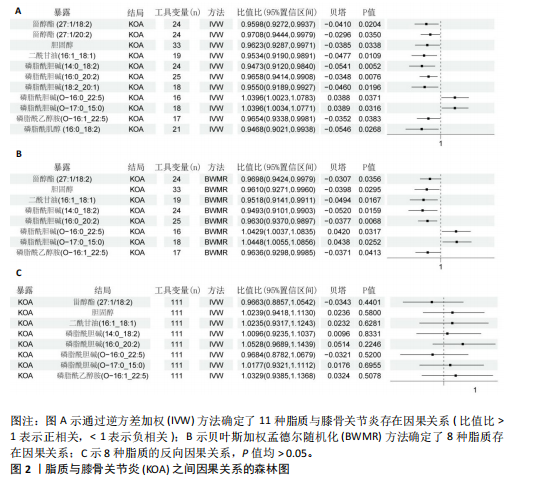
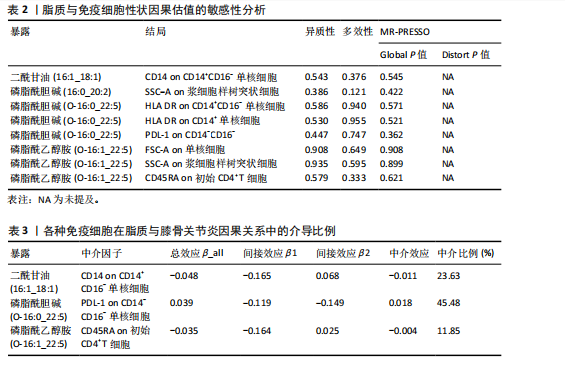
[1] HARRELL CR, MARKOVIC BS, FELLABAUM C, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy of osteoarthritis: Current knowledge and future perspectives. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:2318-2326.
[2] MANDL LA. Osteoarthritis year in review 2018: clinical. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019; 27(3):359-364.
[3] SACITHARAN PK. Ageing and Osteoarthritis. Subcell Biochem. 2019;91:123-159.
[4] BORÉN J, CHAPMAN MJ, KRAUSS RM, et al. Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: pathophysiological, genetic, and therapeutic insights: a consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur Heart J. 2020;41(24):2313-2330.
[5] HAARTMANS MJJ, CLAES BSR, EIJKEL GB, et al. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI-MSI) reveals potential lipid markers between infrapatellar fat pad biopsies of osteoarthritis and cartilage defect patients. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023;415(24):5997-6007.
[6] LOEF M, VAN DE STADT L, BÖHRINGER S, et al. The association of the lipid profile with knee and hand osteoarthritis severity: the IMI-APPROACH cohort. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(8):1062-1069.
[7] KOH JH, YOON SJ, KIM M, et al. Lipidome profile predictive of disease evolution and activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54(2):143-155.
[8] POUSINIS P, GOWLER PRW, BURSTON JJ, et al. Lipidomic identification of plasma lipids associated with pain behaviour and pathology in a mouse model of osteoarthritis. Metabolomics. 2020;16(3): 32.
[9] ZHANG W, SUN G, AITKEN D, et al. Lysophosphatidylcholines to phosphatidylcholines ratio predicts advanced knee osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016;55(9):1566-1574.
[10] VASSILIOU E, FARIAS-PEREIRA R. Impact of Lipid Metabolism on Macrophage Polarization: Implications for Inflammation and Tumor Immunity. Int J Mol Sci. 2023; 24(15):12032.
[11] PEETERS R, JELLUSOVA J. Lipid metabolism in B cell biology. Mol Oncol. 2024;18(7):1795-1813.
[12] LIM SA, SU W, CHAPMAN NM, et al. Lipid metabolism in T cell signaling and function. Nat Chem Biol. 2022;18(5):470-481.
[13] ALBEITUNI S, STIBAN J. Roles of Ceramides and Other Sphingolipids in Immune Cell Function and Inflammation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1161:169-191.
[14] GAO S, ZENG Q, ZENG Y, et al. High density lipoprotein inhibited group II innate lymphoid cells proliferation and function in allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2022;18(1):40.
[15] LIN J, ZHOU J, XU Y. Potential drug targets for multiple sclerosis identified through Mendelian randomization analysis. Brain. 2023;146(8):3364-3372.
[16] OTTENSMANN L, TABASSUM R, RUOTSALAINEN SE, et al. Genome-wide association analysis of plasma lipidome identifies 495 genetic associations. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):6934.
[17] ORRÙ V, STERI M, SIDORE C, et al. Complex genetic signatures in immune cells underlie autoimmunity and inform therapy. Nat Genet. 2020;52(10):1036-1045.
[18] TACHMAZIDOU I, HATZIKOTOULAS K, SOUTHAM L, et al. Identification of new therapeutic targets for osteoarthritis through genome-wide analyses of UK Biobank data. Nat Genet. 2019;51(2):230-236.
[19] EMDIN CA, Khera AV, Kathiresan S, Mendelian Randomization. JAMA. 2017; 318(19):1925-1926.
[20] SKRIVANKOVA VW, RICHMOND RC, WOOLF BAR, et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology Using Mendelian Randomization: The STROBE-MR Statement. JAMA. 2021;326(16):1614-1621.
[21] WANG Q, DAI H, HOU T, et al. Dissecting Causal Relationships Between Gut Microbiota, Blood Metabolites, and Stroke: A Mendelian Randomization Study. J Stroke. 2023;25(3):350-360.
[22] BOWDEN J, DEL GRECO MF, MINELLI C, et al. Assessing the suitability of summary data for two-sample Mendelian randomization analyses using MR-Egger regression: the role of the I2 statistic. Int J Epidemiol. 2016;45(6):1961-1974.
[23] PALAZZO C, NGUYEN C, LEFEVRE-COLAU MM, et al. Risk factors and burden of osteoarthritis. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2016; 59(3):134-138.
[24] BOWDEN J, DEL GRECO MF, MINELLI C, et al. Improving the accuracy of two-sample summary-data Mendelian randomization: moving beyond the NOME assumption. Int J Epidemiol. 2019;48(3):728-742.
[25] ZHAO J, MING J, HU X, et al. Bayesian weighted Mendelian randomization for causal inference based on summary statistics. Bioinformatics. 2020;36(5): 1501-1508.
[26] ZHONG Y, WANG F, MENG X, et al. The associations between gut microbiota and inflammatory skin diseases: a bi-directional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1297240.
[27] HERRERO-MANLEY L, ALABAJOS-CEA A, SUSO-MARTÍ L, et al. Serum lipid biomarkers and inflammatory cytokines associated with onset and clinical status of patients with early knee osteoarthritis. Front Nutr. 2023; 10:1126796.
[28] NANO JL, NOBILI C, GIRARD-PIPAU F, et al. Effects of fatty acids on the growth of Caco-2 cells. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2003;69(4):207-215.
[29] WU P, HUANG Z, SHAN J, et al. Interventional effects of the direct application of “Sanse powder” on knee osteoarthritis in rats as determined from lipidomics via UPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap MS. Chin Med. 2020;15:9.
[30] MURAKAMI C, HOSHINO F, SAKAI H, et al. Diacylglycerol kinase delta and sphingomyelin synthase-related protein functionally interact via their sterile alpha motif domains. J Biol Chem. 2020;295(10): 2932-2947.
[31] HILLS BA, THOMAS K. Joint stiffness and ‘articular gelling’: inhibition of the fusion of articular surfaces by surfactant. Br J Rheumatol. 1998;37(5):532-538.
[32] ROCHA B, CILLERO-PASTOR B, RUIZ-ROMERO C, et al. Identification of a distinct lipidomic profile in the osteoarthritic synovial membrane by mass spectrometry imaging. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(5):750-761.
[33] ZHAI G, PELLETIER JP, LIU M, et al. Activation of The Phosphatidylcholine to Lysophosphatidylcholine Pathway Is Associated with Osteoarthritis Knee Cartilage Volume Loss Over Time. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):9648.
[34] KAPELLOS TS, BONAGURO L, GEMÜND I, et al. Human Monocyte Subsets and Phenotypes in Major Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Front Immunol. 2019;10: 2035.
[35] KYTHREOTOU A, SIDDIQUE A, MAURI FA, et al. PD-L1. J Clin Pathol. 2018;71(3):189-194.
[36] CHA JH, CHAN LC, LI CW, et al. Mechanisms Controlling PD-L1 Expression in Cancer. Mol Cell. 2019;76(3):359-370.
[37] GARCIA-DIAZ A, SHIN DS, MORENO BH, et al. Interferon Receptor Signaling Pathways Regulating PD-L1 and PD-L2 Expression. Cell Rep. 2017;19(6):1189-1201.
[38] WANG X, YANG L, HUANG F, et al. Inflammatory cytokines IL-17 and TNF-alpha up-regulate PD-L1 expression in human prostate and colon cancer cells. Immunol Lett. 2017;184:7-14.
[39] EZAWA K, YAMAMURA M, MATSUI H, et al. Comparative analysis of CD45RA- and CD45RO-positive CD4+T cells in peripheral blood, synovial fluid, and synovial tissue in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Acta Med Okayama. 1997; 51(1):25-31. |