRNA: a rising star in plant biology. J Genet Genomics. 2022;49(12):1081-1092.
[16] ZHOU WY, CAI ZR, LIU J, et al. Circular RNA: metabolism, functions and interactions with proteins. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):172.
[17] KRISTENSEN LS, JAKOBSEN T, HAGER H, et al. The emerging roles of circRNAs in cancer and oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2022;19(3): 188-206.
[18] CHEN LL. The expanding regulatory mechanisms and cellular functions of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(8):475-490.
[19] MISIR S, WU N, YANG BB. Specific expression and functions of circular RNAs. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29(3):481-491.
[20] WANG X, ZHANG S, LV B, et al. Circular RNA PTP4A2 regulates microglial polarization through STAT3 to promote neuroinflammation in ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024;30(4):e14512.
[21] CHEN T, WANG C, ZHU W, et al. mm9_circ_014683 regulates microglia polarization through canonical NFκB signaling pathway in diabetic retinopathy. Cell Signal. 2024;117:111121.
[22] DIENER C, KELLER A, MEESE E. Emerging concepts of miRNA therapeutics: from cells to clinic. Trends Genet. 2022;38(6): 613-626.
[23] VALI R, AZADI A, TIZNO A, et al. miRNA contributes to neuropathic pains. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;253(Pt 4):126893.
[24] SUMAIYA K, PONNUSAMY T, NATARAJASEENIVASAN K, et al. Cardiac Metabolism and MiRNA Interference. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):50.
[25] CHEN W, XU J, WU Y, et al. The potential role and mechanism of circRNA/miRNA axis in cholesterol synthesis. Int J Biol Sci. 2023;19(9): 2879-2896.
[26] DONG Q, HAN Z, TIAN L. Identification of Serum Exosome-Derived circRNA-miRNA-TF-mRNA Regulatory Network in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Using Bioinformatics Analysis and Validation in Peripheral Blood-Derived Mononuclear Cells. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:899503.
[27] MADÈ A, BIBI A, GARCIA-MANTEIGA JM, et al. circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Deregulated Network in Ischemic Heart Failure Patients. Cells. 2023;12(21):2578.
[28] DENG W, CHEN J, WANG X, et al. Paravertebrally-Injected Multifunctional Hydrogel for Sustained Anti-Inflammation and Pain Relief in Lumbar Disc Herniation. Adv Healthc Mater, 2024:e2401227. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202401227.
[29] RUYLE BC, LIMA-SILVEIRA L, MARTINEZ D, et al. Paraventricular nucleus projections to the nucleus tractus solitarii are essential for full expression of hypoxia-induced peripheral chemoreflex responses. J Physiol. 2023;601(19):4309-4336.
[30] DHALIWAL HK, FAN Y, KIM J, et al. Intranasal Delivery and Transfection of mRNA Therapeutics in the Brain Using Cationic Liposomes. Mol Pharm. 2020;17(6):1996-2005.
[31] LIANG SH, ZHAO WJ, YIN JB, et al. A Neural Circuit from Thalamic Paraventricular Nucleus to Central Amygdala for the Facilitation of Neuropathic Pain. J Neurosci. 2020;40(41):7837-7854.
[32] KREINER DS, MATZ P, BONO CM, et al. Guideline summary review: an evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of low back pain. Spine J. 2020;20(7):998-1024.
[33] BAILLY F, TROUVIN AP, BERCIER S, et al. Clinical guidelines and care pathway for management of low back pain with or without radicular pain. Joint Bone Spine. 2021;88(6):105227.
[34] LONG F, LI L, XIE C, et al. Intergenic CircRNA Circ_0007379 Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Progression by Modulating miR-320a Biogenesis in a KSRP-Dependent Manner. Int J Biol Sci. 2023;19(12):3781-3803.
[35] ZHANG S, WANG X, CHEN G, et al. CircRNA Galntl6 sponges miR-335 to ameliorate stress-induced hypertension through upregulating Lig3 in rostral ventrolateral medulla. Redox Biol. 2023;64:102782.
[36] JU J, SONG YN, CHEN XZ, et al. circRNA is a potential target for cardiovascular diseases treatment. Mol Cell Biochem. 2022;477(2): 417-430.
[37] MOHANAPRIYA R, AKSHAYA RL, SELVAMURUGAN N. A regulatory role of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in osteoblast differentiation. Biochimie. 2022;193:137-147.
[38] ALTESHA M A, NI T, KHAN A, et al. Circular RNA in cardiovascular disease. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(5):5588-5600.
[39] HUANG W, WU Y, QIAO M, et al. CircRNA-miRNA networks in regulating bone disease. J Cell Physiol. 2022;237(2):1225-1244.
[40] ZANG J, LU D, XU A. The interaction of circRNAs and RNA binding proteins: An important part of circRNA maintenance and function. J Neurosci Res. 2020;98(1):87-97.
[41] WU C, WANG S, CAO T, et al. Newly discovered mechanisms that mediate tumorigenesis and tumour progression: circRNA-encoded proteins. J Cell Mol Med. 2023;27(12):1609-1620.
[42] MA B, WANG S, WU W, et al. Mechanisms of circRNA/lncRNA-miRNA interactions and applications in disease and drug research. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;162:114672.
[43] KAMEDA S, OHNO H, SAITO H. Synthetic circular RNA switches and circuits that control protein expression in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51(4):e24.
[44] WANG W, LIU C, HE D, et al. CircRNA CDR1as affects functional repair after spinal cord injury and regulates fibrosis through the SMAD pathway. Pharmacol Res. 2024;204:107189.
[45] TONG D, ZHAO Y, TANG Y, et al. Circ-Usp10 promotes microglial activation and induces neuronal death by targeting miRNA-152-5p/CD84. Bioengineered. 2021;12(2):10812-10822.
|